Introduction
The A1C test stands as a cornerstone in diabetes management, offering crucial insights into an individual’s average blood glucose levels over the preceding months. By measuring the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, this test not only aids in diagnosing diabetes but also serves as a vital tool for monitoring ongoing treatment effectiveness. With the rising prevalence of diabetes and its associated complications, understanding A1C results has never been more critical.
This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, how to interpret its results, the factors influencing A1C levels, and practical strategies for improvement. By equipping patients with knowledge and actionable steps, it aims to foster informed decision-making and ultimately enhance health outcomes in the face of this pervasive condition.
Understanding the A1C Test: Significance and Functionality
The A1C test, often called the glycated hemoglobin test, is an essential tool in managing blood sugar, offering an assessment of average blood glucose amounts over the past two to three months as shown in the A1C chart glucose. By assessing the percentage of hemoglobin in the bloodstream that has glucose attached, the A1C chart glucose test provides essential insights into the effectiveness of blood sugar management. Typical A1C readings are usually below 5.7%, whereas figures from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes, and measurements of 6.5% or above confirm a diagnosis of diabetes.
Comprehending the implications of A1C test results and the A1C chart glucose is crucial for patients to make informed lifestyle and medical choices, especially as the importance of A1C testing is emphasized in 2024 for predicting potential complications related to the condition. For example, data from 2020 revealed that approximately:
- 160,000 lower-extremity amputations
- 232,000 hyperglycemic crises
- 51,000 hypoglycemic events
occurred among adults with high blood sugar, showcasing the severe consequences of unmanaged blood glucose levels. Moreover, the prevalence of diagnosed conditions varies across racial and ethnic groups:
- 17.8 million White non-Hispanic adults have been diagnosed, representing a prevalence of 8.5%
- 4.0 million Black non-Hispanic
- 1.8 million Asian non-Hispanic
- 5.0 million Hispanic adults
This disparity emphasizes the need for community wellness programs that focus on education, nutrition, and support in areas like San Marcos. For instance, one patient at the Integrative Wellness Center successfully reversed their type 2 condition through personalized care and community support, illustrating the transformative potential of such programs. The Monitoring Nephropathy rate for Commercial HMO was recorded at 36.0% in 1999, highlighting the importance of ongoing monitoring of diabetes-related conditions.
As Frederick L. Brancati, MD, MHS, aptly stated, ‘Its performance would be best when judged against stronger, most clinically relevant gold standards.’ This underscores the necessity of regular A1C chart glucose testing, which is essential not only for effective management of the condition but also for safeguarding against serious health complications. To learn more about transformative health solutions and success stories, we encourage you to explore our blog and register for further information.
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do the Numbers Mean?
A1C results, which can be viewed on an a1c chart glucose, reflect the average blood sugar readings over approximately three months. For instance, according to the A1C chart glucose, an A1C of 6.0% correlates to an average blood glucose concentration of around 126 mg/dL. People with high blood sugar should strive for an a1c chart glucose measurement below 7.0%, which is usually associated with better health results.
Elevated levels on the a1c chart glucose indicate poor glucose control, increasing the risk of complications linked to the condition, which can result in substantial anxiety for patients. Our holistic approach not only addresses these health metrics but also aims to reduce the anxiety surrounding potential complications by focusing on the underlying causes of the condition. Recent findings indicate that a concerning 19.0% of U.S. adults diagnosed with prediabetes have received this diagnosis from a healthcare professional.
By understanding these results, patients can make informed choices about their diet, exercise, and medication, ultimately leading to improved control of their condition. Notably, the SURPASS-2 study highlights the effectiveness of different treatment options, showing that 36% of patients using Mounjaro at a 15 mg dosage achieved a weight reduction of at least 15% after 40 weeks, further illustrating the link between lifestyle changes and improved a1c chart glucose outcomes. This clinical evidence supports a holistic approach to controlling blood sugar levels, emphasizing the importance of addressing root causes, such as insulin resistance, and utilizing tools like the a1c chart glucose, rather than solely relying on traditional treatments.
Our regimen involves re-examining the source of your condition through personalized assessments and tailored strategies, which can help prevent or prolong the onset of prediabetes or Type 2 conditions. Additionally, it is important to note that the mean daily insulin glargine dose at week 52 was 44 U, providing insight into treatment oversight. For more information about Lilly’s privacy practices, please view the Privacy Statement.
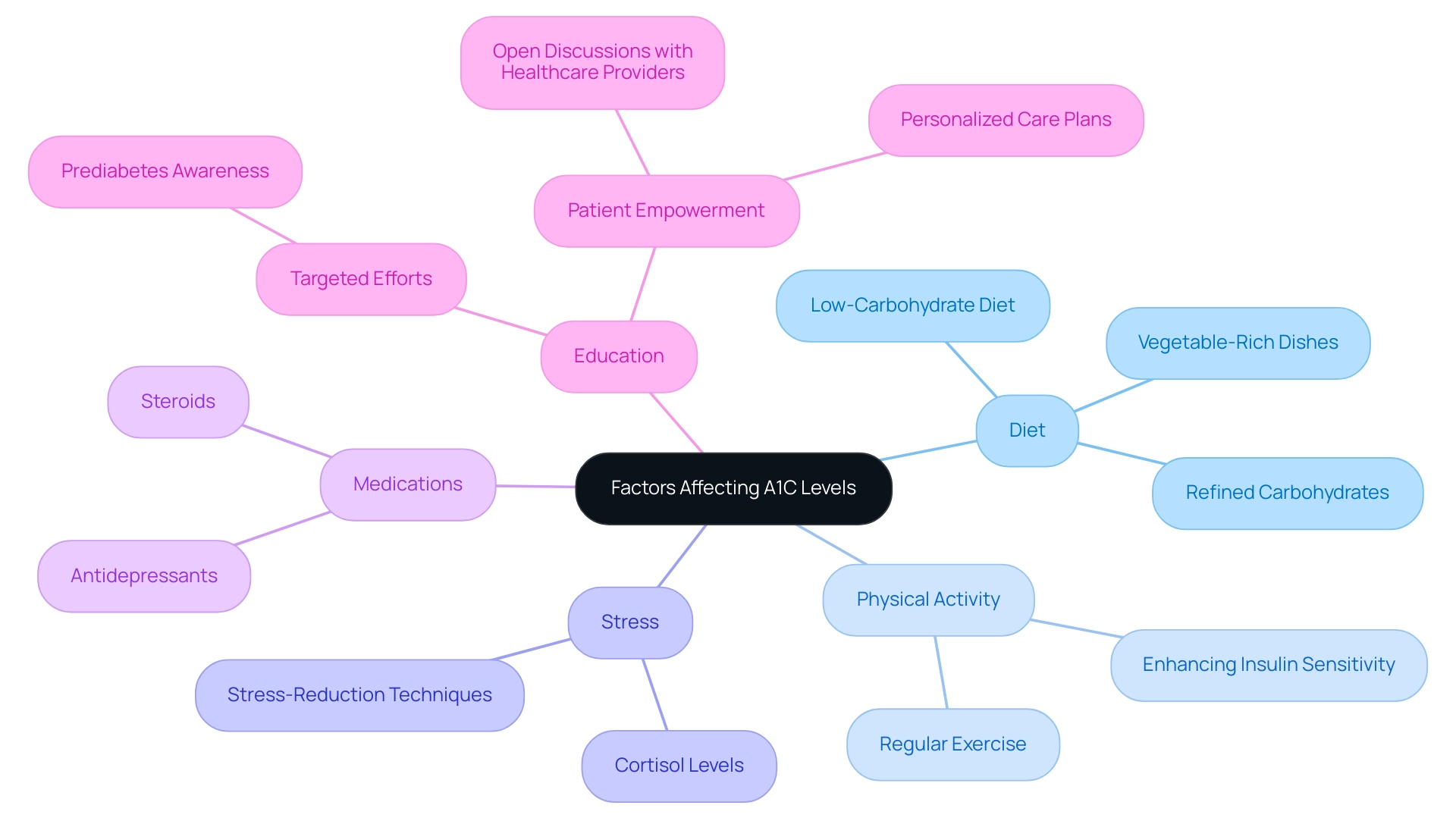
Factors Affecting A1C Levels: What to Consider
Numerous factors significantly affect the a1c chart glucose values, which are crucial for managing diabetes. A primary factor is diet; a diet rich in refined carbohydrates has been associated with elevated blood glucose amounts, while a low-carbohydrate diet intervention can result in significant reductions in hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) values among those with untreated amounts ranging from 6.0% to 6.9%. However, it is important to note that these reductions may be interdependent with weight loss.
Furthermore, regular physical activity plays a vital role in lowering glucose concentrations, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and ultimately contributing to improved A1C results. Stress is another critical element; elevated levels of stress hormones, particularly cortisol, can result in increased blood glucose. Moreover, certain medications, such as steroids and specific antidepressants, have been shown to negatively affect A1C results.
According to recent statistics, prediabetes awareness among Hispanic adults from 2017 to 2020 was only 20.9%, highlighting the need for targeted educational efforts in this demographic to enhance health oversight. Furthermore, a case study from 2021 reported approximately 1.2 million new cases of the condition diagnosed among U.S. adults, emphasizing the importance of understanding A1C management across different age and racial/ethnic groups. Therefore, it is essential for patients to consider these factors when assessing their a1c chart glucose levels.
Engaging in open discussions with healthcare providers about diet, lifestyle choices, and any medications can lead to a well-rounded approach to managing the condition effectively. By adopting a holistic viewpoint that tackles these underlying issues, including lesser-known strategies such as:
- Incorporating more vegetable-rich dishes
- Practicing stress-reduction techniques
- Utilizing personalized care plans
- Enhancing education around [[[health control
patients](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9502664)](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9502664)](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9502664) can empower themselves toward transformative health solutions. Dr. Lydia A. Bazzano’s insights highlight the importance of understanding these elements in optimizing care for individuals with diabetes.
How to Improve A1C Levels: Practical Strategies
Improving A1C levels requires a holistic approach that includes dietary modifications, regular physical activity, and effective medication management, as reflected in the A1C chart glucose, embodying the integrative philosophy at the Integrative Wellness Center. This holistic regimen not only addresses the physical aspects of the condition but also aims to alleviate the anxiety that accompanies concerns about potential complications of the disease. A balanced diet should emphasize whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while limiting the intake of sugars and processed foods.
Studies have shown that individuals who adopt low-carbohydrate diets can achieve weight loss outcomes comparable to those following other dietary plans, contributing to better A1C control. Specifically, participants in the SDPI-HH study had an average fiber intake of 17.2 ± 8.1 g/day on a low-fat diet, underscoring the importance of dietary choices in managing diabetes. Regular physical activity—such as walking, cycling, or swimming—plays a crucial role in enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing blood glucose amounts.
For instance, participants in the SDPI-HH study initially had an average HbA1c value of 7.67 ± 2.01, reflecting a common starting point for many patients. Adhering to prescribed medications and consistently monitoring blood glucose levels using the A1C chart glucose are also essential for maintaining optimal A1C levels. Furthermore, collaborating with a healthcare team, including a health coach specializing in blood sugar management, can provide personalized strategies tailored to individual needs.
Considering the recent focus on cardiovascular disease (CVD) treatment, it is essential to recognize that CVD is a common cause of mortality among individuals with high blood sugar. As stated by the ADA, ‘RCTs do not support recommending omega-3 supplements for primary or secondary prevention of CVD despite the strength of evidence from observational and preclinical studies.’ This emphasizes the essential need for careful consideration of dietary recommendations and their implications for CVD control.
Therefore, managing CVD risk factors through diet and exercise should mirror recommendations for the general population. By reassessing the origin of your condition and applying these thorough control strategies, individuals can strive to reduce their A1C chart glucose levels while improving their overall health and wellbeing.
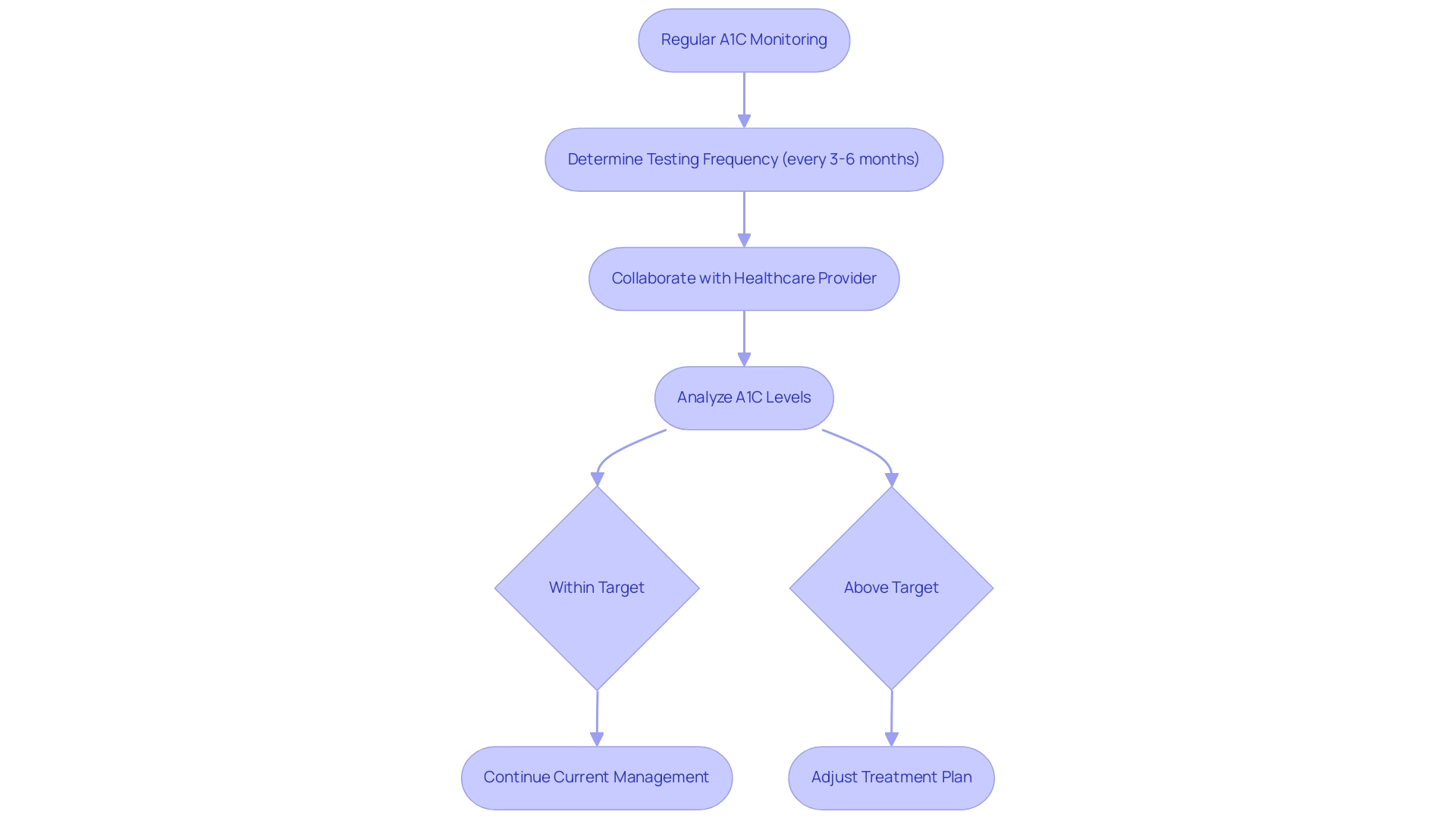
The Role of Regular Monitoring: Keeping Track of Your A1C
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential for effective management, serving as a key indicator of long-term glucose control. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize that education and a holistic approach can empower patients to eliminate anxiety related to complications of blood sugar regulation. Current guidelines recommend individuals with diabetes to undergo A1C testing, which is reflected in the a1c chart glucose, every three to six months, although the frequency may vary based on personal health circumstances and treatment goals.
Consistent tracking of the a1c chart glucose results allows for the identification of trends and aids in making informed adjustments to treatment plans. Diabetes specialists advocate for patients to collaborate closely with their healthcare providers to determine a tailored monitoring schedule that aligns with their specific needs, thereby enhancing patient outcomes. Notably, a 9-year post-DCCT follow-up of the EDIC cohort revealed that participants previously randomized to the intensive treatment arm exhibited a significant 57% reduction in the risk of nonfatal myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death, underscoring the critical role of A1C monitoring.
Understanding the complex relationship between postprandial glucose levels and cardiovascular risk is also vital, as highlighted in case studies comparing postprandial and preprandial glucose targets. While the A1C chart glucose remains the primary predictor of complications, monitoring postprandial glucose can benefit patients whose pre-meal glucose is within target but whose A1C chart glucose is above target. Additionally, incorporating stress management techniques, such as mindfulness practices or regular physical activity, can further support emotional well-being and enhance overall health.
As always, share any concerns or factors that pertain to you with your doctor to ensure a comprehensive approach to your care. For more actionable strategies, consider exploring our four lesser-known power-plays designed to boost your health and empower your journey towards reversing diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test and its implications is crucial for effective diabetes management. This test provides valuable insights into average blood glucose levels over a period of two to three months, allowing patients to assess their diabetes control. Recognizing the significance of A1C results—where levels below 5.7% are considered normal, and values of 6.5% or higher indicate diabetes—empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle and treatment decisions. The disparities in diabetes prevalence among different racial and ethnic groups highlight the urgent need for targeted education and community support to improve health outcomes.
Several factors influence A1C levels, including:
- Diet
- Physical activity
- Stress
- Medication
A balanced diet focused on whole foods and regular exercise can significantly enhance insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose levels. Additionally, understanding the role of stress and potential medication effects is essential for comprehensive diabetes management. Engaging with healthcare providers about these factors can lead to personalized strategies that effectively address individual needs.
Improving A1C levels requires a multifaceted approach, integrating:
- Dietary changes
- Physical activity
- Medication management
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is a cornerstone of this process, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment plans. Patients are encouraged to collaborate with their healthcare teams to establish a monitoring schedule that suits their unique circumstances. By prioritizing education and adopting proactive health strategies, individuals can navigate their diabetes journey more effectively, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and a reduced risk of complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, measures average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. It is crucial for managing blood sugar and assessing the effectiveness of blood sugar management.
What do the A1C test results indicate?
A typical A1C reading is below 5.7%. Readings of 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes, while levels of 6.5% or above confirm a diagnosis of diabetes.
Why is understanding A1C test results important for patients?
Understanding A1C test results is vital for patients to make informed lifestyle and medical choices, especially as these results can predict potential complications related to diabetes.
What are some complications associated with unmanaged blood glucose levels?
Complications can include lower-extremity amputations, hyperglycemic crises, and hypoglycemic events, with significant occurrences reported among adults with high blood sugar.
How do diabetes prevalence rates vary among different racial and ethnic groups?
The prevalence of diagnosed diabetes varies, with 17.8 million White non-Hispanic adults (8.5%), 4.0 million Black non-Hispanic, 1.8 million Asian non-Hispanic, and 5.0 million Hispanic adults diagnosed.
What role do community wellness programs play in managing diabetes?
Community wellness programs focusing on education, nutrition, and support have the potential to transform lives, as evidenced by patients who have successfully reversed their type 2 diabetes through personalized care.
What is the significance of regular A1C testing?
Regular A1C testing is essential for effective diabetes management and for preventing serious health complications.
How does the A1C chart glucose correlate with average blood glucose levels?
An A1C of 6.0% corresponds to an average blood glucose concentration of around 126 mg/dL, with a target of below 7.0% typically linked to better health outcomes.
What are the implications of elevated A1C levels?
Elevated A1C levels indicate poor glucose control, which increases the risk of complications and can cause significant anxiety for patients.
How can patients improve their A1C results?
Patients can improve their A1C results by making informed choices about diet, exercise, and medication, as well as by addressing underlying causes such as insulin resistance.
What recent findings support a holistic approach to managing blood sugar levels?
The SURPASS-2 study showed that 36% of patients using Mounjaro at a 15 mg dosage achieved a weight reduction of at least 15% after 40 weeks, highlighting the connection between lifestyle changes and improved A1C outcomes.