Overview
The article discusses age-specific fasting methods, highlighting how intermittent fasting (IF) can be tailored to meet the needs of different age groups for optimal health benefits. It explains that younger individuals may thrive on more intense fasting schedules like the 16/8 method, while older adults benefit from gentler approaches like the 12/12 method due to their unique health considerations, thus emphasizing the importance of customizing dietary strategies based on age to enhance safety and effectiveness.
Introduction
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained significant attention as a dietary strategy that alternates between eating and fasting periods, but its effectiveness and safety can vary notably across different age groups.
-
Younger adults often embrace more rigorous fasting schedules, reaping benefits such as:
- Weight loss
- Improved metabolic health
-
Older adults must approach fasting with caution, opting for gentler methods that align with their unique health needs.
This article delves into the nuances of intermittent fasting, examining:
- Age-specific approaches
- The critical role of nutrition
- Potential risks involved
By tailoring fasting strategies to individual health profiles, it becomes possible to harness the advantages of this dietary practice while minimizing associated risks, particularly for those managing chronic conditions like diabetes. Understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone considering intermittent fasting as a viable health strategy.
Understanding Intermittent Fasting Across Different Age Groups
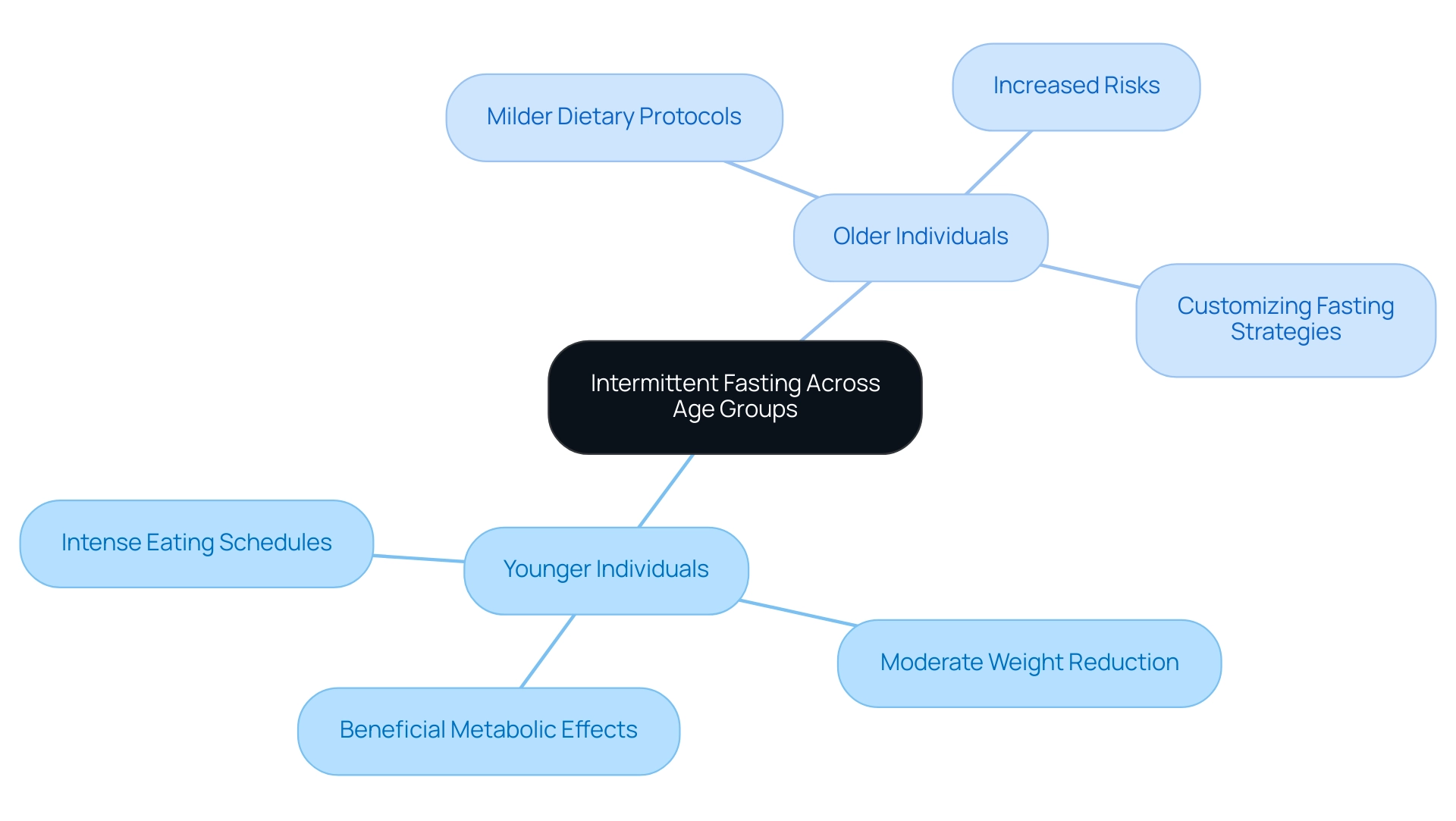
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a dietary method that alternates between periods of eating and not consuming food, and its effectiveness and safety are significantly influenced according to a fasting chart by age. Studies indicate that younger individuals may find more intense eating schedules advantageous, potentially resulting in moderate weight reduction and beneficial metabolic effects. In fact, a study revealed that 85% of respondents were pleased with their experience of the IF diet, highlighting its acceptance among users.
In contrast, older individuals are encouraged to consider milder dietary protocols due to increased risks related to more extreme regimens. According to Dr. Adriana Villasenor from the Moores UCSD Cancer Center, this overview suggests that intermittent eating patterns may be a promising method to lose weight and enhance metabolic well-being for individuals who can endure periods of not consuming food, or consuming very little, for certain hours of the day or days of the week. Furthermore, a case study titled ‘Nightly Intermittent Eating – LeCheminant (2013)’ involving 29 normal weight young men demonstrated the effects of a nightly abstention from food, providing further insight into the experience for this age group.
This focused analysis demonstrates the importance of customizing dietary strategies to personal wellness profiles, especially as ongoing research highlights the requirement for a fasting chart by age to determine the long-term impacts of various dietary regimens across different age categories. Thus, understanding these nuances is vital for creating effective and safe dietary protocols that align with personal health needs and lifestyle factors, especially since alternate day eating regimens can lead to modest weight loss and some positive metabolic effects.
Age-Specific Fasting Methods: Tailoring Approaches for Optimal Health
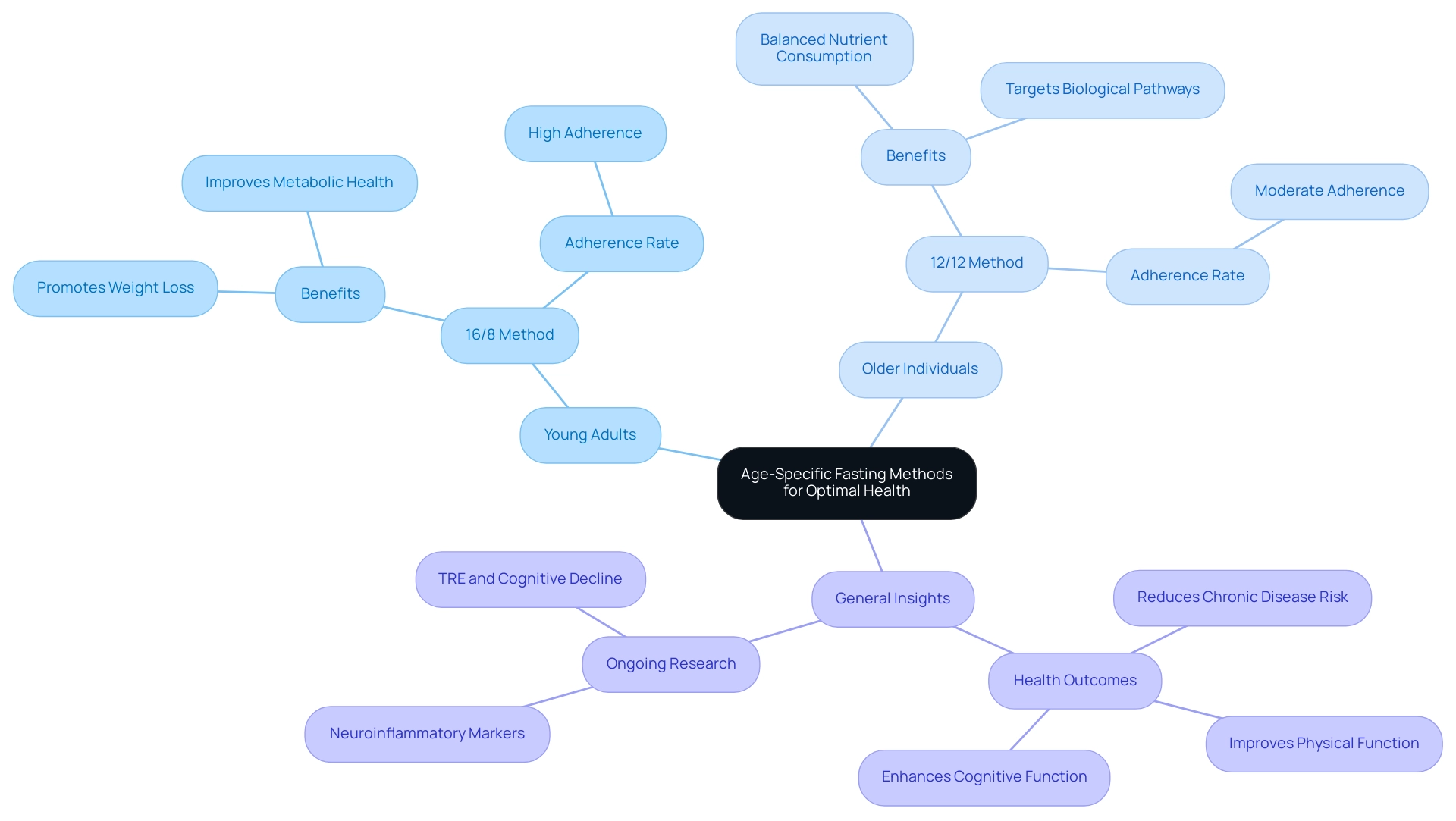
Intermittent eating methods yield different levels of success across various age groups, as indicated in the fasting chart by age. Young adults often find the 16/8 method—characterized by a 16-hour fasting period followed by an 8-hour food intake window—particularly effective. This approach has been shown to promote weight loss and improve metabolic health, with recent success stories highlighting its benefits among this demographic.
Notably, adherence to prescribed time-restricted eating plans is remarkably high, with more than 99% of female participants and 98% of male participants successfully following the regimen. Conversely, older individuals may obtain improved outcomes with a more moderate approach, like the 12/12 method, which permits balanced nutrient consumption while still gaining advantages from abstaining from food. This method also considers the unique wellness challenges faced by seniors, including medication schedules and nutritional requirements.
A systematic review by Glazier et al. highlights that abstaining from food can affect perinatal outcomes and may likewise influence older individuals by targeting biological pathways linked to caloric restriction, thereby potentially lowering chronic disease risk and improving both physical and cognitive function. Customizing dietary approaches to align with a fasting chart by age not only improves adherence but also plays an essential role in promoting overall wellness throughout life.
Moreover, ongoing studies regarding the impacts of time-restricted eating (TRE) on cognitive decline and neuroinflammatory markers in older individuals emphasizes the significance of personalized eating strategies in enhancing long-term health results.
The Role of Nutrition in Fasting Across Ages
Nutrition is fundamental to the success of any dietary regimen, particularly for individuals managing diabetes. A careful approach tailored to different age groups is essential when developing a fasting chart by age. For young individuals, prioritizing nutrient-rich foods high in proteins and healthy fats is essential for maintaining energy levels during the periods indicated in the fasting chart by age.
In contrast, older adults are encouraged to follow the fasting chart by age, which suggests diets high in fiber and antioxidants to support cardiovascular health and effective inflammation management. Type 2 diabetes patients must be particularly attentive to carbohydrate consumption, as it plays an essential role in keeping stable blood sugar levels during both periods of not consuming food and while having meals. Education on managing blood sugar is key to eliminating dependency on insulin and preventing complications such as gestational diabetes.
By understanding how to balance their diet and fasting schedules, patients can significantly reduce their reliance on insulin and other diabetes-related drug therapies. A study involving 34 healthy participants revealed that those engaged in time-restricted eating (TRE) exhibited reduced total cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing HDL levels, highlighting how mindful nutritional choices can lead to significant improvements in well-being. The ongoing discussions surrounding dietary considerations in modern therapy, as illustrated in the case study titled ‘Conclusion of Episode 1,’ further emphasize the importance of nutrition in wellness interventions.
Particular approaches, like seeking advice from a nutritionist or using online meal timing calculators, can enable individuals to make knowledgeable dietary choices, greatly improving the efficiency of dietary practices and turning it into a potent method for wellness enhancement and diabetes control.
Potential Risks and Considerations for Different Age Groups
Fasting, while associated with various health benefits, poses significant risks, especially for individuals managing type 2 diabetes. Younger individuals may encounter issues such as fatigue and irritability if dietary practices are not properly managed. In contrast, older adults are at risk of dehydration and nutrient deficiencies, particularly if they fail to consume sufficient food during designated eating periods.
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, like type 2 diabetes, encounter extra difficulties, as abstaining from food can significantly affect blood sugar levels. A recent survey indicated that 15% of respondents expressed dissatisfaction with their intermittent eating experiences, underscoring the importance of careful consideration. Experts, including Professor Obaid Al-Modaf, emphasize the necessity of consulting healthcare professionals prior to initiating any dietary regimen, particularly for those in higher-risk categories.
Grasping these wellness considerations is essential for effectively applying fasting strategies that enhance well-being without compromising safety. In San Marcos, CA, individuals can also benefit from tailored nutrition plans provided by local practitioners like Dr. Jason Shumard, who emphasizes a personalized approach to diabetes management, including state-of-the-art testing that identifies individual dietary needs. Engaging with community resources, such as outdoor activities and local farmers’ markets, can further support effective lifestyle changes that enhance overall health outcomes for those with diabetes.
Many patients have reported positive experiences with these tailored plans, highlighting the importance of personalized care in managing their condition.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting presents a promising dietary strategy that can yield significant benefits, but its effectiveness and safety are highly contingent upon age and individual health profiles. Younger adults may thrive on more rigorous fasting schedules, such as the popular 16/8 method, which can lead to weight loss and improved metabolic health. Conversely, older adults are better suited to gentler approaches like the 12/12 method, which accommodates their specific health challenges and nutritional needs.
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in the success of any fasting regimen. Younger adults should focus on nutrient-dense foods to sustain energy during fasting periods, while older adults need to prioritize fiber and antioxidants to support their overall health. Special attention must be given to individuals managing diabetes, as balanced carbohydrate intake is vital for maintaining stable blood sugar levels during both fasting and eating windows.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the potential risks associated with intermittent fasting, particularly for those with pre-existing health conditions. Younger individuals may experience fatigue and irritability, while older adults face increased risks of dehydration and nutrient deficiencies. Consulting healthcare professionals before embarking on any fasting regimen is crucial, especially for those in higher-risk categories.
In summary, tailoring intermittent fasting strategies to suit individual age groups and health conditions is essential for maximizing benefits and minimizing risks. By approaching fasting with a personalized mindset, individuals can effectively leverage this dietary practice to enhance their health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is intermittent fasting (IF)?
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a dietary method that alternates between periods of eating and not consuming food.
How does age influence the effectiveness and safety of intermittent fasting?
The effectiveness and safety of intermittent fasting are significantly influenced by age, with younger individuals potentially benefiting from more intense eating schedules, while older individuals are advised to consider milder dietary protocols due to increased risks associated with extreme regimens.
What benefits can younger individuals experience from intermittent fasting?
Younger individuals may experience moderate weight reduction and beneficial metabolic effects from more intense eating schedules.
What did a study reveal about user satisfaction with the IF diet?
A study indicated that 85% of respondents were pleased with their experience of the intermittent fasting diet, highlighting its acceptance among users.
What recommendations are given for older individuals regarding intermittent fasting?
Older individuals are encouraged to consider milder dietary protocols due to the increased risks associated with more extreme fasting regimens.
What does Dr. Adriana Villasenor suggest about intermittent eating patterns?
Dr. Adriana Villasenor suggests that intermittent eating patterns may be a promising method for weight loss and enhanced metabolic well-being for individuals who can tolerate periods of fasting.
What insights were provided by the case study titled ‘Nightly Intermittent Eating – LeCheminant (2013)’?
The case study involving 29 normal weight young men demonstrated the effects of nightly abstention from food, providing further insight into the experience of intermittent fasting for this age group.
Why is it important to customize dietary strategies according to personal wellness profiles?
Customizing dietary strategies is vital because ongoing research highlights the need for a fasting chart by age to determine the long-term impacts of various dietary regimens across different age categories, ensuring that protocols align with personal health needs and lifestyle factors.
What are the potential outcomes of alternate day eating regimens?
Alternate day eating regimens can lead to modest weight loss and some positive metabolic effects.