Introduction
The A1C test is a cornerstone in the management of diabetes, providing critical insights into blood glucose control over a span of two to three months. By measuring the percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin, it not only aids in diagnosing diabetes but also serves as a vital tool for ongoing management.
With alarming statistics indicating that nearly 100 million adults in the U.S. are living with prediabetes or diabetes, understanding the implications of A1C levels becomes essential for both patients and healthcare providers. This article delves into the intricacies of the A1C test, its significance in diabetes management, and how regular monitoring can empower individuals to take charge of their health, reduce anxiety, and ultimately improve their quality of life.
Through a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications and collaboration with healthcare professionals, patients can navigate the complexities of diabetes with greater confidence and success.
Understanding the A1C Test: What It Measures and Why It Matters
The A1C test serves as a vital indicator of blood glucose management in individuals with the condition, and the a1c average blood glucose chart provides insights that can lead to transformative health outcomes. It measures the percentage of glucose that binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, providing data for an a1c average blood glucose chart over the past two to three months. A higher A1C percentage reflects elevated average blood glucose levels, as shown in a1c average blood glucose chart, which may indicate suboptimal control of the condition.
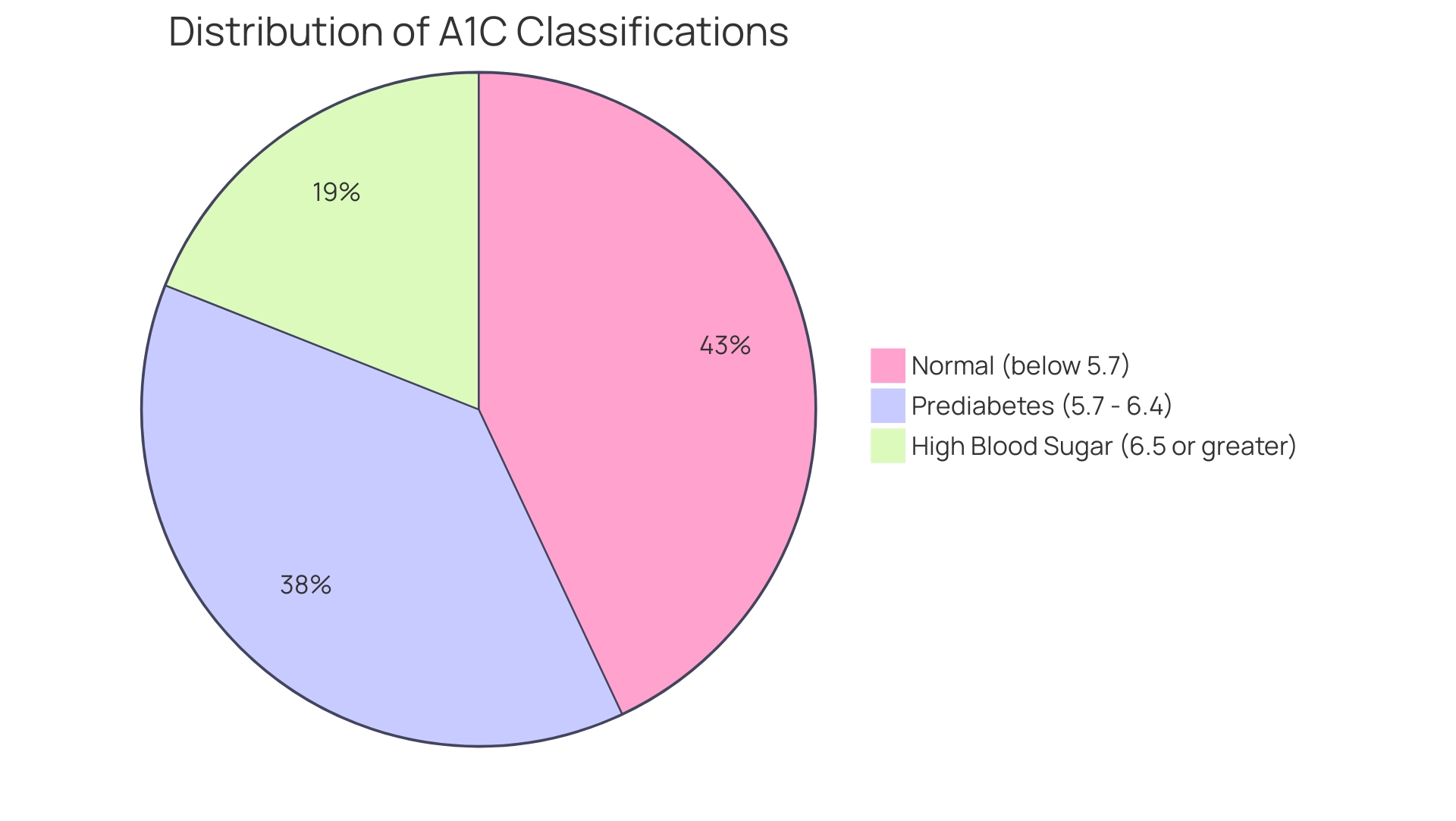
An A1C level below 5.7% is classified as normal, while values between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest prediabetes. An A1C of 6.5% or greater confirms a diagnosis of high blood sugar. In the U.S., around 97.6 million adults aged 18 years or older had prediabetes in 2021, highlighting the essential role of A1C testing for both prevention and oversight.
For individuals handling this condition, regular testing—typically every three months—is essential for monitoring their health and making necessary adjustments to treatment plans. As Roopa Naik states, ‘Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential for effective control of the condition.’ This proactive approach not only helps in achieving better health outcomes but also aligns with the holistic care principles championed by the Integrative Wellness Center.
Through personalized care and education, many individuals have successfully reversed Type 2 diabetes, eliminating anxiety over potential complications. For example, a recent case study at the Integrative Wellness Center showcased an individual who, through customized strategies reflected in their A1C average blood glucose chart, was able to decrease their A1C from 8.5% to 5.9% in only six months, greatly lowering their risk of complications. This demonstrates the influence of effective A1C oversight in promoting individual confidence and peace of mind.
Data from a 2020 case study also shows that among emergency department visits with diabetes as any listed diagnosis, 54.9% were treated and released, underscoring the importance of effective initial management and the role of A1C testing in guiding treatment strategies.
A1C and Estimated Average Glucose: Decoding the Numbers
The A1C test results can be effectively converted into estimated average glucose (eAG) using the formula:
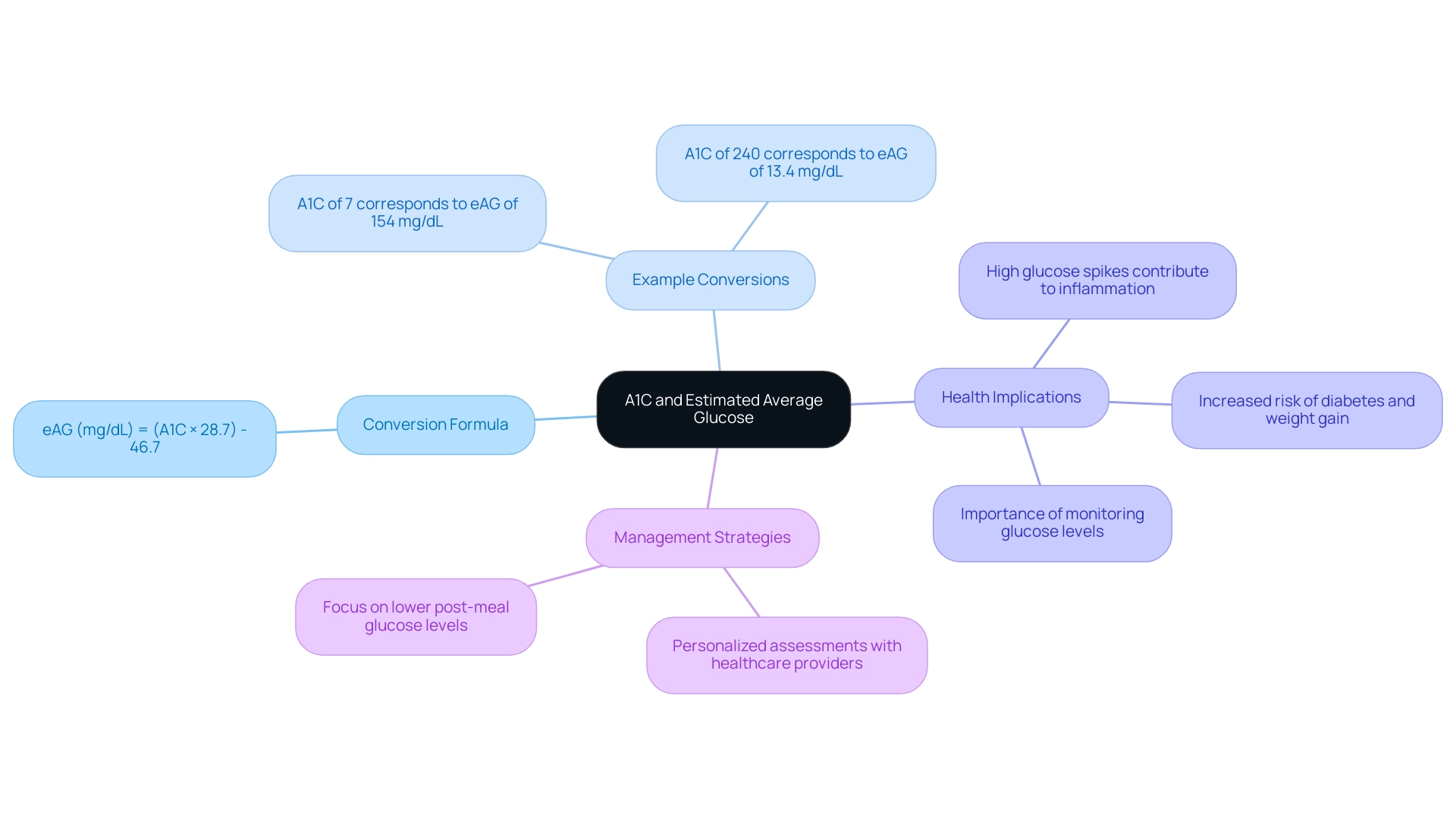
eAG (mg/dL) = [(A1C × 28.7)](https://drshumard.com/how-to-convert-a-1-c-to-e-ag-a-step-by-step-guide/) - 46.7
This conversion is crucial as it enables individuals to interpret their A1C levels with the help of an a1c average blood glucose chart in the context of daily glucose averages, promoting a more comprehensive understanding of their health and reducing anxiety about potential complications. For instance, an A1C value of 7% corresponds to an eAG of approximately 154 mg/dL, while an A1C of 240 corresponds to an eAG of 13.4 mg/dL.
Understanding this relationship enables individuals to manage their day-to-day blood sugar more effectively by using an a1c average blood glucose chart, alleviating worries about spikes and fluctuations. As highlighted by experts on blood sugar, repeated high glucose spikes after meals contribute to inflammation, blood vessel damage, increased risk of complications, and weight gain. Therefore, it is essential for individuals to monitor their glucose levels consistently, facilitating a holistic approach to managing the condition that addresses root causes and empowers patients.
Such insights not only optimize treatment plans and lifestyle choices but also foster peace of mind in managing this condition. Research indicates that lower post-meal glucose levels may be beneficial, reinforcing the importance of personalized assessments of glucose levels in collaboration with healthcare providers at the Integrative Wellness Center.
The Importance of Regular A1C Monitoring
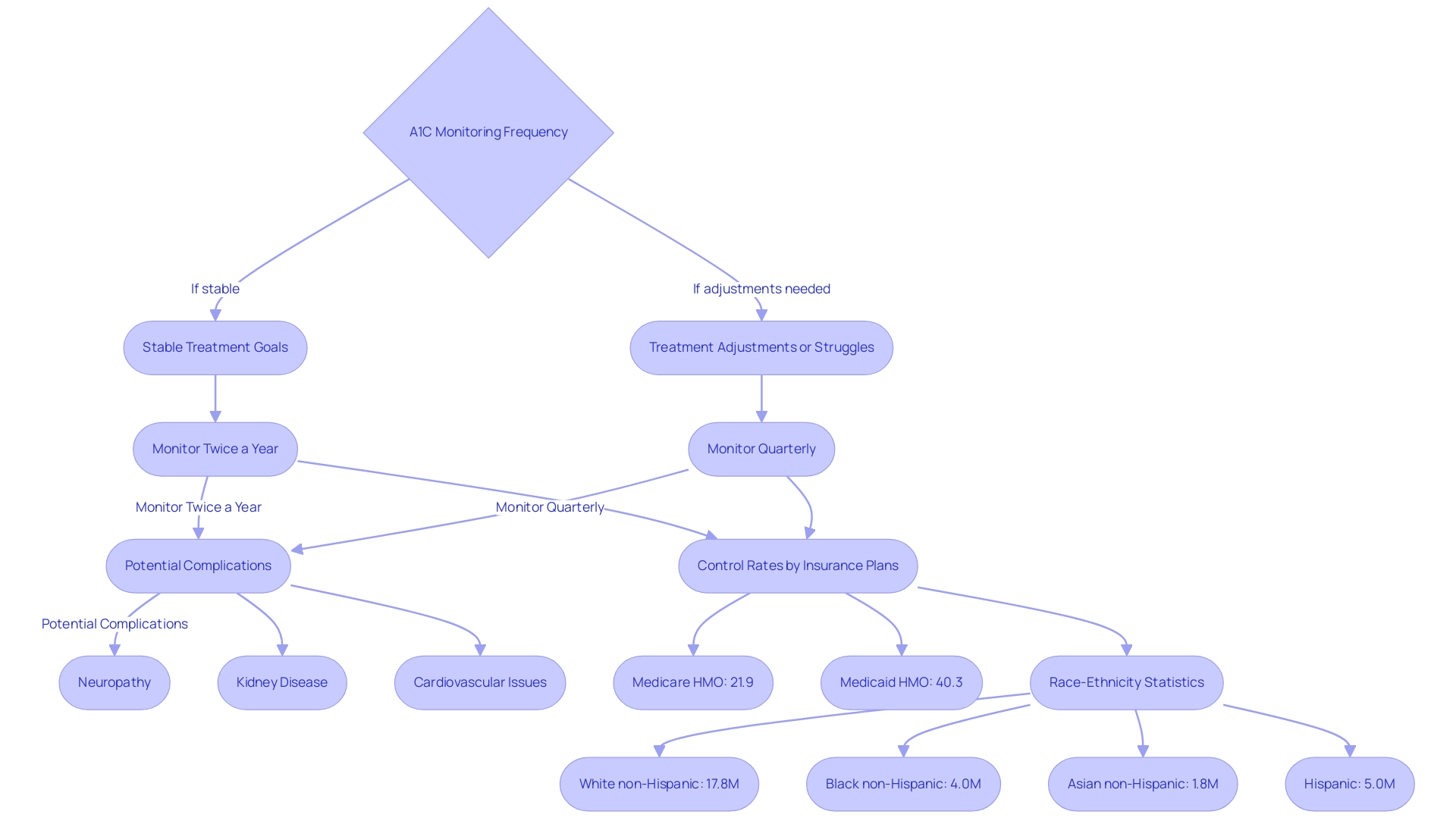
Patients managing diabetes are advised to undergo A1C testing at least twice a year if they are achieving their treatment goals and maintaining stability. However, in circumstances where treatment adjustments are made or when individuals struggle to meet their targets, quarterly assessments become imperative. Regular monitoring of A1C levels through an a1c average blood glucose chart not only allows healthcare professionals to evaluate the efficacy of the prescribed treatment strategies but also empowers individuals with knowledge about their health, thereby alleviating anxiety related to potential complications.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize a holistic approach to blood sugar control, which includes personalized education and support strategies designed to address the root causes of the condition and empower patients in their health journey. This proactive strategy is crucial in mitigating the risk of complications associated with this condition, including:
- Neuropathy
- Kidney disease
- Cardiovascular issues
As Balintescu A. observes, ‘Hemoglobin A1c is a key marker that offers essential insights into the control of blood sugar levels.’
A recent case study highlighted a significant disparity in HbA1c control rates across different health insurance plans from 2009 to 2022, revealing that in 2022, the lowest rate of poor control was recorded at 21.9% for Medicare HMO, while Medicaid HMO exhibited the highest at 40.3%. Furthermore, by race-ethnicity, the following numbers were reported:
- 17.8 million White non-Hispanic
- 4.0 million Black non-Hispanic
- 1.8 million Asian non-Hispanic
- 5.0 million Hispanic adults
This underscores the importance of tailored monitoring strategies. Such data highlights the crucial importance of regular A1C monitoring, as demonstrated by the a1c average blood glucose chart, in improving care and reducing negative health outcomes, showing that effective management strategies can result in better health and quality of life.
The contributions of Cheryl D. Fryar and Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics further emphasize the need for ongoing research and data collection in this critical area, reinforcing the Integrative Wellness Center’s commitment to education and holistic care aimed at alleviating anxiety related to complications from blood sugar issues.
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do the Numbers Mean?
An A1C level below 5.7% is considered normal, reflecting effective glucose control. However, levels ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, serving as a crucial warning sign for individuals to implement lifestyle modifications aimed at preventing the progression to the disease. An A1C measurement of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of elevated blood sugar levels, with levels exceeding 7% suggesting that patients should closely reassess their care strategies within a holistic framework.
Comprehending these benchmarks is essential; as emphasized by Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics, the A1C average blood glucose chart shows a concerning increase in the occurrence of this condition from 1999–2000 to August 2021–August 2023. This highlights the necessity for proactive and informed measures in blood sugar control, particularly through a comprehensive approach that challenges conventional treatment myths. Additionally, many patients experience anxiety regarding the potential complications of the disease, which can impede the efforts to cope.
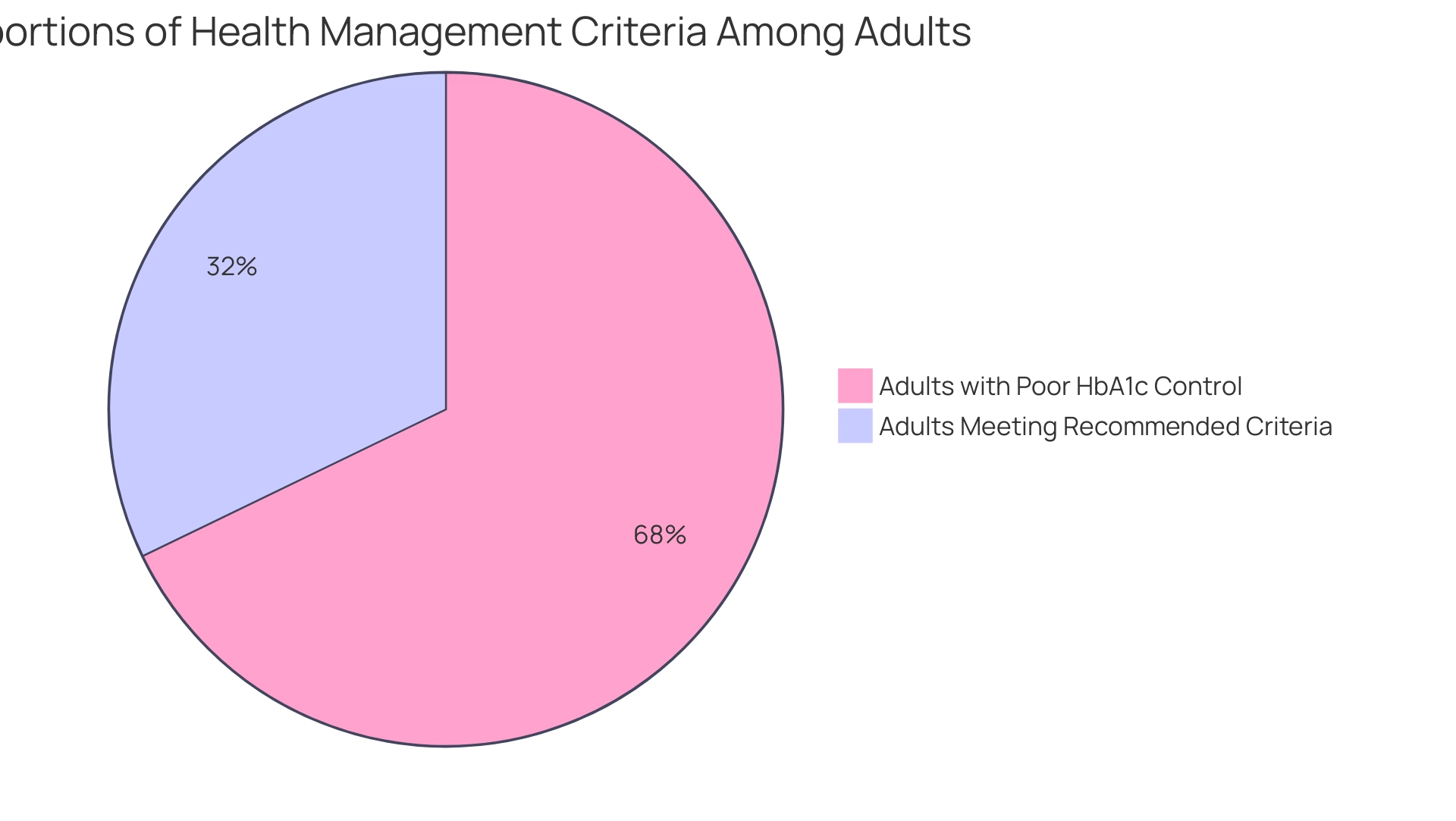
Furthermore, only 11.1% of adults meet all recommended criteria for A1C, blood pressure, cholesterol, and smoking cessation, underscoring the challenges encountered in achieving comprehensive control of the condition. In 2020, 23.4% of Medicare PPO members experienced poor HbA1c control, highlighting the difficulties many face in managing their condition effectively. Notably, 31.9% of adults are physically inactive, complicating management and underscoring the importance of lifestyle changes.
By recognizing and interpreting the A1C results within the context of a holistic approach, and by re-examining the source of their condition, individuals can utilize the A1C average blood glucose chart to take significant steps toward improving their health and effectively managing their situation.
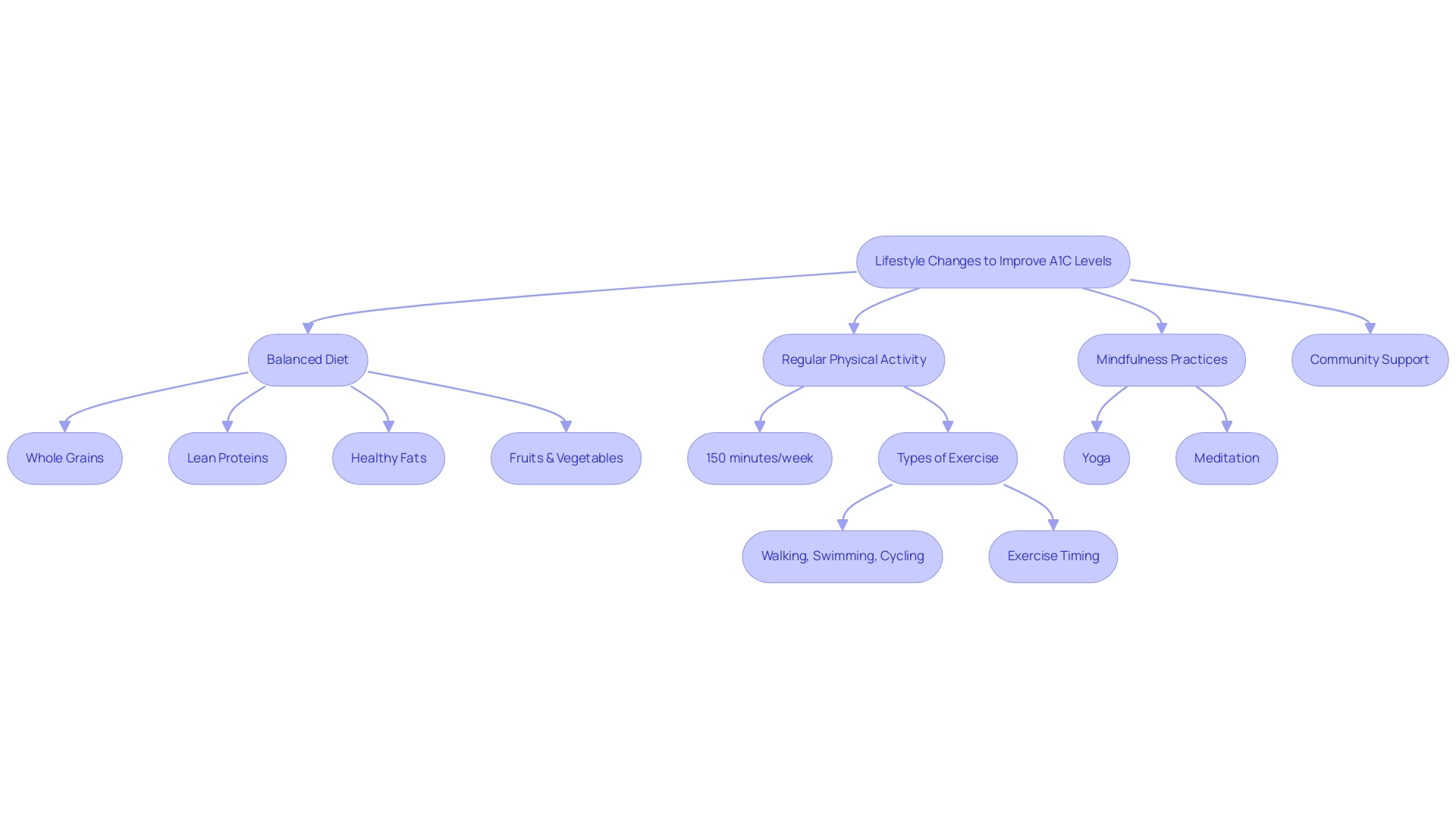
Lifestyle Changes to Improve A1C Levels
To effectively improve A1C levels, individuals must adopt a balanced diet that emphasizes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables. Incorporating whole grain options is vital for blood sugar control and sustained energy levels. Research indicates that prolonged sedentary time increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and premature mortality, making regular physical activity crucial.
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly—such as walking, swimming, or cycling—can significantly benefit glucose control. Jill A Kanaley, PhD at the University of Missouri, highlights the importance of exercise timing to maximize its glucose-lowering effects and addresses common barriers to adopting physical activity that many patients face. Additionally, embracing nature and community support can enhance the effectiveness of these lifestyle changes.
Mindfulness practices such as yoga or meditation can significantly enhance overall well-being and glucose control. These lifestyle changes not only help in reducing A1C levels but also promote a healthier, more active lifestyle, highlighting the role of the A1C average blood glucose chart in effectively controlling blood sugar through diet and exercise. As demonstrated by case studies on exercise and bariatric surgery outcomes, involvement in an exercise program before bariatric surgery has been shown to enhance surgical results, with individuals experiencing better recovery and improved long-term weight control.
This underscores the significant impact of holistic lifestyle changes on A1C levels and overall health. To uncover the four lesser-known power-plays that can further enhance your health and support your journey to reverse this condition, click to register for more information.
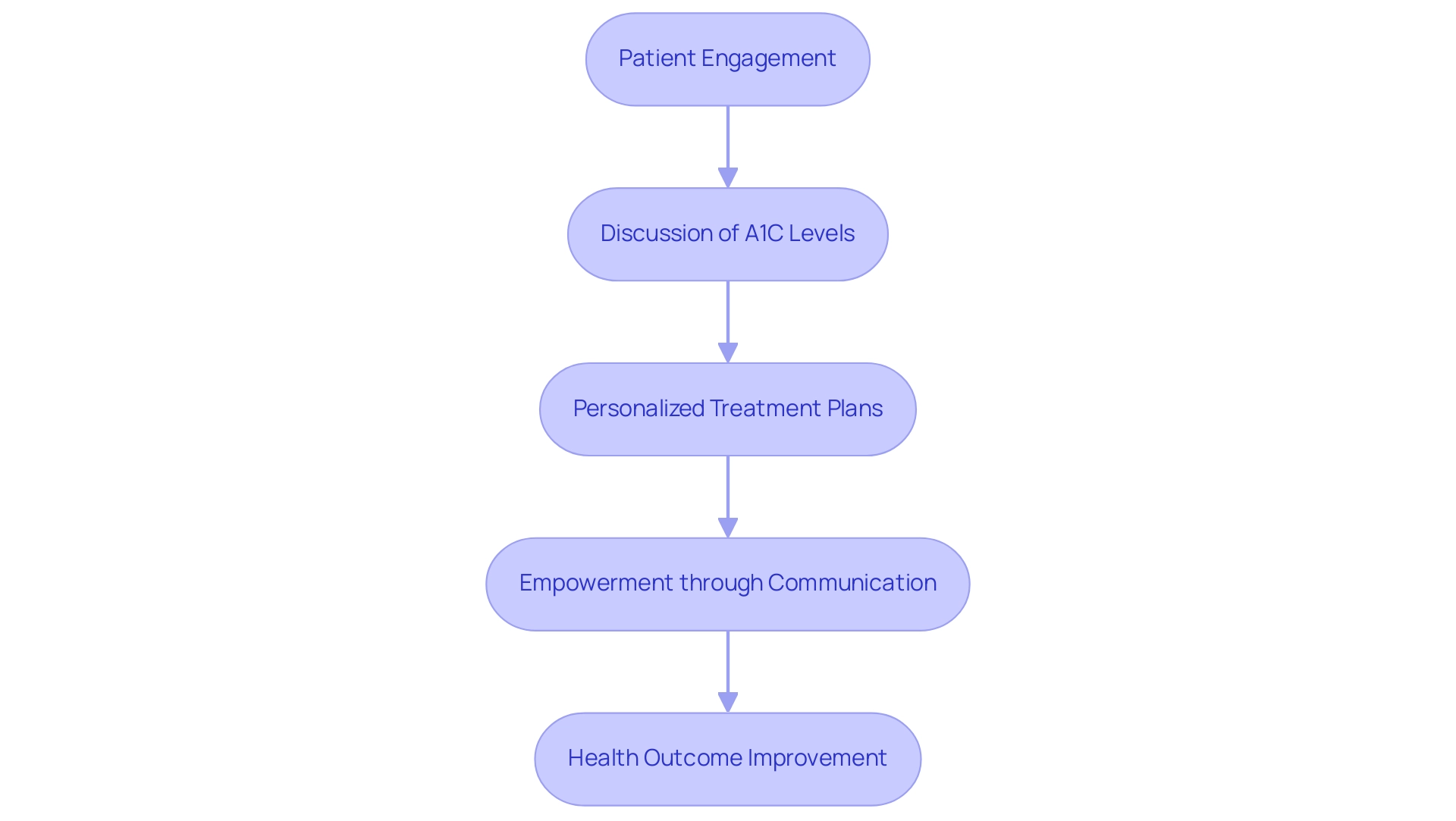
Consulting with Healthcare Providers: The Role of Teamwork in Diabetes Management
Active participation between individuals receiving care and healthcare providers is essential for effective management of the condition, particularly in discussing the A1C average blood glucose chart and treatment plans. This collaborative approach allows for personalized adjustments to medications, dietary recommendations, and exercise regimens, which are crucial for optimizing health outcomes. Research, such as that conducted by Wong et al., demonstrates the positive impact of empowerment programs on managing microvascular diseases, highlighting the importance of communication in diabetes care.
Dr. Tsung-Tai Chen emphasizes, ‘All of these factors are indirectly associated with outcomes through activation of individuals,’ indicating that when individuals are empowered to communicate openly with their providers, they are more likely to achieve favorable results. Additionally, the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego showcases transformative success stories of individuals who have significantly lowered their A1C levels, which can be seen on the A1C average blood glucose chart, and improved their overall health through their holistic approach. For instance, one individual reported a 2-point reduction in A1C after three months of personalized care, illustrating the center’s effectiveness.
A high-risk score on the Life Expectancy Estimator for Older Adults with Diabetes (LEAD) tool is strongly linked to a life expectancy of less than five years, emphasizing the critical importance of effective control and communication. Regular consultations not only enable patients to ask questions and express concerns but also foster a supportive environment that enhances overall diabetes management. For example, a real-world evidence analysis of a Medicare population showed that initiating hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery led to improvements in mean glucose levels and a 10% increase in time in range, demonstrating the tangible benefits of patient-provider collaboration.
To further empower your health transformation, schedule a complimentary consultation at the Integrative Wellness Center, where you can expect a personalized treatment plan tailored to your unique needs and the potential for improved health outcomes. Such proactive engagement may significantly improve A1C outcomes as reflected on the A1C average blood glucose chart, ultimately leading to better health and quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is crucial for individuals living with diabetes and prediabetes. The A1C test not only serves as a diagnostic tool but also plays a pivotal role in ongoing health management. By regularly monitoring A1C levels, patients can gain valuable insights into their blood glucose control and make informed decisions about their treatment strategies. This proactive approach is essential for mitigating the risk of complications and enhancing overall quality of life.
The relationship between A1C levels and estimated average glucose offers a clearer picture of daily glucose management, empowering patients to take charge of their health. Coupled with lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet and regular physical activity, individuals can significantly improve their A1C results. Collaboration with healthcare providers further enriches this journey, fostering a supportive environment where personalized care can thrive.
Ultimately, effective diabetes management hinges on a comprehensive strategy that encompasses:
- Regular monitoring
- Lifestyle modifications
- Open communication with healthcare professionals
By embracing these elements, patients can navigate the complexities of diabetes with greater confidence, reduce anxiety, and achieve better health outcomes. Taking action today can lead to a healthier tomorrow, underscoring the importance of understanding and managing A1C levels in the fight against diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and what does it measure?
The A1C test measures the percentage of glucose that binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, providing an indication of blood glucose management over the past two to three months.
How is the A1C percentage classified?
An A1C level below 5.7% is considered normal, 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, and 6.5% or greater confirms a diagnosis of high blood sugar.
Why is regular A1C testing important?
Regular A1C testing, typically every three months, is essential for monitoring health and making necessary adjustments to treatment plans, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
How can A1C levels influence diabetes management?
Effective A1C oversight can promote individual confidence and peace of mind, as demonstrated by case studies where individuals successfully reduced their A1C levels, decreasing their risk of complications.
What is the estimated average glucose (eAG) and how is it calculated from A1C results?
eAG is a conversion of A1C results into daily glucose averages. It can be calculated using the formula: eAG (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) – 46.7.
Why is understanding the relationship between A1C and eAG important?
Understanding this relationship helps individuals manage their daily blood sugar more effectively and reduces anxiety about potential complications from glucose fluctuations.
What are the health implications of high glucose spikes after meals?
Repeated high glucose spikes can contribute to inflammation, blood vessel damage, increased risk of complications, and weight gain, making consistent glucose monitoring essential.
How can personalized assessments of glucose levels benefit individuals with diabetes?
Personalized assessments can optimize treatment plans and lifestyle choices, fostering peace of mind in managing diabetes and addressing root causes of the condition.