Overview
An A1C level of 5.8% corresponds to an average blood sugar concentration of approximately 126 mg/dL, which places individuals in the prediabetes range and indicates an increased risk of developing metabolic disorders. The article highlights that maintaining an A1C below 7% is optimal for those with Type 2 diabetes, and it emphasizes the importance of lifestyle modifications and regular monitoring to effectively manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Introduction
The A1C test, a cornerstone in diabetes management, provides essential insights into an individual’s average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. This crucial diagnostic tool not only aids healthcare providers in assessing long-term glucose control but also empowers patients with the knowledge required to make informed health decisions.
With rising diabetes prevalence and associated complications, understanding A1C results and their implications is more critical than ever. This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, explores its interpretation, and highlights the lifestyle changes and professional guidance necessary for effective diabetes management, ultimately aiming to equip individuals with the strategies needed to take charge of their health.
Understanding the A1C Test: What It Measures and Its Importance
The A1C test, formally known as the glycated hemoglobin test, serves as a vital diagnostic tool, measuring the percentage of glucose molecules bound to hemoglobin over the preceding two to three months. For individuals diagnosed with Type 2 mellitus, this test provides a comprehensive view on blood sugar readings, enhancing daily monitoring practices. According to the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, the A1C test is crucial for evaluating long-term glucose control and predicting complications, empowering patients to take charge of their health.
The results not only indicate average blood sugar levels but also enable healthcare providers to evaluate the effectiveness of glucose control strategies, especially in understanding what average blood sugar a1c 5.8 equals, aligning with a holistic approach that addresses root causes. Furthermore, the A1C test is instrumental in predicting the likelihood of diabetes-related complications, informing necessary treatment adjustments and lifestyle changes. Recent statistics indicate that around 38.4% of emergency department visits related to metabolic disorders led to hospital admissions in 2020, highlighting the essential need for strong oversight protocols.
A case study from the same year showed there were 202,000 emergency department visits for hypoglycemia, highlighting the importance of continuous A1C monitoring to mitigate such risks. By utilizing the A1C test to its fullest potential, individuals can make informed decisions that significantly reduce their risk of complications related to blood sugar issues. Furthermore, the increasing awareness of monogenic conditions highlights the necessity for precision care, further demonstrating the significance of thorough monitoring within a holistic approach for treatment.
To further enhance health and reverse blood sugar issues, consider integrating lesser-known strategies such as:
- Incorporating whole grains into your diet
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Practicing stress reduction techniques
- Ensuring adequate sleep
These strategies can not only support blood sugar control but also alleviate anxiety regarding potential complications, fostering a more empowered approach to managing the condition.
Interpreting an A1C of 5.8: Implications for Average Blood Sugar Levels
An A1C measurement of 5.8% indicates that A1C 5.8 equals what average blood sugar concentration of approximately 126 mg/dL, placing individuals within the prediabetes range. This status indicates a heightened risk of progressing to a metabolic disorder, as research highlights that individuals with an A1C level of 5.8% exhibit a 3.5-fold increased risk for men and a 5.2-fold increased risk for women. According to the 1997 ADA criteria, the condition is defined based on plasma glucose results from the 75-g OGTT, emphasizing the clinical relevance of A1C testing.
For individuals already diagnosed with type 2, keeping an A1C below 7% is typically viewed as optimal, indicating that an A1C of 5.8 equals what average blood sugar, which suggests effective disease control. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize a holistic approach to reversing type 2 by addressing the root causes of the condition. This involves personalized care strategies that empower patients to reclaim their health.
For example, one patient, Jane, successfully reduced her A1C from 8.5% to 5.6% within six months through our tailored program, which included dietary changes and lifestyle modifications. It is vital that A1C results are understood in conjunction with a thorough evaluation of overall health, lifestyle selections, and individual treatment goals, as care is fundamentally personalized. The financial effect of this condition is considerable, with total projected expenses of diagnosed cases in the United States hitting $413 billion in 2022, emphasizing the necessity for effective oversight and prevention strategies.
Moreover, as the occurrence of diagnosed diabetes in the United States increased from 6.3% to 8.3% between 2004 and 2021, with estimates among U.S. counties varying from 4.4% to 17.9% in 2021, understanding A1C values and their implications becomes increasingly crucial for effective diabetes prevention and control strategies. Our patients often express gratitude for the support and guidance they receive, with one stating, ‘The Integrative Wellness Center has changed my life, helping me understand my condition and take control of my health.
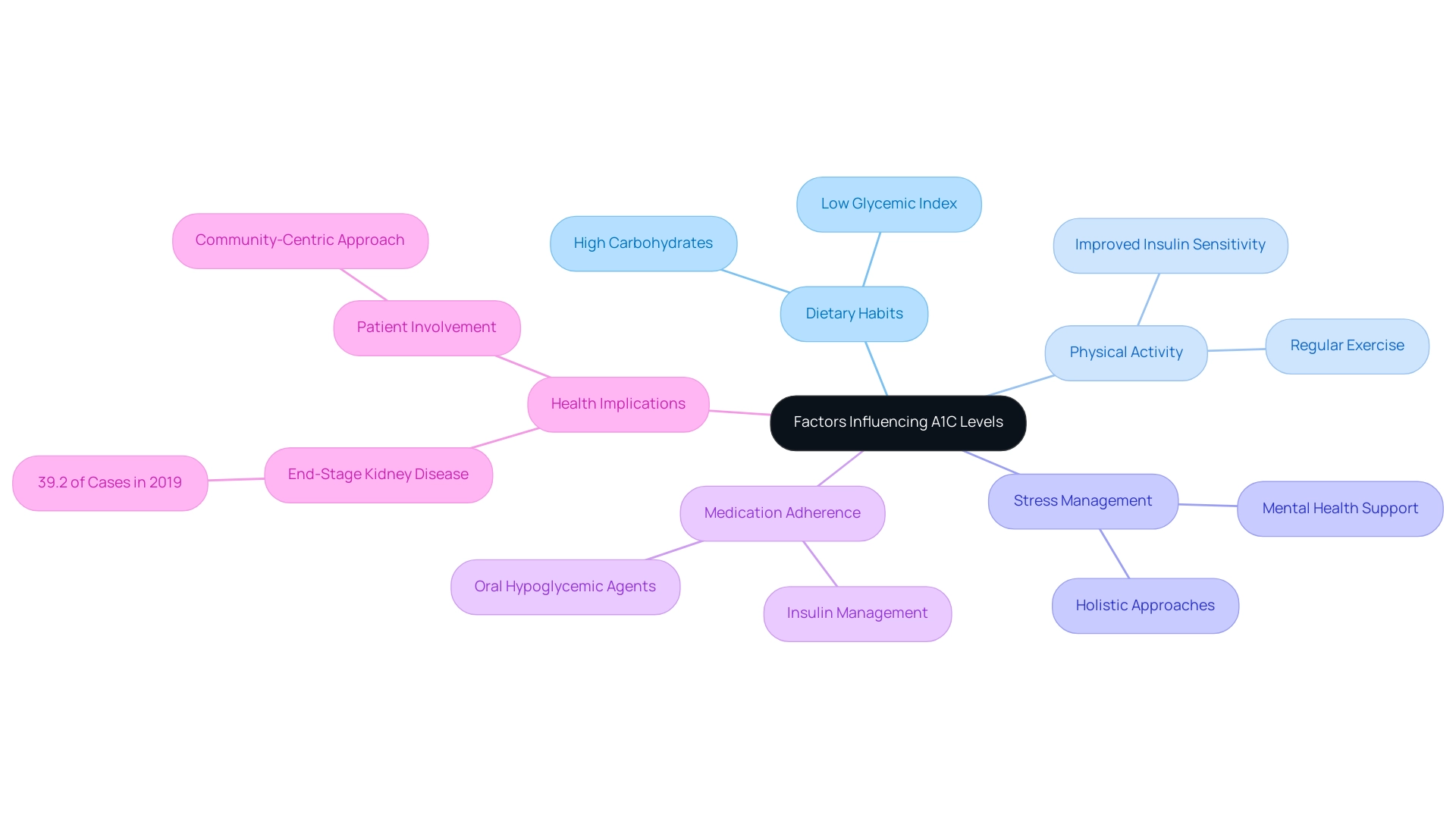
Factors Influencing A1C Levels
A variety of factors can significantly influence A1C values, including dietary habits, physical activity, stress management, and medication adherence, leading to the question of what average blood sugar corresponds to A1C 5.8. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we recognize that a diet rich in carbohydrates can result in increased blood sugar readings, which can raise A1C percentages; thus, it’s important to understand what A1C 5.8 equals as the average blood sugar. Conversely, participating in regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, which can potentially reduce A1C values, leading to inquiries such as what average blood sugar corresponds to A1C 5.8.
Our holistic approach focuses on addressing the root causes of diabetes, empowering patients to take control of their health. For example, one patient shared, ‘After modifying my diet and becoming active, I not only observed my A1C readings decrease, but I also felt more in control of my life.’ Recent research highlights the significance of following prescribed medications, such as insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents, in managing blood glucose effectively and in determining what average blood sugar corresponds to A1C 5.8.
In fact, the condition was the primary cause of end-stage kidney disease for 39.2% of cases in 2019, highlighting the serious implications of A1C levels, such as what average blood sugar corresponds to A1C 5.8, and the necessity for effective management. It is essential for individuals with this condition to work closely with their healthcare providers, as interprofessional teamwork is vital for successful health outcomes. This approach is exemplified in case studies like ‘Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes with HbA1c,’ which demonstrate the success of interventions for managing blood sugar levels, particularly in understanding what average blood sugar corresponds to A1C 5.8, while also advocating for alternative methods such as estimated average glucose.
Additionally, we acknowledge the vital role of patient involvement in managing this condition, as noted by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, emphasizing a community-centric approach to reversing Type 2 and addressing related health issues like hypothyroidism. Managing this condition can also bring about anxiety, but by re-examining the source and implementing a holistic regimen, patients can alleviate some of this worry and focus on their health journey.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve A1C Levels
To effectively manage A1C measurements, individuals should consider that a1c 5.8 equals what average blood sugar while implementing a series of lifestyle modifications within a holistic framework that addresses the root causes of diabetes and the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications. A balanced diet, rich in whole foods, plays a crucial role; it is advisable to focus on consuming an abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Such dietary choices can significantly aid in stabilizing blood sugar, which relates to understanding what a1c 5.8 equals what average blood sugar.
Moreover, participating in consistent physical activity—aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly—has been demonstrated to improve insulin sensitivity, positively affecting A1C values. Recent studies have revealed that structured training programs are linked to significant reductions in HbA1c levels, emphasizing the importance of exercise in conjunction with lifestyle changes. Furthermore, stress reduction methods, such as mindfulness practices, yoga, or meditation, can be advantageous for blood sugar regulation and are essential to a comprehensive strategy for addressing this health condition.
Integrating these lifestyle changes not only aids in lowering A1C but also helps in understanding what a1c 5.8 equals what average blood sugar for overall health and well-being. Comprehending the psychological obstacles, like those emphasized in the case study on psychological insulin resistance, is essential for creating effective approaches for managing the condition. Addressing these psychological factors, including anxiety about complications, is essential for adopting comprehensive lifestyle changes that lead to optimal health outcomes in individuals with type 2.
Furthermore, specific holistic methodologies, such as re-examining the source of your condition, can empower patients to take control of their health. Statistics indicate that at a 12-month follow-up, 83% of standard care participants adhered to prescribed glucose-lowering medication, emphasizing the significance of combining medication with lifestyle modifications for effective control of blood sugar.
The Role of Regular Monitoring and Professional Guidance
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is crucial for effective management of the condition, particularly to understand what average blood sugar A1C 5.8 equals, along with routine blood sugar checks. This practice empowers Type 2 individuals to track their glycemic control and make informed adjustments to their treatment plans. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize a holistic approach that addresses the root causes of this condition, equipping patients with the knowledge and tools to eliminate anxiety over potential complications and the worry about developing traumatic and debilitating issues related to it.
The guidance provided by healthcare professionals—such as physicians, dietitians, and educators—offers personalized insights tailored to each individual’s unique needs. Notably, Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics has highlighted the significant impact of professional guidance in understanding the prevalence of the condition, stating that ‘the insights gathered can significantly inform clinical decision-making.’ Additionally, engaging in support groups for those with health conditions fosters a sense of community and encouragement, further empowering individuals in their health journey.
By harnessing these resources, patients can proactively manage their condition and achieve their health objectives. With 29.4 million adults identified with this condition in 2021, along with 8.7 million undiagnosed, consistent A1C monitoring becomes increasingly critical for improving overall health outcomes. Furthermore, the rise in excess medical expenses per individual linked to the condition, from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022, highlights the financial implications of effective management.
Importantly, Hispanic adults represented 5.0 million diagnosed diabetes cases and 1.9 million undiagnosed cases, highlighting the urgent need for targeted monitoring and professional guidance to address these demographic disparities.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing A1C levels is paramount for individuals navigating diabetes. The A1C test serves as a critical indicator of average blood sugar levels, providing essential insights into long-term glucose control and the potential risk of complications. By interpreting A1C results within the broader context of lifestyle choices and health objectives, patients can take informed steps toward better health outcomes.
Implementing lifestyle changes, such as:
- Adopting a balanced diet
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing stress
plays a significant role in improving A1C levels. A holistic approach that addresses the underlying causes of diabetes, along with professional guidance, empowers individuals to reclaim control over their health. Continuous monitoring of A1C levels, coupled with support from healthcare professionals, enhances the ability to manage diabetes effectively and reduce anxiety associated with potential complications.
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, the importance of understanding A1C results cannot be overstated. By prioritizing regular check-ups and embracing comprehensive management strategies, individuals can mitigate risks and enhance their quality of life. Taking charge of one’s health through informed decisions and proactive measures is essential in the ongoing journey of diabetes management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, measures the percentage of glucose molecules bound to hemoglobin over the past two to three months. It is crucial for evaluating long-term glucose control, predicting complications, and empowering patients with Type 2 diabetes to manage their health effectively.
What does an A1C result indicate about average blood sugar levels?
An A1C measurement of 5.8% corresponds to an average blood sugar concentration of approximately 126 mg/dL, indicating a prediabetes status and a heightened risk of developing metabolic disorders.
What are the risks associated with an A1C level of 5.8%?
Individuals with an A1C level of 5.8% have a 3.5-fold increased risk for men and a 5.2-fold increased risk for women of progressing to a metabolic disorder.
What is considered an optimal A1C level for individuals diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes?
For individuals already diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes, maintaining an A1C level below 7% is typically viewed as optimal, indicating effective disease control.
How can individuals reduce their A1C levels?
Individuals can reduce their A1C levels through personalized care strategies that include dietary changes, regular physical activity, stress reduction techniques, and ensuring adequate sleep.
What is the significance of continuous A1C monitoring?
Continuous A1C monitoring is essential for mitigating risks associated with blood sugar issues, such as hypoglycemia, and for making informed decisions about treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
What are some statistics related to diabetes and A1C testing?
In 2020, approximately 38.4% of emergency department visits related to metabolic disorders resulted in hospital admissions. Additionally, there were 202,000 emergency department visits for hypoglycemia, emphasizing the need for strong oversight and monitoring.
How does the Integrative Wellness Center approach diabetes management?
The Integrative Wellness Center emphasizes a holistic approach to reversing Type 2 diabetes by addressing root causes and implementing personalized care strategies that empower patients to reclaim their health.
What financial impact does diabetes have in the United States?
The total projected expenses for diagnosed diabetes cases in the United States reached $413 billion in 2022, highlighting the necessity for effective prevention and oversight strategies.