Overview
The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to effectively use an A1C to blood glucose converter, emphasizing its importance in managing blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes. It supports this by detailing the process of selecting a trusted converter, entering A1C values, calculating results, and interpreting these results in the context of comprehensive health management, highlighting the critical role of A1C monitoring in diabetes care.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding A1C levels is not just a medical necessity; it is a lifeline for individuals striving to maintain their health. A1C, a measure of average blood glucose over the past two to three months, serves as a crucial indicator for managing type 2 diabetes. With alarming statistics highlighting diabetes as a leading cause of death, the importance of regular A1C monitoring cannot be overstated.
This article delves into the significance of A1C in blood glucose management, offering insights into:
- The correlation between A1C levels and daily glucose readings
- Practical tools for conversion
- Comprehensive strategies for effective diabetes care
By embracing a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes and community support, individuals can take proactive steps towards better health outcomes and a deeper understanding of their condition.
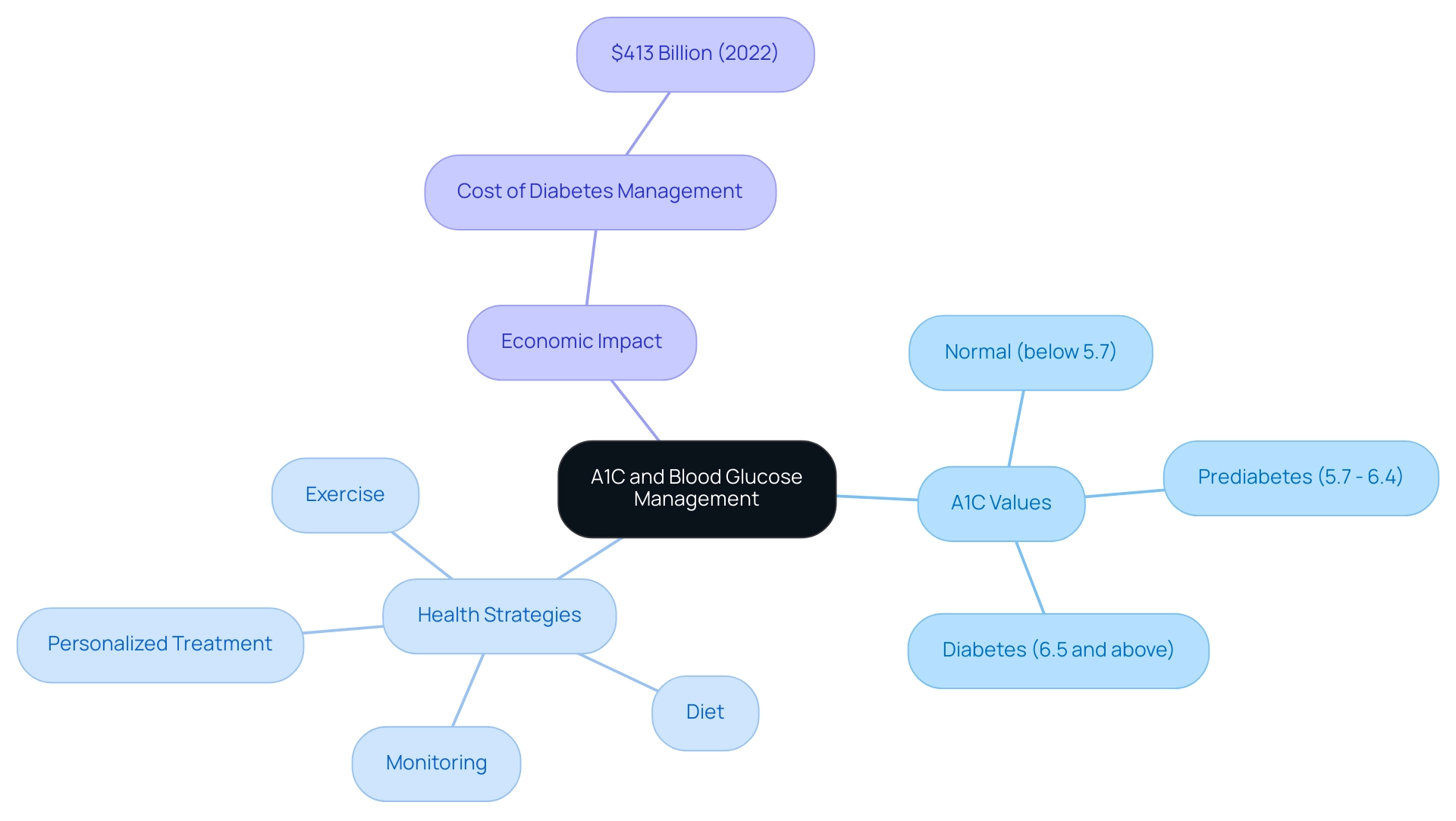
Understanding A1C: The Key to Blood Glucose Management
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is an essential test that acts as an a1c to blood glucose converter, indicating the average glucose concentrations over the past two to three months. For individuals controlling type 2 conditions, understanding the a1c to blood glucose converter is essential, as it serves as a standard for blood sugar regulation over time. Typically, an A1C value between 5.7% and 6.4% suggests prediabetes, whereas a value of 6.5% or above can be confirmed as diabetes using an a1c to blood glucose converter.
Regular monitoring of A1C levels through an a1c to blood glucose converter empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding management strategies, particularly when considering personalized treatment approaches, such as Dr. Jason Shumard’s program, which emphasizes unique solutions tailored to individual needs. Recent data suggests that the Pearson correlation coefficient between A1C Now and A1C Lab values was notably high at 0.83, underscoring the reliability of A1C testing in assessing glucose control. With this condition being the eighth leading cause of death in the United States in 2021, resulting in 103,294 fatalities, it is imperative to prioritize A1C monitoring as part of an effective care plan.
Furthermore, incorporating holistic solutions and essential lifestyle changes—such as embracing a diabetes-friendly diet with fresh, local ingredients, engaging in outdoor activities, and implementing four lesser-known strategies to enhance health—can significantly improve outcomes. Additionally, the total direct and indirect estimated costs of diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar in the United States in 2022 were $413 billion, highlighting the economic impact of management and the critical role A1C monitoring plays in this context. Ann L. Albright, PhD, RD, from the CDC, emphasizes that the selection of specific A1C thresholds will ultimately depend on the interventions likely to be employed and the trade-offs involved between sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value.
By closely monitoring A1C values and using an a1c to blood glucose converter as part of a comprehensive approach to managing blood sugar, individuals can better control their health and reduce the risks associated with the condition.
The Connection Between A1C Levels and Blood Glucose
The connection between A1C values and average glucose is vital in managing diabetes effectively, particularly when utilizing an a1c to blood glucose converter. For instance, an A1C measurement of 6.0% usually relates to an average glucose concentration of roughly 126 mg/dL. This correlation is fundamental for patients, as it helps translate daily glucose readings into meaningful long-term control indicators through an a1c to blood glucose converter.
A rise in A1C levels often signifies that blood glucose levels have been elevated consistently over recent months, which may require using an a1c to blood glucose converter to evaluate the necessity for potential adjustments in treatment strategies. Dr. Rich Bergenstal emphasizes that
Therapy decisions should not be based on just one metric
underscoring the importance of a comprehensive approach to managing the condition. In addition to monitoring A1C, embracing a holistic lifestyle is vital.
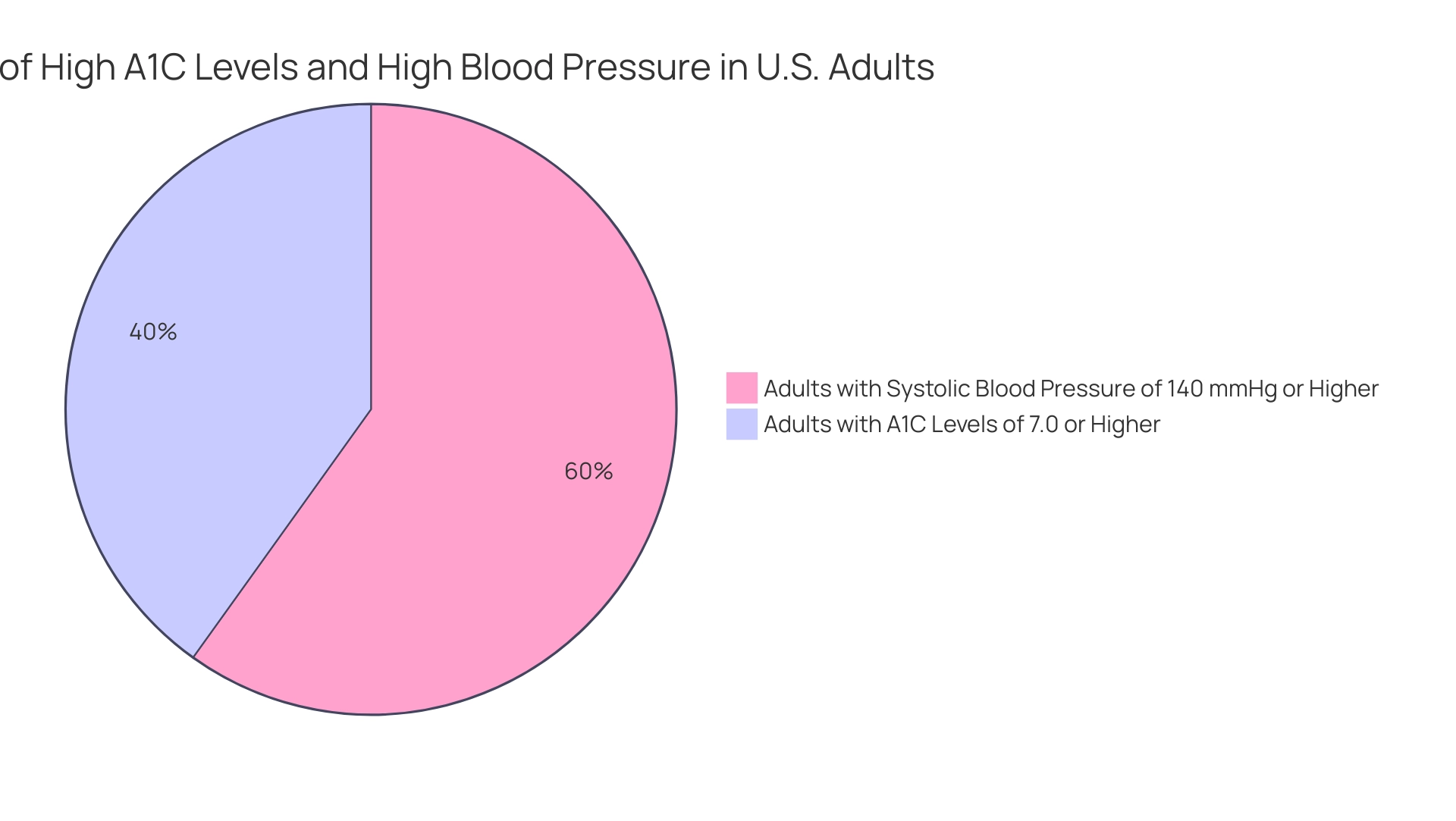
In San Marcos, CA, individuals are encouraged to engage in outdoor activities for regular exercise, maintain a balanced diet enriched with local produce such as avocados and berries, and participate in community wellness programs that provide support and resources tailored to managing health conditions. Furthermore, it is important to note that 70.8% of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions had a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or were on medication for high blood pressure, highlighting the interconnectedness of blood pressure and management of this condition. Current findings reveal that among adults with this condition, 47.4% maintain A1C values of 7.0% or higher, illustrating the urgent need for enhanced management strategies, such as using an a1c to blood glucose converter, to achieve better glycemic control.
This prevalence emphasizes the findings of the case study titled ‘A1C Levels in Adults with Diabetes,’ which indicates significant variations in A1C levels across different age groups. Additionally, with this condition being the eighth leading cause of death in the United States, effective management strategies are more urgent than ever. By recognizing the implications of A1C on overall health and incorporating lifestyle changes, including community support and engagement, patients can better navigate their diabetes journey.
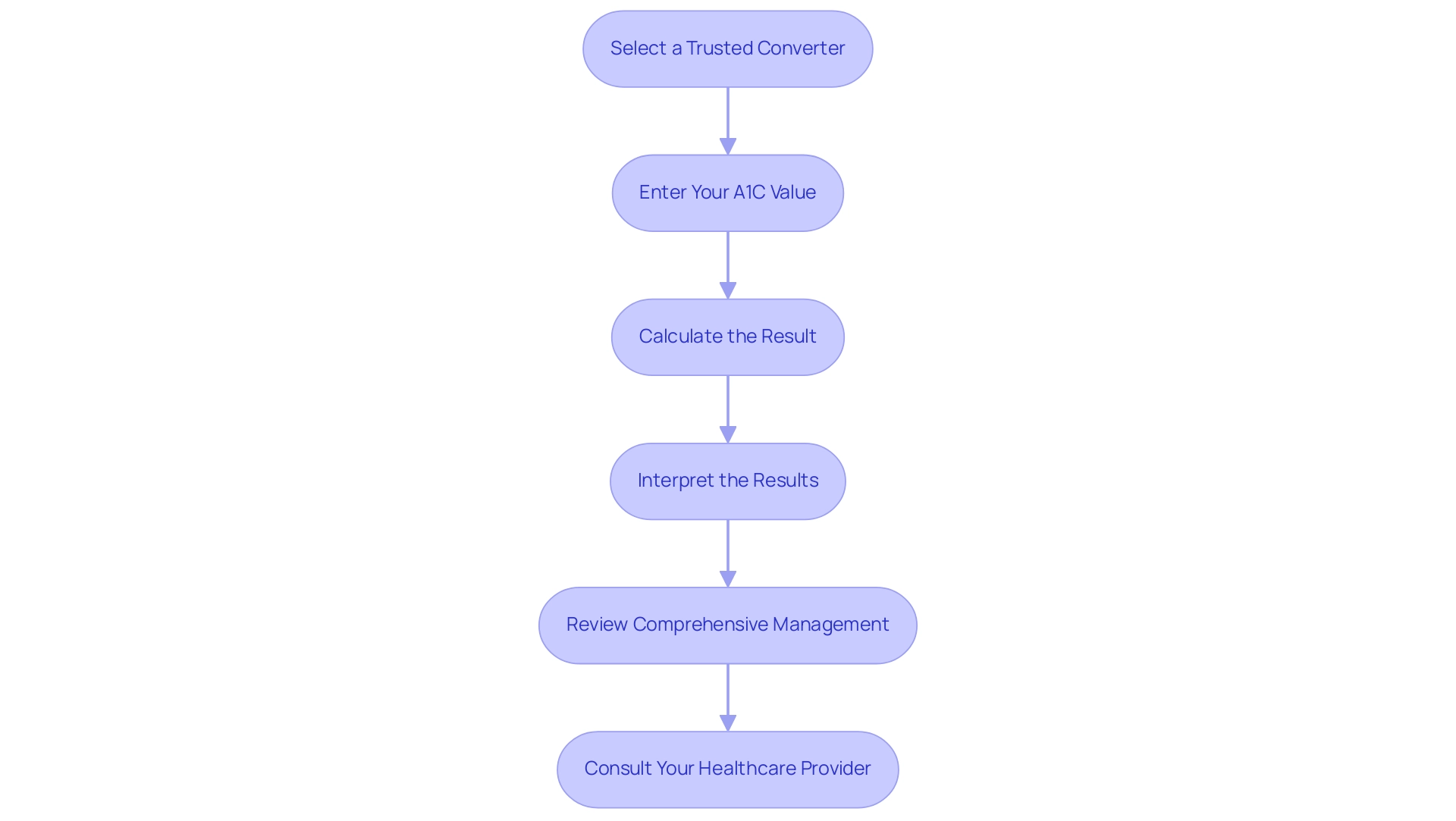
Step-by-Step Guide to Using an A1C to Blood Glucose Converter
- Select a Trusted Converter: Start by identifying a reliable a1c to blood glucose converter. Reputable sources, such as the American Diabetes Association, offer tools that ensure accuracy in your calculations.
- Enter Your A1C Value: Input your A1C percentage into the a1c to blood glucose converter. For example, if your A1C reading is 7.0%, simply enter
7.0. This step is crucial, as accurate entry is key to obtaining reliable results. - Calculate the Result: After entering your A1C into the a1c to blood glucose converter, click the ‘Calculate’ button. The converter will provide your estimated average glucose level expressed in mg/dL. For instance, an A1C of 10.0 corresponds to an estimated average glucose (eAG) of 240 mg/dL, highlighting the significance of these conversions in daily diabetes management.
- Interpret the Results: Use the output from the a1c to blood glucose converter to gain insights into your blood glucose control. For example, an estimated average of 154 mg/dL indicates a need for more vigilant monitoring of your glucose levels, aligning with expert recommendations. Regularly reviewing your progress and setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can enhance motivation and control. This structured approach allows for adjustments based on your evolving health metrics. Research indicates that goal-setting persistence scores can positively impact performance, demonstrating the effectiveness of structured goal-setting.
- Review Comprehensive Management: It’s crucial to review your day-to-day self-checks alongside regular A1C tests. This comprehensive approach, in collaboration with your healthcare team, ensures a holistic understanding of your condition management. Incorporating functional medicine strategies can be particularly beneficial in addressing individual health profiles. Tracking methods such as fitness apps and journals can aid in this process, providing a clear overview of your daily metrics.
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Finally, it’s essential to discuss your results with your healthcare team. This collaboration is essential for making informed decisions about your health management plan. As noted by Vivian Fonseca in Diabetes Care, translating the hemoglobin A1C assay into actionable guidance is crucial for optimizing care. Regular consultations ensure that your management strategies are tailored to your specific needs and circumstances. Additionally, evidence from the case study titled ‘Combining CGM and HbA1c for Accuracy’ suggests that integrating both methods can lead to improved accuracy in glycemic assessment, further reinforcing the importance of a well-rounded approach.
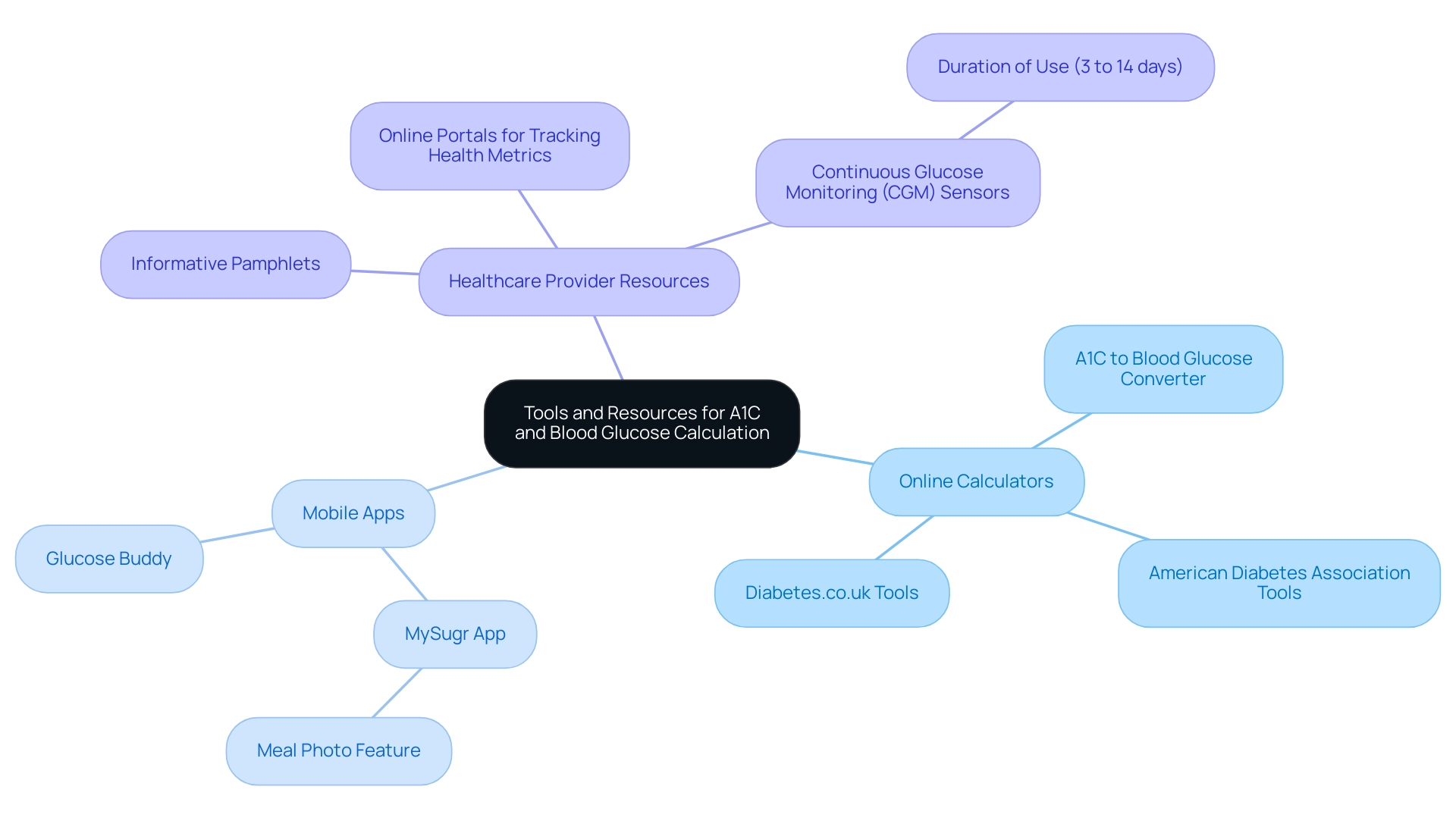
Tools and Resources for A1C and Blood Glucose Calculation
A range of instruments, including an A1C to blood glucose converter, are accessible to help individuals in determining A1C and glucose measurements, each enhancing a more knowledgeable strategy for managing the condition.
- Online Calculators: Platforms such as the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes.co.uk offer user-friendly tools, such as the A1C to blood glucose converter, that simplify the process of translating A1C results to estimated average glucose (eAG) figures, which are essential for understanding progress in reversing type 2 conditions.
- Mobile Apps: Applications such as MySugr and Glucose Buddy enable users to monitor their glucose readings effortlessly. These apps not only calculate A1C values based on the data inputted by the user but also provide features that improve overall condition management. For instance, the Meal Photo feature in the MySugr app enables users to log their meals in detail, fostering a deeper understanding of how different foods influence their blood sugar levels. This functionality has demonstrated its ability to assist users in refining their meal selections and enhancing their carb counting skills, ultimately improving their health management. As Rachel Stahl Salzman, a registered dietitian and certified care and education specialist, observes, “The best app for an individual with health conditions depends on their specific needs and preferences,” emphasizing the significance of exploring various options tailored to personal health goals.
- Healthcare Provider Resources: Many healthcare providers, in line with Dr. Jason Shumard’s holistic approach, offer valuable tools and resources for their patients. These can include informative pamphlets and online portals designed for tracking various health metrics. Effectively managing the condition requires a multidisciplinary approach involving various healthcare professionals to enhance patient outcomes. Additionally, Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) sensors can remain on the patient for 3 to 14 days, providing ongoing insights into blood glucose levels.
Utilizing these tools not only enhances your understanding of the condition but also supports effective management strategies, ensuring you can engage proactively with your health and explore integrative functional medicine strategies for reversing type 2. Don’t forget, by attending our next event, you can receive Dr. Jason Shumard’s book for free, which delves deeper into these strategies. Register now to secure your copy and learn about four lesser-known power-plays that can significantly boost your health and aid in diabetes reversal!
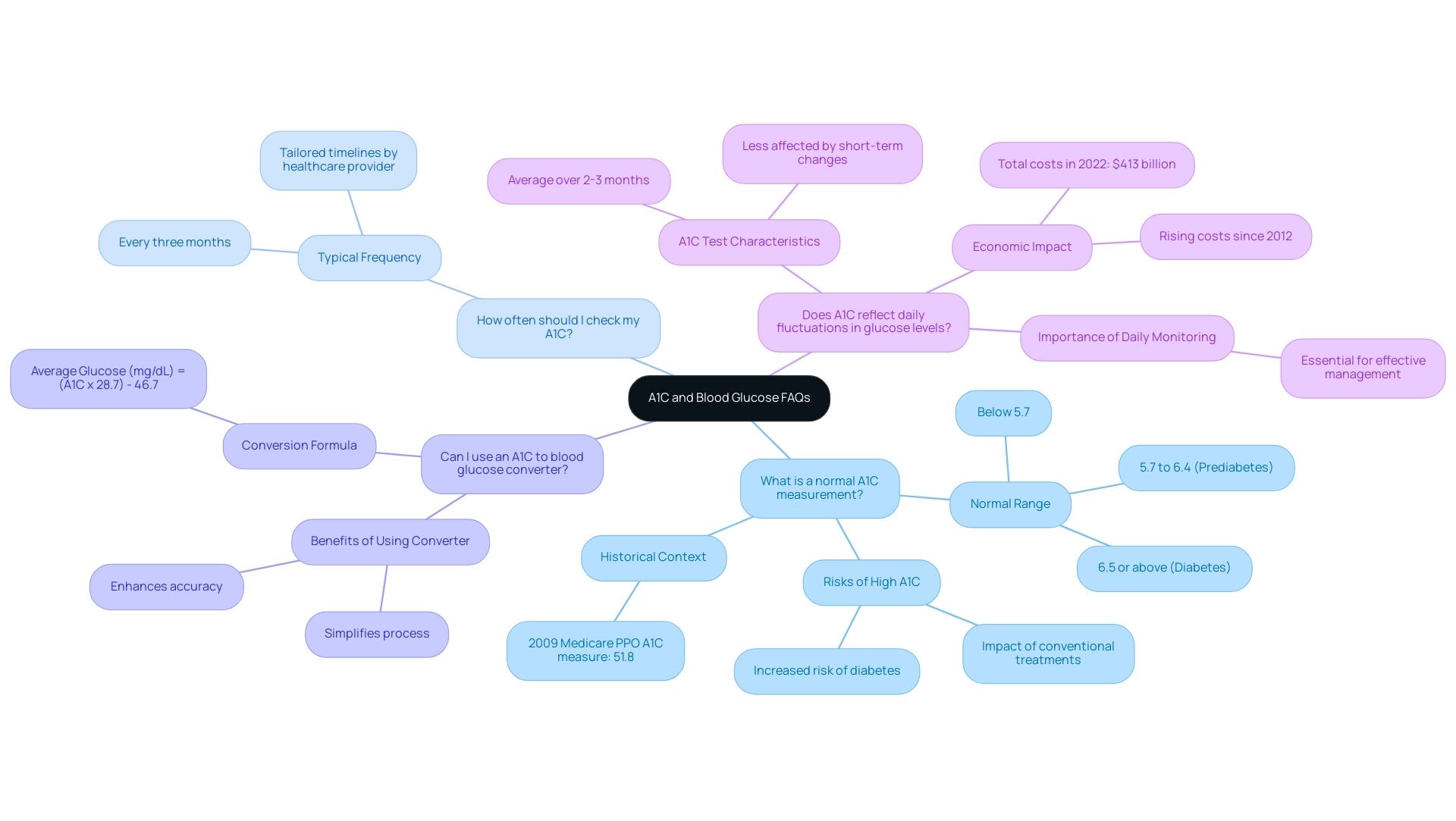
Frequently Asked Questions About A1C and Blood Glucose
-
What is a normal A1C measurement? A normal A1C measurement is generally regarded as below 5.7%. Levels from 5.7% to 6.4% imply prediabetes, whereas a level of 6.5% or above signifies the condition. Understanding where your A1C falls is crucial, especially considering the alarming statistics surrounding hospital safety—7,000 incorrect medications and 80,000 hospital-acquired infections showcase the potential dangers of conventional treatments. As Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, a holistic approach to health is essential, particularly for individuals with type 2. This is further underscored by testimonials indicating that insulin resistance can be exacerbated by conventional treatments, highlighting the risks involved. Within the prediabetes A1C range of 5.7 to 6.4 percent, the higher the A1C, the greater the risk of developing the condition. Additionally, in 2009, the A1C measure for Medicare PPO was recorded at 51.8, providing historical context for A1C levels.
-
How often should I check my A1C? For optimal diabetes management, individuals should typically have their A1C tested every three months. However, your healthcare provider may suggest a different timeline tailored to your specific health situation and treatment changes.
-
Can I use an a1c to blood glucose converter to convert A1C to glucose levels without a calculator? Yes, using the a1c to blood glucose converter, you can convert A1C to average glucose levels with the formula:
Average Glucose (mg/dL) = (A1C x 28.7) – 46.7.
While this method is straightforward, many find that using an a1c to blood glucose converter simplifies the process and enhances accuracy.
-
Does A1C reflect daily fluctuations in glucose levels? A1C tests do not capture daily variations in glucose levels; rather, they provide an average over the preceding two to three months. Regular monitoring of daily blood glucose levels remains essential for effective management of the condition. Furthermore, the economic impact of this condition is substantial, with the total direct and indirect estimated costs of diagnosed cases in the U.S. in 2022 reaching $413 billion. This underscores the necessity for effective management and prevention strategies, advocating for a more personalized, functional medicine approach to diabetes care, which can address the unique needs of each patient.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C levels is fundamental for effective diabetes management, acting as a crucial indicator of average blood glucose over the past two to three months. This article outlined the significant correlation between A1C and daily glucose readings, underscoring the need for regular monitoring to inform treatment decisions and adjust strategies as necessary. By emphasizing the importance of holistic lifestyle changes, such as adopting a diabetes-friendly diet and engaging in community support, individuals can take proactive steps toward better health outcomes.
The practical tools and resources highlighted, including reliable A1C to blood glucose converters and innovative mobile applications, empower individuals to take charge of their diabetes management. These tools facilitate a deeper understanding of how daily choices impact overall health, allowing for more informed decision-making. Furthermore, the staggering economic implications of diabetes management, estimated at $413 billion in the U.S. in 2022, reinforce the urgency for effective care strategies that prioritize A1C monitoring.
In conclusion, by embracing a comprehensive approach that combines regular A1C testing, lifestyle modifications, and community resources, individuals living with diabetes can better navigate their health journey. The key to managing diabetes effectively lies in understanding one’s A1C levels and utilizing the available tools to foster informed choices, ultimately leading to improved health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is A1C and why is it important?
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is a test that indicates the average glucose concentrations over the past two to three months. It is important for individuals managing type 2 diabetes as it serves as a standard for blood sugar regulation over time.
What do different A1C values indicate?
An A1C value between 5.7% and 6.4% suggests prediabetes, while a value of 6.5% or above can confirm diabetes.
How does the A1C to blood glucose converter work?
The A1C to blood glucose converter translates A1C measurements into average glucose concentrations. For example, an A1C of 6.0% typically corresponds to an average glucose level of approximately 126 mg/dL.
Why is regular monitoring of A1C levels important?
Regular monitoring of A1C levels helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about management strategies, particularly for personalized treatment approaches.
What lifestyle changes can improve A1C levels?
Incorporating a diabetes-friendly diet with fresh, local ingredients, engaging in outdoor activities, and implementing holistic health strategies can significantly improve A1C levels and overall health outcomes.
What are the economic implications of diabetes management?
The total direct and indirect estimated costs of diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar in the United States were $413 billion in 2022, highlighting the significant economic impact of effective diabetes management.
How prevalent are high A1C levels among adults with diabetes?
Among adults with diabetes, 47.4% maintain A1C values of 7.0% or higher, indicating a need for improved management strategies.
What additional health concerns are associated with diabetes management?
There is a notable connection between blood pressure and diabetes, with 70.8% of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions having a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or being on medication for high blood pressure.
What is the significance of the Pearson correlation coefficient in A1C testing?
A high Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.83 between A1C Now and A1C Lab values indicates the reliability of A1C testing in assessing glucose control.
What does Dr. Rich Bergenstal emphasize regarding therapy decisions for diabetes?
Dr. Bergenstal emphasizes that therapy decisions should not be based on just one metric, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive approach to diabetes management.