Overview
The article focuses on understanding A1C thresholds for diabetes, which are critical for diagnosing and managing blood sugar levels, with specific thresholds defined for normal, prediabetes, and diabetes conditions. It emphasizes that maintaining these thresholds through regular A1C testing and lifestyle changes—such as improved nutrition, physical activity, and stress management—can significantly enhance patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding the significance of A1C levels is paramount for both patients and healthcare providers. The A1C test, a key indicator of average blood glucose levels over a period of two to three months, serves as a crucial tool in diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes. With established thresholds guiding clinical decisions—normal, prediabetes, and diabetes—individuals can better navigate their health journeys.
However, the implications of A1C extend beyond mere numbers; they encompass lifestyle factors, emotional well-being, and personalized care strategies. This article delves into the multifaceted role of A1C in diabetes management, highlighting essential lifestyle modifications, the importance of regular testing, and the intricate interplay of various factors affecting A1C levels.
By fostering a comprehensive understanding of these elements, patients can take proactive steps toward improved health outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
The Role of A1C in Diabetes Diagnosis
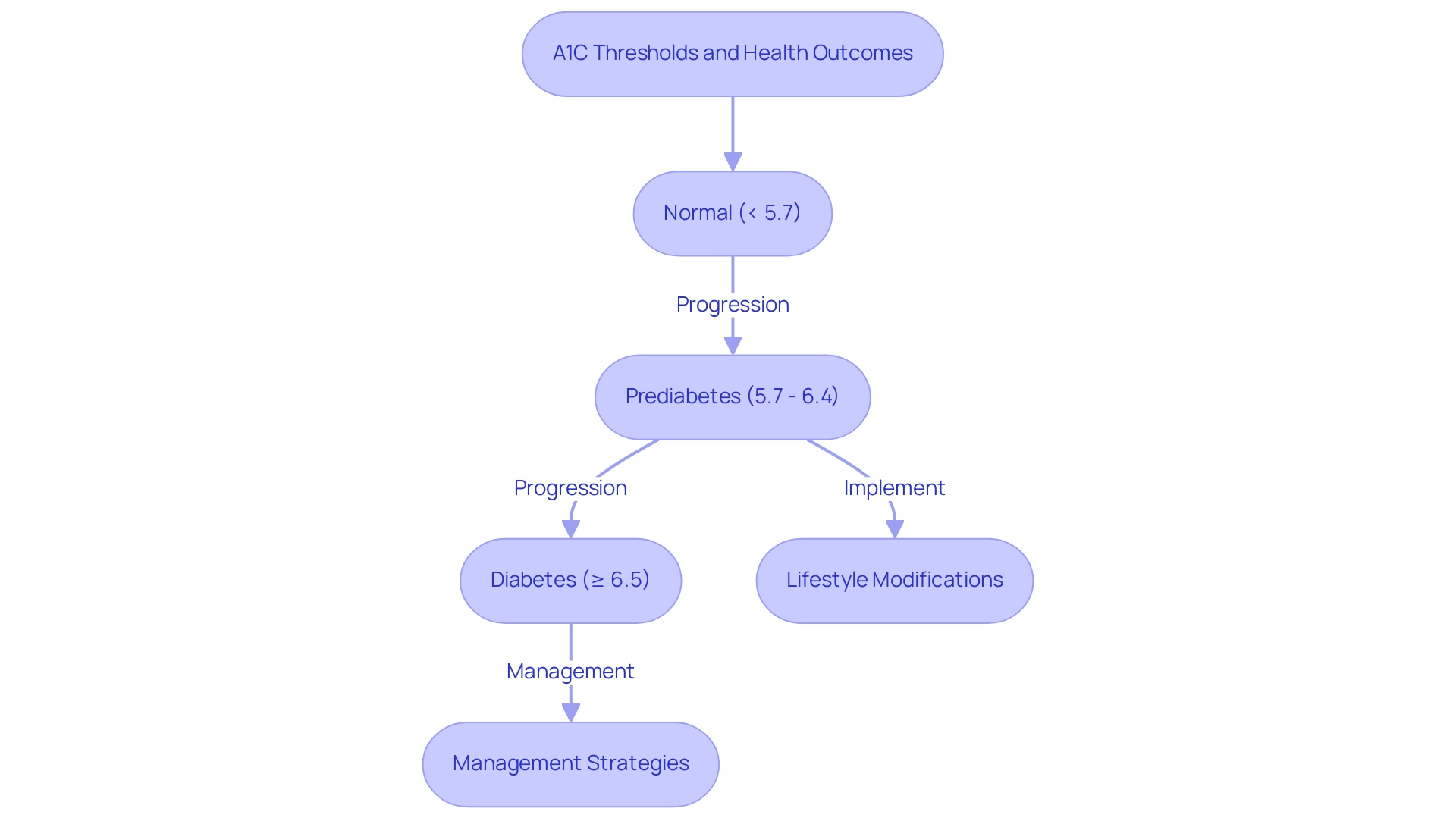
The A1C test, often called the glycated hemoglobin test, is crucial in assessing average blood glucose readings over a span of two to three months. This diagnostic tool plays a pivotal role in identifying both high blood sugar and prediabetes conditions. According to established guidelines, the A1C threshold for diabetes is defined as:
- An A1C measurement of less than 5.7% being categorized as normal
- Readings ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes
A confirmed diagnosis of a blood sugar disorder is established when the A1C level meets the A1C threshold for diabetes of 6.5% or higher. Additionally, the optimal fasting plasma glucose (FPG) cutoff for predicting undiagnosed hyperglycemia is 5.5 mmol/L (99 mg/dL), with 70% sensitivity and 94% specificity. The A1C test is preferred over daily blood glucose testing due to its ability to provide a more comprehensive picture of glucose control over time, making it an essential element of effective management strategies for maintaining the A1C threshold for diabetes.
Nam H. Cho notes,
This was a large, prospective cohort study that used stringent criteria to diagnose the condition and to evaluate the usefulness of A1C level in screening and in the prediction of new-onset cases.
This highlights the test’s critical role in guiding clinical decisions and improving patient outcomes, particularly concerning the A1C threshold for diabetes. Furthermore, understanding the pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes, influenced by genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors, underscores the complexity of this condition and the need for comprehensive, personalized management approaches.
The integrative wellness strategy, concentrating on the root causes of the condition and empowering patients through education, plays a crucial role in enhancing health outcomes and potentially reversing Type 2. Additionally, addressing the anxiety surrounding the concern of potential complications related to the condition is essential in the holistic approach, as it can significantly affect patients’ overall well-being. For instance, a transformative success story from our center involved a patient who, through our personalized care and holistic regimen, not only improved their A1C measurements but also reported a significant reduction in anxiety related to their condition, showcasing the effectiveness of our approach.
Understanding A1C Thresholds: From Normal to Prediabetes and Diabetes
A1C thresholds play a critical role in managing blood sugar and are defined as follows:
- Normal: An A1C reading of less than 5.7% indicates that an individual is not at risk for developing the condition.
- Prediabetes: An A1C measurement ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicates a heightened risk for developing type 2 sugar intolerance. At this stage, it is essential to implement lifestyle modifications, including improved dietary choices, enhanced physical activity, and effective weight management strategies. Emphasizing a holistic approach can further empower patients to tackle these risks at the core.
- Diabetes: A diagnosis of this condition is confirmed with an A1C measurement that meets the A1C threshold for diabetes of 6.5% or higher. For those diagnosed, management strategies may involve regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, dietary adjustments, and potentially the use of medication or insulin therapy. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we focus on reversing type 2 conditions through functional medicine that addresses insulin resistance and offers transformative patient experiences.
The importance of these thresholds is highlighted by the median county-level prevalence of diagnosed conditions, which rose from 6.3% in 2004 to 8.3% in 2021, reflecting a growing public health concern. As noted by Yoshinaga, the combination of A1C and OGTT enables more precise prediction of progression to the condition in those with glucose intolerance. This is further supported by the case study titled ‘Yoshinaga 1996,’ which reported incidence rates of 52.1% for individuals with A1C levels of ≥6.8%. Such findings highlight the necessity for both patients and healthcare providers to understand the A1C threshold for diabetes, which enables the customization of effective management strategies that can lead to improved health outcomes.
Additionally, incorporating sleep-promoting routines, as recommended in the latest guidelines, may further enhance management of blood sugar levels, emphasizing the comprehensive care required for effective treatment. Numerous patients have shared their experiences, expressing relief from anxiety surrounding their health management as they embrace a holistic approach. By reevaluating the origin of the condition, we empower our patients to take charge of their health and well-being.
The Importance of Regular A1C Testing
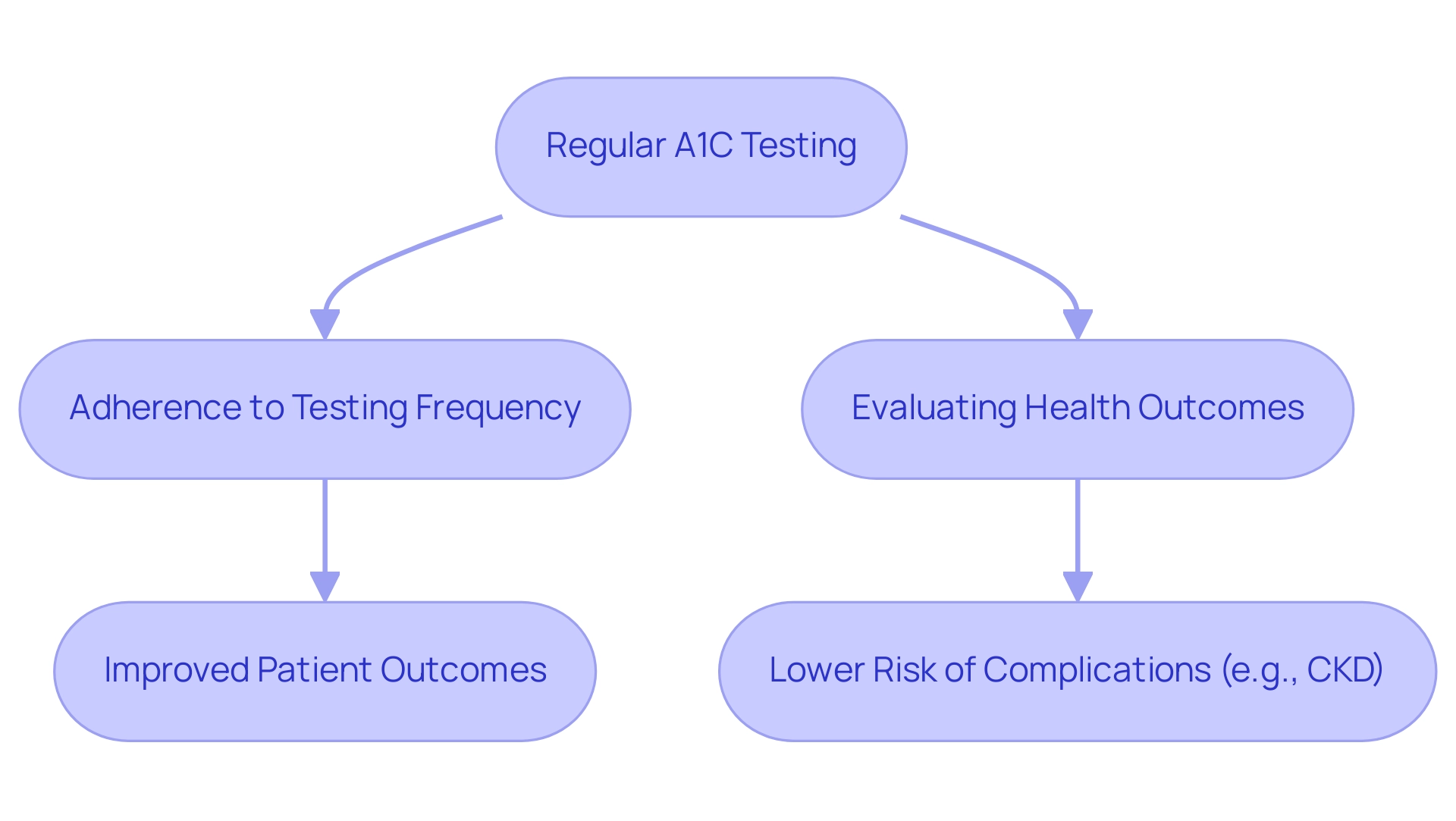
For individuals managing blood sugar levels, adhering to the A1C threshold for diabetes is crucial for long-term health and finding new peace in life. The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners (RACGP) states that ‘high adherence to the A1C threshold for diabetes testing frequency is essential for effective diabetes management.’ Patients are usually advised to have A1C tests a minimum of twice annually; however, this frequency should increase if treatment strategies change or if their glucose readings remain uncontrolled, especially in relation to the A1C threshold for diabetes.
Regular A1C testing serves as a vital tool for healthcare providers to evaluate the effectiveness of blood glucose management over time and ensure it remains below the A1C threshold for diabetes, allowing for informed adjustments to treatment strategies. A recent longitudinal cohort study conducted in Australia, which analyzed electronic health records from 254 general practices, underscored the importance of consistent testing. The study revealed that adherence to A1C testing correlates with improved patient outcomes and maintaining the A1C threshold for diabetes significantly lowers the risk of developing complications, such as chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Specifically, regression analyses indicated that high adherence to HbA1c testing frequency was associated with a significantly lower risk of developing CKD compared to low adherence, particularly when evaluated against the A1C threshold for diabetes. By remaining informed about A1C measurements, individuals with blood sugar issues can adopt proactive measures in their lifestyle, reducing worry regarding possible complications and improving their overall wellness through a comprehensive and holistic strategy for managing their condition.
Factors Affecting A1C Levels
A1C measurements are influenced by multiple factors that are critical in determining the A1C threshold for diabetes management. Understanding these elements can empower individuals to make informed lifestyle decisions.
- Diet: The intake of high-carbohydrate meals and sugary foods can significantly raise glucose concentrations, subsequently affecting A1C outcomes.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, nutritionists stress that a balanced diet abundant in whole foods and vegetable-rich meals is crucial for stabilizing sugar levels and enhancing overall health. Moreover, integrating lesser-known strategies like mindful eating and meal timing can further improve dietary effectiveness.
- Exercise: Participating in consistent physical activity is crucial for reducing sugar concentrations and enhancing glucose regulation. Recent studies suggest that structured exercise programs not only lower A1C values but also encourage long-term commitment to healthy habits, aligning with the comprehensive approaches advised for reversing the condition. Activities such as yoga and tai chi can also assist in managing stress and alleviating anxiety related to complications from this condition.
- Condition: Both acute and chronic ailments can interfere with normal glucose amounts, leading to fluctuations that may distort A1C results. Observing health conditions during sickness is essential for precise management of blood sugar issues, emphasizing the significance of tackling health at the foundational aspect.
- Medications: Different medications can also influence sugar concentrations, either elevating or lowering them. It is important for individuals to communicate with healthcare providers regarding any medications they are taking and their potential impacts on the A1C threshold for diabetes, as traditional treatments may not effectively address underlying causes. Identifying these factors can assist in customizing individualized management strategies.
Integrating insights from recent research and expert views can further clarify the relationships between these factors and the A1C threshold for diabetes, providing a more comprehensive approach to care. Significantly, statistics indicate that 8.0% of U.S. adults aged 18 years or older with diagnosed blood sugar issues had a non-HDL concentration of 190 mg/dL or higher, highlighting the necessity of effective management strategies. Moreover, the overall direct and indirect projected expenses of diagnosed conditions in the United States hit $413 billion in 2022, highlighting the financial strain of the illness and the urgent requirement for efficient strategies to control A1C values. Addressing the anxiety surrounding potential complications of this condition is essential for empowering individuals to take control of their health.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve A1C Levels
Enhancing management of the A1C threshold for diabetes requires a multifaceted approach that tackles the root causes through significant lifestyle changes. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize a holistic regimen tailored to empower patient health and alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications of diabetes. Here are essential strategies to consider:
- Nutrition: A balanced diet is crucial. Emphasizing whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables can lead to improved glucose control. It is advisable to limit the intake of processed foods and added sugars, which often contribute to sugar spikes.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly—such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling—can be highly beneficial. Consistent physical exercise not only reduces glucose concentrations but also improves insulin responsiveness, which is essential for effectively managing type 2 conditions. As Dr. Deepak N. Parchwani observes, “Additional clinical research is necessary to determine the effectiveness of exercise intervention in a more differentiated manner for type 2 metabolic disorders subpopulations across different stages of the condition and various degrees of co-morbidity.”
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is fundamental to glucose control. Research indicates that even modest weight loss can lead to significant improvements in A1C readings, underscoring the importance of weight management in maintaining the A1C threshold for diabetes care.
- Stress Management: High stress can negatively impact blood sugar rates. Applying stress-reduction methods like mindfulness, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can be effective in keeping glucose stability. Addressing anxiety related to diabetes can further enhance these efforts, promoting overall well-being.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar readings is essential to stay within the A1C threshold for diabetes. This practice allows individuals to identify patterns in their glucose readings, enabling informed decisions regarding dietary and lifestyle adjustments.
Recent findings highlight that among patients who adhered to lifestyle modifications, 14 out of 24 experienced a decrease in HbA1c levels. In contrast, those who did not see improvements had a significantly longer duration of the condition (p=0.025). Such statistics highlight the critical nature of lifestyle interventions in managing blood sugar conditions.
Additionally, insights from the case study titled “Medication Use Trends in p-CGM Users vs Nonusers” reveal that while the use of biguanides and sulfonylureas decreased slightly in both groups, the p-CGM group showed an increased likelihood of using GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors at follow-up compared to nonusers. This highlights how lifestyle changes can interact with medication use to improve control of blood sugar. Furthermore, insights from educators emphasize the significance of personalized nutrition and exercise plans customized to individual needs, which can lead to more effective control of the condition.
The holistic regimen we implement at the Integrative Wellness Center focuses on these aspects, ensuring a comprehensive approach to reversing diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of A1C levels in diabetes management is crucial for effective disease control and improved health outcomes. The A1C test serves as a vital diagnostic tool, allowing healthcare providers to categorize individuals into normal, prediabetic, or diabetic categories based on their blood glucose levels over time. This classification not only aids in diagnosis but also informs personalized treatment strategies that can significantly impact patients’ health journeys.
Regular A1C testing is essential for monitoring progress and adapting management plans. Adhering to recommended testing frequencies can lead to better health outcomes and lower risks of complications. Moreover, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress management play a pivotal role in influencing A1C levels. By adopting a holistic approach that addresses these elements, individuals can better manage their diabetes and enhance their overall well-being.
Ultimately, the interplay between A1C levels and lifestyle choices highlights the importance of comprehensive diabetes care. Empowering patients through education and personalized strategies fosters a proactive approach to health management. By understanding and actively managing A1C levels, individuals can navigate their diabetes journeys more effectively, leading to improved health and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test?
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, measures average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months and is essential for identifying high blood sugar and prediabetes conditions.
What are the A1C thresholds for diabetes?
The A1C thresholds are categorized as follows: Normal: Less than 5.7%, Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%, Diabetes: 6.5% or higher.
Why is the A1C test preferred over daily blood glucose testing?
The A1C test provides a more comprehensive overview of glucose control over time, making it a crucial tool for effective management of diabetes.
What is the significance of fasting plasma glucose (FPG) in relation to the A1C test?
The optimal FPG cutoff for predicting undiagnosed hyperglycemia is 5.5 mmol/L (99 mg/dL), which has 70% sensitivity and 94% specificity.
How does the A1C test influence clinical decisions and patient outcomes?
The A1C test plays a critical role in guiding clinical decisions and improving patient outcomes by helping to monitor and manage blood sugar levels effectively.
What lifestyle modifications are recommended for individuals with prediabetes?
Individuals with prediabetes should implement lifestyle changes such as improved dietary choices, increased physical activity, and effective weight management strategies.
How does the Integrative Wellness Center approach the management of Type 2 Diabetes?
The center focuses on reversing Type 2 Diabetes through functional medicine that addresses insulin resistance and promotes a holistic approach to patient care.
What has been the trend in the prevalence of diagnosed diabetes conditions from 2004 to 2021?
The median county-level prevalence of diagnosed diabetes conditions increased from 6.3% in 2004 to 8.3% in 2021, indicating a growing public health concern.
What additional strategies may enhance blood sugar management?
Incorporating sleep-promoting routines, as recommended in the latest guidelines, may further improve blood sugar management.
How do patients benefit from a holistic approach to managing their health?
Many patients report relief from anxiety related to their health management and feel empowered to take charge of their well-being through a comprehensive, holistic approach.