Overview
The article focuses on understanding and managing a hemoglobin A1c level of 5.5%, which is generally considered within the normal range but may indicate a risk for prediabetes. It emphasizes the importance of regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications such as nutrition and exercise, and personalized healthcare strategies to effectively manage blood sugar levels and prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes.
Introduction
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) serves as a pivotal indicator in the management of diabetes, providing crucial insights into long-term blood glucose levels and overall metabolic health. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, understanding the implications of HbA1c testing becomes increasingly important for both patients and healthcare providers.
This article delves into the significance of HbA1c, exploring:
- Its role in diagnosing and monitoring diabetes
- The health implications associated with various HbA1c levels
- Effective strategies for managing and lowering these levels
By highlighting the importance of:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Medical interventions
- Ongoing monitoring
it aims to empower individuals to take charge of their health and mitigate the risks associated with diabetes.
Understanding Hemoglobin A1c: What It Is and Why It Matters
Hemoglobin A1c is an essential blood examination that evaluates the average blood glucose concentrations over a two to three-month timeframe, playing a significant role in transformative health solutions for Type 2 sugar intolerance and hypothyroidism. This test yields significant insights into long-term blood sugar control, enabling patients to empower themselves through education and personalized care. The level of hemoglobin A1c 5.5 is reported as a percentage; for instance, an HbA1c of 5.5% signifies that approximately 5.5% of the hemoglobin in the bloodstream has glucose molecules attached.
Such measurements are essential for both diagnosing and monitoring the condition, aiding healthcare providers in evaluating the effectiveness of treatment strategies and making necessary adjustments to patient care plans. Recent data shows a rising awareness of prediabetes, with 93.0% of individuals having undergone cholesterol checks, reflecting an increased focus on managing related medical conditions that affect metabolic control. Moreover, age-adjusted estimates indicate that the occurrence of total glucose intolerance has increased to 14.3% overall, emphasizing the crucial need for continuous tracking of blood sugar levels in enhancing patient outcomes and tackling public welfare issues.
As noted by Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H., the prevalence of diagnosed blood sugar conditions has shown an upward trend, highlighting the importance of regular testing for hemoglobin A1c 5.5 within community wellness programs aimed at empowering patients and alleviating anxiety over complications through holistic care. To further enhance health and reverse this condition, it is essential to consider four lesser-known strategies:
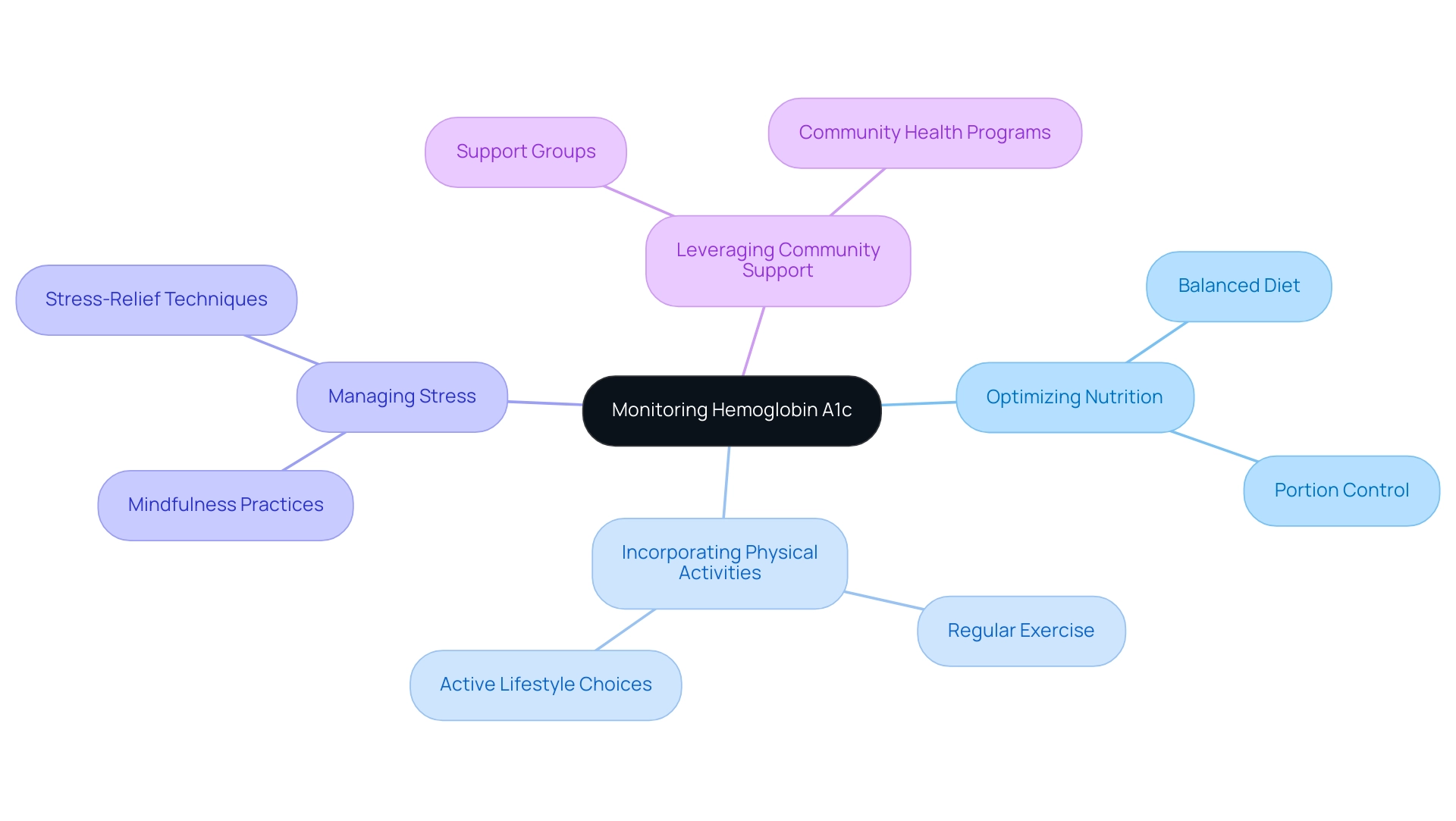
- Optimizing nutrition
- Incorporating specific physical activities
- Managing stress effectively
- Leveraging community support systems
Addressing these strategies can help patients overcome the frustrations often experienced with conventional management approaches, fostering a more comprehensive and effective diabetes care plan.
Interpreting an HbA1c Level of 5.5: Health Implications and Risks
A reading of hemoglobin A1C 5.5% is generally categorized as within the normal range; however, it can indicate a heightened risk for prediabetes, especially when sustained over time. Research indicates that individuals with an HbA1C in this range may benefit from regular monitoring of their blood sugar levels. Consulting with healthcare providers to assess personal risk factors is crucial.
Dr. Francis M. Hoe highlights the importance of vigilance, noting that
Our findings are notable in that 15.2% of individuals who developed T2D required insulin beyond 6 months of diagnosis.
This statistic underscores the need for proactive health management, as illustrated by patients like M.L., who, after enrolling in a holistic program at the Integrative Wellness Center, achieved significant health improvements. M.L.
- lost 55 pounds
- reduced their A1C from 9.1 to 5.7
- improved their fasting glucose from 133 to 85
Additionally, their regular MD has cut their blood pressure medications in half, showcasing the effectiveness of personalized care and attention. Furthermore, it is important to consider that the hospitalization rate for hypoglycemia was 2.2 per 1,000 adults with the condition in 2020, emphasizing the risks associated with managing the illness.
Although a reading of hemoglobin A1C 5.5% does not correspond to a diagnosis of the condition, it serves as a critical reminder to pay attention to dietary choices, physical activity, and overall lifestyle. The diagnostic procedure for this condition involves self-reporting for confirmed cases and evaluations through fasting plasma glucose and A1C measurements for undiagnosed cases. Introducing precautionary steps at this point is crucial to prevent the advancement to elevated blood sugar readings, thus lowering the likelihood of developing type 2 conditions later on.
Current studies emphasize the role of A1C as a valuable tool in identifying individuals at risk, supporting the necessity for lifestyle interventions, much like those successfully undertaken by patients at the Integrative Wellness Center. This holistic approach not only addresses the root causes of diabetes but also helps alleviate the anxiety surrounding potential complications, empowering patients to take control of their health.
Effective Strategies for Managing and Lowering HbA1c Levels
To effectively control and reduce blood sugar metrics, individuals should consider the following strategies:
-
Balanced Diet: Emphasizing whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, is crucial. Reducing refined sugars and carbohydrates can assist in stabilizing blood glucose readings.
Recent findings indicate that individuals with higher genetic risk scores for type 2 diabetes (T2D) who also maintain a high-quality diet experience better glycemic control, which is crucial for managing hemoglobin A1c 5.5 values. Notably, individuals in the highest tertile of the genetic risk score and the lowest tertile of diet quality had a 2.29-fold increase in T2D risk compared to those in the lowest tertile of GRS and the highest tertile of diet quality.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly, such as brisk walking or cycling, can significantly enhance insulin sensitivity. Expert opinions suggest that exercise not only aids in weight management but also plays a critical role in blood sugar control.
-
Consistent Monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar amounts allows individuals to understand how their food choices, physical activity, and medications impact glucose control, enabling timely adjustments to their management plans.
-
Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can markedly enhance blood sugar readings.
Evidence indicates that individuals with improved diet quality and suitable weight management approaches tend to have reduced blood sugar levels. A cross-sectional study of White British participants found that better diet quality was inversely associated with hemoglobin A1c 5.5 levels, reinforcing the importance of nutrition in managing blood sugar.
-
Stress Management: Implementing stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation is essential, as stress can adversely affect blood sugar control. This holistic regimen not only focuses on dietary and lifestyle modifications but also addresses the root causes of the condition, which can alleviate anxiety surrounding potential complications of the disease. By re-evaluating the origin of the condition, individuals can empower themselves to take charge of their health.
Kirsten S. Dorans, ScD, emphasizes, “This dietary approach may be an option for people with or at high risk of T2D to improve glycemic and other markers and should be studied further and over longer time periods in other populations and settings.” This highlights the effectiveness of dietary approaches, coupled with lifestyle modifications, as interventions for individuals at high risk of T2D.
Frequently Asked Questions About HbA1c Testing
Common inquiries regarding blood glucose testing include:
- When should I get tested? For individuals with diabetes, the recommended frequency for hemoglobin A1c testing is at least twice a year. However, those who sustain stable blood sugar concentrations may be eligible for less frequent testing, as guided by their healthcare provider. Notably, 45.8% of patients had a Charlson Comorbidity Index score of 0, indicating that many individuals may have fewer health complications, which can influence their testing frequency.
- What do the results signify? A blood sugar level below 5.7% is categorized as normal. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest prediabetes, while a hemoglobin A1c of 5.5 or higher is indicative of the condition. Understanding these thresholds is crucial for proactive health management and can help empower patients to take control of their health through education at the Integrative Wellness Center, ultimately reducing anxiety about potential diabetes complications.
- Is home testing an option? Although several home testing kits are available, it is essential to have any results verified by a healthcare provider to ensure accuracy and appropriate follow-up.
- What steps should I follow if my blood sugar measurement is high? If your results show a high blood sugar measure, it is essential to consult your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance on holistic lifestyle modifications and treatment options tailored to your specific health circumstances, addressing root causes and empowering you to manage your health effectively. Integrating methods like balanced nutrition, consistent physical activity, and stress management techniques can greatly aid in reducing blood glucose and improving overall health. For example, a case study on screening for glucose intolerance in individuals with HIV highlights the necessity of continuous assessment and consultation with healthcare professionals. Regular monitoring is crucial; if initial screening results are normal, further testing should occur annually. This highlights the significance of specialist knowledge in controlling blood sugar metrics and easing worries about possible complications, ultimately assisting you in achieving tranquility in your wellness journey.
Lifestyle Changes and Medical Interventions for Optimal HbA1c Management
Achieving and maintaining hemoglobin A1c 5.5 values necessitates a multifaceted approach that includes both lifestyle modifications and medical interventions.
-
Holistic Approach:
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we start by reassessing the origin of your condition, tackling wellness at the foundational aspect through a holistic regimen. This process empowers patients to take control of their health and well-being, potentially alleviating the anxiety associated with the concerns surrounding complications.
-
Lifestyle Changes:
Adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and practicing effective stress management are critical components that can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control. Research shows that individuals aged 20-35 years experienced an average weight reduction of 3.5 kg through lifestyle interventions, which highlights the concrete advantages of such changes in managing hemoglobin A1c 5.5. Moreover, with a significant proportion of individuals with type 2 diabetes presenting with multiple uncontrolled cardiovascular risk factors, as highlighted in recent studies, these lifestyle changes become even more crucial.
-
Medical Interventions:
Healthcare providers may recommend medications such as metformin to assist in managing blood sugar levels, particularly in cases where lifestyle adjustments alone are insufficient. Walker et al. (2015) highlighted that lifestyle changes—including weight management, dietary choices, and increased physical activity—contribute significantly to positive shifts in glycemic characteristics.
Regular consultations with healthcare professionals ensure tailored support and allow for necessary adjustments to treatment plans based on individual progress. By integrating dietary adjustments, physical activity, and, when appropriate, pharmacological interventions, patients can establish a comprehensive management plan that promotes long-term health and wellness. This holistic strategy is essential, especially considering the ethnic differences in responses to lifestyle interventions noted in recent studies, which underscore the need for personalized approaches to diabetes management.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels is essential in the fight against diabetes. This article has explored the critical role of HbA1c in diagnosing and monitoring diabetes, emphasizing that regular testing is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. The implications of various HbA1c levels highlight the importance of proactive health management, particularly for those at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Effective strategies for managing and lowering HbA1c levels include:
- Adopting a balanced diet
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels
- Implementing stress management techniques
These lifestyle modifications, when combined with appropriate medical interventions, can significantly improve blood glucose control and overall health outcomes. The case studies presented illustrate how personalized care can lead to substantial health improvements, reinforcing the importance of tailored approaches in diabetes management.
Ultimately, empowering individuals to take charge of their health through education and community support is crucial in mitigating the risks associated with diabetes. By embracing a holistic approach that includes both lifestyle changes and medical support, individuals can effectively manage their HbA1c levels and improve their long-term health prospects. The journey towards better health begins with informed choices and proactive engagement in one’s care plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Hemoglobin A1c and why is it important?
Hemoglobin A1c is a blood test that evaluates average blood glucose concentrations over a two to three-month period. It plays a significant role in managing Type 2 sugar intolerance and hypothyroidism by providing insights into long-term blood sugar control.
What does a Hemoglobin A1c level of 5.5% indicate?
A Hemoglobin A1c level of 5.5% signifies that approximately 5.5% of the hemoglobin in the bloodstream has glucose molecules attached. While it is generally considered within the normal range, it can indicate a heightened risk for prediabetes, especially if sustained over time.
How does regular monitoring of Hemoglobin A1c benefit individuals?
Regular monitoring of Hemoglobin A1c helps individuals track their blood sugar levels, assess personal risk factors, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment strategies, allowing for necessary adjustments in patient care plans.
What recent trends have been observed regarding blood sugar conditions?
Recent data indicates a rising awareness of prediabetes, with 93.0% of individuals undergoing cholesterol checks. Additionally, the occurrence of total glucose intolerance has increased to 14.3%, highlighting the need for continuous tracking of blood sugar levels.
What are some strategies for managing blood sugar levels effectively?
Four lesser-known strategies for effective management include optimizing nutrition, incorporating specific physical activities, managing stress effectively, and leveraging community support systems.
Can a Hemoglobin A1c reading of 5.5% lead to a diagnosis of diabetes?
No, a reading of Hemoglobin A1c 5.5% does not correspond to a diagnosis of diabetes. However, it serves as a critical reminder to pay attention to dietary choices, physical activity, and overall lifestyle to prevent the advancement to elevated blood sugar readings.
What role does lifestyle intervention play in managing diabetes?
Lifestyle interventions are essential for identifying individuals at risk and can help address the root causes of diabetes. Successful programs, like those at the Integrative Wellness Center, empower patients to take control of their health and alleviate anxiety surrounding potential complications.
What is the significance of personalized care in managing blood sugar conditions?
Personalized care is crucial as it can lead to significant health improvements, such as weight loss and reductions in A1c levels, as demonstrated by patients who have engaged in holistic health programs.