Introduction
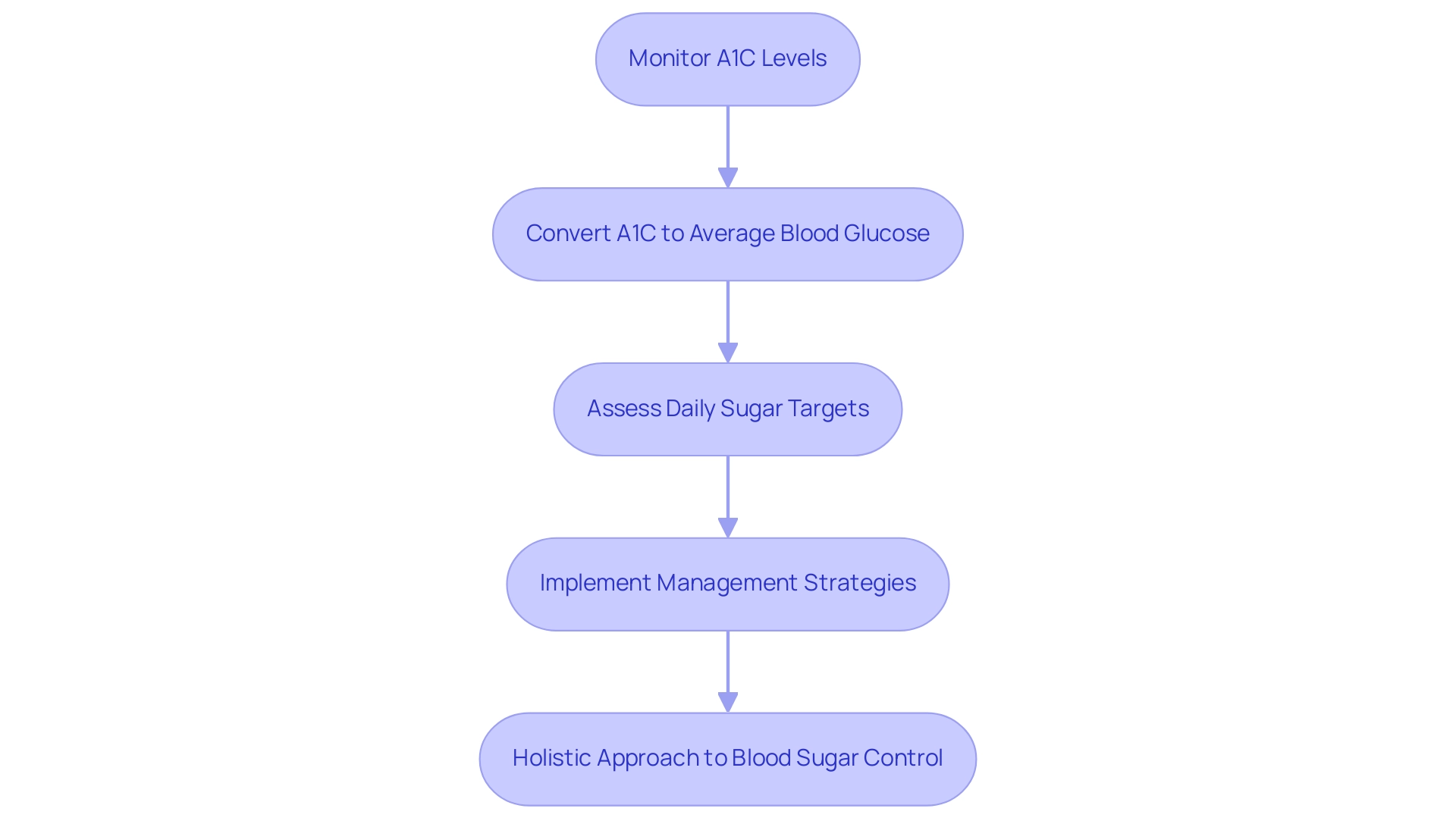
Understanding A1C levels is crucial for effective diabetes management, as this key blood test provides insights into average blood glucose levels over the previous two to three months. For individuals living with diabetes, maintaining an optimal A1C level is linked to a lower risk of complications, making it an essential focus for both patients and healthcare providers.
With the rising prevalence of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in the population, the importance of regular A1C monitoring cannot be overstated. This article delves into the significance of A1C testing, the relationship between A1C and average blood glucose readings, and the factors that can influence the accuracy of these tests.
By equipping readers with a comprehensive understanding of A1C, the article aims to empower individuals to take charge of their health and make informed decisions about their diabetes management strategies.
Understanding A1C: Definition and Importance in Diabetes Management
A1C, also referred to as glycated hemoglobin, is an essential blood test that plays a crucial role in A1C chart conversion to assess your average blood sugar levels over the prior two to three months. This metric is essential for managing blood sugar levels and plays a crucial role in A1C chart conversion, providing a comprehensive view of glucose control beyond daily readings. The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals diagnosed with the condition aim to maintain an A1C level below 7%, as this target can be effectively tracked through an A1C chart conversion, which is associated with a decreased risk of complications related to the disease.
It is equally important for those diagnosed with gestational conditions (GDM) to undergo lifelong screening for prediabetes and type 2 disorders, as early detection can significantly enhance health outcomes. Significantly, a study of individuals aged 60 and older indicated an undiagnosed prevalence of 6.8%, highlighting the critical role of A1C chart conversion in this demographic. Furthermore, with an estimated 97.6 million adults aged 18 and older having prediabetes, representing 38.0% of the adult U.S. population, the public health implications of A1C chart conversion are profound.
By comprehending your A1C results with an A1C chart conversion, you can make informed modifications to your health plan, ensuring it is effective and tailored, thus empowering you on your journey to reverse Type 2. To further enhance your health and manage diabetes effectively, consider incorporating these four essential strategies:
- Improving nutrition
- Increasing physical activity
- Managing stress
- Utilizing community support
Many have found success through personalized care; for instance, one patient shared, “After following a tailored plan and receiving support from my healthcare team, my A1C levels dropped significantly, which was reflected in the A1C chart conversion, and I feel more energetic than ever.
Utilizing A1C Conversion Charts for Effective Diabetes Management
A1C conversion charts serve as crucial resources for A1C chart conversion, assisting in the transformation of hemoglobin A1C percentages into estimated average sugar (eAG) levels, which aids in understanding blood sugar control. For instance, an A1C level of 7% equates to an eAG of approximately 154 mg/dL. Understanding this relationship empowers patients to make informed choices regarding dietary adjustments, medication modifications, and overall lifestyle changes.
Recent advancements, including the utilization of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), enhance the accuracy of these conversions by providing real-time data on blood glucose levels. Clinical trial evidence suggests that CGMs lower rates of hypoglycemia in groups using insulin, highlighting their significance in glucose regulation. These tools can be complemented by online conversion calculators, which assist in ensuring precise interpretations of A1C results.
As Vivian Fonseca mentioned in her editorial, ‘the translation of A1C to eAG is essential for effective control of blood sugar levels,’ making A1C chart conversion a valuable resource for individuals navigating their treatment plans. Furthermore, a case study demonstrates that A1C can be effectively calculated from average sugar levels using CGM data, providing a practical example of how these tools can assist in managing blood sugar. Additionally, clinical evidence underscores the importance of a partnership with healthcare providers during this process, particularly when aligning on treatment goals and making considerations regarding the risks associated with lowering A1C to near-normal levels, especially in patients with long-standing type 2 conditions.
The Benefits of Regular A1C Monitoring and Management
Regular monitoring of hemoglobin A1C levels is essential for individuals managing their condition, as it allows for effective A1C chart conversion that offers a thorough perspective of blood sugar regulation over time. This proactive approach not only facilitates early detection of rising A1C levels—indicating potential adjustments in medications or lifestyle choices—but also empowers patients to take charge of their health and find new peace in life. Research shows that maintaining lower A1C levels is associated with a decreased risk of diabetes-related complications, such as neuropathy and cardiovascular disease, alleviating worries about future health issues.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize a holistic approach to reversing the condition by addressing root causes and educating patients, helping them eliminate anxiety over potential complications. Blood glucose monitoring (BGM) is a crucial element of effective therapy, especially for individuals using insulin, which emphasizes the importance of A1C chart conversion in overall health care. For optimal control, we recommend a routine A1C chart conversion testing schedule—typically every three months.
Furthermore, as highlighted by Balintescu A. in ‘Hemoglobin A1c and Permissive Hyperglycemia in Patients in the Intensive Care Unit with Insulin Resistance,’ the critical relationship between A1C levels and complications cannot be overstated. Consistent monitoring, supported by the latest statistics from 2024, can significantly reduce the incidence of such complications, making it an essential practice for effective diabetes management. Additionally, advancements in blood sugar meters, including less painful lancing devices and the ability to reapply blood to strips, enhance user experience and accessibility, particularly for visually impaired individuals utilizing meters with integrated speech capabilities.
By embracing these practices, patients can eliminate worry and embrace a healthier, more peaceful life.
Connecting A1C Levels to Average Blood Glucose Readings
A1C levels act as an essential marker of average blood sugar over a specified duration, usually two to three months. An elevated A1C level, defined as 6.5% or more, indicates poor blood sugar management, making A1C chart conversion a crucial diagnostic standard for the condition. Comprehending this relationship is crucial for patients, as it directly affects daily sugar targets and overall health results.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we believe in a holistic approach to blood sugar control, addressing the root causes of the condition rather than merely treating symptoms. This approach could help you lose the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding the potential complications of your disease. Consistent observation of both A1C and daily sugar levels enables individuals to efficiently modify their control strategies through A1C chart conversion.
For instance, recent findings highlight that patients who actively engage in A1C chart conversion and tracking both metrics achieve better glycemic control. As Balintescu A. observed in research concerning the effects of A1C in intensive care environments, the oversight of blood sugar levels is essential for enhancing patient results. Furthermore, a study titled ‘Concordance and Discordance in Diabetes Diagnosis’ revealed that relying solely on fasting plasma glucose (FPG) could lead to delayed diagnosis, highlighting the importance of A1C chart conversion.
The study found that isolated elevated HbA1c was more common than isolated elevated FPG in low- and middle-income regions, underscoring the importance of a dual approach in monitoring. By embracing a collaborative care approach, backed by a multidisciplinary healthcare team, we can improve the precision of health strategies and enable patients to take control of their well-being through a personalized holistic plan.
Factors Influencing A1C Accuracy and Interpretation
The accuracy of A1C test results is important for a1c chart conversion and can be significantly influenced by various factors, including:
- Anemia
- Certain hemoglobinopathies
- Recent blood transfusions
According to the CDC’s National Diabetes Statistics Report, these conditions may lead to misleading A1C values, which can consequently impact management strategies for the condition, making a1c chart conversion essential. Furthermore, the case study titled ‘Challenges in Glucose Testing’ highlights that while glucose testing is inexpensive and widely available, it is subject to high diurnal variation and potential misreporting, complicating the interpretation of A1C results.
Medications and dietary supplements may also alter test outcomes, necessitating careful consideration. For individuals with Type 2 diabetes, it is crucial to maintain open communication with healthcare providers regarding any underlying health issues or medications that could influence the a1c chart conversion results. Dr. Jane Smith, a specialist in blood sugar disorders, observes, ‘Patients must comprehend how their health condition can affect A1C results, as this information is essential for effective a1c chart conversion and oversight.’
Such discussions not only help to mitigate the risk of misinterpretation but also empower patients to take an active role in their health journey. As Roopa Naik emphasizes, understanding these nuances is vital for effective management of blood sugar levels, particularly in light of the prevalent conditions that influence a1c chart conversion results among patients. By tackling root causes and promoting a comprehensive understanding of health through specific strategies such as:
- Dietary adjustments
- Stress management techniques
- Regular physical activity
Patients can enhance their management strategies beyond conventional approaches.
This holistic regimen not only supports better A1C results but also promotes overall well-being, aligning with the transformative health solutions necessary for reversing diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is fundamental for those living with diabetes, as it provides a comprehensive overview of blood glucose control over time. The article highlights the importance of regular A1C monitoring, emphasizing its role in reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. By maintaining A1C levels below 7%, individuals can significantly improve their health outcomes and take proactive steps in their diabetes management.
Utilizing A1C conversion charts and continuous glucose monitors enhances patients’ understanding of their blood glucose levels, enabling informed lifestyle choices and medication adjustments. The relationship between A1C and average blood glucose readings is critical, with regular monitoring allowing for timely interventions that can lead to better overall health.
Moreover, recognizing the factors that influence A1C accuracy is essential for effective diabetes management. Conditions such as anemia and specific medications can distort test results, underscoring the need for open communication with healthcare providers. By addressing these nuances and adopting a holistic approach to health, individuals can empower themselves in their diabetes journey.
Ultimately, A1C testing is not just a measure but a vital tool in the management of diabetes. By understanding and prioritizing A1C levels, individuals can navigate their path to better health, reduce anxiety about complications, and foster a proactive approach to living well with diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is A1C and why is it important?
A1C, also known as glycated hemoglobin, is a blood test that measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and provides a comprehensive view of glucose control beyond daily readings.
What A1C level is recommended for individuals with diabetes?
The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals diagnosed with diabetes aim to maintain an A1C level below 7% to decrease the risk of complications related to the disease.
How does A1C chart conversion assist in diabetes management?
A1C chart conversion helps individuals understand their A1C results in relation to estimated average glucose (eAG) levels, enabling them to make informed decisions about dietary adjustments, medication, and lifestyle changes.
What is the significance of A1C for those with gestational diabetes (GDM)?
Individuals diagnosed with gestational diabetes should undergo lifelong screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, as early detection can significantly improve health outcomes.
What is the prevalence of prediabetes among adults in the U.S.?
An estimated 97.6 million adults aged 18 and older have prediabetes, representing 38.0% of the adult U.S. population.
What strategies can help manage diabetes effectively?
Four essential strategies for managing diabetes include improving nutrition, increasing physical activity, managing stress, and utilizing community support.
How do continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) enhance diabetes management?
CGMs provide real-time data on blood glucose levels, which can lower rates of hypoglycemia in insulin-using groups and improve the accuracy of A1C to eAG conversions.
How can A1C levels be calculated from average sugar levels?
A1C can be effectively calculated from average sugar levels using data from continuous glucose monitors, providing a practical way to manage blood sugar.
Why is it important to partner with healthcare providers when managing A1C levels?
Partnering with healthcare providers is crucial for aligning treatment goals and considering the risks associated with lowering A1C to near-normal levels, especially in patients with long-standing type 2 diabetes.