Overview
The article explores the connection between adrenaline and blood sugar levels, emphasizing how adrenaline regulates glucose release during stress and exercise, and its implications for individuals with type 2 diabetes. It supports this by detailing the physiological mechanisms of adrenaline in glucose metabolism, the detrimental effects of chronic stress on blood sugar regulation, and the importance of holistic management strategies, including mindfulness, exercise, and nutrition, to improve health outcomes for diabetic patients.
Introduction
The intricate relationship between adrenaline and blood sugar regulation is a crucial aspect of managing type 2 diabetes, particularly in the context of stress and physical exertion. Adrenaline, known for its role in the body’s acute stress response, triggers significant physiological changes that impact glucose metabolism.
As this hormone mobilizes energy reserves during times of stress or intense activity, it becomes essential to understand how these fluctuations affect blood sugar levels. Recent studies highlight the challenges faced by individuals with diabetes, where elevated adrenaline can lead to insulin resistance and complicate effective management of their condition.
This article delves into the mechanisms by which adrenaline influences blood sugar dynamics, the implications of stress on glucose regulation, and the strategies that can be employed to maintain stability in blood sugar levels. By exploring these interconnected factors, a clearer path emerges for individuals seeking to enhance their health and navigate the complexities of diabetes management.
The Role of Adrenaline in Regulating Blood Sugar Levels
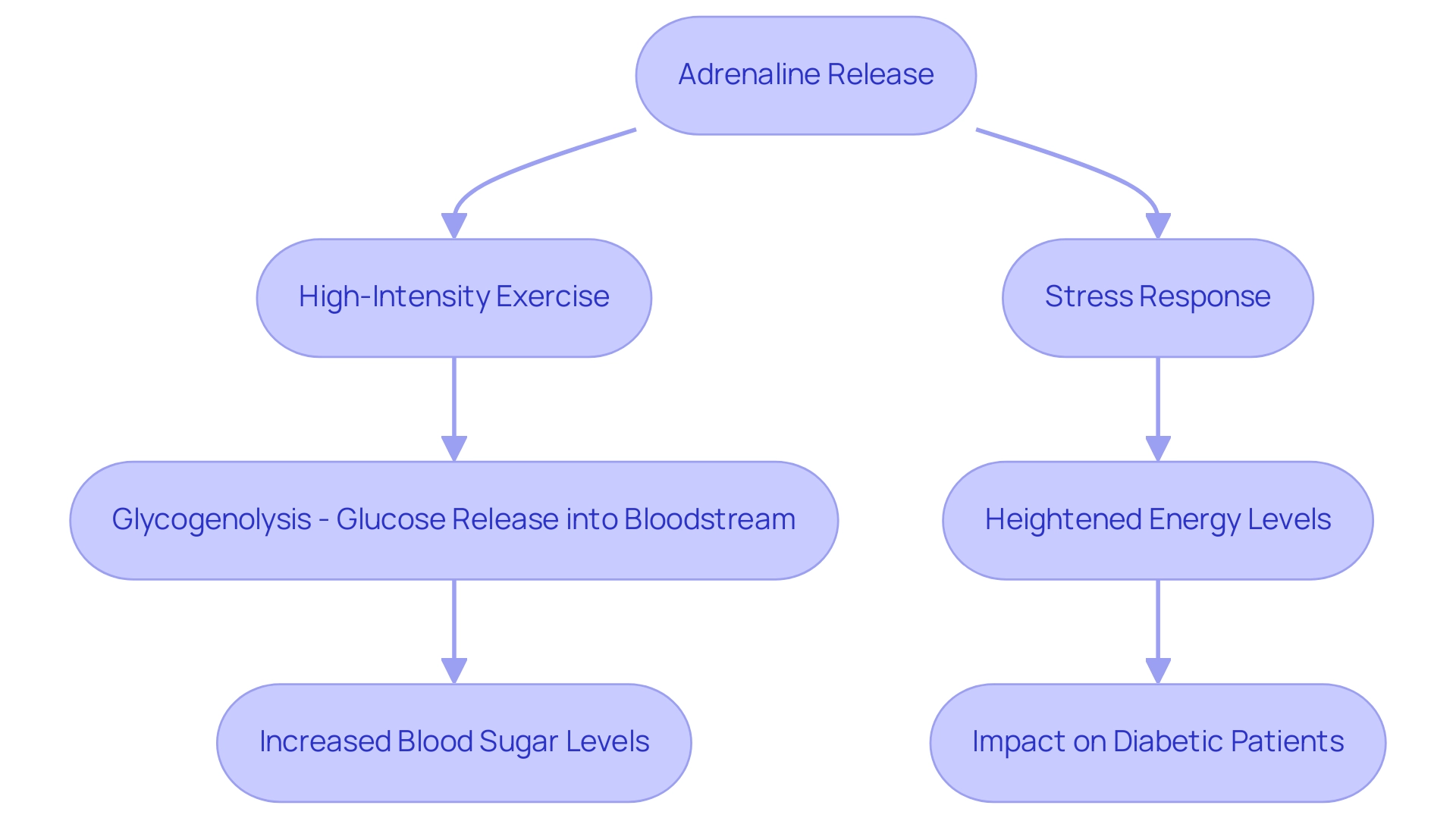
Adrenaline, or epinephrine, is a critical hormone produced by the adrenal glands, primarily involved in the body’s acute stress response. Upon release, a surge of energy triggers a series of physiological changes, prominently including the mobilization of energy reserves. Specifically, during high-intensity exercise, the hormone stimulates the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream through a process known as glycogenolysis.
This mechanism is vital for providing immediate energy necessary to manage stressful situations. Recent research indicates that for elite long-distance athletes, daily glucose concentrations were significantly higher in the three days leading up to a race (6.4 ± 0.7 mM) compared to the three days following the event (6.1 ± 1.1 mM), with statistical significance (p < 0.001). Such fluctuations highlight the significance of adrenaline and blood sugar in managing glucose concentrations during times of physical activity.
For individuals with type 2 diabetes, understanding this mechanism is essential, as the chronic or excessive release of epinephrine can lead to persistently heightened levels of adrenaline and blood sugar, complicating the management of the condition and potentially increasing anxiety regarding the complications of the illness. This highlights the necessity of a holistic approach to diabetes care, where understanding metabolic pathways and hormone interactions is fundamental to addressing root causes and empowering patient health. Implementing a holistic regimen that includes continuous glucose monitoring, combined with heart rate and oxygen consumption analysis, is recommended for a better understanding of glucose dynamics during exercise.
Additionally, it is noteworthy that during moderate exercise, plasma levels of epinephrine rise without a significant increase in secretion from the adrenal medulla, which highlights the body’s adaptive response to physical activity. As noted by Fitzgerald, ‘Overall, these observations support the view that this hormone is not of major significance in maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis and is not a major factor in the development of essential hypertension.’ This perspective is essential for understanding how the hormone’s role in glucose metabolism, particularly in relation to adrenaline and blood sugar, can impact overall health in diabetic patients, reinforcing the need for integrative approaches to diabetes management that not only address the physiological aspects but also help reduce anxiety related to the disease.
How Stress and Adrenaline Affect Blood Sugar Fluctuations
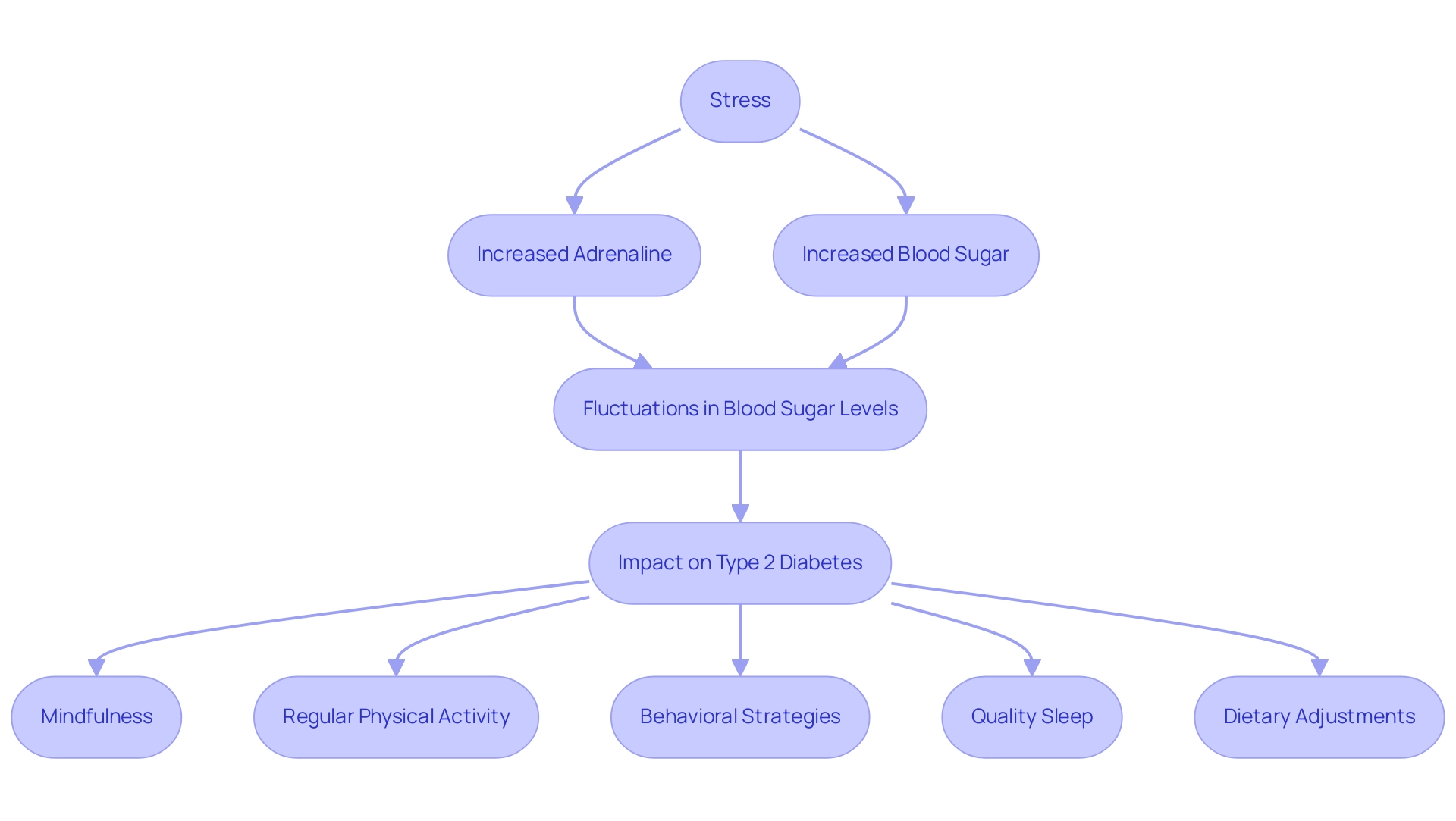
Stress, whether experienced in short episodes or as a persistent condition, significantly increases levels of adrenaline and blood sugar hormones in the body. This hormonal rise can lead to significant fluctuations in both adrenaline and blood sugar concentrations. During instances of intense stress, the activation of adrenaline and blood sugar levels by epinephrine triggers the body’s ‘fight or flight’ response, preparing it to react to perceived dangers.
For individuals managing type 2 diabetes, these spikes can aggravate their condition, complicating blood sugar regulation. Chronic stress can lead to a continuous state of hyperglycemia, as repeated surges of adrenaline and blood sugar disrupt normal metabolic pathways. Research suggests that individuals with persistent hyperglycemia have a 1.43-fold heightened risk of developing depression compared to those with consistently low fasting plasma glucose measurements (M. Kwon, Journal of Affective Disorders), emphasizing the critical need for effective stress management.
To address these challenges holistically, it is essential to re-examine the sources of diabetes and incorporate techniques such as:
- Mindfulness
- Regular physical activity
- Behavioral strategies for mitigating the adverse effects of stress
Quality sleep is also essential for health and glucose regulation; inadequate sleep can lead to insulin resistance and raise sugar amounts. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a calming bedtime environment can help regulate sugar levels.
Furthermore, exploring lesser-known strategies, such as specific dietary adjustments and targeted supplements, can enhance health and support the reversal of this condition. In light of recent findings, individualized target blood glucose ranges are recommended for patients, emphasizing the importance of personalized approaches to managing the condition that empower patients through education and tailored care.
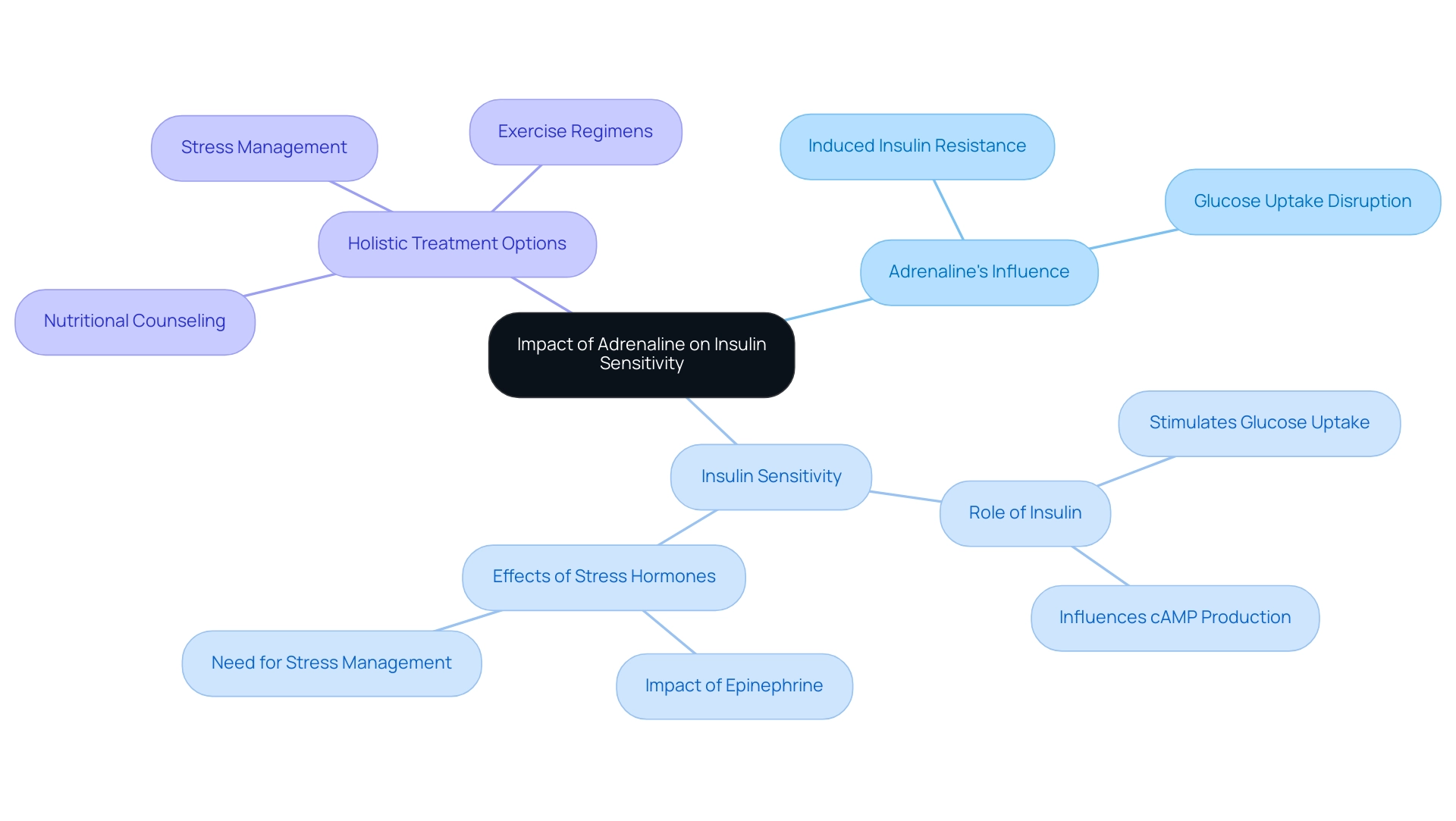
The Impact of Adrenaline on Insulin Sensitivity
Adrenaline exerts a significant influence on insulin sensitivity, primarily by inducing insulin resistance in various tissues. Elevated levels of adrenaline and blood sugar can disrupt insulin’s role in promoting glucose uptake into muscle and adipose tissues, leading to increased concentrations of glucose in the bloodstream. This condition poses challenges for individuals managing type 2.
At the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego, we recognize the importance of addressing these challenges holistically. Our personalized care approach has led to transformative patient success stories, such as patients who have successfully reversed their type 2 diabetes through tailored lifestyle changes and dietary adjustments. We offer comprehensive insights and treatment options, including:
- Nutritional counseling
- Stress management techniques
- Exercise regimens
All designed to empower patients in their health journey.
Notably, recent studies have shown that insulin can stimulate the uptake of glucose analogs, such as 3-methylglucose and 2-deoxyglucose, into thigh muscles by fivefold, underscoring insulin’s critical role in glucose metabolism. Furthermore, research titled ‘Glucose and Camp Interaction in Insulin Secretion’ clarifies that glucose not only triggers insulin release but also influences intracellular calcium and Camp production within beta cells, modulating their activation patterns. As UP-B, a guarantor of recent studies, stated, ‘Integrity and accuracy of the data are paramount in understanding these metabolic pathways.’
This highlights the importance of reliable data in exploring these interactions. Moreover, the connection between stress hormones, including epinephrine, and insulin resistance emphasizes the pressing need for effective stress management strategies to better control adrenaline and blood sugar. By reducing hormone surges, individuals can improve their insulin sensitivity, thereby boosting their health and assisting in the maintenance of stable glucose amounts.
At our center, we begin by reassessing the origin of your condition, enabling us to tackle health at the foundational aspect through a comprehensive regimen.
Strategies for Managing Adrenaline Levels and Blood Sugar Control
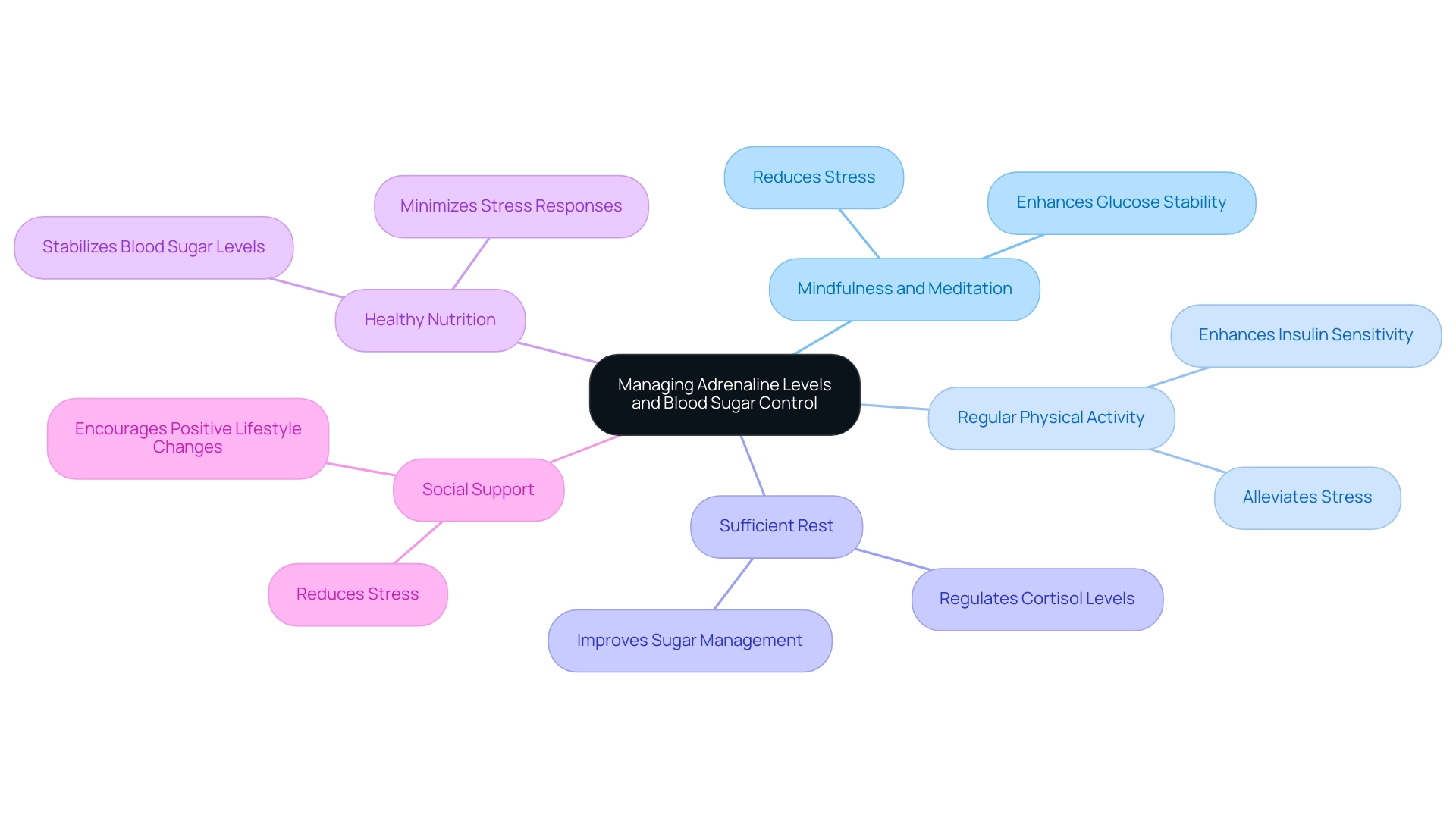
To effectively manage adrenaline levels and mitigate their impact on blood sugar, individuals with type 2 diabetes can adopt a variety of strategies:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness methods can greatly diminish stress, resulting in reduced hormone release, which is essential for sustaining stable glucose amounts. This aligns with a holistic approach that emphasizes re-examining the source of your condition and addresses the root causes, empowering patient health.
- Regular Physical Activity: Moderate exercise not only alleviates stress but also enhances insulin sensitivity, thereby promoting better glucose regulation. This is vital for challenging traditional treatments and understanding insulin resistance.
- Sufficient Rest: Focusing on sleep hygiene is crucial for regulating cortisol and adrenaline concentrations, which aids in enhanced sugar management. Inadequate sleep can worsen insulin resistance and complicate management of blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in whole foods is fundamental for stabilizing blood sugar levels and minimizing stress responses. This nutritional approach is critical in reversing the condition and should be tailored to individual needs.
- Social Support: Being part of a supportive community can reduce stress and encourage positive lifestyle changes, which are vital for effective management of the condition. As Jennifer Purdie observes, “If you’re feeling stressed about your condition, know that you aren’t alone”; this emphasizes the significance of social support in managing the illness.
By incorporating these strategies, individuals can significantly enhance their ability to manage both adrenaline and blood sugar levels, contributing to improved stability. Additionally, addressing the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of this condition is crucial. Considering that the overall expense of this condition in the US was approximately $174 billion in 2007, effective management strategies are not only essential for personal health but also for alleviating the economic burden linked to it.
Furthermore, understanding complications of type 2 conditions, such as nerve and renal damage, underscores the necessity of these strategies in preventing severe health issues.
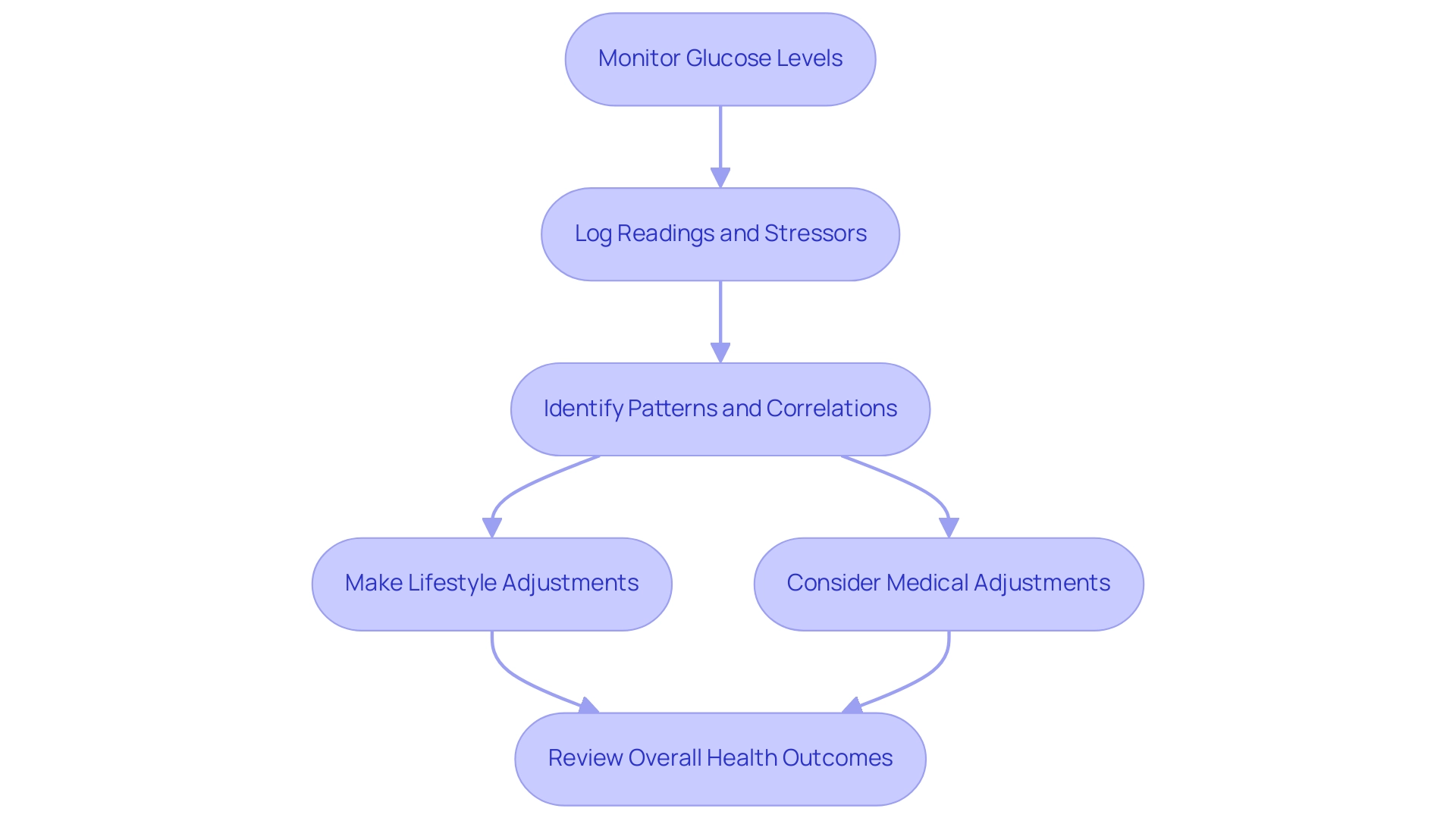
Monitoring and Understanding Blood Sugar Patterns
Consistent observation of glucose levels is essential for individuals identified with type 2 condition, particularly considering the 5,293 newly identified cases among children and teenagers aged 10 to 19 during 2017-2018. This statistic underscores the growing prevalence of diabetes and the need for effective monitoring. By maintaining a detailed log of glucose readings alongside notes on stressors or significant life events, patients can identify patterns and correlations related to adrenaline and blood sugar that may inform necessary adjustments in lifestyle, medication, and stress management strategies.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are particularly beneficial in this context, offering real-time data that enhances awareness of adrenaline and blood sugar fluctuations. As noted by Maria Ida Maiorino, CGM improves glycemic control by expanding Time in Range (TIR) and decreasing Time Below Range (TBR), Time Above Range (TAR), and glucose variability in both type 1 and type 2 conditions. Furthermore, a significant portion of adults with the condition, 47.4%, had an A1C value of 7.0% or higher, indicating a pressing need for improved management strategies.
Complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage can arise from poorly managed diabetes, which underscores the importance of a proactive approach. Emphasizing a holistic approach allows patients to address the root causes of their condition, empowering them to take charge of their health through a multidisciplinary strategy that includes:
- Education on diet
- Exercise
- Medication adjustments
- The importance of managing adrenaline and blood sugar
For example, incorporating regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and stress reduction techniques can significantly impact overall health.
This approach not only enhances glycemic control but also considers the socioeconomic factors impacting health, ultimately aiming to improve overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between adrenaline and blood sugar regulation is vital for individuals managing type 2 diabetes. The article highlights how adrenaline, released during stress or physical exertion, can significantly influence glucose metabolism. Elevated adrenaline levels mobilize energy reserves, which, while beneficial during acute stress, can lead to insulin resistance and complicate blood sugar management for those with diabetes.
Chronic stress and its associated adrenaline surges can create a cycle of hyperglycemia, increasing the risk of depression and other health complications. The importance of stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and regular physical activity, emerges as a critical strategy for controlling blood sugar levels. Additionally, establishing healthy sleep patterns and a balanced diet can further support metabolic health and reduce the adverse effects of stress.
Monitoring blood sugar patterns through continuous glucose monitoring provides valuable insights that can guide lifestyle adjustments and enhance diabetes management. By adopting a holistic approach that addresses both physiological and psychological factors, individuals can better navigate the complexities of their condition. This comprehensive strategy not only empowers patients but also emphasizes the significance of personalized care in achieving stable blood sugar levels and promoting overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is adrenaline and what role does it play in the body?
Adrenaline, or epinephrine, is a critical hormone produced by the adrenal glands, primarily involved in the body’s acute stress response. It triggers a surge of energy and physiological changes, including the mobilization of energy reserves, especially during high-intensity exercise.
How does adrenaline affect glucose levels during exercise?
During high-intensity exercise, adrenaline stimulates the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream through a process called glycogenolysis, providing immediate energy to manage stressful situations.
What recent research findings highlight the relationship between adrenaline and glucose in athletes?
Recent research indicates that elite long-distance athletes had significantly higher daily glucose concentrations in the three days leading up to a race compared to the three days following the event, highlighting the significance of adrenaline and blood sugar in managing glucose concentrations during physical activity.
Why is understanding adrenaline’s mechanism important for individuals with type 2 diabetes?
For individuals with type 2 diabetes, chronic or excessive release of adrenaline can lead to persistently elevated adrenaline and blood sugar levels, complicating diabetes management and increasing anxiety regarding potential complications.
What holistic approaches are recommended for diabetes management?
A holistic approach to diabetes care includes understanding metabolic pathways and hormone interactions, continuous glucose monitoring, and analyzing heart rate and oxygen consumption during exercise.
How does exercise influence adrenaline levels?
During moderate exercise, plasma levels of adrenaline rise without a significant increase in secretion from the adrenal medulla, indicating the body’s adaptive response to physical activity.
What are the effects of stress on adrenaline and blood sugar levels?
Stress significantly increases levels of adrenaline and blood sugar hormones, leading to fluctuations that can aggravate conditions like type 2 diabetes and cause a continuous state of hyperglycemia.
What strategies can help manage stress and its effects on diabetes?
Effective stress management techniques include mindfulness, regular physical activity, behavioral strategies to mitigate stress effects, and ensuring quality sleep to regulate insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels.
What dietary and lifestyle adjustments can support diabetes management?
Specific dietary adjustments, targeted supplements, and establishing a consistent sleep routine can enhance health and support the reversal of diabetes. Individualized target blood glucose ranges are also recommended for personalized care.
What is the significance of personalized approaches in diabetes management?
Personalized approaches empower patients through education and tailored care, addressing individual needs and improving overall health outcomes in managing diabetes.