Overview
The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to convert A1C levels to mg/dl, emphasizing the formula used for this conversion and its significance in diabetes management. It supports this by detailing the conversion process, illustrating its importance for understanding average blood glucose levels, and highlighting how this knowledge can empower patients to better manage their health and mitigate complications associated with high blood sugar.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, the A1C test emerges as a cornerstone for assessing long-term blood glucose control. By providing a snapshot of average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, this test not only aids in diagnosing diabetes but also informs treatment strategies that can significantly alter patient outcomes.
Understanding the implications of A1C results is crucial, as they guide individuals in making informed decisions about their health. With alarming statistics highlighting the prevalence of diabetes complications, it becomes evident that effective monitoring and management of A1C levels are imperative.
This article delves into the intricacies of the A1C test, from its interpretation and conversion to practical strategies for maintaining healthy levels, ensuring that readers are well-equipped to navigate their diabetes journey.
Understanding the A1C Test: What It Measures and Its Importance
The A1C test serves as a vital tool for assessing average blood glucose levels over the preceding two to three months, and the results can be expressed as a1c to mg/dl. This metric is essential in the diagnosis and oversight of type 2, providing insight into blood sugar control. Specifically, an A1C result of 6.5% or above confirms a diagnosis of the condition, while values ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes when converting a1c to mg/dl.
Grasping these thresholds is pivotal for effective management of the condition, as they directly inform treatment strategies and necessary lifestyle adjustments. Recent statistics reveal that in 2020, various healthcare plans reported differing rates of HbA1c control:
- 53.2% for Commercial HMO
- 48.4% for Commercial PPO
- 45.0% for Medicaid HMO
- 62.9% for Medicare HMO
- 67.1% for Medicare PPO
with Medicare PPO achieving the highest control rate of patients maintaining A1C levels below 8.0%. These figures emphasize the critical nature of A1C testing in managing blood sugar levels and the importance of converting a1c to mg/dl to prevent associated health complications.
Furthermore, the Integrative Wellness Center has empowered patients through holistic approaches that address the root causes of the condition and facilitate transformative outcomes. For instance, one patient, after following the center’s personalized care plan, reported a significant reduction in their A1C levels, which translates to mg/dl from 8.5% to 6.2%, alleviating their anxiety about potential complications. A case study titled ‘Specific Causes of Hospitalization for Diabetes Patients’ detailed alarming statistics, including:
- 368,000 cases of ischemic heart disease
- 321,000 cases of stroke
- 232,000 cases of hyperglycemic crisis
in 2020, highlighting the significant health challenges faced by adults with high blood sugar.
Additionally, the prevalence of diagnosed conditions related to high blood sugar was notably higher among adults living in nonmetropolitan areas compared to those in metropolitan regions, emphasizing the importance of A1C testing and the conversion of a1c to mg/dl in diverse populations to mitigate serious complications.
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting A1C to mg/dl: The Formula Explained
To accurately convert A1C to mg/dl, the following formula is utilized:
mg/dl = [[(A1C × 30)](https://drshumard.com](https://drshumard.com/understanding-a-1-c-formulas-a-complete-tutorial-for-accurate-diabetes-management/)/understanding-a-1-c-formulas-a-complete-tutorial-for-accurate-diabetes-management/) - 60
For instance, if an individual’s A1C is measured at 7.0%, the conversion would be calculated as follows:
(7.0 × 30) - 60 = 150 mg/dl
This calculation is crucial for understanding one’s average blood glucose level in mg/dl, which can offer a more familiar reference point for many managing diabetes. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we highlight the importance of consistent tracking of A1C and related blood glucose levels, as these metrics are essential for effective control of the condition. We also provide personalized education and support strategies designed to empower patients, helping them eliminate anxiety over potential complications.
Recent guidelines underscore the importance of education in this area, especially as prediabetes awareness among Hispanic adults was reported at 20.9% from 2017 to 2020, highlighting the need for targeted approaches within this demographic. Diabetes educators frequently stress the significance of these conversions, with Roopa Naik noting, ‘Disclosure: Roopa Naik declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies,’ reinforcing the professional perspective on the importance of understanding the A1C to mg/dl conversion. Furthermore, a case study titled ‘Trends in Prevalence of Diabetes (2001–2020)’ revealed that the age-adjusted prevalence of total blood sugar conditions among adults significantly increased from 10.3% to 13.2%.
This context illustrates the critical need for individuals to grasp the A1C to mg/dl conversion process to navigate their health management strategies effectively. By addressing root causes and providing holistic care, the Integrative Wellness Center aims to empower patients and reduce their concern about complications related to the condition.
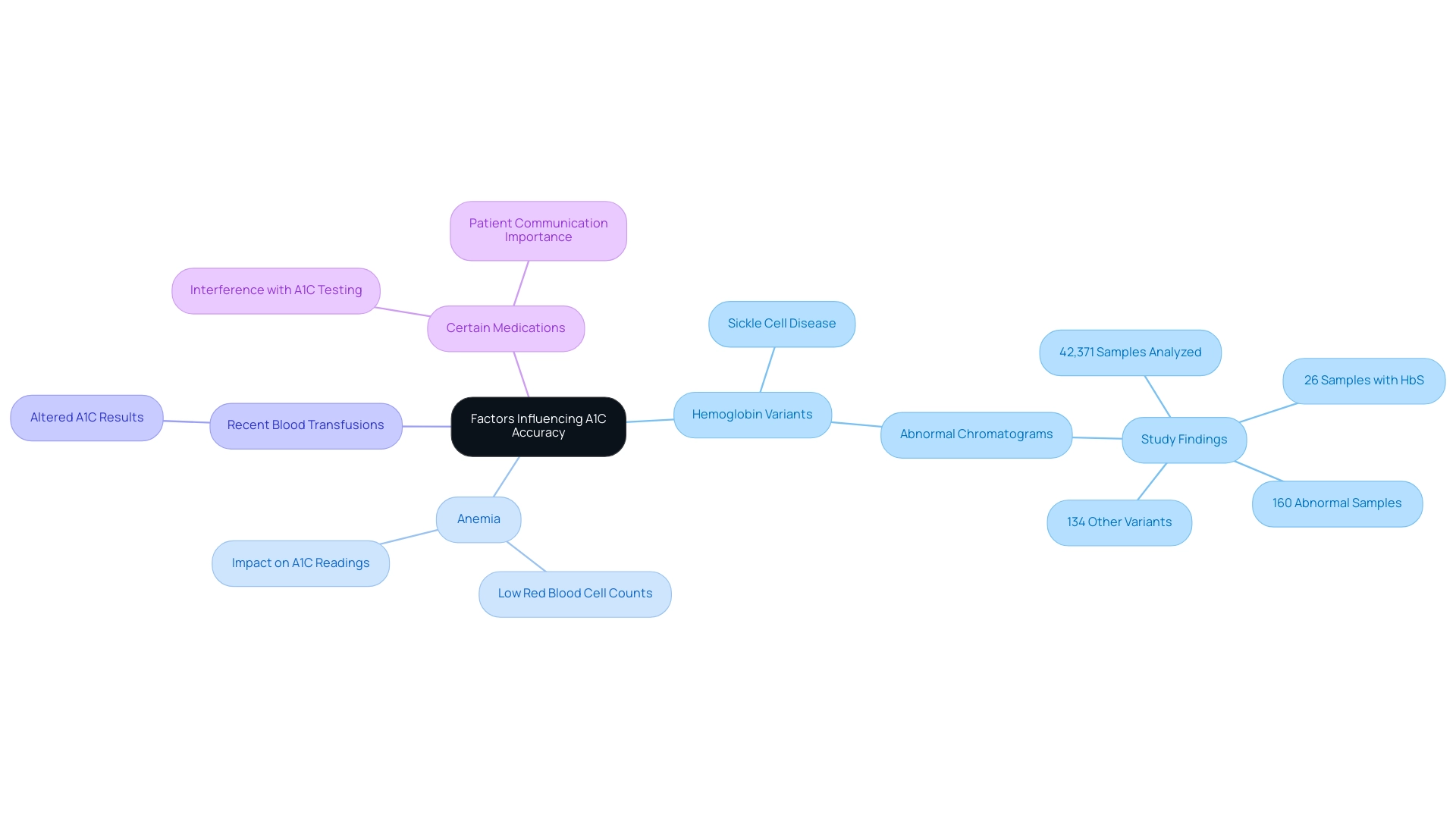
Factors Influencing A1C Accuracy: What You Need to Know
The accuracy of A1C test results can be influenced by several critical factors:
- Hemoglobin Variants: Conditions such as sickle cell disease and other hemoglobin gene variants can significantly alter the structure of hemoglobin, leading to discrepancies in A1C measurements. A study analyzing over 42,371 blood samples found that 160 exhibited abnormal chromatograms, with 26 samples showing HbS. This highlights the necessity for laboratories to recognize and adapt to local hemoglobin variants in their testing methods.
- Anemia: Individuals with low red blood cell counts may experience inaccurately low A1C readings, which can misrepresent their glycemic control. This prevalence of anemia among individuals with high blood sugar necessitates careful consideration when interpreting A1C results.
- Recent Blood Transfusions: A period of altered A1C results may follow blood transfusions, affecting the reliability of the test during this time.
- Certain Medications: Various medications can interfere with A1C testing, making it essential for patients to communicate any health conditions or medications they are taking with their healthcare provider. Ghulam Qadir Chanihoon emphasizes that
it is very important to [ensure the accuracy of HbA1c results](https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0009898121002679) and to identify cases of variant hemoglobin in the measurement process. Moreover, it’s important to note that there is currently no conclusive evidence supporting the substitution of fructosamine for A1C in glycemic control assessment.
Additionally, A1C values may be falsely high or low depending on the laboratory method used for measurement in individuals with HBAs. These factors collectively underscore the complexity of accurately assessing glycemic control, particularly when converting A1C to mg/dl through testing.
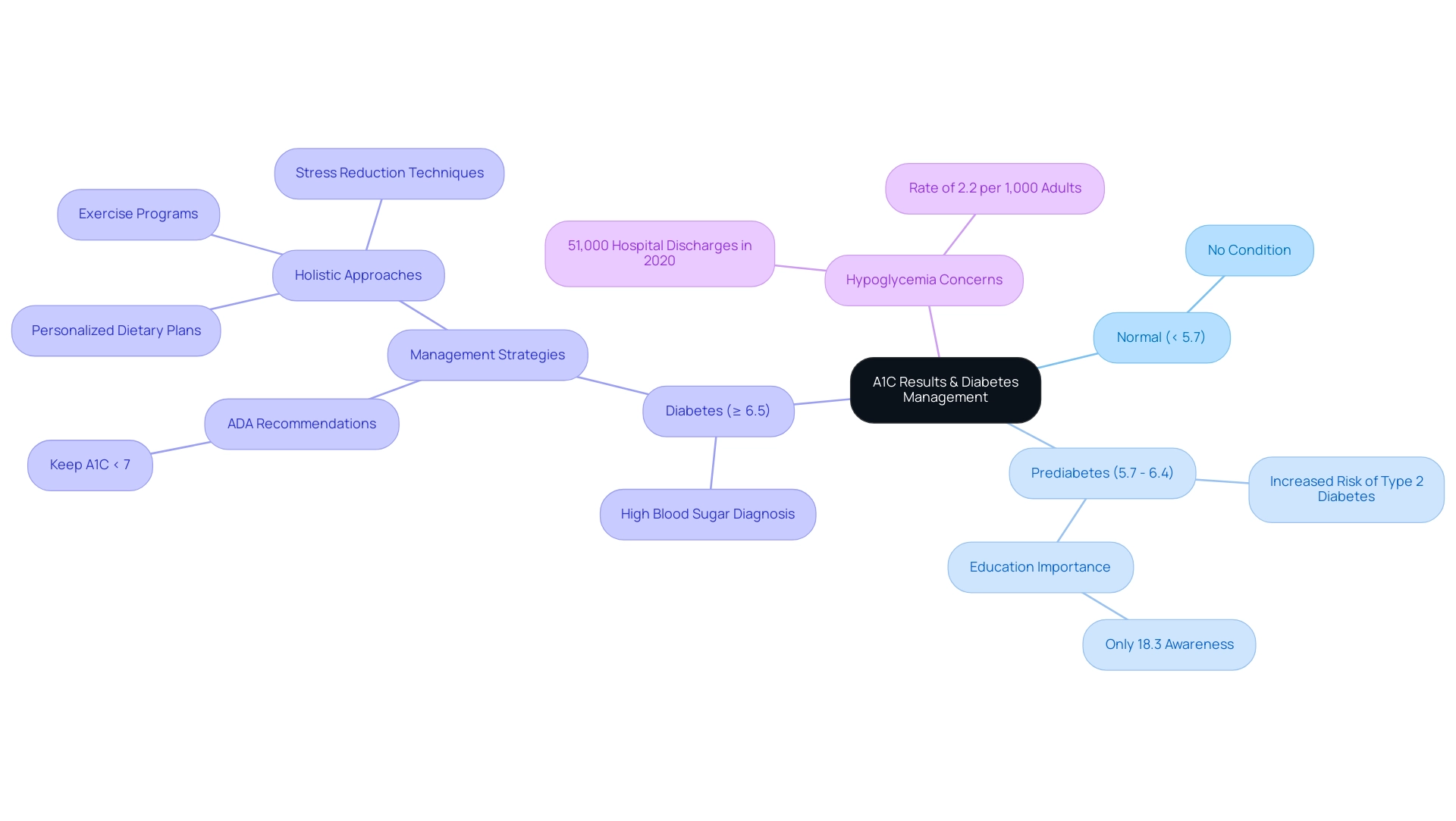
Interpreting A1C Results: Understanding Your Diabetes Management
A1C results are categorized into separate groups that help in comprehending blood glucose levels and risk:
- Below 5.7%: Indicates normal blood sugar levels, signifying no condition.
- 5.7% to 6.4%: Indicates prediabetes, suggesting a heightened risk of developing type 2 conditions in the future, which can be measured by converting A1C to mg/dl.
- 6.5% or higher A1C to mg/dl: Validates a diagnosis of the condition related to high blood sugar.
For those controlling their condition, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) suggests keeping an A1C level below 7%, which can be converted from A1C to mg/dl. This target is essential for lowering the risk of complications related to this condition and easing concerns about developing traumatic and debilitating issues associated with it.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize a holistic approach to diabetes care, empowering patients through education and addressing root causes to enhance overall health. Our unique methodologies encompass personalized dietary plans, exercise programs, and stress reduction techniques tailored to individual needs.
Regular monitoring of A1C levels, including the conversion of A1C to mg/dl, is essential, as adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication may be necessary based on individual results. The persistent occurrence of hypoglycemia continues to be a concern, with around 51,000 hospital discharges in 2020 linked to this complication among adults with high blood sugar, highlighting the need for careful oversight strategies.
Significantly, only 18.3% of individuals with more than a high school education recognize their prediabetes status, highlighting the importance of education in controlling the condition. As noted by A.B., ‘Information from the study can aid policymakers and healthcare providers/educators in their decision-making to bolster programs that benefit patients and the public’s well-being.’
Improved comprehension of A1C results, particularly in understanding how to convert A1C to mg/dl, can greatly enhance patient outcomes, assisting healthcare providers in creating effective strategies tailored to individual needs while reducing anxiety related to diabetes complications.
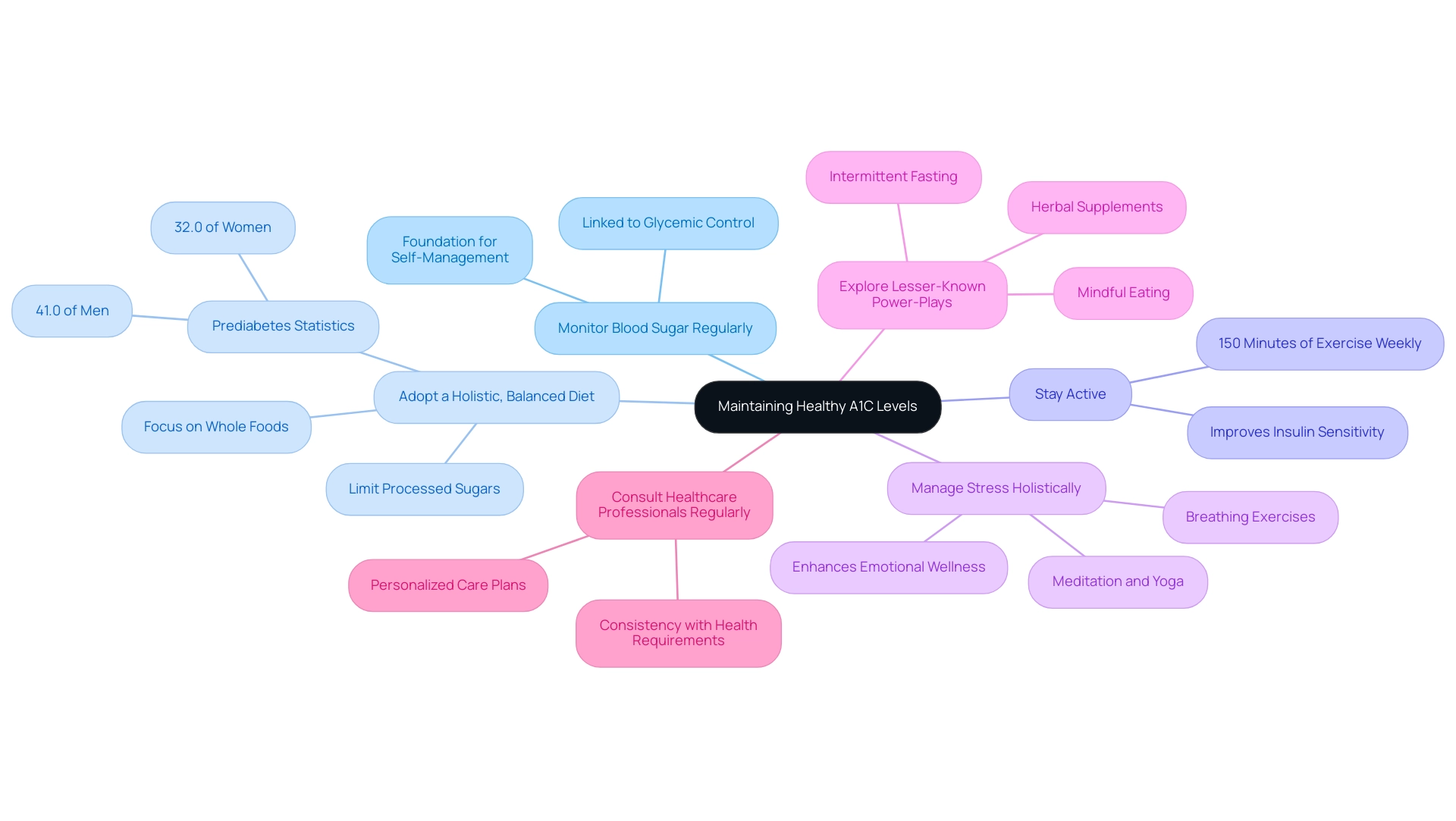
Tips for Maintaining Healthy A1C Levels: A Guide for Better Management
To effectively maintain healthy A1C values, it is crucial to implement the following strategies:
- Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly: Frequent blood glucose monitoring is essential for understanding your unique patterns and making informed adjustments to your management plan. This practice lays the groundwork for effective self-management, ultimately leading to improved glycemic outcomes. Notably, monitoring frequency is closely linked to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Adopt a Holistic, Balanced Diet: Emphasize a diet rich in whole foods, particularly focusing on whole grains and a variety of vegetables, which are essential for blood sugar regulation and overall health. Limiting processed sugars and refined carbohydrates is essential, as recent findings indicate a direct correlation between diet and measurements of A1C to mg/dl. Nutritionists emphasize the importance of whole food selections in managing the condition effectively, particularly considering that 41.0% of men and 32.0% of women have been recognized as having prediabetes.
- Stay Active: Participating in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly can greatly assist in controlling blood sugar. Physical activity not only assists with weight regulation but also improves insulin sensitivity, a crucial element in blood sugar control.
- Manage Stress Holistically: Increased stress levels can negatively impact blood sugar regulation. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or even simple breathing exercises can be beneficial in reducing stress, promoting better glycemic control, and enhancing overall health. Moreover, tackling anxiety related to blood sugar control can enhance emotional wellness and A1C levels.
- Explore Lesser-Known Power-Plays: Consider incorporating lesser-known strategies such as mindful eating, leveraging the benefits of intermittent fasting, or utilizing herbal supplements that may support blood sugar regulation. These approaches can complement traditional methods and enhance your overall health journey.
- Consult Healthcare Professionals Regularly: Regular consultations with your healthcare provider are imperative for personalizing your diabetes care plan. These check-ins guarantee that your approach stays consistent with your health requirements and any shifts in your condition.
In light of recent studies, it has been observed that there is no clear connection between the frequency of self-monitoring and HbA1c values for individuals treated with insulin, oral agents, or exclusively through dietary adjustments. Therefore, while monitoring is essential, it must be complemented by other proactive strategies for optimal results. Real-world data, such as the 2020 emergency department visits involving hyperglycemic crises, highlight the critical need for effective management, as 84.4% of these cases resulted in hospital admissions.
This underscores the importance of maintaining a diligent approach to managing A1C to mg/dl levels through lifestyle modifications and professional guidance.
Conclusion
Monitoring A1C levels is an essential component of effective diabetes management, providing crucial insights into long-term blood glucose control. The A1C test not only aids in diagnosing diabetes but also serves as a guide for tailoring treatment strategies, emphasizing the importance of understanding the thresholds that indicate normal, prediabetes, and diabetes. With alarming statistics pointing to the prevalence of diabetes complications, recognizing the significance of A1C results is critical for making informed health decisions.
Converting A1C levels to mg/dl offers a familiar metric for many individuals managing diabetes, reinforcing the need for regular monitoring and education. Various factors can influence the accuracy of A1C results, such as:
- Hemoglobin variants
- Anemia
- Recent blood transfusions
Awareness of these factors is vital to ensure accurate assessments of glycemic control, underscoring the complexity of diabetes management.
Ultimately, maintaining healthy A1C levels requires a multifaceted approach, including:
- Regular blood sugar monitoring
- A balanced diet
- Physical activity
- Stress management
Engaging with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance can further enhance diabetes management strategies. As individuals prioritize their health and implement these strategies, the potential for improved outcomes and reduced complications becomes significantly greater. Taking proactive steps today is essential for navigating the diabetes journey effectively and achieving lasting health improvements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test assesses average blood glucose levels over the preceding two to three months and is essential for diagnosing and managing type 2 diabetes, providing insight into blood sugar control.
What do the A1C result thresholds indicate?
An A1C result of 6.5% or above confirms a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, while values between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes.
Why is understanding A1C thresholds important?
Understanding these thresholds is crucial for effective management of diabetes as they inform treatment strategies and necessary lifestyle adjustments.
What were the A1C control rates reported by different healthcare plans in 2020?
The reported A1C control rates were: 53.2% for Commercial HMO, 48.4% for Commercial PPO, 45.0% for Medicaid HMO, 62.9% for Medicare HMO, and 67.1% for Medicare PPO.
What is the significance of the A1C control rates?
The A1C control rates highlight the importance of A1C testing in managing blood sugar levels and preventing health complications.
How can A1C levels affect health outcomes?
High A1C levels are associated with serious health challenges, including ischemic heart disease, stroke, and hyperglycemic crises.
How does the prevalence of high blood sugar conditions vary geographically?
The prevalence of diagnosed conditions related to high blood sugar is higher among adults in nonmetropolitan areas compared to those in metropolitan regions.
How is the conversion from A1C to mg/dl calculated?
The conversion formula is: mg/dl = (A1C × 30) – 60. For example, an A1C of 7.0% converts to 150 mg/dl.
Why is tracking A1C and blood glucose levels important?
Consistent tracking of A1C and blood glucose levels is essential for effective diabetes management and helps reduce anxiety about potential complications.
What demographic shows a need for targeted education regarding prediabetes?
Awareness of prediabetes among Hispanic adults was reported at 20.9% from 2017 to 2020, indicating a need for targeted educational approaches within this demographic.
What role does the Integrative Wellness Center play in diabetes management?
The Integrative Wellness Center provides holistic care and personalized education to empower patients, addressing root causes of diabetes and helping them manage their condition effectively.