Overview
The article focuses on the importance of understanding A1C conversion to blood sugar charts for effective diabetes management. It emphasizes that these charts provide crucial insights into average blood sugar levels over time, enabling individuals and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment and lifestyle adjustments, thereby improving overall health outcomes.
Introduction
Diabetes management has become increasingly vital in today’s health landscape, with A1C testing emerging as a cornerstone for monitoring blood sugar levels over time. This crucial metric not only provides insight into average glucose control but also serves as a guide for healthcare providers and patients alike in making informed decisions about treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
With statistics revealing a significant prevalence of diabetes across various demographics, understanding A1C is essential for effective management and prevention strategies. This article delves into the importance of A1C testing, the relationship between A1C levels and blood sugar, and the multifaceted approaches individuals can adopt to enhance their health outcomes while managing diabetes.
Understanding A1C: The Key to Blood Sugar Management
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, serves as an essential test that provides insights into average sugar levels over the preceding two to three months. This metric is indispensable for effective diabetes management, allowing individuals and healthcare providers to evaluate long-term glucose control. Understanding the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart is essential, as it presents a comprehensive view of blood sugar trends compared to daily readings.
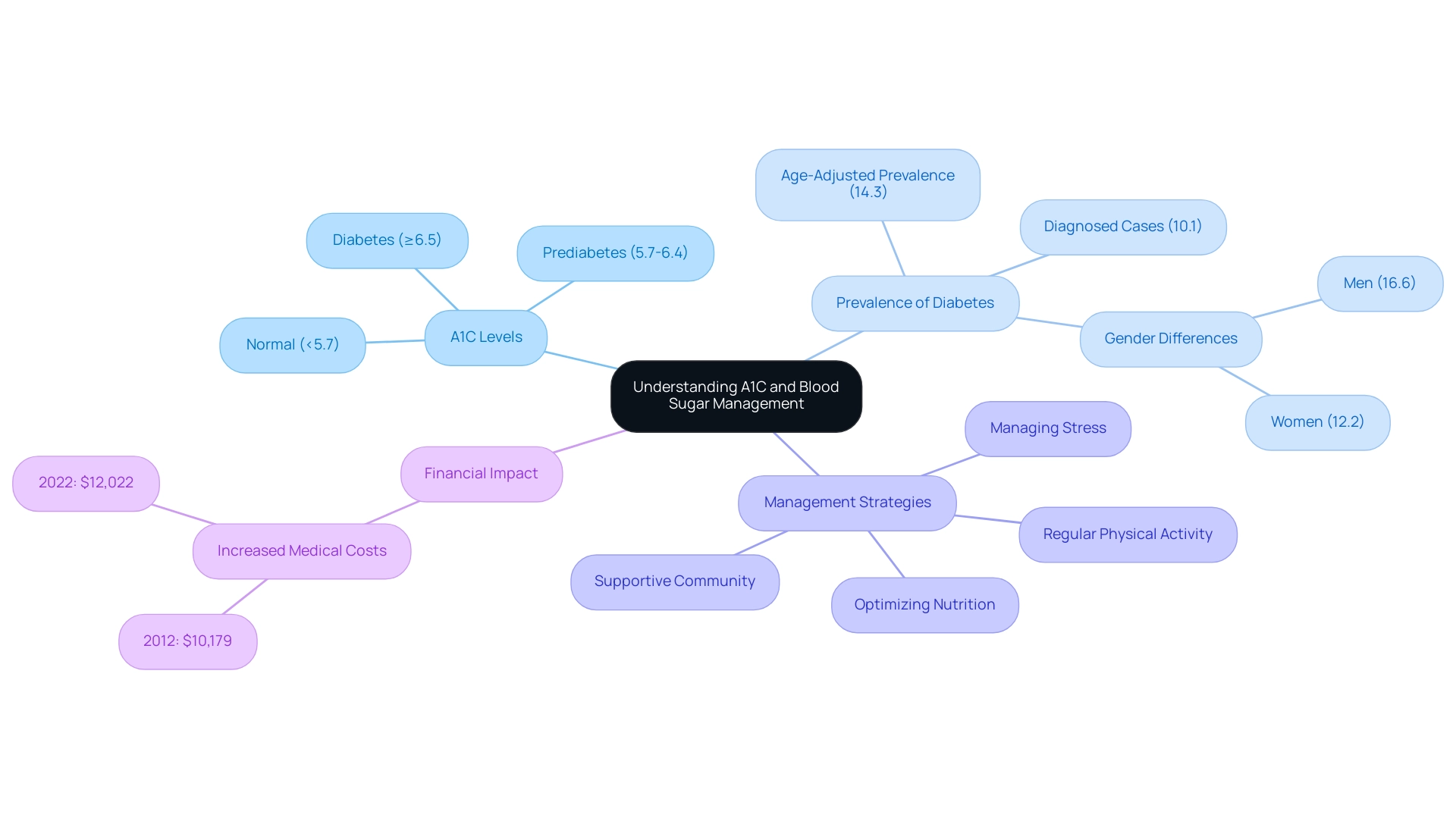
According to recent guidelines, an A1C level below 5.7% is deemed normal. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of the condition. Regular A1C monitoring is pivotal for guiding treatment strategies and informing necessary lifestyle adjustments.
As emphasized by Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H., the age-adjusted prevalence of total and diagnosed cases of the disease has risen between 1999–2000 and August 2021–August 2023. This statistic emphasizes the necessity for ongoing monitoring to manage the condition effectively. Furthermore, the age-adjusted estimates indicate that overall, 14.3% of adults are affected, with diagnosed cases at 10.1%.
Notably, the age-adjusted incidence of diagnosed metabolic disorder among adults aged 18 years or older was 6.2 per 1,000 adults in 2000. Additionally, excess medical expenses related to the condition increased from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022, emphasizing the financial impact of managing the disease. The prevalence rates also reveal significant differences between genders, with 16.6% of men and 12.2% of women affected.
Such statistics highlight the importance of A1C testing as a fundamental element of care for individuals with blood sugar issues, particularly within community wellness programs that utilize the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart and focus on education, nutrition, and holistic support at the Integrative Wellness Center. To further enhance health and potentially reverse this condition, it is essential to consider four lesser-known strategies:
- Optimizing nutrition
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing stress effectively
- Fostering a supportive community
Addressing the anxiety surrounding complications related to blood sugar issues is also crucial, as it can significantly impact overall health and well-being.
Essential A1C to Blood Sugar Conversion Charts
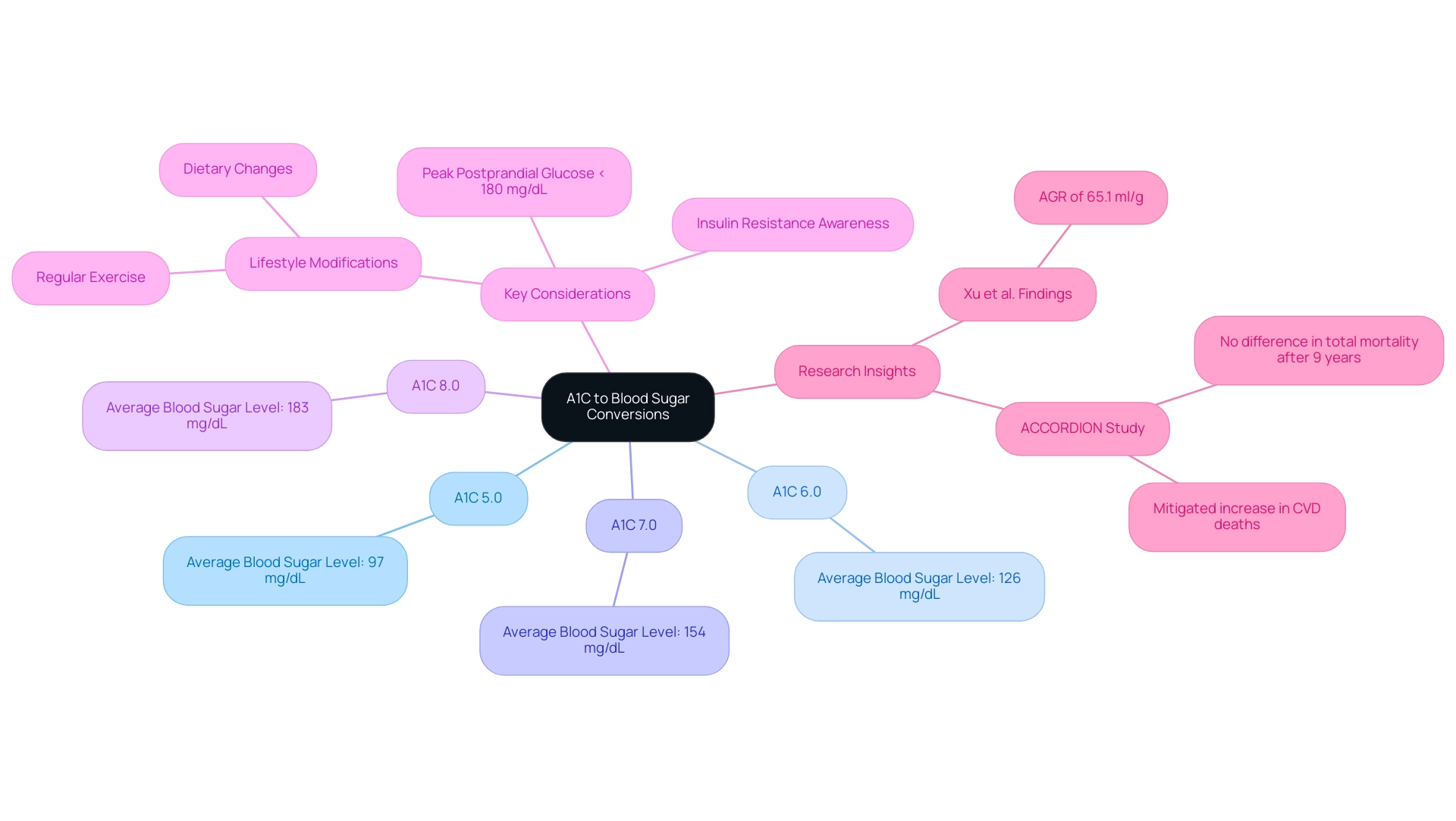
A1C conversion to blood sugar charts are vital resources for individuals managing diabetes, offering a quick reference to understand the relationship between A1C values and estimated average sugar (eAG). Below are critical conversions that illustrate this relationship:
- An A1C of 5.0% corresponds to an average blood sugar level of approximately 97 mg/dL.
- An A1C of 6.0% corresponds to an average glucose level of 126 mg/dL.
- An A1C of 7.0% indicates an average sugar level of 154 mg/dL.
- An A1C of 8.0% equates to about 183 mg/dL.
It is important to note that the peak postprandial capillary plasma glucose should ideally be <180 mg/dL (<10.0 mmol/L), providing a benchmark for effective sugar management. These conversion charts, such as the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart, are invaluable in helping individuals set realistic targets for effective condition management.
However, understanding A1C results also requires awareness of insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated glucose concentrations. Conventional therapies for this condition, while effective for some, can sometimes worsen insulin resistance and result in serious health complications. Thus, it’s crucial to explore integrative approaches that focus on lifestyle modifications, including diet and exercise, to improve insulin sensitivity.
For pregnant individuals, managing sugar concentrations is especially critical to prevent gestational diabetes. Approaches such as regular tracking of glucose measurements, maintaining a balanced diet rich in whole foods, and participating in suitable physical activity can significantly reduce risks associated with high sugar during pregnancy.
According to Xu et al., “an AGR of 65.1 ml/g is the expected value for an individual with a typical RBC lifespan of 105 days and a glycation rate of 0.62 mL/g per day,” which emphasizes the significance of understanding A1C results in relation to daily glucose concentrations. Furthermore, the ACCORDION study, which followed participants from the ACCORD trial, highlights that after 9 years of follow-up, there was no difference in total mortality, and the increase in CVD deaths was mitigated after returning to conventional control post-intensive treatment. Comprehending how A1C results influence daily sugar levels enables more informed decisions concerning dietary choices, exercise, and medication adherence.
As this condition remains a major health issue, having access to an A1C conversion to blood sugar chart is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals to enhance care.
The Importance of Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose and A1C
Self-monitoring of glucose levels (SMBG) is a crucial practice for individuals managing diabetes. This approach entails regularly monitoring glucose readings with a glucometer, offering instant insights into how diet, exercise, and medication affect sugar concentrations. For instance, one patient shared how regular SMBG allowed them to adjust their meals and insulin dosage effectively, leading to improved health and peace of mind.
When paired with A1C testing, the a1c conversion to blood sugar chart offers a more comprehensive understanding of glucose management. Regular monitoring enables individuals to identify patterns, make informed dietary choices, and modify treatment plans as needed. It is advisable for those with blood sugar issues to measure their glucose levels several times a day, especially before and after meals, to sustain optimal control and avert potential complications.
A recent study highlighted that 93% of patients with the condition had their cholesterol checked, which underscores the importance of comprehensive health management in conjunction with SMBG practices. Furthermore, it is critical to note that 10.1% of U.S. adults with diagnosed blood sugar issues reported severe vision difficulty or blindness in 2021, emphasizing the serious consequences of poor glucose management. Research has illuminated how digitization enhances the self-monitoring experience; as Hiroshi Arima noted,
Effects of Digitization of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Records Using a Mobile App and the Cloud System on Outpatient Management of Diabetes: Single-Armed Prospective Study.
Additionally, the ABCs of Diabetes Management study revealed that only 11.1% of adults met all criteria for A1C, blood pressure, cholesterol, and smoking, highlighting the ongoing challenges in achieving optimal management of the condition. Regular SMBG not only complements A1C testing but also significantly impacts management outcomes, making the a1c conversion to blood sugar chart an essential tool for effective care. By empowering patients with the knowledge and tools to monitor their health, SMBG helps alleviate anxiety about potential complications, fostering a proactive approach to managing the condition.
Interpreting Your A1C Results: What They Mean for Your Health
Interpreting A1C results using the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart is critical for effective management of the condition, particularly in the context of a holistic approach to addressing the root causes. An A1C measurement below 7%, as indicated on the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart, is frequently the goal for many adults with high blood sugar, reflecting sufficient glycemic control. Conversely, levels exceeding this threshold may indicate a need for lifestyle adjustments or medication changes based on the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart.
For example, the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart shows that an A1C between 7% and 8% suggests a heightened risk for diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease or neuropathy. According to recent guidelines, individuals with an A1C above 8% face even greater health risks, making it crucial to consult an A1C conversion to blood sugar chart for necessary immediate intervention. Patients should engage in discussions with their healthcare providers regarding their A1C results and utilize the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart to formulate a personalized management plan that caters to their unique health needs and goals.
The Integrative Wellness Center focuses on empowering patients through comprehensive insights and treatment options, showcasing transformative success stories of individuals overcoming chronic health challenges. For instance, one patient, after adopting a holistic regimen that included dietary changes and stress management techniques, successfully reduced their A1C from 9% to 6.5% within six months. Additionally, as Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics noted, the prevalence of total, diagnosed, and undiagnosed conditions related to blood sugar regulation continues to be a pressing public health concern, especially with the awareness of prediabetes among Hispanic adults at 20.9%, underscoring the need for targeted interventions.
Furthermore, individuals diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) should undergo lifelong screening for prediabetes and type 2 disorders, as GDM often indicates underlying β-cell dysfunction, increasing the risk of developing type 2 disorders post-delivery. It is also crucial to acknowledge the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of this condition. This emotional factor should be considered in management strategies, as comprehending and controlling the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart is crucial for minimizing the long-term dangers linked to blood sugar conditions and achieving enduring health enhancements.
Benefits of Lowering Your A1C Levels for Better Health
Individuals controlling their blood sugar can gain significant health advantages by reducing A1C numbers, which can be monitored using an A1C conversion to blood sugar chart. Research indicates that each 1% reduction in A1C correlates with a remarkable 30% decrease in the risk of diabetes-related complications, including:
- Retinopathy
- Nephropathy
- Neuropathy
Furthermore, achieving lower A1C readings significantly enhances overall quality of life by alleviating symptoms associated with elevated blood sugar, which can be understood through an A1C conversion to blood sugar chart, such as:
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
Beyond these immediate effects, maintaining a healthy A1C is linked to improved cardiovascular health, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. The financial implications of managing the condition are also significant, with excess medical costs per person increasing from $10,179 to $12,022 from 2012 to 2022, underscoring the importance of effective A1C management.
Emphasizing a holistic approach, which includes lifestyle modifications such as better nutrition and increased physical activity, empowers individuals to effectively lower their A1C levels and address the underlying causes of the condition.
This aligns with clinical practice guidelines that recommend increased volumes of aerobic and combined exercise to foster better glycemic control. Additionally, by addressing the source of the condition, patients may also experience a reduction in the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of their illness.
As noted by Jill Hutt, Vice President of Member Services at the Greater Philadelphia Business Coalition on Health, the Coalition’s Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) aims to reduce diabetes rates through effective initiatives, highlighting the critical role that informed lifestyle choices and a comprehensive approach play in diabetes management.
Conclusion
Monitoring A1C levels is essential for effective diabetes management, providing a clear picture of long-term blood sugar control. This article has highlighted the importance of understanding A1C metrics, which categorize individuals into various risk groups and guide treatment options. Regular A1C testing, combined with self-monitoring of blood glucose, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health.
The relationship between A1C levels and overall health cannot be overstated. Lowering A1C levels significantly reduces the risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and other diabetes-related conditions. Moreover, adopting a holistic approach that includes:
- Optimizing nutrition
- Engaging in physical activity
- Managing stress
- Fostering supportive environments
can lead to improved health outcomes.
As diabetes continues to be a pressing public health concern, understanding and managing A1C levels is crucial for individuals and healthcare providers alike. By prioritizing regular testing and making lifestyle adjustments, individuals can not only enhance their quality of life but also mitigate the financial burdens associated with diabetes management. Moving forward, a proactive approach to A1C monitoring will be vital in navigating the complexities of diabetes care and achieving lasting health improvements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is A1C and why is it important?
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is a test that provides insights into average sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is essential for diabetes management as it allows individuals and healthcare providers to evaluate long-term glucose control.
What do different A1C levels indicate?
An A1C level below 5.7% is considered normal, levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, and an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diabetes diagnosis.
How prevalent is diabetes in adults?
As of the latest data, 14.3% of adults are affected by diabetes, with diagnosed cases at 10.1%. The prevalence has increased from 1999-2000 to 2021-2023.
What financial impact does diabetes have?
The medical expenses related to diabetes management increased from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022, highlighting the financial burden of the condition.
What are the key strategies for managing blood sugar levels?
Key strategies include optimizing nutrition, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress effectively, and fostering a supportive community.
What is the relationship between A1C values and average blood sugar levels?
An A1C of 5.0% corresponds to an average blood sugar level of approximately 97 mg/dL, while an A1C of 6.0% corresponds to 126 mg/dL, and an A1C of 7.0% indicates 154 mg/dL.
Why is it important to understand A1C results in relation to insulin resistance?
Understanding A1C results is crucial because insulin resistance can lead to elevated glucose levels. Some conventional therapies may worsen insulin resistance, so exploring lifestyle modifications is important.
How should pregnant individuals manage their blood sugar levels?
Pregnant individuals should regularly track glucose measurements, maintain a balanced diet rich in whole foods, and participate in suitable physical activities to prevent gestational diabetes.
What is the significance of the A1C conversion to blood sugar chart?
The A1C conversion to blood sugar chart is a vital resource for individuals managing diabetes, helping them understand the relationship between A1C values and estimated average glucose levels for better management of their condition.