Overview
The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to use an A1C to blood sugar calculator, emphasizing its importance in managing diabetes by converting A1C test results into estimated average glucose (eAG) readings. This process is essential for patients to monitor their long-term blood sugar control and make informed adjustments to their treatment plans, as evidenced by case studies and statistics demonstrating improved health outcomes through regular A1C monitoring.
Introduction
The A1C test serves as a cornerstone in the management of diabetes, offering critical insights into a patient’s average blood sugar levels over the preceding months. For those navigating the complexities of diabetes, understanding A1C results is not merely about numbers; it is about taking proactive steps towards improved health outcomes.
With the alarming rise in diabetes prevalence, which has surged from 5.9% in the late 1990s to over 10% in recent years, the importance of regular A1C monitoring has never been clearer.
This article delves into the significance of A1C testing, how to interpret results, and practical strategies for effective blood sugar management, equipping readers with the knowledge necessary to engage actively in their diabetes care.
Understanding A1C: The Foundation of Blood Sugar Management
The A1C to blood sugar calculator is an essential instrument for controlling blood sugar, gauging average glucose amounts over the past two to three months and displaying the outcomes as a percentage. For individuals diagnosed with the condition, maintaining an A1C level below 7% is generally advisable, and using an A1C to blood sugar calculator can help ensure adequate blood sugar control. This benchmark is crucial because it correlates directly with the risk of complications associated with blood sugar issues; thus, utilizing an A1C to blood sugar calculator is essential for assessing the effectiveness of a health control plan.
Regular A1C testing serves as an essential A1C to blood sugar calculator, enabling patients to monitor their long-term glucose control and informing necessary adjustments to their treatment strategies. Transformative patient experiences at Dr. Jason Shumard’s center illustrate the potential for reversing type 2 conditions through personalized functional medicine. For instance, one patient shared,
‘I lost 55 lbs.
My A1C started at 9.1 after 8 months; it is now 5.7.’
Another noted,
‘I feel so much better… I lost a lot of weight, have more energy and feel great.
I am not depressed anymore and I don’t need my meds anymore!!!’
The age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed condition has increased significantly from 5.9% in 1999–2000 to 10.1% in August 2023, underscoring the growing concern regarding management of the illness. Furthermore, case studies have shown that the prevalence of total health condition is 6.8% in underweight or normal weight adults, increasing to 24.2% in those with obesity, highlighting the critical correlation between obesity and the occurrence of the condition.
According to the National Center for Health Statistics, the prevalence of diagnosed conditions also varies significantly with educational attainment, decreasing from 14.6% in adults with a high school degree or less to 7.3% in those with a bachelor’s degree or more. This highlights the significance of knowledgeable governance practices that can result in improved health outcomes. By consistently monitoring A1C readings with an A1C to blood sugar calculator and participating in comprehensive treatment choices, patients can take proactive measures in their care, ultimately aiming to prevent complications and sustain optimal health.
Call 858-564-7081 to discover how Dr. Shumard can help you restore your health and get your life back!
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the A1C to Blood Sugar Calculator
-
Gather Your A1C Result: Secure your most recent A1C test result from your healthcare provider. This value is usually shown as a percentage, with levels above 6.4% regarded as possibly detrimental, emphasizing the significance of consistent tracking in your health journey. Access a reputable A1C to blood sugar calculator by locating it through trusted healthcare websites. These tools are designed to provide accurate conversions and can be an essential resource in managing diabetes, allowing for better understanding and personalization of your treatment plan.
-
Input Your A1C Value: Enter your A1C percentage into the specified field of the calculator. Ensure that the value is precise, as this directly affects the conversion outcome, promoting effective strategies.
- Calculate: Click the ‘Calculate’ button to convert your A1C result into estimated average glucose (eAG) readings, which are usually displayed in mg/dL. This conversion is essential for comprehending your average blood sugar levels over the preceding months and can assist in adjustments to your plan.
- Review the Results: Upon calculation, the tool will present your eAG. This metric is crucial in assessing your blood sugar regulation and can guide your health strategies. As highlighted by specialists, utilizing an A1C to blood sugar calculator to convert A1C results into eAG is essential for effective control of blood sugar. Discuss any significant findings with your healthcare provider, as they can offer tailored advice and adjustments to your care plan based on your results. Remember that A1C targets can vary based on individual circumstances, so it’s important to engage in conversations about personalized A1C goals with your healthcare provider.
-
Utilize Conversion Formulas: For a quick reference, you can use the formula:
eAG (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) – 46.7. This formula helps you understand how your A1C values relate to daily glucose monitoring practices, which is crucial for effective management.
- Understand the Context: With the rising prevalence of this condition, which has increased from 5.9% in 1999–2000 to 10.1% in August 2021–August 2023, understanding A1C and eAG conversion is more critical than ever. This knowledge empowers you to take charge of your health and engage in informed discussions with your healthcare providers about your treatment strategies.
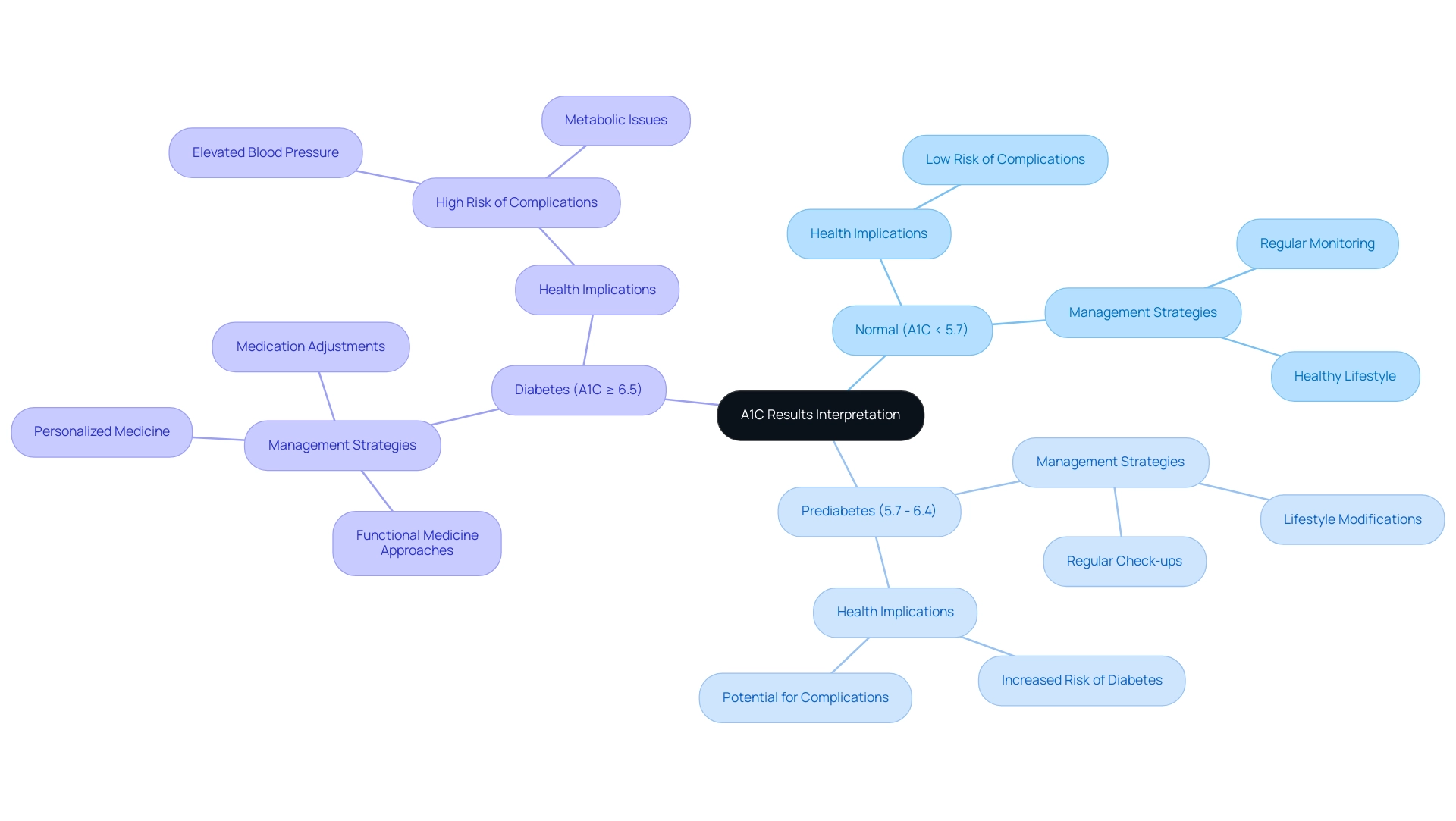
Interpreting Your A1C Results: What They Mean for Your Health
Comprehending your A1C and estimated Average Glucose (eAG) results is essential for effective management of the condition, which can be aided by using an a1c to blood sugar calculator. An A1C measurement below 5.7% is regarded as normal, while readings from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes, and an A1C of 6.5% or above verifies a diagnosis of diabetes. For individuals diagnosed with the condition, maintaining an A1C measurement below 7% is generally advised to reduce complications.
Elevated A1C levels indicate consistently high blood sugar, which can raise the risk of health complications related to elevated blood sugar levels, including high blood pressure; you can monitor these levels using an a1c to blood sugar calculator, and notably, 70.8% of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions have a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or are on medication for high blood pressure. It is crucial to talk about your results with your healthcare provider, who can assist you in identifying the best strategies, including personalized functional medicine methods that tackle the root causes of your condition. These tailored strategies may involve comprehensive assessments and diagnostic tests to identify factors contributing to your condition, as well as targeted supplements and lifestyle modifications to enhance metabolic health and empower your management.
Current guidelines stress the importance of individualized glycemic goals, particularly for older adults, where medication adjustments may be required to avoid adverse effects such as hypoglycemia. Additionally, the prevalence of diagnosed blood sugar conditions varies significantly based on education, with rates decreasing from 14.6% among adults with a high school degree or less to 7.3% in those with a bachelor’s degree or more, according to the National Center for Health Statistics. Participating in these discussions guarantees that you are informed and actively involved in your health management, thereby promoting long-term health enhancements while avoiding inconvenient and expensive treatment plans.
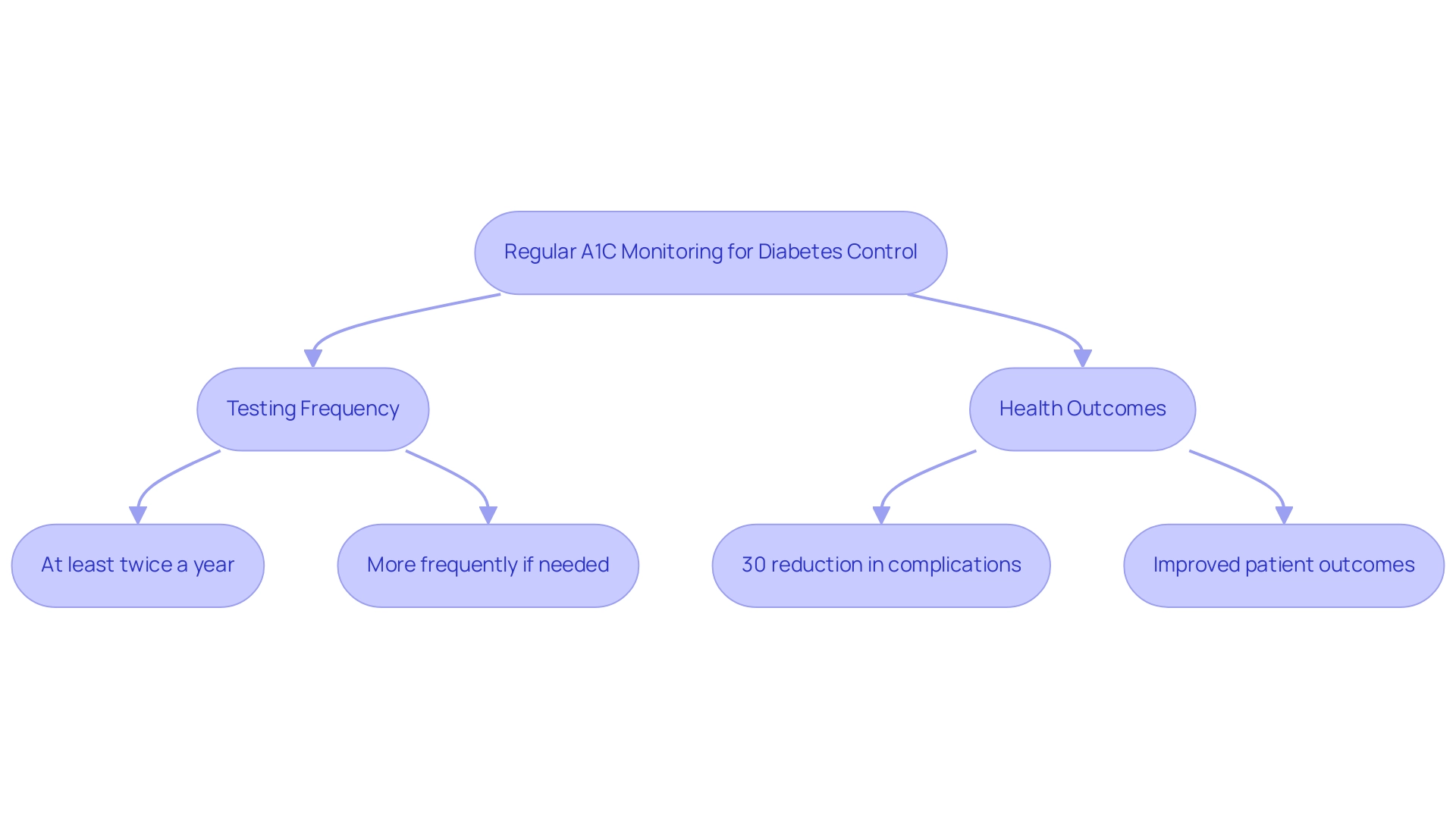
The Importance of Regular A1C Monitoring for Diabetes Control
Regular A1C testing is essential for effective management of the condition, as it empowers patients to take control of their health by using an a1c to blood sugar calculator to gain a comprehensive view of long-term blood sugar control. This proactive monitoring not only facilitates timely adjustments to treatment plans but also helps individuals avoid inconvenient and costly treatment regimens that can lead to exhausting sugar spikes and crashes. According to the 2024 recommendations, individuals with this condition should undergo A1C testing at least twice a year.
However, more frequent testing is advisable when treatment regimens change or if target blood sugar levels are not being met. This approach aligns with Dr. Jason Shumard’s holistic philosophy, emphasizing personalized care to eliminate insulin dependency and prevent complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and renal issues. Recent statistics reveal that individuals who adhere to regular A1C monitoring experience a 30% reduction in diabetes-related complications compared to those who do not.
Furthermore, a case study on advocacy for this condition highlights the importance of consistent A1C monitoring in childcare settings, demonstrating how early interventions can significantly improve health outcomes for young children with this illness. Robert A. Gabbay, a member of the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, emphasizes this necessity, stating:
- “The revised care guidelines underscore the critical role of regular A1C testing in managing the condition effectively.”
Recent findings further support that regular A1C monitoring, which can be tracked using an a1c to blood sugar calculator, correlates with improved patient outcomes, reinforcing the necessity of adhering to these testing frequencies to optimize blood sugar management and enhance overall health.
Common Questions About A1C Testing and Calculators
-
How often should I get my A1C tested?
- For individuals with well-controlled diabetes, it is advisable to have your A1C tested at least twice a year. Regular monitoring is essential to ensure ongoing glycemic control and to identify any potential adjustments needed in management strategies by utilizing an a1c to blood sugar calculator. At our clinic, we focus on state-of-the-art testing that can help pinpoint your exact dietary needs, contributing to a personalized treatment plan. Significantly, among adults with diabetes, 47.4% have an A1C value of 7.0% or higher, emphasizing the challenges many encounter in managing blood glucose effectively. To better understand your unique dietary requirements, consider scheduling a consultation with our functional medicine practitioners.
-
What is a normal A1C value?
- A normal A1C level is considered to be below 5.7%. Scores ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes, while an A1C value of 6.5% or above is indicative of the condition. Comprehending these classifications is essential for effective diabetes control and utilizing an a1c to blood sugar calculator to prevent complications. Our approach emphasizes the importance of personalized care strategies based on your unique experience, including tailored nutrition plans that can address specific dietary needs influenced by your A1C results, which can be evaluated with an a1c to blood sugar calculator.
-
Can I use a home test for A1C?
- Yes, home testing kits for A1C are available and can be a convenient option for monitoring your levels. However, it is crucial to confirm any home test results with a healthcare professional to ensure accuracy and proper handling. Additionally, factors such as higher BMI have been associated with elevated FPG and HbA1c values, which may impact the reliability of home testing. At our clinic, we encourage consultation with a functional medicine practitioner to tailor your nutrition plan effectively based on your individual results and needs.
-
What factors can affect my A1C results?
- Various factors, including conditions like anemia, certain medications, and other health issues, can impact A1C results. It is important to discuss any potential influences on your results with your healthcare provider, especially when using an a1c to blood sugar calculator, to ensure comprehensive diabetes management. Furthermore, studies have indicated differences in A1C measurements among various demographics, including African Americans and non-Hispanic whites, which can provide important context for understanding individual A1C results. This understanding is essential in creating a personalized care plan that addresses your specific needs, including dietary adjustments that can help manage your A1C levels effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is crucial for anyone living with diabetes. The A1C test provides a vital glimpse into long-term blood sugar control, helping patients gauge their health status and adjust their management strategies accordingly. An A1C level below 7% is generally recommended for those with diabetes, while consistent monitoring can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with the disease.
The process of interpreting A1C results and utilizing tools like A1C to blood sugar calculators empowers individuals to take charge of their health. By translating A1C percentages into estimated average glucose levels, patients can better understand their blood sugar fluctuations and make informed decisions about their treatment plans. Engaging in regular discussions with healthcare providers about these results further enhances personalized care, ensuring that management strategies are tailored to individual needs.
Regular A1C monitoring is not just a preventive measure; it is a pathway to improved health outcomes. Statistics show that individuals who adhere to routine testing experience significantly fewer complications. As diabetes prevalence continues to rise, the importance of proactive management cannot be overstated. Armed with the right knowledge and tools, individuals can navigate their diabetes journey more effectively, fostering long-term health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the A1C to blood sugar calculator?
The A1C to blood sugar calculator helps individuals control blood sugar by gauging average glucose levels over the past two to three months and presenting the results as a percentage.
What A1C level is generally advisable for individuals with diabetes?
It is generally advisable for individuals diagnosed with diabetes to maintain an A1C level below 7%.
How does regular A1C testing benefit patients?
Regular A1C testing allows patients to monitor their long-term glucose control and informs necessary adjustments to their treatment strategies.
What are some patient experiences reported at Dr. Jason Shumard’s center?
Patients have reported significant improvements, such as weight loss and reduced A1C levels, with one patient stating their A1C decreased from 9.1 to 5.7 after 8 months.
How has the prevalence of diagnosed diabetes changed over time?
The age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed diabetes has increased from 5.9% in 1999–2000 to 10.1% in August 2023.
What is the correlation between obesity and diabetes prevalence?
The prevalence of diabetes is significantly higher in individuals with obesity, at 24.2%, compared to 6.8% in underweight or normal weight adults.
How does educational attainment affect the prevalence of diagnosed diabetes?
The prevalence of diagnosed diabetes decreases with higher educational attainment, from 14.6% in adults with a high school degree or less to 7.3% in those with a bachelor’s degree or more.
What steps should be taken to use the A1C to blood sugar calculator?
- Gather your most recent A1C result from your healthcare provider. 2. Access a reputable A1C to blood sugar calculator. 3. Input your A1C percentage into the calculator. 4. Click ‘Calculate’ to convert your A1C result into estimated average glucose (eAG) readings. 5. Review the results and discuss any significant findings with your healthcare provider.
What formula can be used for quick reference to convert A1C to eAG?
The formula for converting A1C to eAG is: eAG (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) – 46.7.
Why is understanding A1C and eAG conversion important?
Understanding A1C and eAG conversion is crucial for managing diabetes effectively, especially given the rising prevalence of the condition, empowering individuals to take charge of their health and engage in informed discussions with healthcare providers.