Overview
To convert A1C to blood sugar levels, it’s important to understand the essential formula:
eAG (mg/dL) = (28.7 x A1C) – 46.7.
This formula helps individuals grasp their average glucose levels over time, which can feel overwhelming at first. Many patients find that using this conversion not only aids in effective diabetes management but also empowers them to set realistic health goals.
It’s crucial to recognize that making informed lifestyle choices can significantly improve overall well-being. By understanding their numbers, individuals can take meaningful steps toward healthier living. This journey may seem daunting, but remember, you are not alone. With the right tools and support, you can navigate your path to better health.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding the A1C test is incredibly important. This vital diagnostic tool measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, offering invaluable insights into your health status. With the number of diabetes diagnoses on the rise, especially among younger individuals, the significance of A1C testing truly cannot be overstated. It not only helps in detecting diabetes but also plays a key role in ongoing care, guiding you toward healthier choices and better management of your condition.
It’s important to recognize that many people face challenges in managing diabetes. As healthcare professionals emphasize the value of regular monitoring and personalized strategies, this article explores the intricacies of the A1C test, its implications for health, and effective methods for maintaining optimal levels. Through a comprehensive approach, you can reclaim your health and enhance your quality of life. Remember, you are not alone on this journey, and with the right support, a healthier future is within reach.
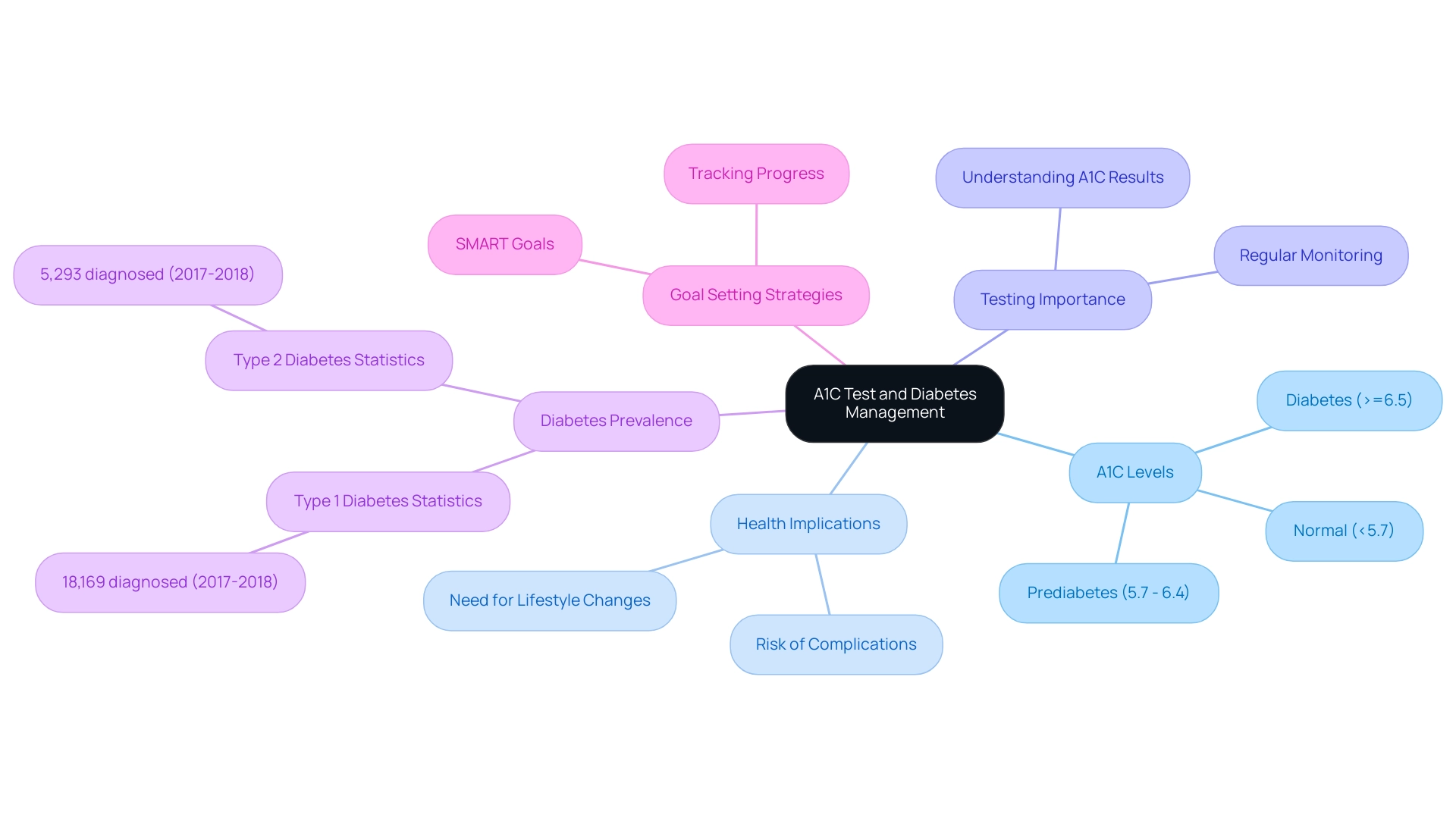
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key to Diabetes Management
The A1C test, often referred to as the hemoglobin A1C test, is a vital tool in managing blood sugar levels, offering insights into the average glucose amounts over the past two to three months. This test reveals the percentage of glucose that has attached to hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen. Understanding A1C values is crucial for effective diagnosis and management of diabetes.
A standard A1C level is classified as below 5.7%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms the condition. Recognizing these thresholds is essential for patients to understand their health status and the potential need for lifestyle changes or medical intervention.
It’s important to acknowledge the increasing prevalence of diabetes, particularly among children and adolescents. In 2017-2018, approximately 5,293 children aged 10 to 19 were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, highlighting the critical need for early detection and management through A1C testing. Many patients find that being aware of factors that can lead to false-positive or false-negative A1C results is vital, as these can significantly influence their management of blood sugar levels.
The significance of the A1C test extends beyond mere diagnosis; it plays an essential role in ongoing care. As we look ahead to 2025, experts continue to emphasize the importance of regular A1C testing as a foundational aspect of managing diabetes, particularly in relation to blood sugar levels. Research indicates that maintaining A1C readings below 7% can substantially reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition. Real-world experiences show that A1C testing can be effective in diagnosing diabetes, with many patients reporting improved well-being after recognizing the connection between A1C and blood sugar levels and making informed choices about their health.
As the landscape of diabetes management evolves, the A1C test remains a cornerstone, guiding both patients and healthcare providers toward better health outcomes. Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their wellness and well-being.” This commitment to patient education and empowerment is further illustrated by the center’s resources, which have led to positive outcomes for those who engage with A1C testing related to blood sugar levels.
To enhance their journey, patients are encouraged to adopt structured goal-setting strategies. Setting specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals related to A1C values and overall health can be incredibly beneficial. By prioritizing goal-setting and tracking progress consistently, individuals can cultivate a sense of achievement, maintain engagement in their health management, and ultimately enhance their overall wellness.
Converting A1C to Blood Sugar: The Essential Formula
Converting A1C to estimated average glucose (eAG) is an important step in understanding your blood sugar levels. To do this, you can use the formula:
eAG (mg/dL) = [(28.7 x A1C)](https://drshumard.com/how-to-convert-a-1-c-to-e-ag-a-step-by-step-guide/) - 46.7
For example, if your A1C is 7%, the calculation would be
eAG = (28.7 x 7) - 46.7
resulting in an eAG of approximately 154 mg/dL. This conversion is crucial, as it helps you correlate your A1C with your blood sugar levels, paving the way for more effective management of your condition.
Current guidelines suggest that individuals with diabetes should have their A1C tested at least twice a year if they are meeting their treatment goals. This regular monitoring is essential for understanding long-term glucose control and making necessary adjustments to treatment plans. Many patients find that by implementing SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—they can enhance their focus and motivation in managing their diabetes.
For instance, consider setting a goal to lower your eAG by 10 mg/dL over the next month. Achieving this can lead to better health outcomes. Recent statistics reveal that a significant portion of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes—80.6%—have a systolic blood pressure of 130 mmHg or higher or are on medication for hypertension. This underscores the importance of comprehensive management strategies that include monitoring A1C alongside other wellness metrics.
In practical terms, converting A1C to eAG empowers you to take charge of your well-being. For example, if your A1C is 8%, you would calculate your eAG as follows:
eAG = (28.7 x 8) - 46.7
which gives you an eAG of approximately 183 mg/dL. This knowledge allows you to set realistic daily blood sugar levels and make informed lifestyle choices, fostering a sense of achievement and accountability in your health journey.
It’s also important to be aware that falsely low A1C values can occur due to conditions such as hemoglobin variants (C, D, E, and S traits), while falsely high values may result from iron deficiency. Therefore, discussing your A1C results with your healthcare provider is essential for accurate interpretation and effective management.
A recent case study highlighted the significance of interprofessional collaboration in managing blood sugar levels. By working together, healthcare professionals can ensure precise interpretation of A1C values and enhance your adherence to treatment plans. This personalized approach aligns with the principles of functional medicine, emphasizing tailored strategies for managing type 2 conditions based on individual wellness profiles.
To monitor your progress effectively, consider using various tracking methods, such as fitness apps, journals, and pedometers. These tools can help you keep a record of your daily blood sugar levels and track your adherence to SMART goals. As we approach 2025, updates to the A1C to eAG conversion formula and guidelines continue to evolve, reflecting ongoing research and clinical insights.
Staying informed about these changes can significantly improve your management techniques, ultimately leading to better wellness outcomes. Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes that by providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center creates an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.
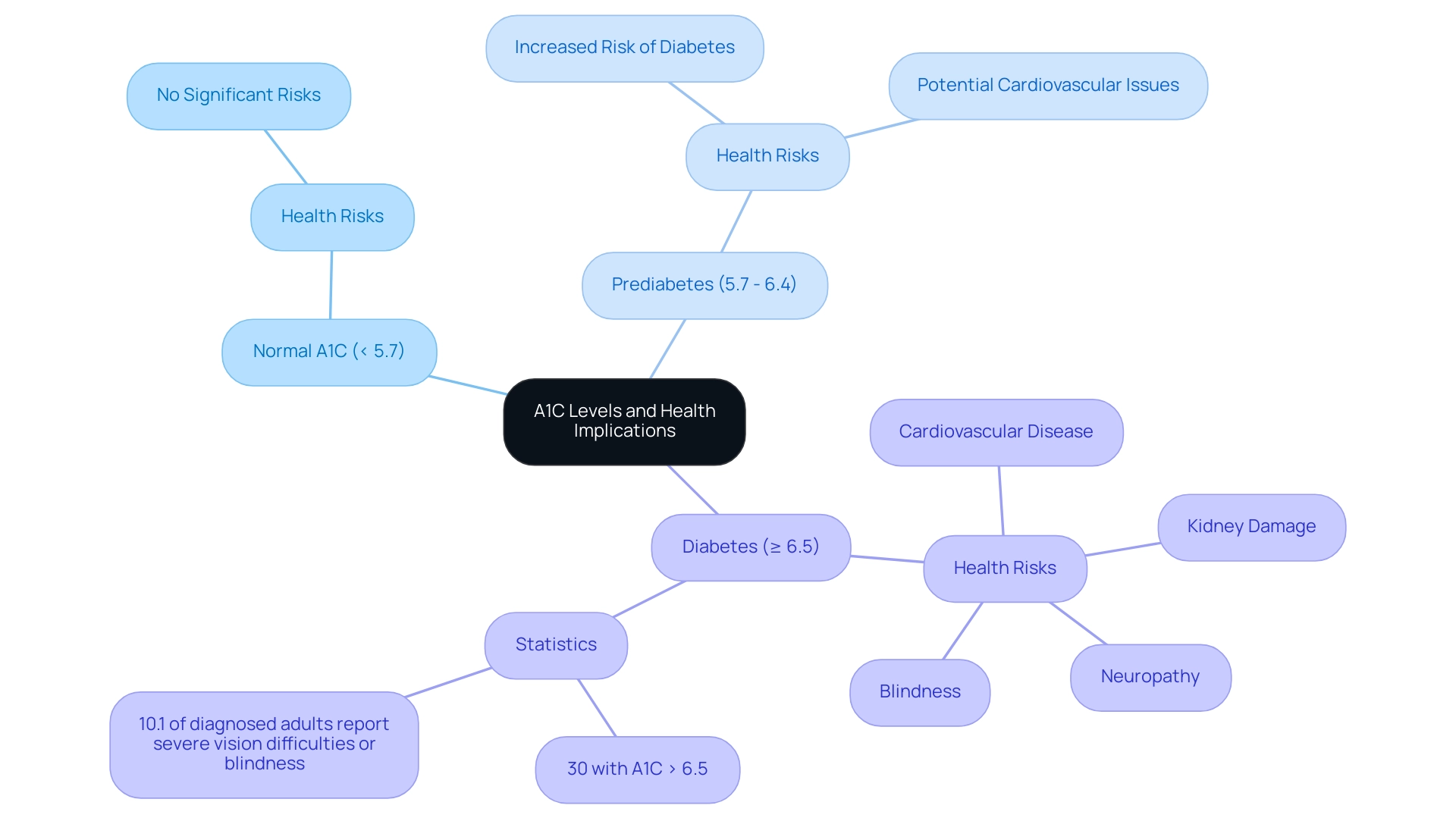
Interpreting A1C Levels: What Do They Mean for Your Health?
A1C readings serve as a vital sign, connecting blood sugar regulation over time and offering essential insights into managing one’s condition. An A1C below 5.7% is considered normal, while values between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes. A reading of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of a blood sugar disorder.
It’s important to recognize that elevated A1C values are linked to an increased risk of serious health complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and neuropathy. Chronic hyperglycemia can lead to irreversible complications, highlighting the necessity for proactive management strategies.
Statistics reveal that approximately 30% of individuals with high blood sugar have A1C readings exceeding 6.5%, illustrating the correlation between A1C and blood sugar levels, which places them at a heightened risk for these complications. The implications of high A1C levels are particularly concerning; for example, this condition is recognized as the leading cause of new cases of blindness among adults aged 18-64, with 10.1% of diagnosed adults reporting severe vision difficulties or blindness in 2021. This underscores the critical need for preventive care and effective management strategies.
A case study titled ‘Vision Disability Linked to Diabetes’ emphasizes this point, showcasing the severe consequences of unmanaged blood sugar issues.
Transformative patient experiences at Integrative Wellness Center illustrate the potential for reversing type 2 diabetes through Dr. Jason Shumard’s holistic approach. One patient shared, “I was depressed, no energy, and had insomnia. I hated how I felt and looked. I was in a ‘cookie cutter’ treatment that was not working for me. I was on 2 different meds that weren’t working and was told that I needed insulin. If you have the opportunity to join this family, DO IT! It will be the most important choice you will ever make in your life.” Another noted, “I lost 55 lbs. My A1C started at 9.1 after 8 months it is now 5.7. My regular MD has cut my blood pressure meds in half and will start reducing my other prescriptions in the near future.” These testimonials highlight the effectiveness of personalized care and lifestyle modifications in managing A1C levels while enhancing overall well-being.
Healthcare professionals stress the importance of tracking A1C measurements as they relate to blood sugar levels. As Dr. Jason Shumard observed, “By offering patients actionable insights and practical tools, the center promotes an atmosphere where individuals can regain their well-being.” Understanding the implications of A1C on blood sugar levels can empower patients to adhere to their treatment plans and make necessary lifestyle adjustments.
Many patients find that real-world instances abound, with numerous individuals indicating significant wellness improvements after gaining a clearer understanding of how A1C relates to blood sugar levels and making focused adjustments.
As we move into 2025, the discussion surrounding A1C values continues to evolve, with new studies shedding light on the implications of differing A1C values. Staying informed about these developments can further motivate individuals to take charge of their health, ultimately leading to better outcomes and a reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions. Additionally, the UK JBDS guideline suggests that the lower limit of glucose in the inpatient population should be 108 mg/dl, providing further context for effective blood sugar management strategies.
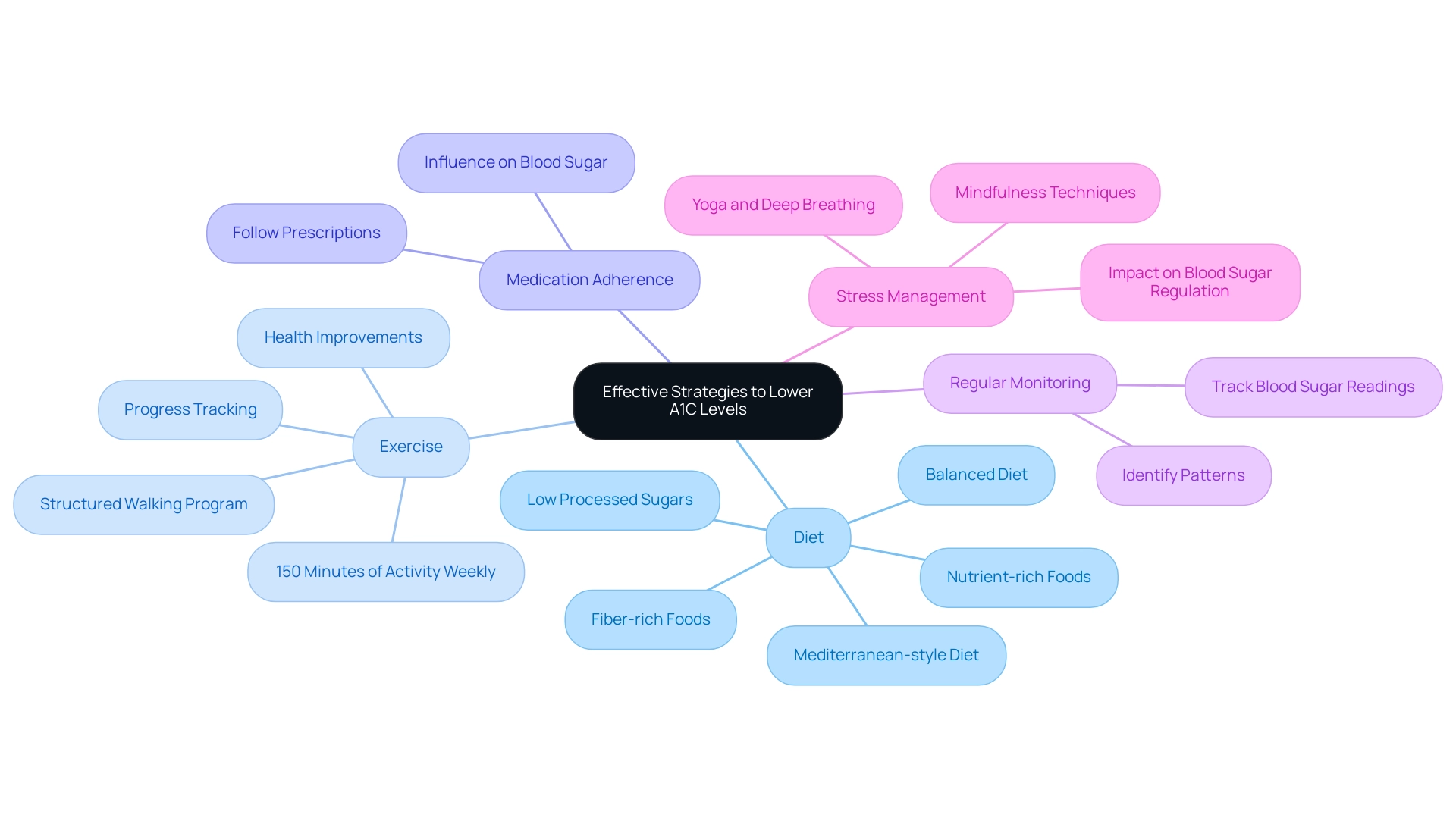
Effective Strategies to Lower Your A1C Levels
To effectively lower your A1C levels, consider implementing the following strategies:
-
Diet: It’s essential to emphasize a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, such as fresh vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Customized nutrition strategies, within the framework of functional medicine, can be adjusted to your unique requirements. This approach emphasizes nutrient-rich foods that stabilize blood sugar and enhance metabolic function. Research suggests that diets rich in fiber and low in processed sugars can lead to significant improvements in A1C to blood sugar levels. For instance, many individuals who adopted a Mediterranean-style diet experienced a notable reduction in their A1C readings over six months.
-
Exercise: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate physical activity each week. Regular exercise not only improves insulin sensitivity but also plays a crucial role in reducing blood sugar levels. Many patients find that following a structured walking program, as outlined in the walking program PDF, can be particularly beneficial. Starting with a daily walk of 10-15 minutes and gradually increasing duration and frequency can lead to substantial health improvements. It’s also important to track your progress using a journal or an app, as this can help maintain motivation and allow you to celebrate your achievements along the way. Statistics indicate that individuals who engage in regular physical activity can reduce their A1C to blood sugar levels by as much as 0.5% to 1% over time.
-
Medication Adherence: It is vital to take medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Following your medication routine can significantly influence your capacity to manage blood sugar effectively.
-
Regular Monitoring: Keeping a close eye on your blood sugar readings allows you to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your diet and exercise routines. This proactive approach is essential for effective diabetes management.
-
Stress Management: Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine. Managing stress is essential, as increased stress can negatively impact blood sugar regulation. Incorporating these techniques can enable you to sustain improved blood sugar levels and overall well-being.
It’s important to recognize that 70.8% of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions had elevated blood pressure, emphasizing the necessity for thorough wellness management alongside A1C reduction. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.” Furthermore, findings indicate that a significant percentage of adults with high blood sugar had A1C readings of 7.0% or higher, underscoring the urgency of effective management strategies related to A1C to blood sugar levels.
The use of standardized tools for psychosocial screening should also be considered to ensure comprehensive care in managing blood sugar.
These strategies not only help in reducing A1C to blood sugar levels but also enhance overall wellness and well-being. Real-life examples from patients who have successfully implemented these changes highlight the transformative impact of a holistic approach to managing this condition. By focusing on personalized nutrition, structured exercise, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can reclaim their health and improve their quality of life.
The Role of Monitoring and Healthcare Collaboration in Diabetes Management
Consistent tracking of blood glucose readings is a fundamental aspect of successfully managing a1c to blood sugar levels. It enables individuals to identify patterns and triggers that influence their glucose levels, facilitating timely interventions. Collaborating with healthcare providers—including doctors, dietitians, and diabetes educators—ensures that patients receive personalized care tailored to their unique needs.
This collaborative method not only enhances the quality of care but also results in better outcomes. For instance, a recent case study highlighted the transformative experience of a patient who, after participating in Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, reported significant improvements in their well-being, including weight loss, increased energy, and a reduction in medication needs. This aligns with the findings from the case study titled ‘Deintensification of Diabetes Treatment in Older Adults,’ which emphasizes the importance of tailoring treatment to individual needs.
Engaging actively with your healthcare team empowers you to take charge of your health management. By discussing monitoring options and treatment adjustments with your providers, you can develop a comprehensive strategy that aligns with your wellness goals. Have you considered how regular check-ups can support your journey? Statistics indicate that a staggering 70.8% of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes have elevated blood pressure, emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring not just for blood sugar but for overall wellness management.
This connection highlights how blood sugar levels, specifically a1c to blood sugar levels, and blood pressure are interrelated, making consistent monitoring essential for comprehensive care. Expert insights emphasize that consistent a1c to blood sugar levels monitoring is vital for recognizing fluctuations and making informed decisions about diet and medication. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, ‘By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.’ The holistic method implemented by Dr. Shumard, which incorporates lifestyle strategies such as nutrition, exercise, and community support, empowers patients to effectively manage their condition.
As healthcare collaboration continues to evolve in 2025, the focus on integrated care models is expected to yield even better outcomes for individuals with blood sugar management issues. Furthermore, advance care planning is essential for individuals with this condition, allowing them to clarify their values and preferences for end-of-life care. By fostering an environment of teamwork and support, individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to a more empowered approach to managing diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is essential for effective diabetes management. It provides clear indicators of blood sugar control over time, allowing individuals to take proactive steps in their health journeys. Regular monitoring of A1C, along with the conversion to estimated average glucose (eAG), empowers patients to set realistic goals and make informed lifestyle choices.
It’s important to recognize that the significant rise in diabetes diagnoses, particularly among younger populations, underscores the urgent need for awareness and education surrounding A1C testing. Many patients find that embracing a comprehensive approach—one that includes personalized nutrition, consistent physical activity, and adherence to treatment plans—can lead to significant improvements in their A1C levels and overall well-being.
Collaboration with healthcare providers further strengthens diabetes management strategies. This ensures that patients receive tailored care and support, which is crucial for navigating the complexities of diabetes. As the landscape of diabetes management continues to evolve, staying informed about A1C testing and its implications will be vital in empowering individuals to reclaim their health.
Ultimately, with the right tools, knowledge, and support, a healthier future is attainable. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Together, we can navigate the challenges and celebrate the successes along the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, measures the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months by indicating the percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells. It is crucial for diagnosing and managing diabetes.
What do different A1C levels indicate?
A standard A1C level is below 5.7%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms diabetes. Understanding these thresholds helps patients recognize their health status and the need for lifestyle changes or medical intervention.
How prevalent is diabetes among children and adolescents?
The prevalence of diabetes is increasing, particularly among children and adolescents. In 2017-2018, approximately 5,293 children aged 10 to 19 were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, highlighting the need for early detection through A1C testing.
What is the significance of maintaining A1C readings below 7%?
Maintaining A1C readings below 7% can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Regular A1C testing is emphasized as a foundational aspect of diabetes management.
How can patients effectively manage their A1C levels?
Patients can manage their A1C levels by setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—related to their A1C values and overall health. This approach helps them stay engaged and track their progress.
How do you convert A1C to estimated average glucose (eAG)?
The formula to convert A1C to eAG is: eAG (mg/dL) = (28.7 x A1C) – 46.7. For example, an A1C of 7% results in an eAG of approximately 154 mg/dL.
How often should individuals with diabetes have their A1C tested?
Individuals with diabetes should have their A1C tested at least twice a year if they are meeting their treatment goals. Regular monitoring is essential for understanding long-term glucose control.
What factors can affect A1C test results?
Conditions such as hemoglobin variants can lead to falsely low A1C values, while iron deficiency may result in falsely high values. It is important to discuss A1C results with a healthcare provider for accurate interpretation.
What role does interprofessional collaboration play in managing A1C levels?
Interprofessional collaboration among healthcare professionals ensures precise interpretation of A1C values and enhances adherence to treatment plans, aligning with functional medicine principles for personalized diabetes management.
What tools can help patients track their progress in managing diabetes?
Patients can use various tracking methods such as fitness apps, journals, and pedometers to record daily blood sugar levels and monitor adherence to their SMART goals.