Introduction
An A1C level of 6.2% serves as a critical indicator of an individual’s health status, marking the threshold between normal glucose levels and the onset of prediabetes. This reading, while not yet indicative of diabetes, signals an urgent need for lifestyle changes to prevent progression to more serious health issues.
With the prevalence of prediabetes on the rise, understanding the implications of this measurement is essential for effective management and prevention strategies. This article delves into the following topics:
- The health risks associated with an A1C of 6.2%
- The importance of regular monitoring
- Actionable lifestyle modifications that can empower individuals to take control of their health and mitigate future complications
By addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of prediabetes, individuals can cultivate a comprehensive approach to managing their condition and improving their overall well-being.
Understanding the Implications of an A1C Level of 6.2
An A1C level indicates that a person’s average blood glucose over the past two to three months has been high, and in this case, A1C is 6.2, yet it remains below the limit for blood sugar conditions. As per the American Diabetes Association, A1C levels are categorized as follows:
- Normal (below 5.7%)
- Prediabetes (5.7% to 6.4%)
- High blood sugar (6.5% or higher)
Consequently, since the A1C is 6.2%, it categorizes the individual as prediabetic, indicating an urgent need for lifestyle modifications.
These modifications may include:
- Implementing dietary adjustments, particularly incorporating vegetable-rich dishes to support blood sugar regulation
- Increasing physical activity to reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related issues
The prevalence of prediabetes in the United States is notable; as of August 2021–August 2023, the prevalence of total sugar-related disorders was reported at 14.3% (95% CI: 12.1–16.7), highlighting the significance of this condition. Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics emphasizes this concern, stating, ‘Prevalence of total, diagnosed, and undiagnosed blood sugar issues in adults: United States, August 2021–August 2023.’
Furthermore, understanding the varieties of this condition is crucial; for instance, C-peptide testing can be instrumental in differentiating between types of this disorder and guiding management strategies. Therefore, comprehending and responding to the fact that A1C is 6.2 is essential for effective management and prevention of the condition, enabling patients to adopt a holistic approach to their well-being. Alongside these lifestyle adjustments, think about investigating four lesser-known strategies that can greatly improve your well-being and assist in reducing the stress related to managing blood sugar.
Sign up now to uncover genuine solutions and take the next step towards regaining your well-being.
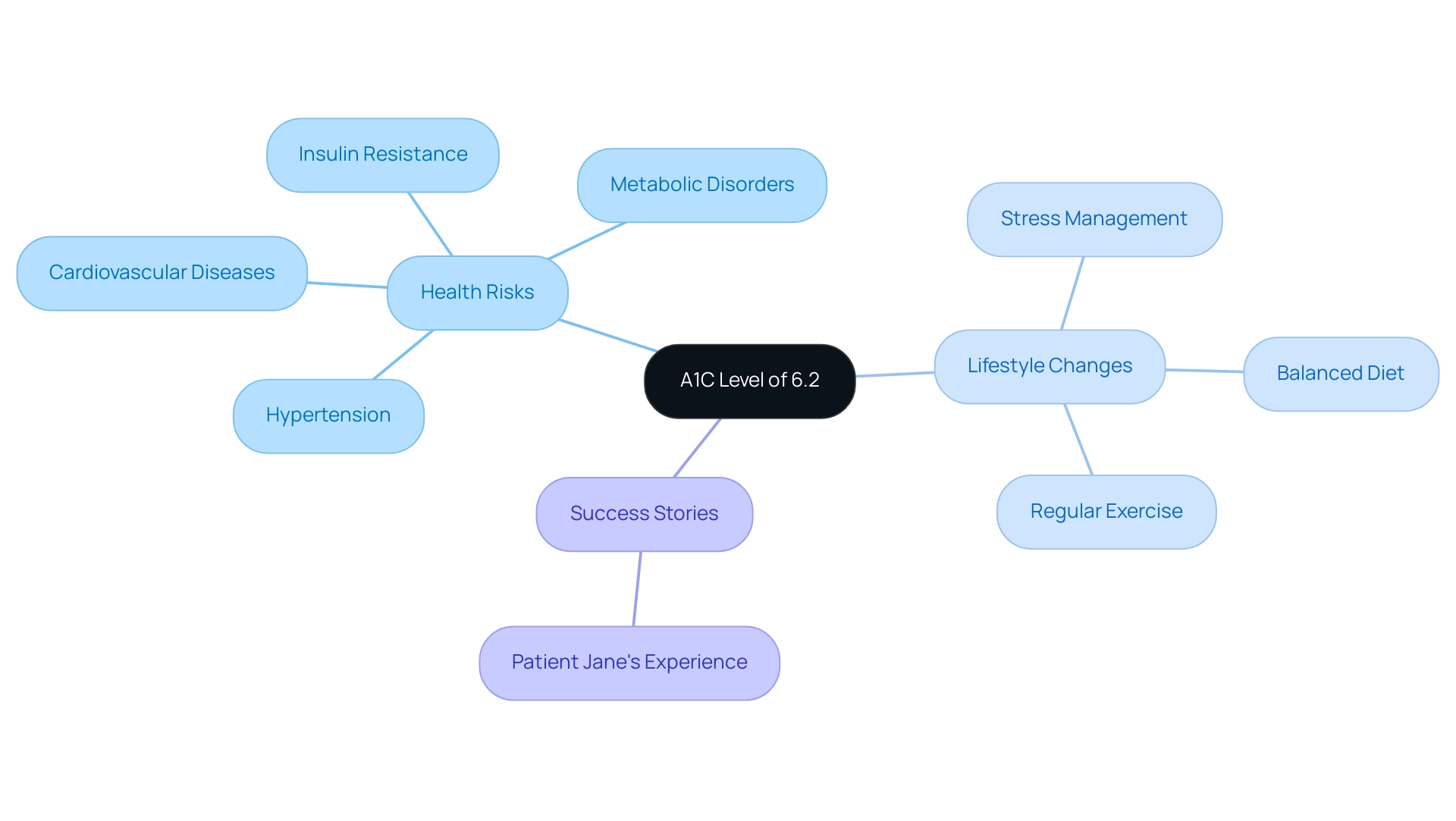
Health Risks Linked to an A1C of 6.2: What You Need to Know
An A1C level of 6.2% indicates that a1c is 6.2, which presents several significant health risks, especially the increased likelihood of progressing to type 2. Current research highlights that people with prediabetes often face heightened risks for cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and various metabolic disorders. At this juncture, the body may exhibit early signs of insulin resistance, potentially leading to serious complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and an increased risk of heart disease.
Notably, the baseline mean A1C for people who develop diabetes is 6.8, compared to 6.2 for those without diabetes (Preiss). Given these risks, it is crucial for people whose a1c is 6.2 to engage in regular monitoring and adopt proactive lifestyle changes. These changes, which involve a balanced diet and regular exercise, are crucial in reducing risks and enhancing overall well-being.
Recent studies further highlight the significance of addressing these medical concerns, as individuals whose a1c is 6.2 not only risk developing serious conditions but also encounter potential long-term cardiovascular problems. Importantly, while the A1C test provides insights into long-term blood glucose levels, it does not account for sudden fluctuations; thus, a comprehensive approach to monitoring is essential (A1C Test and Short-Term Blood Glucose Changes). Additionally, the financial implications of managing the condition are significant, with the excess medical costs per person increasing from $10,179 to $12,022 between 2012 and 2022.
At the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego, we empower patients through comprehensive insights and treatment options, including personalized dietary plans, exercise regimens, and stress management techniques. Our holistic approach has transformed the lives of many patients, such as Jane, who successfully reversed her prediabetes through our tailored program, demonstrating the effectiveness of our methodologies. We are dedicated to assisting our patients on their path to reverse type 2 conditions and tackle other chronic medical concerns.
Lifestyle Changes to Lower A1C Levels
To effectively lower an A1C level when the A1C is 6.2%, one should implement comprehensive lifestyle changes rooted in a holistic approach, which begins by re-examining the source of the condition. A balanced diet is essential, emphasizing whole grains, a variety of fruits and vegetables, and lean proteins, while minimizing processed foods and sugars. Current dietary recommendations suggest that patients focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods that support overall health, addressing the underlying causes of the condition.
Regular physical activity is also crucial; engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week—through activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming—can significantly impact A1C levels. Among the 24 patients who modified their lifestyle, 14 showed a decrease in HbA1c levels, with some achieving results where A1C is 6.2, highlighting the effectiveness of these changes. Moreover, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly enables people to understand the correlation between their dietary choices and physical activity on their A1C outcomes.
Incorporating stress management techniques, including mindfulness practices or yoga, further enhances blood sugar control and empowers people to challenge misconceptions related to the condition. It is also important to acknowledge the anxiety that often accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of this condition. As you consider these changes, ask yourself, ‘How might you adjust that goal so you are highly confident you can do it this week?’
This emphasizes the importance of setting achievable goals in your lifestyle modifications. Additionally, it is important to recognize the challenges that healthcare providers face when adapting intensive lifestyle interventions in office practice, as outlined in the case study on ‘Challenges in Office Practice.’ By focusing on both physical and mental wellness, including the anxiety associated with diabetes, people can develop a more effective strategy for managing their diabetes and reaching their wellness objectives, ultimately tackling issues at the root level.
The Role of Regular Monitoring and Medical Consultation
Routine assessment of A1C levels is crucial for persons, especially when their A1C is 6.2%, as it acts as a vital indicator of glycemic regulation and overall wellness management. It is advisable for individuals to consult their healthcare providers to establish a structured plan for regular blood tests, typically recommended every three to six months. This frequency enables prompt changes to treatment strategies and lifestyle alterations, improving overall management of the condition and empowering patients to take charge of their wellbeing.
Additionally, ensuring adequate carbohydrate intake (at least 150 g/day) for three days prior to OGTT testing is critical, as it can impact A1C levels and overall management of the condition. Healthcare professionals at the Integrative Wellness Center are equipped to offer personalized advice tailored to an individual’s health status, medications, and any existing conditions. Engaging in open dialogue with healthcare providers not only ensures that patients are informed about the latest research and treatment options but also fosters effective management strategies, ultimately alleviating anxiety over potential complications.
The Integrative Wellness Center emphasizes a holistic approach, providing support that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of managing the condition. By focusing on root causes and incorporating lifestyle changes, patients can find peace and reduce their worries about complications. The case study titled ‘Clinical Significance of HbA1c’ underscores that HbA1c, which indicates A1C is 6.2, serves as a crucial measure for assessing long-term glucose control, reflecting the average blood sugar levels over the past three months.
The American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee emphasizes the importance of these consultations in their 2024 Standards of Care in Diabetes, reinforcing the critical role of regular A1C monitoring in diabetes management and the holistic approach to reversing diabetes through addressing root causes.
Understanding the Emotional Impact of Prediabetes
Receiving a diagnosis of prediabetes, where it is identified that the A1C is 6.2%, can evoke significant emotional responses, including anxiety, fear, and uncertainty regarding future well-being outcomes. Recognizing these emotions is essential for people navigating this transition. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we have witnessed transformative patient experiences where people, like Jane Doe, who shared, ‘I was overwhelmed when I found out about my prediabetes, but the support I received helped me regain control of my well-being,’ successfully reversed Type 2 Diabetes and addressed hypothyroidism through functional medicine.
Research shows that many people with this condition face increased mental wellness challenges; as noted by Shao et al., ‘many doctors pay less attention to poor mental well-being, because they believe it is ‘anticipated’ in patients with this condition.’ Consequently, it becomes essential for people to proactively seek support from healthcare providers, counseling services, or community support groups. Programs focused on education and nutrition in San Marcos have proven effective, with statistical analyses, including chi-squared tests and one-way ANOVA, providing empirical support for the positive effects of such networks on overall well-being.
This indicates that a robust support network can serve as a vital source of encouragement and motivation. Furthermore, interacting with educational resources can empower individuals by improving their understanding of diabetes management, ultimately fostering a sense of control over their outcomes. Furthermore, an ROC curve analysis evaluating the diagnostic ability of HbA1c, where A1C is 6.2, as a predictor of mental well-being outcomes reported an AUC of 0.643, suggesting a moderate sensitivity/specificity relationship.
This underscores the importance of addressing mental health in those diagnosed with prediabetes, as various support resources, including community wellness programs, are available that can significantly alleviate the emotional burdens associated with this diagnosis. For more insights on managing diabetes and accessing community support, visit our blog.
Conclusion
An A1C level of 6.2% serves as a crucial warning sign, indicating the onset of prediabetes and the urgent need for lifestyle changes. This article has explored the health risks associated with this reading, highlighting the increased likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and other serious health conditions. Regular monitoring and proactive medical consultations are essential for effectively managing this condition and preventing further complications.
Implementing lifestyle modifications—such as:
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing stress
can significantly lower A1C levels and improve overall health. As demonstrated, these changes are not just beneficial but necessary for reversing the trajectory towards diabetes and enhancing quality of life.
Moreover, addressing the emotional impact of a prediabetes diagnosis is equally important. The anxiety and fear that often accompany such news can be alleviated through support networks and educational resources that empower individuals to take control of their health. By fostering a holistic approach that encompasses both physical and emotional well-being, individuals can navigate their journey with confidence and resilience.
In conclusion, understanding and acting upon an A1C level of 6.2% is vital for preventing the progression to diabetes. Through consistent monitoring, lifestyle changes, and emotional support, individuals can reclaim their health and mitigate the risks associated with prediabetes. Now is the time to take proactive steps towards a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does an A1C level of 6.2% indicate?
An A1C level of 6.2% indicates that a person’s average blood glucose over the past two to three months has been high, categorizing them as prediabetic.
How are A1C levels categorized according to the American Diabetes Association?
The American Diabetes Association categorizes A1C levels as follows: Normal (below 5.7%), Prediabetes (5.7% to 6.4%), and High blood sugar (6.5% or higher).
What lifestyle modifications are recommended for someone with an A1C of 6.2%?
Recommended lifestyle modifications include implementing dietary adjustments, such as incorporating more vegetable-rich dishes, and increasing physical activity to reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related issues.
What is the prevalence of prediabetes in the United States?
As of August 2021 to August 2023, the prevalence of total sugar-related disorders in the United States was reported at 14.3%.
Why is it important to understand the A1C level of 6.2%?
Understanding an A1C level of 6.2% is crucial for effective management and prevention of the condition, allowing individuals to adopt a holistic approach to their well-being.
What are the health risks associated with an A1C level of 6.2%?
An A1C level of 6.2% is associated with increased risks for developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and various metabolic disorders, as well as early signs of insulin resistance.
How does A1C level relate to diabetes development?
The baseline mean A1C for people who develop diabetes is 6.8%, while it is 6.2% for those without diabetes, indicating that those with higher A1C levels are at greater risk for developing diabetes.
What are the financial implications of managing high A1C levels?
The excess medical costs per person for managing conditions related to high A1C levels increased from $10,179 to $12,022 between 2012 and 2022.
What approaches does the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego take for patients with high A1C levels?
The Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego provides comprehensive insights and treatment options, including personalized dietary plans, exercise regimens, and stress management techniques to help patients reverse type 2 conditions.