Overview
The article focuses on the implications and management strategies associated with an HbA1c level of 5.6%, which is considered normal but indicates a need for vigilance, especially for individuals at risk for type 2 diabetes. It emphasizes the importance of lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels, to maintain this level and prevent progression to prediabetes or diabetes, supported by evidence from case studies and expert recommendations.
Introduction
Understanding HbA1c levels is essential for effective diabetes management, particularly for those at risk of type 2 diabetes. An HbA1c level of 5.6% may seem reassuringly within the normal range, but it carries significant implications for long-term health.
This article delves into the meaning behind this measurement, emphasizing the importance of continuous monitoring and proactive lifestyle adjustments to prevent progression toward diabetes. It also explores effective management strategies:
- The critical role of nutrition
- The necessity of regular physical activity
- The importance of maintaining an adaptive management plan
Through a comprehensive approach, individuals can not only manage their HbA1c levels but also enhance their overall well-being and reduce the anxiety associated with diabetes.
Understanding HbA1c: Significance and Implications of a Level of 5.6
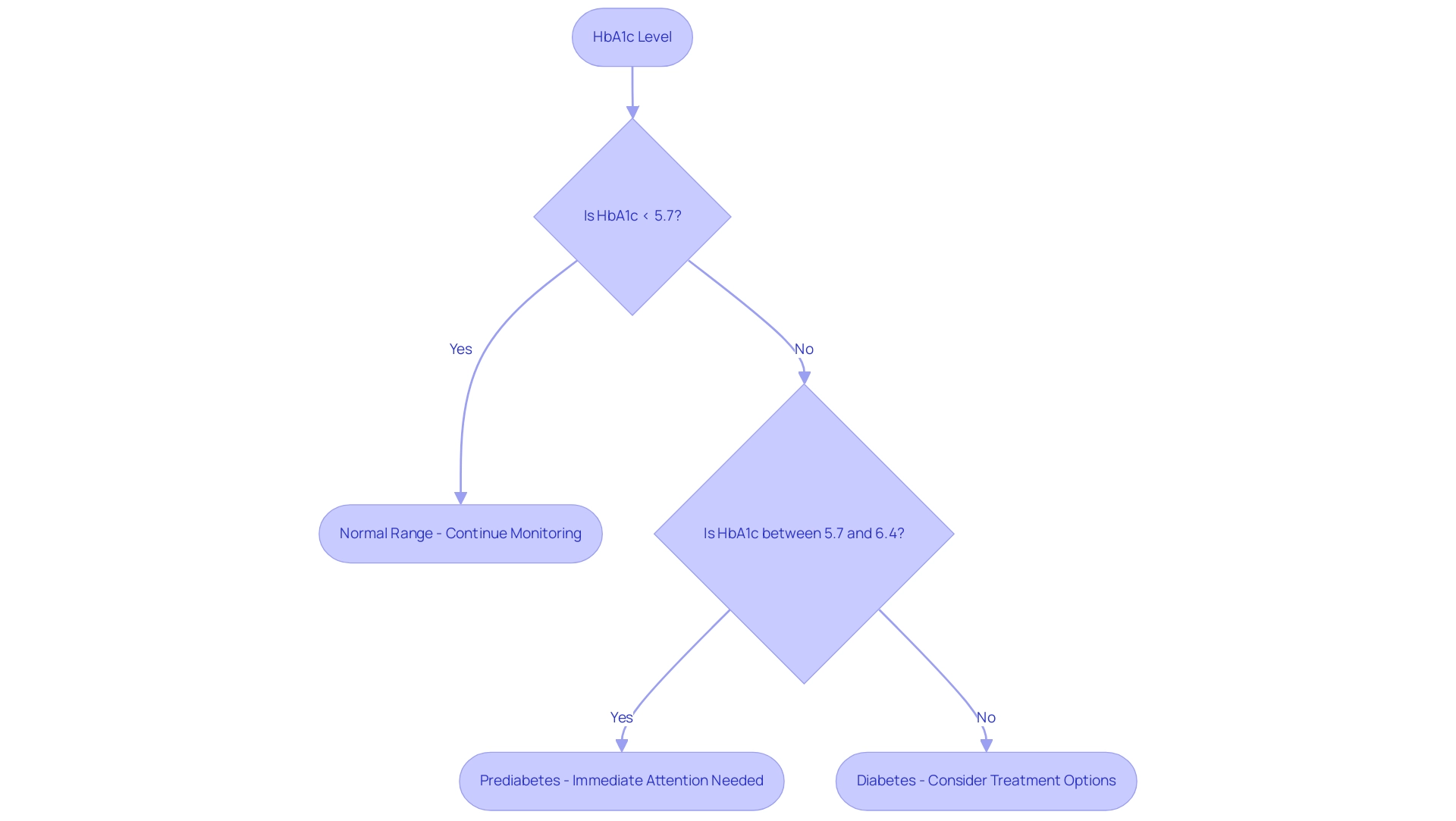
Glycated hemoglobin acts as an essential blood examination that reflects the average blood glucose concentrations over a duration of two to three months. A measurement of HbA1c 5.6% falls within the normal range, yet it holds significant implications for individuals, especially for those with or at risk for type 2 diabetes. The standard benchmark suggests that maintaining an HbA1c below 5.7% is indicative of good health.
In contrast, values between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate the presence of prediabetes, a condition that warrants immediate attention. Consequently, a measure of HbA1c 5.6% indicates that the individual is effectively managing their blood sugar levels. However, alertness is crucial to maintain this standard and prevent any possible advancement toward greater values that would be categorized as a serious condition.
Martensson J. underscores the significance of these stages by stating, ‘Hemoglobin A1c is a crucial metric in understanding the management of this condition.’ This emphasizes the necessity for ongoing observation and lifestyle modifications to reduce future risks linked to high blood sugar levels. Furthermore, the holistic approach utilized at the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego emphasizes addressing the root causes of the condition, empowering patients through personalized care that has led to transformative success stories in reversing type 2.
For instance, one patient successfully reduced their HbA1c from 7.5% to 5.4% within six months through tailored dietary and lifestyle changes. The financial implications of managing the condition are significant, with excess medical costs per person increasing from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022. This highlights the importance of effective treatment options.
Additionally, a recent case study highlighted that diagnosed cases of the condition among U.S. adults varies by county, ranging from 4.4% to 17.9%, indicating the necessity for localized health interventions. Future larger prospective cohort studies are recommended to offer more dependable evidence concerning the connection between glycated hemoglobin and mortality in cardiovascular disease patients with sugar metabolism disorders, highlighting the developing comprehension of glycated hemoglobin’s role in management.
Effective Management Strategies for Maintaining Optimal HbA1c Levels
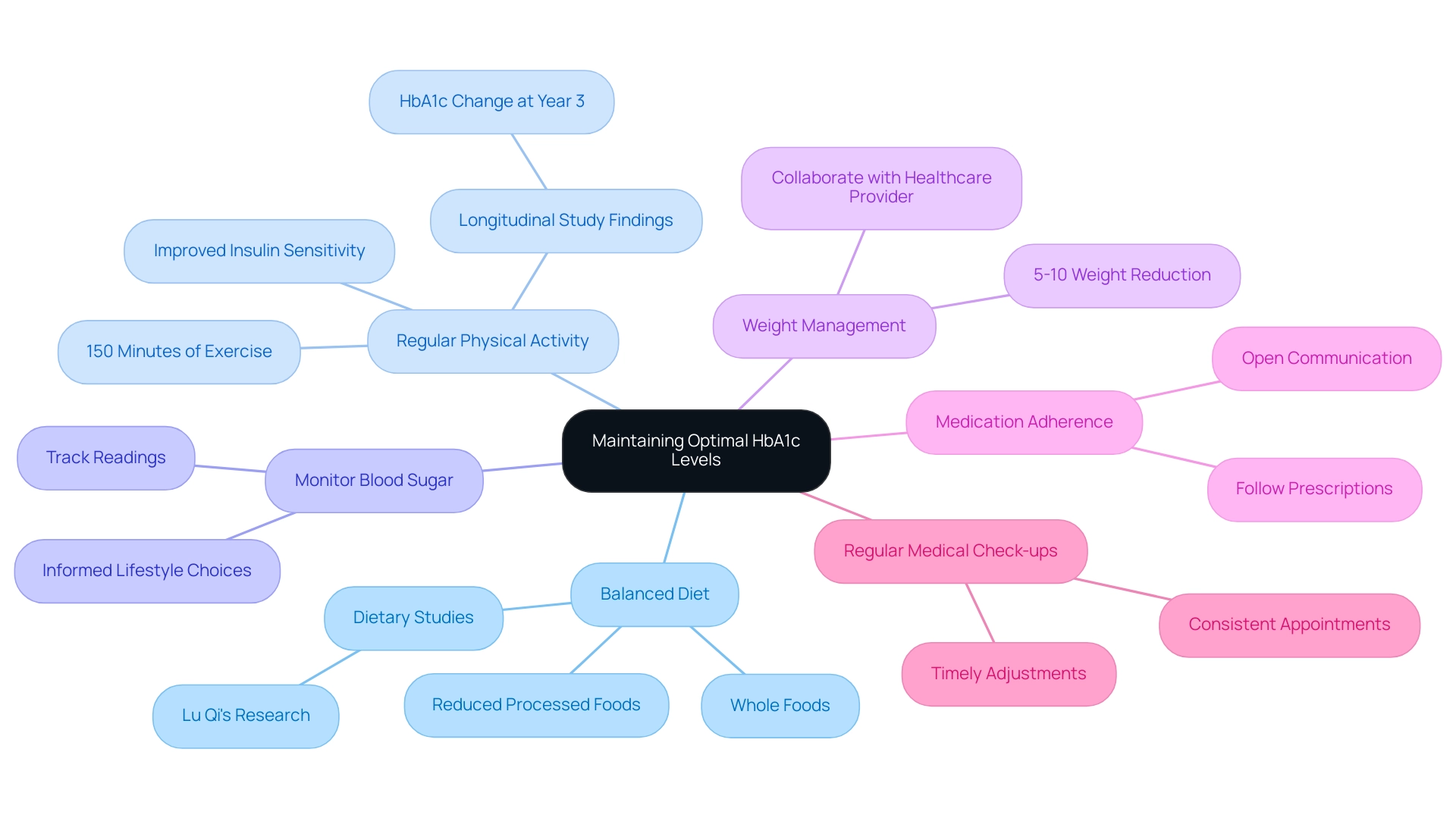
To effectively sustain optimal blood sugar metrics through a holistic approach, it is essential to implement several key strategies that not only regulate the condition but also reduce the anxiety surrounding potential complications:
-
Adopt a Balanced Diet: Emphasize whole foods, including an abundance of vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Minimizing processed foods and added sugars is crucial, as these can significantly spike blood glucose.
Recent studies suggest that dietary choices are closely connected to blood sugar measurements, highlighting the significance of nutrition in diabetes care. As highlighted by Lu Qi, MD, PhD, in a recent study on low-carbohydrate dietary interventions, diet plays a crucial role in effectively managing blood sugar readings.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Participating in regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps in reducing blood sugar. A longitudinal study discovered that participants who raised their activity rates showed significant enhancements in their blood glucose control.
Significantly, at follow-up year 3, participants with no increase in physical activity or healthy food score had a change in blood sugar levels of 0.19 ± 1.87, illustrating the importance of lifestyle changes.
-
Monitor Blood Sugar Readings: Consistently tracking your blood glucose readings is vital for understanding how various foods and activities impact your body.
This practice empowers patients to make informed lifestyle choices, ultimately supporting better glycemic control and challenging traditional treatment myths.
-
Weight Management: For individuals who are overweight, even a modest weight reduction of 5-10% can lead to substantial improvements in hba1c 5.6 levels.
Collaborating with a healthcare provider to set achievable weight loss goals is essential for effective diabetes management.
-
Medication Adherence: If medications are prescribed, it is essential to take them as instructed by your healthcare provider to help control blood sugar.
Open communication regarding any concerns about medications can facilitate better management.
-
Regular Medical Check-ups: Schedule consistent appointments with your healthcare team to monitor your blood sugar readings and overall health.
This proactive approach ensures timely adjustments to your management plan as needed.
As highlighted in a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association, integrating physical activity and dietary management is vital for optimal care of the condition. The case study titled ‘Impact of Physical Activity and Healthy Food Scores on Blood Sugar Levels’ further illustrates that active participants with high healthy food scores had lower blood sugar readings, reinforcing the effectiveness of these strategies and the holistic approach at the Integrative Wellness Center.
Significantly, by reassessing the origin of your diabetes and applying these strategies, you can not only enhance your blood sugar control but also alleviate the anxiety that comes with concerns about possible complications of your condition.
The Role of Nutrition in HbA1c Management
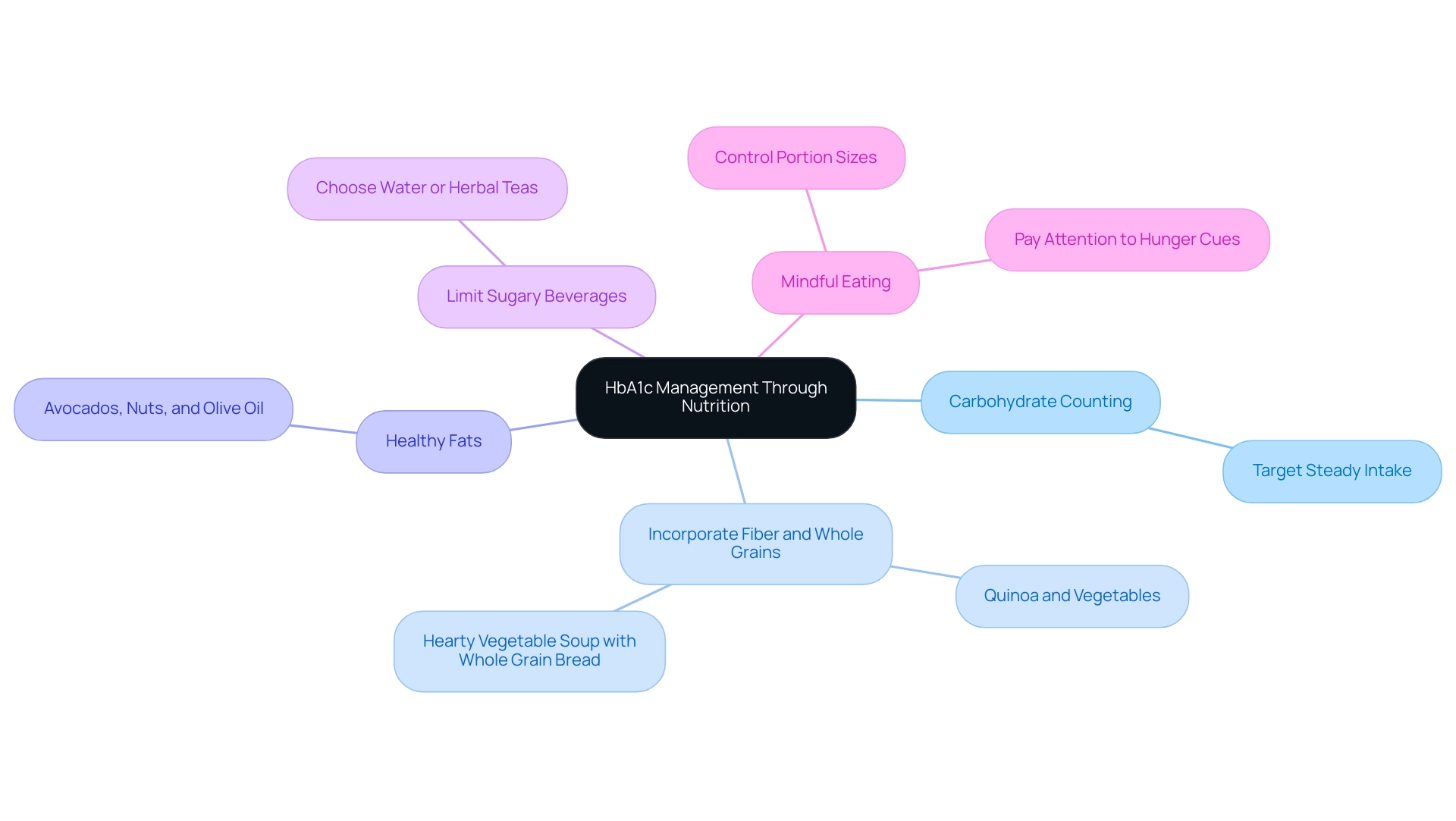
Effective management of hba1c 5.6 values hinges on proper nutrition. Several key nutritional strategies can aid in this effort:
-
Carbohydrate Counting: Understanding how to count carbohydrates allows for better intake management.
It is recommended to target a steady carbohydrate quantity at each meal, which aids in sustaining stable sugar levels.
-
Incorporate Fiber and Whole Grains: Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains like quinoa and brown rice, play a crucial role in regulating glucose levels by slowing digestion.
San Marcos restaurants are increasingly incorporating these healthier grains into their menus, supporting glucose control and providing lasting energy.
Current dietary recommendations emphasize sufficient fiber intake, which is associated with modest reductions in A1C levels, potentially achieving an hba1c 5.6.
Specific vegetable-rich dishes, such as stir-fried vegetables with quinoa or a hearty vegetable soup served with whole grain bread, can further enhance sugar regulation.
-
Healthy Fats: Including sources of healthy fats—like avocados, nuts, and olive oil—can enhance insulin sensitivity, a vital factor for individuals managing type 2 diabetes.
-
Limit Sugary Beverages: The consumption of sugary drinks leads to rapid spikes in glucose levels.
Choosing water, herbal teas, or low-sugar substitutes is advised for staying hydrated without negatively impacting glucose amounts.
-
Mindful Eating: Practicing mindful eating by paying close attention to hunger cues and portion sizes can prevent overeating, thereby promoting better blood sugar control.
The prevalence of prediabetes in the U.S. population aged over 65 years is estimated at 46.6%, compared to 24.3% in the 18–44 years age group, which underscores the importance of managing HbA1c 5.6 levels across different age demographics.
The Indian Diabetes Prevention Study underscores the significance of dietary interventions, highlighting that avoiding simple sugars and refined carbohydrates, alongside increasing physical activity and fiber intake, significantly reduces the incidence of type 2 diabetes in populations at risk.
As Castro MR notes, “Hypoglycemia (low glucose levels)” can complicate management, which reinforces the need for careful dietary planning.
By customizing dietary approaches to personal requirements, it becomes feasible to effectively assist in managing blood sugar levels.
Additionally, incorporating whole grains into meals can be as simple as swapping white rice for brown rice or adding oats to smoothies, providing practical ways to enhance dietary choices.
The Importance of Regular Physical Activity
Participating in consistent physical exercise is essential for properly regulating blood sugar values and attaining optimal readings, particularly within the scope of a comprehensive strategy for managing the condition. Managing diabetes can often lead to anxiety surrounding potential complications, but addressing these emotional aspects is essential for overall well-being. Research indicates that individuals who maintain an active lifestyle often experience significant improvements in their glucose control.
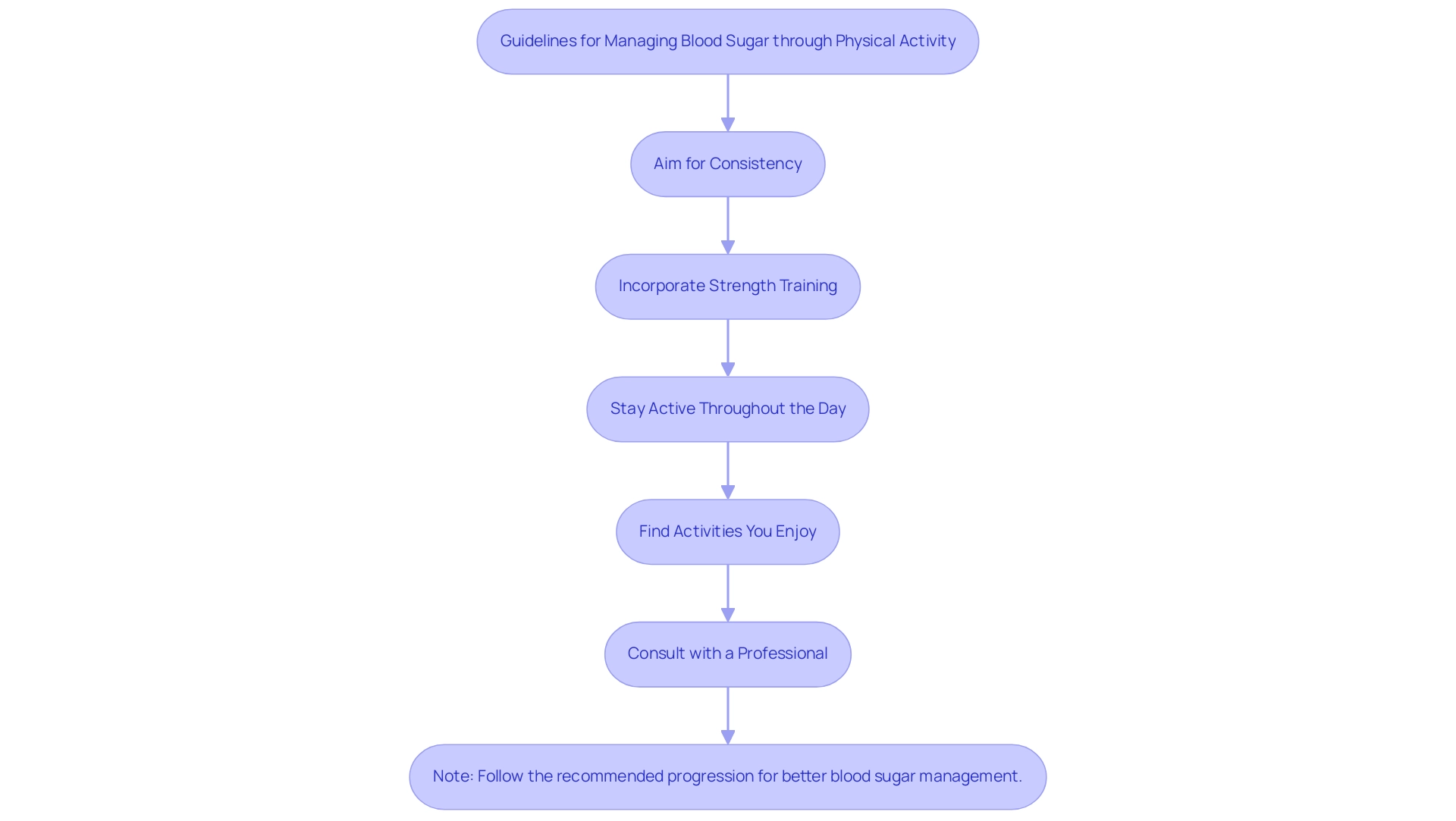
According to a study funded by JSPS KAKENHI Grants, regular physical activity can result in a reduction in blood sugar markers by about 0.5% to 1% for individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Here are essential guidelines to follow:
-
Aim for Consistency: Strive for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
This level of activity not only aids in weight management but also significantly reduces hba1c 5.6 levels, empowering patients to take control of their health.
-
Incorporate Strength Training: Include strength training exercises at least twice a week.
Building muscle mass enhances insulin sensitivity, which is particularly beneficial for glucose metabolism.
-
Stay Active Throughout the Day: Seek opportunities to incorporate movement into your routine.
Simple changes, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator or walking during breaks, can collectively contribute to better glucose control.
-
Find Activities You Enjoy: Selecting exercises that you find enjoyable will help maintain motivation and adherence to your routine, which is vital for long-term success.
-
Consult with a Professional: If you are new to exercise or have specific health concerns, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or fitness professional.
They can help you design a safe and effective exercise plan tailored to your individual needs.
As highlighted by C.H., a patient who transformed their health through personalized care at the Integrative Wellness Center, overcoming barriers to traditional treatment can lead to profound improvements in well-being. C.H. discovered that by adhering to a customized exercise plan, they not only enhanced their physical well-being but also reduced some of the anxiety related to their condition.
By following these guidelines, you can promote better blood sugar management and improve your overall health, while also addressing the emotional challenges that may arise.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Management Plan
Tracking your blood sugar measurements is essential for efficient management of your condition and general well-being. As Mårtensson J. indicates, ‘Hemoglobin A1c 5.6 and Permissive Hyperglycemia in Patients in the Intensive Care Unit with Diabetes’ underscores the significance of understanding hemoglobin levels, particularly hba1c 5.6, in effectively managing blood sugar. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we believe that addressing the root causes of this condition through a holistic regimen is essential for empowering patient health and finding new peace in life.
Here are several key steps to follow:
- Keep a Log: Maintain a detailed record of your blood sugar readings, A1c results, dietary intake, and physical activity. This practice aids in identifying trends and potential areas for improvement in your management plan.
- Schedule Regular Check-ups: Collaborate with your healthcare team to arrange regular check-ups. These appointments are crucial for evaluating your blood sugar metrics and reviewing your management strategy.
The case study titled ‘Clinical Significance of Glycated Hemoglobin’ highlights that the hba1c 5.6 metric serves as a key indicator of overall glycemic control and is utilized to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions for blood sugar management, reinforcing the importance of regular testing.
- Be Open to Adjustments: Flexibility is vital; be prepared to adjust your diet, exercise routine, or medication based on your healthcare team’s recommendations and your monitoring data.
- Set Realistic Goals: Establish achievable short-term and long-term objectives for your blood sugar levels and overall health. Realistic objectives not only motivate you but also provide a sense of accomplishment as you progress.
- Communicate with Your Healthcare Team: Maintain an open line of communication with your healthcare team. Regular discussions about your progress and any challenges you encounter can facilitate necessary adjustments and provide valuable support.
Additionally, programs like Diabetes INSIDE demonstrate a system-wide approach to managing the condition, underscoring the significance of HbA1c 5.6 monitoring within that framework. By adhering to these steps and embracing a holistic approach that includes re-examining the source of your diabetes, individuals can effectively manage their diabetes, alleviate anxiety over potential complications, and improve their overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing HbA1c levels is crucial for preventing the progression of type 2 diabetes and enhancing overall health. A level of 5.6% may fall within the normal range, yet it signifies the need for vigilance and proactive measures to maintain blood sugar control. Continuous monitoring, along with strategic lifestyle changes, can significantly impact long-term health outcomes.
Key strategies for effective management include:
- Adopting a balanced diet focused on whole foods
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Maintaining a structured management plan that prioritizes weight management and medication adherence
Each of these elements plays a vital role in stabilizing HbA1c levels and reducing anxiety associated with diabetes.
Ultimately, by implementing these comprehensive management strategies and collaborating closely with healthcare providers, individuals can not only achieve better control over their HbA1c levels but also foster a sense of empowerment in their health journey. This proactive approach not only mitigates the risks associated with diabetes but also enhances overall well-being, paving the way for a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and why is it important?
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is a blood examination that reflects average blood glucose concentrations over two to three months. It is important because it helps assess the management of blood sugar levels, particularly for individuals with or at risk for type 2 diabetes.
What does an HbA1c level of 5.6% indicate?
An HbA1c level of 5.6% falls within the normal range and indicates that the individual is effectively managing their blood sugar levels. However, it is crucial to maintain this level to prevent progression to higher values.
What are the implications of HbA1c values between 5.7% and 6.4%?
Values between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate the presence of prediabetes, a condition that requires immediate attention to prevent progression to type 2 diabetes.
How can individuals manage their blood sugar levels effectively?
Individuals can manage their blood sugar levels effectively by adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, monitoring blood sugar readings, managing weight, adhering to prescribed medications, and scheduling regular medical check-ups.
What dietary changes are recommended for managing blood sugar levels?
It is recommended to emphasize whole foods, including vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats, while minimizing processed foods and added sugars.
How much physical activity is recommended for individuals managing blood sugar levels?
A minimum of 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, is recommended to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar.
Why is monitoring blood sugar readings important?
Consistently tracking blood glucose readings is vital for understanding how different foods and activities impact blood sugar levels, empowering individuals to make informed lifestyle choices.
What is the significance of weight management in blood sugar control?
For individuals who are overweight, even a modest weight reduction of 5-10% can lead to substantial improvements in HbA1c levels.
What role do medications play in managing blood sugar levels?
If prescribed, it is essential to take medications as instructed by a healthcare provider to help control blood sugar levels effectively.
Why are regular medical check-ups important for individuals managing diabetes?
Regular medical check-ups allow for consistent monitoring of blood sugar readings and overall health, ensuring timely adjustments to the management plan as needed.