Overview
An A1C level of 5.9% indicates an average blood sugar concentration of approximately 126 mg/dL, categorizing the individual as prediabetic and highlighting an increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes and related health complications. The article supports this by explaining that such a level not only reflects concerns regarding blood sugar management but also emphasizes the importance of lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and collaboration with healthcare professionals to mitigate potential health risks.
Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is crucial for assessing diabetes risk and managing overall health. An A1C reading of 5.9% serves as a significant indicator, marking the transition from normalcy to prediabetes, and highlights the need for proactive health measures. This article delves into the implications of such a level, exploring the connection between A1C and various health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular issues
- Kidney disease
It emphasizes the importance of:
- Regular monitoring
- Lifestyle modifications
- Nutritional strategies
in mitigating risks associated with elevated A1C levels. By examining effective management techniques and the role of physical activity, the article provides a comprehensive overview of how individuals can take charge of their health and prevent the progression of diabetes.
Understanding A1C: What Does a Level of 5.9 Indicate?
The A1C test serves as a vital diagnostic tool that measures the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood coated with sugar, known as glycated hemoglobin. An A1C of 5.9 is what average blood sugar measurement indicates, reflecting an average blood glucose concentration of approximately 126 mg/dL over the preceding two to three months, which categorizes the individual as prediabetic. This classification is crucial, as it indicates that while the condition has not been diagnosed, there exists a heightened risk for its development.
According to Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics, the prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed conditions in adults remains a significant concern, underscoring the necessity of monitoring A1C values as part of a holistic strategy to manage Type 2 health issues. Factors such as dietary choices, physical activity, and overall health status can cause fluctuations in A1C measurements; thus, regular monitoring empowers patients to make informed decisions regarding lifestyle modifications and necessary medical interventions. Emphasizing lesser-known power-plays, such as:
- Incorporating stress reduction techniques
- Optimizing sleep quality
- Leveraging community support programs
can significantly enhance health outcomes.
Notably, 93.0% of individuals have had their cholesterol checked, highlighting the importance of comprehensive health monitoring in managing blood sugar levels. Additionally, recent updates on FDA approvals for pharmacotherapy options provide healthcare providers with the latest treatment alternatives available for obesity management, which is pertinent to controlling A1C levels. Grasping the implications of A1C is crucial, especially given that the average medical expenses related to this condition have increased substantially—from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022.
Staying informed about these changes is crucial for effective management and prevention of the condition.
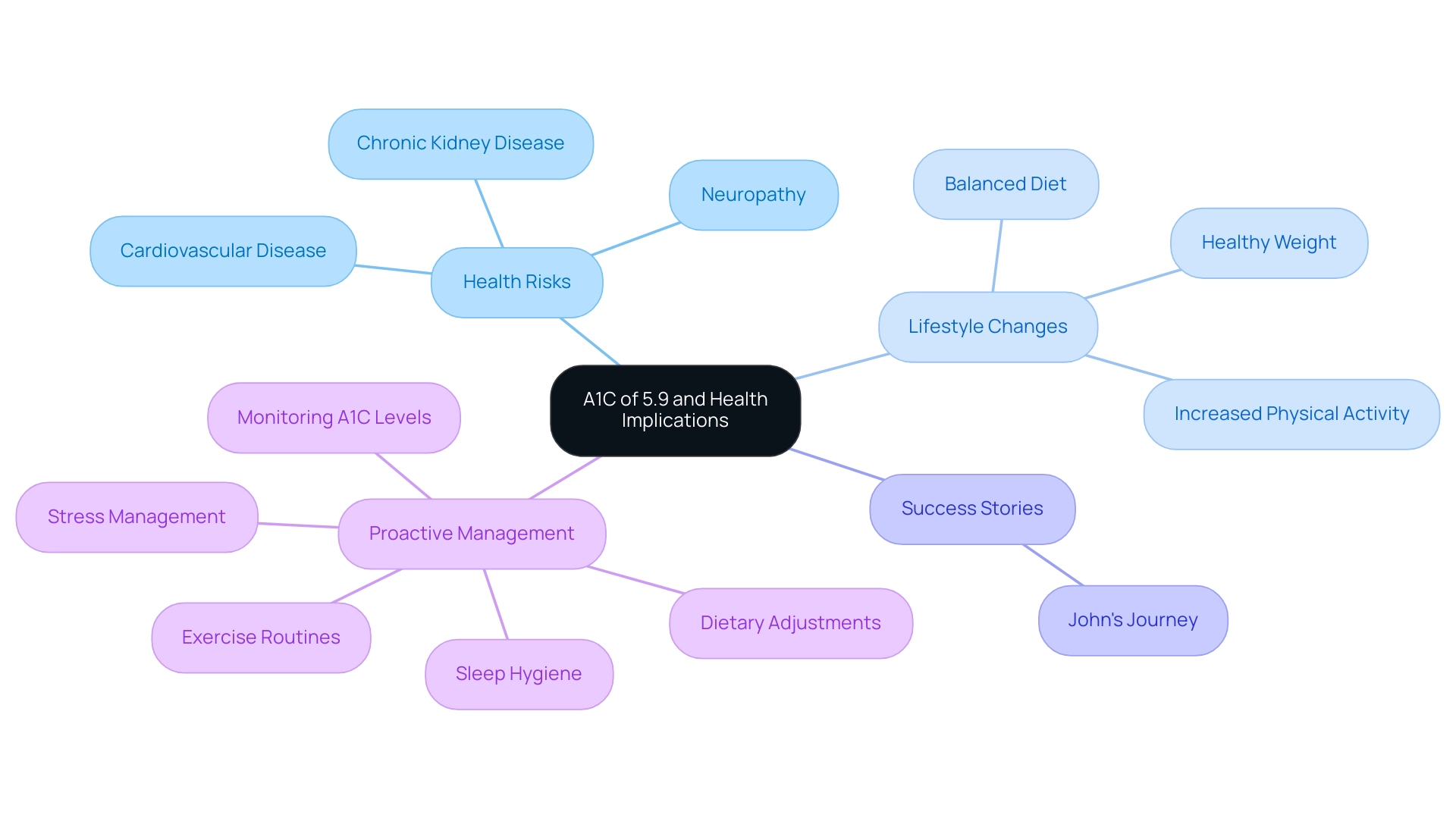
Health Implications of an A1C of 5.9: What You Need to Know
An A1C measurement of 5.9% indicates that an A1C of 5.9 is what average blood sugar signifies, reflecting a heightened risk of advancing to type 2 metabolic disorder, which can lead to severe health issues like cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and chronic kidney disease. Notably, the top quartile for A1C is defined as 5.7–6.4%, suggesting that an A1C of 5.9 is what average blood sugar indicates falls within a concerning range. Recent studies indicate that individuals with an A1C of 5.9, which is what average blood sugar corresponds to, are particularly vulnerable to heart failure risks, as highlighted by findings from a middle-aged bi-ethnic population without blood sugar issues, where elevated A1C readings (≥5.5–6.0%) showed a stronger correlation with heart failure than fasting glucose amounts.
Additionally, the Yoshinaga 1996 study, which involved 819 Japanese participants, emphasizes the importance of tracking A1C measurements in understanding diabetes risk. To reduce these risks, individuals are encouraged to adopt lifestyle changes such as:
- Embracing a balanced diet that highlights whole foods
- Increasing physical activity
- Attaining a healthy weight
Regular consultations with healthcare professionals, like those at the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego, are essential to devise a personalized management plan that focuses on:
- Monitoring A1C levels
- Implementing dietary adjustments
- Establishing exercise routines
Empowering patients through comprehensive insights and treatment options can lead to transformative outcomes, as illustrated by success stories from the Integrative Wellness Center, such as John, who reversed his type 2 condition through personalized care that included tailored meal plans and consistent exercise routines. Additionally, integrating education on stress management and sleep hygiene plays a pivotal role in supporting blood sugar control and enhancing overall health and well-being. As noted by specialists in blood sugar management, proactive health management is crucial—let your doctor know if any risk factors apply to you.
Embracing lifestyle changes has proven successful for many, demonstrating that such modifications can significantly reduce diabetes risk and improve quality of life. For instance, patients are encouraged to set achievable goals, such as incorporating 30 minutes of daily exercise and gradually adjusting their diet to include more whole foods, which can lead to significant improvements in their A1C results.
Monitoring and Managing A1C Levels: Effective Strategies
Efficient oversight of A1C readings requires a proactive strategy for blood sugar monitoring, which is essential to the comprehensive care philosophy at the Integrative Wellness Center. We start by re-evaluating the origin of your diabetes, enabling us to tackle health at the core. Regular monitoring is essential as it enables individuals to identify patterns and triggers that may influence blood sugar fluctuations, ultimately reducing anxiety over potential complications.
A CV value ≥36% indicates an unstable blood sugar profile, underscoring the importance of consistent monitoring. Keeping a food journal can help in identifying eating patterns that lead to increased sugar amounts. Participating in regular physical activity—whether through walking, swimming, or cycling—has been demonstrated to significantly improve sugar metabolism and support overall health.
Collaboration with healthcare professionals is critical in establishing a comprehensive management plan that may include medication when appropriate. Moreover, the integration of technology, particularly continuous blood sugar monitors, offers invaluable real-time feedback, empowering individuals to make informed decisions regarding their diet and activity levels. As highlighted by lead author I.B.H., “Continuous sugar monitoring plays a crucial role in managing the condition.”
The ongoing advancements in blood sugar testing technology present an opportunity for improved A1C management, since an A1C of 5.9 is what average blood sugar helps to enhance overall health outcomes for individuals managing Type 2 metabolic disorder. For instance, the case study titled ‘Translating A1C Assay into Estimated Average Glucose’ highlights how translating A1C results into estimated average glucose values can provide a clearer understanding of blood sugar control, as an A1C of 5.9 is what average blood sugar reflects, further strengthening effective management strategies through a holistic lens.
LEARN MORE about our holistic regimen and how it can help you achieve better health outcomes.
The Importance of Nutrition in Managing A1C Levels
Nutrition is a cornerstone in the management of A1C values for individuals with type 2 conditions, especially when viewed through a holistic lens that addresses the root causes of the illness. By re-examining the source of your diabetes, we can alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications. An effective dietary regimen typically includes:
- Whole grains
- A variety of fruits and vegetables
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
Such foods contribute to stable blood sugar levels by providing a balanced intake of essential nutrients. In contrast, it is vital to minimize the consumption of:
- Processed foods
- Sugary drinks
- High-glycemic index items
as these can lead to significant spikes in blood sugar. Meal planning, along with portion control, emerges as a crucial strategy for sustaining healthy eating habits.
According to nutrition specialists, total energy intake (and thus portion sizes) is a significant factor regardless of which eating pattern the individual with a blood sugar condition decides to adopt. Furthermore, magnesium supplementation has been demonstrated to yield beneficial effects on blood sugar levels, with a weighted mean difference of −4.64 mg/dL, emphasizing the significance of nutrient consumption in managing this condition. Integrating insights from comprehensive studies emphasizes the complex interactions of glucose, lipids, and amino acids, further underscoring the necessity of a holistic approach to dietary management.
Collaborating with a registered dietitian can enhance dietary management by tailoring meal plans to fit individual health objectives and specific dietary preferences. Additionally, embracing a Mediterranean-style eating pattern, abundant in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), has demonstrated potential in enhancing glycemic control and lowering cardiovascular risk factors, establishing it as a beneficial approach within the overall dietary framework for individuals managing type 2. These nutritional strategies are not merely about food choices; they are integral to effective management of blood sugar levels and achieving optimal metabolic control, empowering patients to reclaim their health.
To learn more about how a holistic approach can assist you in managing your condition effectively, consider reaching out to our team.
Physical Activity: A Key Component in Blood Sugar Management
Consistent physical activity is a cornerstone in the holistic management of blood sugar and the enhancement of insulin sensitivity, particularly for type 2 diabetes patients. Engaging in a minimum of 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity exercise—such as brisk walking or cycling—has been shown to significantly lower A1C levels, suggesting that an A1C of 5.9 is what average blood sugar should be. A recent study highlighted that two weeks of afternoon high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE) training improved continuous monitor (CGM)-monitored glycemia, illustrating how exercise can actively combat insulin resistance and reduce reliance on traditional treatments.
Furthermore, incorporating strength training exercises at least twice a week not only improves muscle mass but also promotes better glucose uptake, effectively addressing the underlying causes of the condition. It is paramount for individuals to engage in activities they enjoy, as this fosters consistency in their exercise routines and empowers them in their health journey. Short bouts of activity throughout the day, like standing during work hours or choosing stairs over elevators, can further enhance overall fitness and effective blood sugar control.
As Dr. Jill A Kanaley notes, ‘Other topics addressed include exercise timing to maximize its glucose-lowering effects and barriers to physical activity adoption and maintenance.’ Recent studies indicate that such physical activities not only enhance glycemic control but may also support cognitive function. For example, although the Look AHEAD trial indicated no cognitive advantages after 8-9 years, a meta-analysis proposed a small to moderate positive impact of exercise on memory and executive function, highlighting the diverse benefits of a comprehensive approach to managing type 2.
Importantly, by re-examining the source of your diabetes, we can alleviate the anxiety surrounding the potential complications of the disease, reinforcing the importance of a holistic regimen that addresses health at the root level.
Conclusion
An A1C level of 5.9% serves as a critical warning sign, indicating a transition into the prediabetic range and highlighting the need for immediate attention to health management strategies. As detailed, this level is associated with significant risks, including the potential for developing serious complications such as cardiovascular disease and kidney issues. Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their lifestyle choices and medical interventions.
Implementing lifestyle modifications—such as:
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing stress
can markedly reduce the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes. Collaborative efforts with healthcare professionals can tailor these strategies to individual needs, enhancing the effectiveness of management plans. The integration of technology, such as continuous glucose monitors, further supports individuals in achieving better health outcomes.
Ultimately, understanding and managing A1C levels is not merely about preventing diabetes; it is about reclaiming health and improving overall well-being. By embracing a proactive approach—centered on nutrition, physical activity, and regular health monitoring—individuals can significantly enhance their quality of life and mitigate the risks associated with elevated blood sugar levels. Taking these steps today can pave the way for a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and what does it measure?
The A1C test measures the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is coated with sugar, known as glycated hemoglobin. It reflects average blood glucose concentration over the preceding two to three months.
What does an A1C level of 5.9% indicate?
An A1C level of 5.9% indicates an average blood sugar measurement that reflects a heightened risk of developing type 2 diabetes, categorizing the individual as prediabetic.
Why is monitoring A1C values important?
Monitoring A1C values is crucial as it helps manage Type 2 health issues, allowing individuals to make informed decisions regarding lifestyle modifications and necessary medical interventions.
What lifestyle factors can affect A1C measurements?
Factors such as dietary choices, physical activity, stress levels, and overall health status can cause fluctuations in A1C measurements.
What are some recommended lifestyle changes to improve A1C levels?
Recommended lifestyle changes include incorporating stress reduction techniques, optimizing sleep quality, embracing a balanced diet with whole foods, increasing physical activity, and leveraging community support programs.
How prevalent is the monitoring of cholesterol levels among individuals?
Approximately 93.0% of individuals have had their cholesterol checked, highlighting the importance of comprehensive health monitoring in managing blood sugar levels.
What recent advancements exist in pharmacotherapy for obesity management related to A1C levels?
Recent updates on FDA approvals have provided healthcare providers with new treatment alternatives for obesity management, which is pertinent to controlling A1C levels.
What are the potential health risks associated with an A1C level of 5.9%?
An A1C level of 5.9% is associated with an increased risk of developing severe health issues such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and chronic kidney disease.
How can individuals reduce their risk of diabetes?
Individuals can reduce their risk of diabetes by adopting lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, increasing physical activity, and regularly consulting with healthcare professionals for personalized management plans.
What success stories illustrate the effectiveness of personalized care in managing A1C levels?
Success stories, such as that of John from the Integrative Wellness Center, demonstrate that personalized care, including tailored meal plans and consistent exercise routines, can lead to significant improvements and even reversal of type 2 diabetes.