Overview
The article focuses on how to effectively use A1C calculator charts for diabetes management, emphasizing their importance in tracking blood glucose levels and making informed health decisions. It supports this by detailing the correlation between A1C levels and average blood glucose, illustrating how understanding these metrics can empower individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles and reduce diabetes-related complications.
Introduction
The A1C test stands as a cornerstone in the management of diabetes, providing critical insights into an individual’s blood glucose levels over a two to three-month period. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, understanding the significance of this test becomes increasingly vital for both patients and healthcare providers.
With a recommended target of 7% or lower for most adults, the A1C measurement not only helps gauge the effectiveness of treatment plans but also plays a crucial role in mitigating the risk of complications associated with the disease.
This article delves into the intricacies of the A1C test, offering practical strategies for:
- Utilizing A1C results to enhance diabetes management
- Interpreting results accurately
- Exploring effective methods for lowering A1C levels
Through a comprehensive examination of these elements, individuals can empower themselves with the knowledge necessary to navigate their health journey confidently.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key Component in Diabetes Management
The A1C test, or glycated hemoglobin test, quantitatively measures the percentage of hemoglobin that has glucose attached to it over the preceding two to three months. This vital evaluation is especially significant for individuals managing their condition, as it provides a dependable indication of average blood glucose readings. Notably, in 2000, HbA1c screening rates were reported at 78.4% for Commercial HMO, highlighting the prevalence of A1C testing among patients with high blood sugar.
Healthcare providers utilize A1C results to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment strategies, particularly within a holistic framework that addresses root causes and empowers patient health at the Integrative Wellness Center. For most adults with this condition, an A1C level of 7% or lower is generally recommended, as elevated levels are associated with a heightened risk of complications, such as cardiovascular disease and neuropathy. Recent data indicates that the financial implications of managing diabetes-related conditions have increased significantly, with excess medical costs per person rising from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022.
This highlights the importance of A1C testing in possibly reducing these costs through extensive insights and treatment options focused on reversing type 2. Furthermore, a case study named ‘Yoshinaga 1996’ involving 819 Japanese government officials with A1C ≥ 6.2% demonstrated a clear connection between A1C values and the occurrence of diabetes-related issues, reinforcing the significance of monitoring A1C measurements. Comprehending your A1C results through the a1c calculator chart not only assists in tracking health conditions but also enables you to make knowledgeable decisions about your well-being and treatment options.
This is particularly significant as numerous patients face anxiety linked to the possible complications of blood sugar issues; therefore, monitoring A1C readings can help reduce some of these worries by offering clear metrics to inform their health choices. Aligning with transformative patient success stories emerging from personalized care at the Integrative Wellness Center, a significant percentage of adults with diabetes are striving to achieve these A1C targets, which can be monitored using an a1c calculator chart, reflecting the ongoing importance of this test in effective diabetes management.
Utilizing A1C Calculators and Charts for Effective Diabetes Control
To effectively utilize a1c calculator chart, begin by entering your most recent A1C results alongside your blood glucose readings. Numerous online calculators are available that can convert your A1C percentage into an estimated average blood glucose value, providing a clearer picture of your overall glycemic control. Furthermore, the a1c calculator chart can visually depict the correlation between A1C values and blood glucose levels, facilitating a better understanding of your progress over time.
Frequently refreshing these tools is crucial, as it enables you to establish achievable objectives and closely track advancements in your health care. Considering that the median county-level prevalence of diagnosed conditions increased from 6.3% in 2004 to 8.3% in 2021, the significance of accessible resources for care cannot be overstated. Vivian Fonseca emphasizes the significance of translating the hemoglobin A1C assay to enhance patient understanding and engagement in their care.
Notably, non-Hispanic Black children and adolescents have the highest incidence of type 2 conditions, highlighting the urgency for effective monitoring tools. Recent studies suggest that while hyperglycemia is a risk factor for complications, personalized approaches to A1C management are crucial for optimal outcomes. By utilizing these a1c calculator charts, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving better control of their condition.
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do the Numbers Mean?
A1C results are presented as a percentage, providing valuable insights into long-term blood sugar control. According to the latest guidelines from the American Diabetes Association, which have been updated for 2024, an A1C level below 5.7% is classified as normal. Levels ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of the condition.
For individuals controlling their blood sugar, the target A1C is typically set at 7% or lower, though this may vary based on individual health conditions and goals. Significantly, higher BMI has been linked to a greater likelihood of increased A1C values, with a prevalence ratio of 1.07 for every 5-unit rise in BMI. Moreover, comprehending the variability in diagnosed diabetes prevalence—ranging from 4.4% to 17.9% across various counties—emphasizes the necessity for localized public health strategies to effectively tackle diabetes care and prevention.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we prioritize transformative patient experiences, empowering individuals to take charge of their health. For example, one of our patients, Jane, shared how her A1C readings dropped significantly after engaging with our personalized care approach, leading to improved overall health. Engaging in discussions with your healthcare provider regarding A1C results is essential, as they can offer critical interpretations tailored to your overall health status.
This collaborative approach allows for necessary adjustments to treatment plans, ensuring proactive oversight of the condition. Comprehending these A1C measurements using an A1C calculator chart not only assists in personal health management but also enables patients to make informed choices regarding their care. Schedule your FREE Diabetes Evaluation with Dr. Jason Shumard today to explore how our patient-centered care can support your journey towards better health.
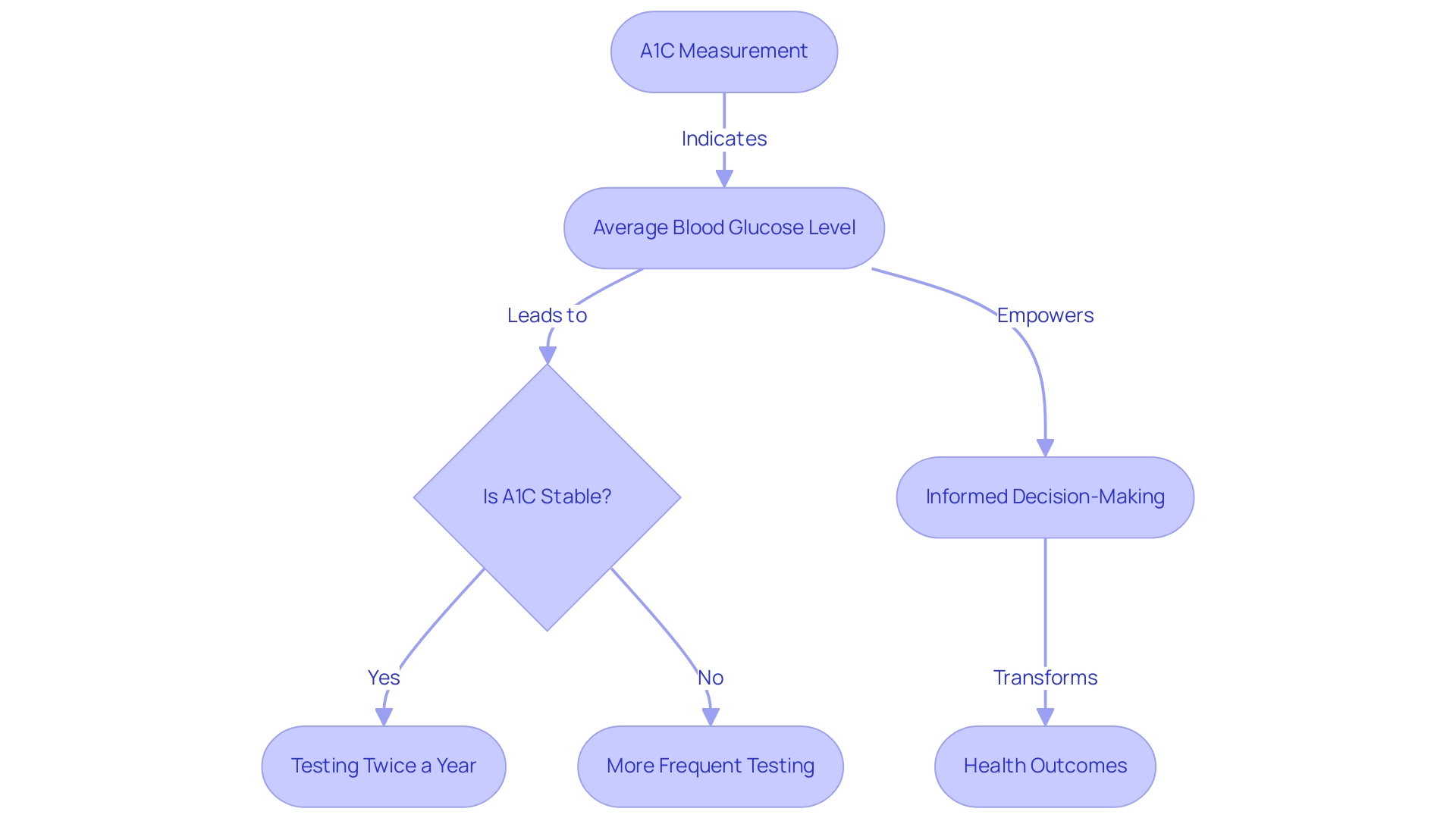
The Connection Between A1C Levels and Average Blood Glucose
Studies consistently show a strong relationship between A1C measurements and average blood glucose readings over time, which is essential for patients aiming to reduce anxiety regarding complications related to blood sugar issues. For instance, an A1C of 6% corresponds to an average blood glucose level of approximately 126 mg/dL. This relationship highlights the necessity of regular blood glucose monitoring, as daily fluctuations can significantly influence overall A1C results.
According to Vivian Fonseca, a respected authority in metabolic health, translating the hemoglobin A1C assay emphasizes the value of A1C as a superior method for assessing long-term glycemic control. It’s important to note that the American Diabetes Association (ADA) updated its preprandial glycemic target in 2015, raising it from 70–130 mg/dL to 80–130 mg/dL, reflecting a shift in the standards for blood sugar control. Understanding the connection between A1C and blood glucose empowers individuals to use an A1C calculator chart to observe the tangible effects of their lifestyle choices on their health metrics.
This holistic approach is essential for transforming health outcomes, as supported by the A1C-Derived Average Glucose Study Group Trial, which established a correlation coefficient of 0.840 through analysis of A1C measurements across diverse patient demographics. This strong correlation suggests that the A1C calculator chart can serve as a dependable predictor of average glucose concentrations, which is vital for informed decision-making in managing blood sugar. Additionally, patients with stable glycemia may require A1C testing only twice a year, while those with unstable conditions may need more frequent testing, emphasizing the practical implications of A1C monitoring for personalized patient care at the Integrative Wellness Center.
To further enhance your health and reverse the condition, consider exploring the four lesser-known power-plays detailed in our blog. Click to register and empower your journey towards better health.
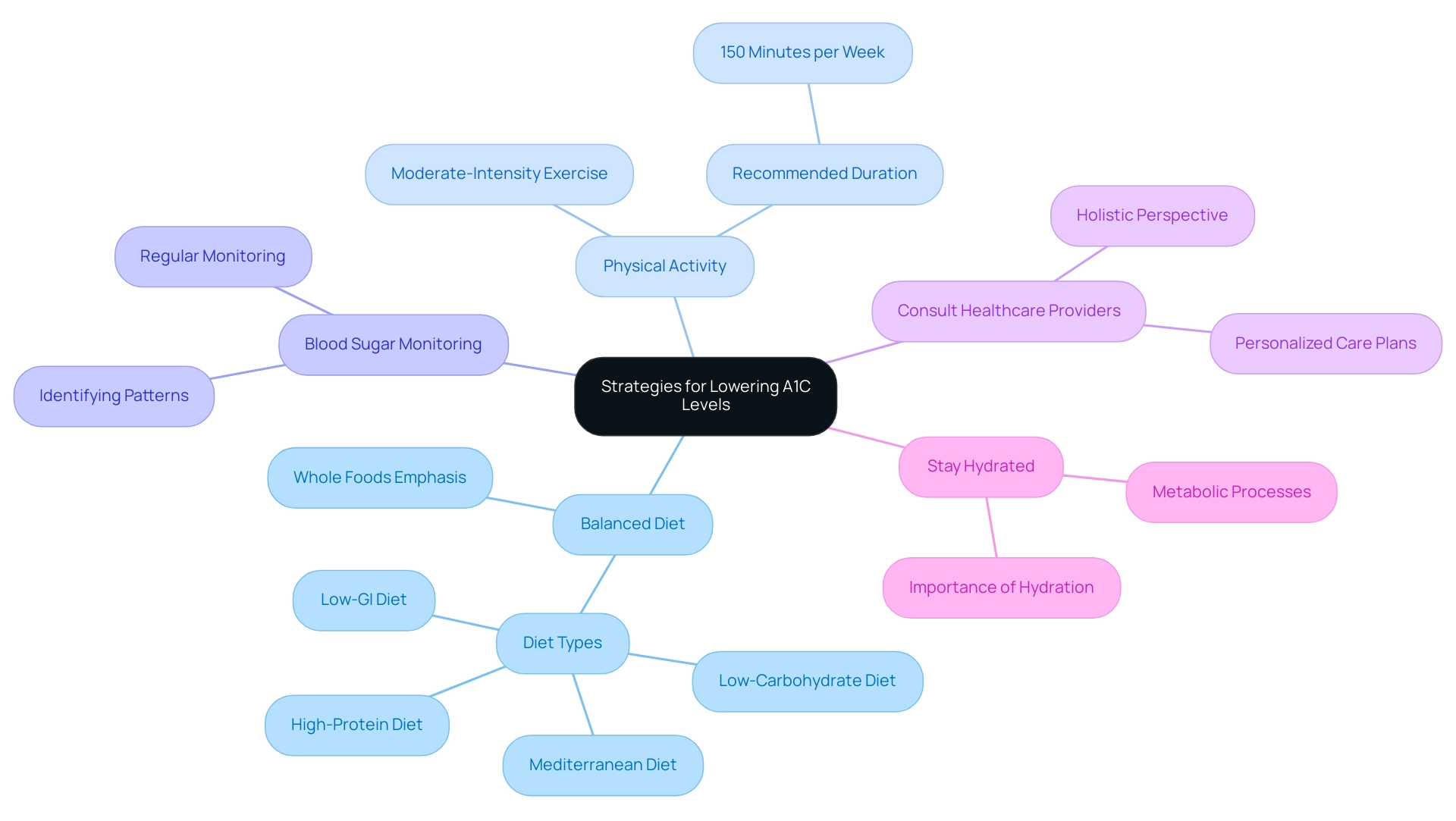
Strategies for Lowering A1C Levels and Enhancing Diabetes Management
To effectively lower A1C values and alleviate the anxiety surrounding potential complications of diabetes, individuals should consider implementing the following holistic strategies that address the root causes of diabetes, utilizing an A1C calculator chart:
-
Adopt a Balanced Diet:
Emphasizing whole foods, such as vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, is crucial. Limiting processed foods and sugars can lead to significant improvements in glycemic control, as evidenced by a systematic review that highlighted the benefits of low-carbohydrate, low-GI, Mediterranean, and high-protein diets. In particular, the Mediterranean diet demonstrated the most substantial positive impact on A1C values.
A systematic assessment titled “Effect of Various Diets on Glycemic Control” found that these diets showed significant improvements in glycemic control, with the Mediterranean diet having the largest effect.
-
Increase Physical Activity:
Participating in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week, such as brisk walking or cycling, can improve insulin sensitivity and aid in better blood sugar control. Studies show a strong link between physical activity and reduced A1C values, reinforcing the idea that exercise is an essential element of effective control of blood sugar.
-
Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly:
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels enables individuals to identify patterns that may necessitate adjustments in diet or medication. This proactive strategy can result in more effective control of blood sugar levels and enhanced A1C outcomes.
-
Consult with Healthcare Providers:
Regular consultations with healthcare professionals are essential to customize diabetes care plans to individual needs, emphasizing a holistic perspective. Personalized strategies based on the latest research can significantly impact A1C reduction efforts.
-
Stay Hydrated:
Maintaining adequate hydration is vital for managing blood sugar and overall health. Adequate hydration can assist in the effective operation of metabolic processes, further aiding in A1C level control.
Additionally, re-examining the source of your condition can provide important insights that empower you to take control of your health. The economic consequences of treating diabetes are considerable, with additional healthcare expenses per individual rising from $10,179 to $12,022 between 2012 and 2022. Additionally, the occurrence of diagnosed conditions in U.S. counties fluctuates, spanning from 4.4% to 17.9%, emphasizing the necessity for effective care.
By consistently applying these holistic strategies, individuals can work towards effectively lowering their A1C levels and enhancing their overall diabetes management while utilizing an A1C calculator chart to navigate common myths surrounding the disease.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is essential for effective diabetes management, as it provides crucial insights into long-term blood glucose control. This article has highlighted the significance of maintaining an A1C level of 7% or lower to reduce the risk of complications and improve overall health outcomes. By leveraging resources such as A1C calculators and charts, individuals can gain a clearer understanding of their glucose levels and track their progress, empowering them to take proactive steps in their diabetes care.
Interpreting A1C results accurately is vital, as it enables patients to engage in informed discussions with healthcare providers about their treatment plans. The strong correlation between A1C levels and average blood glucose reinforces the importance of regular monitoring, allowing individuals to observe how their lifestyle choices impact their health metrics. With the implementation of holistic strategies—such as adopting a balanced diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals—individuals can effectively lower their A1C levels and enhance their diabetes management.
Ultimately, the A1C test serves as a powerful tool in navigating the complexities of diabetes. By understanding the intricacies of this assessment and applying practical strategies, individuals can confidently manage their condition and work towards achieving optimal health outcomes. Prioritizing A1C monitoring and education is not just a matter of health; it is a vital step towards reducing the financial burdens associated with diabetes management and improving quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test?
The A1C test, or glycated hemoglobin test, measures the percentage of hemoglobin that has glucose attached to it over the preceding two to three months, providing an indication of average blood glucose levels.
Why is the A1C test important for individuals managing diabetes?
The A1C test is important as it offers a reliable indication of average blood glucose readings, helping healthcare providers evaluate the effectiveness of treatment strategies and manage the condition holistically.
What is the recommended A1C level for most adults with diabetes?
For most adults with diabetes, an A1C level of 7% or lower is generally recommended to reduce the risk of complications, such as cardiovascular disease and neuropathy.
How have the financial implications of managing diabetes changed over the years?
The excess medical costs per person for managing diabetes-related conditions have increased from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022, highlighting the importance of effective management strategies like A1C testing.
What does the case study ‘Yoshinaga 1996’ demonstrate?
The case study ‘Yoshinaga 1996’ involving 819 Japanese government officials with A1C ≥ 6.2% demonstrated a clear connection between A1C values and the occurrence of diabetes-related issues, reinforcing the significance of monitoring A1C measurements.
How can individuals track their A1C results?
Individuals can track their A1C results by using an A1C calculator chart, which helps in understanding health conditions and making informed decisions about treatment options.
What is the process for using an A1C calculator chart?
To use an A1C calculator chart, enter your most recent A1C results alongside your blood glucose readings. Online calculators can convert A1C percentages into estimated average blood glucose values.
Why is it important to frequently refresh A1C tracking tools?
Frequently refreshing A1C tracking tools is crucial as it helps establish achievable objectives and closely monitor advancements in health care.
What demographic has the highest incidence of type 2 diabetes?
Non-Hispanic Black children and adolescents have the highest incidence of type 2 diabetes, emphasizing the need for effective monitoring tools.
How can personalized approaches to A1C management benefit individuals?
Personalized approaches to A1C management are crucial for optimal outcomes, allowing individuals to take proactive steps towards better control of their condition.