Introduction
In the landscape of diabetes management, the A1C test stands out as a vital tool for assessing blood sugar control over time. Unlike daily glucose monitoring, which can fluctuate due to various factors, the A1C test provides a comprehensive view of an individual’s average blood sugar levels over the preceding months. This long-term perspective is essential for diagnosing and managing conditions like prediabetes and diabetes, enabling healthcare providers to tailor effective treatment plans.
With rising obesity rates and a growing number of individuals at risk, understanding A1C levels has never been more crucial. This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, its role in diagnosing diabetes, and effective strategies for lowering A1C levels, while also addressing the importance of regular monitoring to prevent complications and promote overall health.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key Indicator of Blood Sugar Levels
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, quantifies the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has bonded with glucose. This measurement is especially important because, unlike daily blood sugar tests that can exhibit significant fluctuations due to various factors such as stress or diet, the A1C test indicates an individual’s average blood sugar readings over the past two to three months. This long-term view makes it a crucial tool for diagnosing and monitoring both A1C and prediabetes as well as diabetes.
It enables healthcare providers to evaluate how effectively a patient’s blood sugar readings are being managed, thereby informing treatment decisions. A transformative success story from our Integrative Wellness Center illustrates this point: M.L., a diabetic for 10 years, experienced significant health improvements after engaging with our holistic regimen. With personalized care from Dr. Shumard, M.L.
- lost 55 lbs
- their A1C levels improved from 9.1 to 5.7 over eight months
- their fasting glucose decreased from 133 to 85, leading to a reduction in blood pressure medications
This holistic approach not only addressed M.L.’s physical health but also helped alleviate the anxiety associated with managing this condition.
Regular observation, as emphasized by the Monitoring Nephropathy rate for Commercial HMO recorded at 36.0% in 1999, is crucial in the care of individuals with blood sugar issues. Recent studies emphasize the essential role of A1C testing in controlling blood sugar levels and managing A1C and prediabetes, indicating that regular monitoring can significantly lower the risk of complications linked to this condition. As noted by Balintescu A. in the ‘Crit Care Clin’ journal, ‘Hemoglobin A1c and Permissive Hyperglycemia in Patients in the Intensive Care Unit with Diabetes,’ the A1C test is indispensable for understanding glycemic control, especially in complex patient populations, including those in intensive care settings.
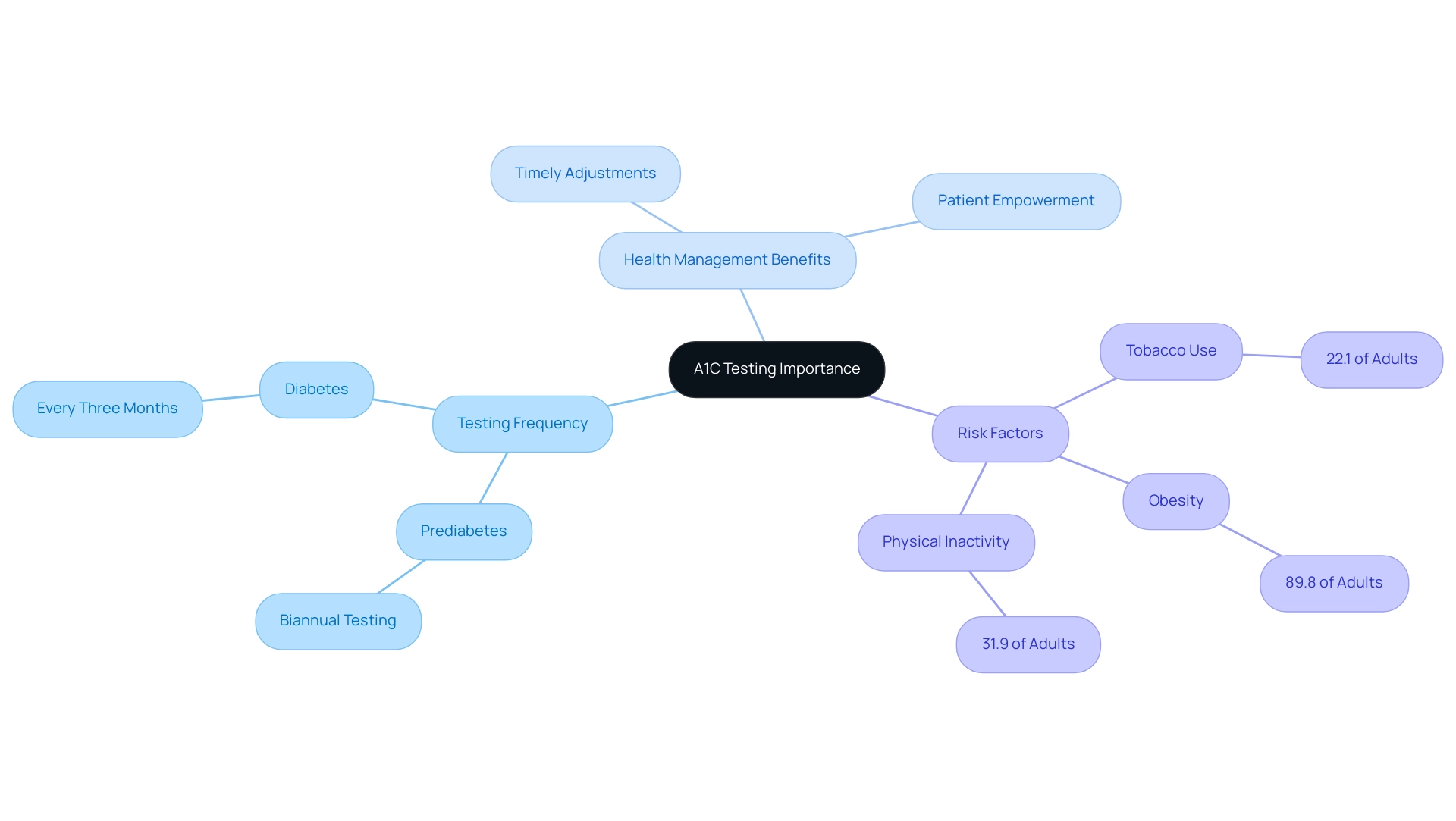
Furthermore, a case study on ‘Risk Factors for Diabetes-Related Complications’ revealed that among U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions:
- 22.1% were tobacco users
- 89.8% were overweight or had obesity
- 31.9% were physically inactive
This emphasizes the relevance of A1C testing in assessing the risk factors.
The Role of A1C Levels in Diagnosing Prediabetes and Diabetes
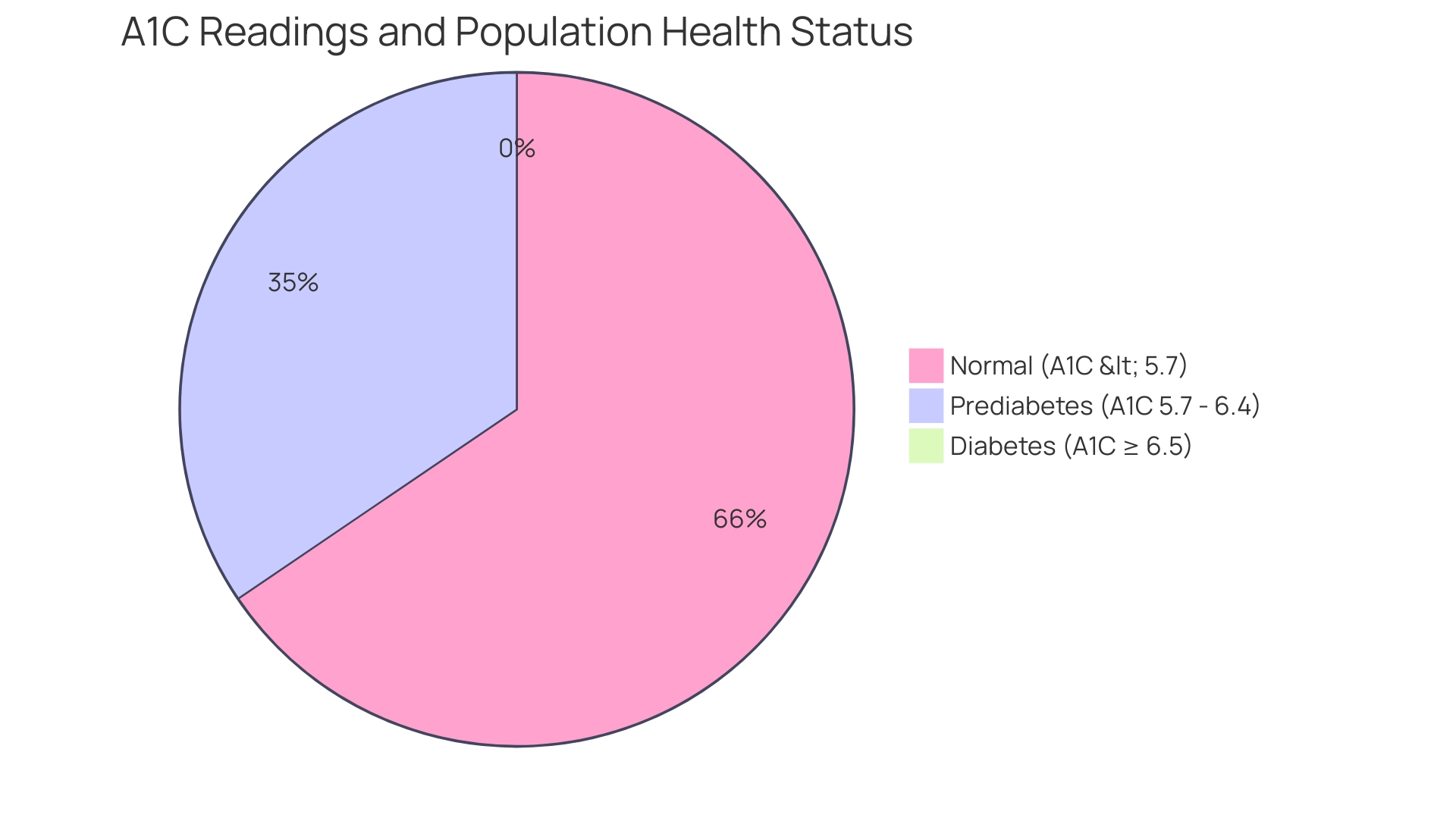
A1C readings are crucial markers in the diagnosis and management of blood sugar disorders, especially regarding A1C and prediabetes, where:
- An A1C below 5.7% is considered normal
- Readings between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes
- An A1C of 6.5% or higher suggests the presence of diabetes
According to the latest data, approximately 34.5% of the U.S. adult population has A1C readings that indicate a condition of A1C and prediabetes, highlighting the urgency for early intervention.
Significantly, 93.0% of individuals had their cholesterol checked, highlighting the importance of regular health monitoring alongside A1C measurements. These classifications are critical for healthcare providers as they assess a patient’s risk and tailor appropriate interventions. Understanding one’s A1C levels is vital for guiding necessary lifestyle changes and medical treatments concerning A1C and prediabetes.
As highlighted by prominent endocrinologists, regular monitoring and interpretation of A1C results are essential in preventing the advancement of a condition related to A1C and prediabetes. However, it is essential to challenge traditional approaches; a holistic regimen, which addresses the root causes of insulin resistance, can empower patients to reverse Type 2. Transformative patient experiences at the Integrative Wellness Center showcase how lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes, reinforcing the notion that proactive health measures are crucial for at-risk populations.
Many clients have shared their success stories, expressing how the holistic approach not only improved their A1C readings but also addressed their concerns regarding A1C and prediabetes, helping them lose the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of the disease. This knowledge empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health effectively.
Effective Strategies for Lowering A1C Levels and Managing Prediabetes
To effectively lower A1C values and address a1c and prediabetes, individuals are encouraged to adopt a holistic approach that emphasizes a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, while significantly reducing processed foods and sugars. Recent dietary recommendations for 2024 highlight the importance of these food groups for improving glycemic control. Consistent physical activity is also essential; participating in a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week can result in significant enhancements in blood sugar control.
Studies show that regular exercise is associated with a decrease in A1C values, emphasizing the relationship between physical activity and prediabetes management. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy weight through careful calorie control and portion sizes is vital for effective regulation of A1C and prediabetes. Incorporating stress reduction techniques and ensuring adequate sleep are also important factors that contribute to overall health and can positively influence A1C levels and prediabetes.
As noted by nutrition experts, practicing sleep-promoting routines is key to overall well-being. Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H. highlights the urgent requirement for effective A1C oversight, stating, ‘The age-adjusted prevalence of total and diagnosed conditions associated with high blood sugar increased between 1999–2000 and August 2021–August 2023.’
Additionally, it is essential for patients to be informed about the potential side effects and long-term risks associated with traditional treatments for managing blood sugar, such as Ozempic (semaglutide), which aids in informed decision-making regarding their treatment options. To ease the worries related to the possible issues of this condition, it is essential to reassess the origin of your health issue, enabling a more customized and effective strategy. Embracing a comprehensive strategy that incorporates dietary adjustments, physical exercise, and lifestyle changes is crucial for effective management of a1c and prediabetes at the Integrative Wellness Center.
Identifying Risk Factors for Prediabetes and Elevated A1C Levels
Common risk factors for prediabetes encompass several lifestyle and genetic components, including:
- Being overweight
- Engaging in a sedentary lifestyle
- Having a family history of the condition
Age is also a significant factor, with individuals over 45 being at higher risk. Additional contributors include:
- High blood pressure
- Abnormal cholesterol levels
- A history of gestational conditions
Current statistics indicate that nearly 93.0% of patients with this condition have had their cholesterol checked, underscoring the importance of monitoring health issues that may exacerbate risk. Alarmingly, in 2020, there were 202,000 emergency department visits for hypoglycemia, equating to 8.6 per 1,000 adults with blood sugar issues, highlighting the critical need for effective care. As the prevalence of obesity continues to rise, particularly in nonmetropolitan areas where diagnosed sugar-related health issues are elevated, awareness of these risk factors becomes increasingly vital.
This heightened awareness equips individuals to recognize the necessity for lifestyle changes and seek appropriate guidance from healthcare professionals. Recent case studies illustrate the disparities in prediabetes awareness across different racial and ethnic groups, with:
- Asian non-Hispanic individuals showing the highest awareness at 30.1%
- White non-Hispanic individuals having the lowest at 17.3%
These disparities emphasize the need for culturally tailored health education strategies to effectively reach diverse populations.
Recognizing these risk factors allows for proactive management of A1C levels and insulin resistance, which is crucial for understanding A1C and prediabetes, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes. It is essential for Type 2 patients to explore transformative health solutions beyond conventional approaches, including understanding the potential life-threatening consequences of traditional treatments. Additionally, participating in community wellness programs that emphasize education, nutrition, and support, along with applying four lesser-known strategies—such as:
- Mindful eating
- Incorporating resistance training
- Optimizing sleep
- Managing stress
can significantly enhance health and assist in reversing the condition.
The Importance of Regular A1C Testing in Health Management
For individuals with prediabetes, it is recommended to have their A1C and prediabetes levels tested at least biannually, while those diagnosed with the condition should undergo testing every three months. This frequency of monitoring is crucial as it allows for timely adjustments to dietary and lifestyle interventions, as well as modifications to medication regimens when necessary. Regular A1C testing not only keeps individuals informed about their glucose control but also empowers them to engage in productive discussions with their healthcare providers regarding their management plans.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize a holistic approach to reversing the condition by addressing root causes and providing comprehensive insights into treatment options. By effectively managing A1C and prediabetes, patients can discover new peace in their lives, alleviating anxiety about potential complications. Based on recent suggestions, monitoring A1C levels is crucial for enhancing health outcomes.
The importance of regular oversight is emphasized by the statistic that in 2020, there were 202,000 emergency department visits for hypoglycemia, equating to 8.6 visits per 1,000 adults with this condition, highlighting the consequences of poor glucose management. Furthermore, a transformative patient success story at our center illustrates how personalized care from Dr. Shumard has empowered patients to reverse type 2. A case study titled ‘Risk Factors for Diabetes-Related Complications’ revealed that among U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes:
- 22.1% were tobacco users
- 89.8% were overweight or had obesity
- 31.9% were physically inactive
This case study demonstrated that patients who engaged in regular A1C monitoring and made lifestyle changes significantly reduced their risk of complications, emphasizing the importance of understanding A1C and prediabetes for effective health management and improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The A1C test serves as a critical benchmark for assessing long-term blood sugar control, making it indispensable in the management of diabetes and prediabetes. By providing a comprehensive view of average blood sugar levels over two to three months, the A1C test enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment strategies. As obesity rates and diabetes prevalence continue to rise, understanding A1C levels becomes increasingly vital for early diagnosis and intervention.
Implementing effective strategies to lower A1C levels is essential for individuals at risk. A holistic approach, encompassing:
- Dietary changes
- Regular exercise
- Lifestyle modifications
has shown promise in not only improving A1C levels but also in reducing the anxiety associated with diabetes management. Proactive health measures, such as consistent monitoring and engaging in community wellness programs, empower patients to take control of their health and mitigate the risk of complications.
In summary, regular A1C testing is crucial for effective diabetes management. It provides the necessary feedback to adjust lifestyle interventions and medication regimens, ensuring that individuals stay informed and engaged in their health journey. By prioritizing A1C monitoring and adopting a comprehensive approach to health, individuals can significantly enhance their well-being and reduce the impact of diabetes on their lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, measures the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has bonded with glucose. It is important because it provides an average of blood sugar readings over the past two to three months, making it crucial for diagnosing and monitoring A1C, prediabetes, and diabetes.
How does the A1C test differ from daily blood sugar tests?
Unlike daily blood sugar tests, which can fluctuate significantly due to factors like stress or diet, the A1C test offers a long-term view of blood sugar levels, reflecting average levels over the past two to three months.
What are the classifications of A1C readings?
An A1C below 5.7% is considered normal. Readings between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes. An A1C of 6.5% or higher suggests diabetes.
What percentage of the U.S. adult population has concerning A1C readings?
Approximately 34.5% of the U.S. adult population has A1C readings that indicate a condition of A1C and prediabetes, highlighting the need for early intervention.
How can the A1C test influence treatment decisions?
The A1C test enables healthcare providers to evaluate how effectively a patient’s blood sugar levels are being managed, which informs treatment decisions and necessary lifestyle changes.
What role does regular monitoring of A1C levels play in diabetes management?
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential in controlling blood sugar levels and managing A1C and prediabetes, significantly lowering the risk of complications associated with these conditions.
Can lifestyle changes impact A1C levels?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet and regular exercise can help improve A1C readings and prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes.
What is a success story related to A1C management mentioned in the article?
A success story from the Integrative Wellness Center details a patient, M.L., who lost 55 lbs, improved their A1C levels from 9.1 to 5.7, and decreased their fasting glucose from 133 to 85 over eight months through a holistic regimen.
What common risk factors are associated with diabetes-related complications?
Among U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions, 22.1% were tobacco users, 89.8% were overweight or had obesity, and 31.9% were physically inactive, highlighting the relevance of A1C testing in assessing risk factors.
How does the A1C test contribute to understanding glycemic control in complex patient populations?
The A1C test is indispensable for understanding glycemic control, especially in complex patient populations, including those in intensive care settings, as it provides critical insights into blood sugar management.