Overview
Caring for after-exercise blood sugar levels is vital, especially for individuals navigating the challenges of type 2 diabetes. It’s important to recognize that monitoring and strategically planning physical activity can make a significant difference. Understanding how different types of exercise—like aerobic, anaerobic, and resistance training—affect glucose levels is crucial. Many patients find that pre- and post-exercise monitoring empowers them to tailor their fitness routines effectively.
Imagine feeling confident in your ability to manage your blood sugar through thoughtful exercise choices. By learning about these effects, you can take actionable steps toward a healthier lifestyle. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; countless others share similar experiences and concerns. Together, we can explore ways to make your fitness routine work for you, ensuring that your blood sugar levels remain stable and manageable.
Introduction
In the quest for effective management of type 2 diabetes, exercise stands out as a powerful ally, especially in communities like San Marcos, CA. Many individuals face the complexities of blood sugar control, and it’s important to recognize that understanding the intricate relationship between physical activity and glucose levels is vital. Have you ever considered how different types of exercise can impact your health? From the immediate benefits of aerobic workouts to the nuanced effects of resistance training, each type offers unique advantages and challenges.
Moreover, the timing of your exercise, combined with personalized strategies, can significantly influence your outcomes. Many patients find that by embracing a holistic approach—one that combines education, community support, and tailored fitness regimens—they can empower themselves to reclaim their health and enhance their overall well-being. This article delves into the multifaceted connection between exercise and blood sugar management, providing insights and practical strategies for those looking to optimize their health journey. Let’s explore how you can take actionable steps toward a healthier lifestyle together.
Understanding the Connection Between Exercise and Blood Sugar Levels
Physical activity is a fundamental aspect in the regulation of glucose concentrations for people with type 2 diabetes, particularly in the lively community of San Marcos, CA. Participating in physical exercise encourages muscles to require additional glucose for energy, leading to a reduction in glucose concentration. This effect can continue for several hours, affecting after-exercise blood sugar levels. It’s important to recognize the significance of careful observation of glucose levels prior to, during, and after workouts.
By understanding this relationship, individuals can effectively plan their workout sessions to mitigate the risks of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
- Physical activity significantly improves glucose absorption by muscles, facilitating better glucose regulation.
- Consistent physical activity is associated with enhanced insulin sensitivity, which is vital for sustaining stable glucose amounts.
Tracking glucose levels is crucial to avert negative consequences during and after physical activity, especially in relation to after-exercise blood sugar levels. This ensures a secure and productive workout experience.
In San Marcos, the area’s beautiful parks and trails offer an ideal setting for regular physical activity. Many patients find that statistics indicate every additional hour of sedentary activity beyond eight hours per day correlates with a 1% increase in the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This highlights the importance of incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines as part of Dr. Shumard’s holistic approach to health, which emphasizes reclaiming health through reduced sedentary behavior.
Practical instances demonstrate the significant effect of physical activity on glucose regulation. Individuals involved in Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program have noted substantial enhancements in their glucose levels, crediting their achievements to the program’s focus on education, tailored care, and organized physical activity components. The program motivates participants to adopt an outdoor lifestyle, using local parks for refreshing walks or hikes. This not only helps in glucose management but also improves overall well-being.
Expert opinions reinforce the notion that physical activity is vital for glucose management. As noted by Dr. Shumard, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” This holistic approach not only addresses the symptoms of diabetes but also empowers patients to take control of their health through informed lifestyle choices.
Additionally, a study titled “Inflammation and Immunological Disarrays Associated with Acute Physical Activity in Type 2 Diabetes” highlights how physical activity influences inflammatory responses, further supporting the importance of integrating movement into diabetes management strategies.
In conclusion, physical activity plays a crucial role in regulating glucose amounts for individuals with type 2 diabetes. By understanding how physical activity affects glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity, individuals can make informed decisions that enhance their overall health and well-being. Embracing a holistic lifestyle, including nutrition—such as a balanced diet rich in local produce like avocados and berries—community support, and stress management, can lead to transformative changes in diabetes management.
How Different Types of Exercise Affect Blood Sugar
Different types of exercise can significantly influence blood sugar levels, and understanding these effects is crucial for effective diabetes management.
- Aerobic Exercise: Engaging in activities such as walking, running, and cycling generally leads to a reduction in blood sugar levels during and after the workout. This is primarily due to increased insulin sensitivity, which enhances the body’s ability to utilize glucose. Studies indicate that combining aerobic activity with pharmacologic therapies, such as metformin, can result in a notable 21% reduction in postprandial hyperglycemia. This underscores the effectiveness of this approach in managing diabetes. As noted by Mohamed A. Elrayess, incorporating physical activity into treatment plans is essential for optimal outcomes. In San Marcos, CA, individuals can utilize the area’s parks and trails for regular aerobic activity, which not only aids in glucose management but also encourages overall wellness. This personalized approach aligns with functional medicine principles, emphasizing customizing activity regimens based on individual health profiles and needs.
- Anaerobic Exercise: Many patients find that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and weightlifting can cause temporary spikes in blood sugar levels. This reaction is attributed to the release of stress hormones like adrenaline during intense physical activity. While these spikes may be concerning, they are often short-lived and can be managed with careful monitoring. Real-life examples illustrate that individuals who incorporate anaerobic activities into their routines can still achieve significant improvements in overall glycemic control when combined with aerobic activities. Personalized functional medicine strategies, such as those provided by Dr. Jason Shumard, highlight the significance of comprehending how various physical activity modalities influence individual health profiles, including the necessity for specific evaluations and diagnostic tests to guide these choices.
- Resistance Training: It’s important to recognize that this type of physical activity is beneficial for building muscle mass and improving insulin sensitivity over time. However, it may also result in short-term elevations in after-exercise blood sugar levels immediately following the workout. The essential factor is to balance resistance training with cardiovascular activities to enhance glucose control. The case study titled ‘Combination Therapy in Diabetes Management’ illustrates how including physical activity into pharmacologic therapy can enhance glycemic control and reduce postprandial hyperglycemia. In San Marcos, community wellness programs can provide support and resources for individuals looking to integrate resistance training into their diabetes management plans, guided by the expertise of professionals like Dr. Jason Shumard.
Recommendations:
- Opt for aerobic exercises for immediate blood sugar control, especially after meals, and consider utilizing local trails for walking or jogging.
- Include resistance training in your routine for lasting advantages, but remain attentive in tracking after-exercise blood sugar levels.
By understanding the distinct impacts of these physical activity modalities, individuals can tailor their fitness regimens to better manage their diabetes and enhance their overall health. Customized management approaches, as promoted by functional medicine, are crucial, as various activity types can have diverse impacts on glucose concentrations.
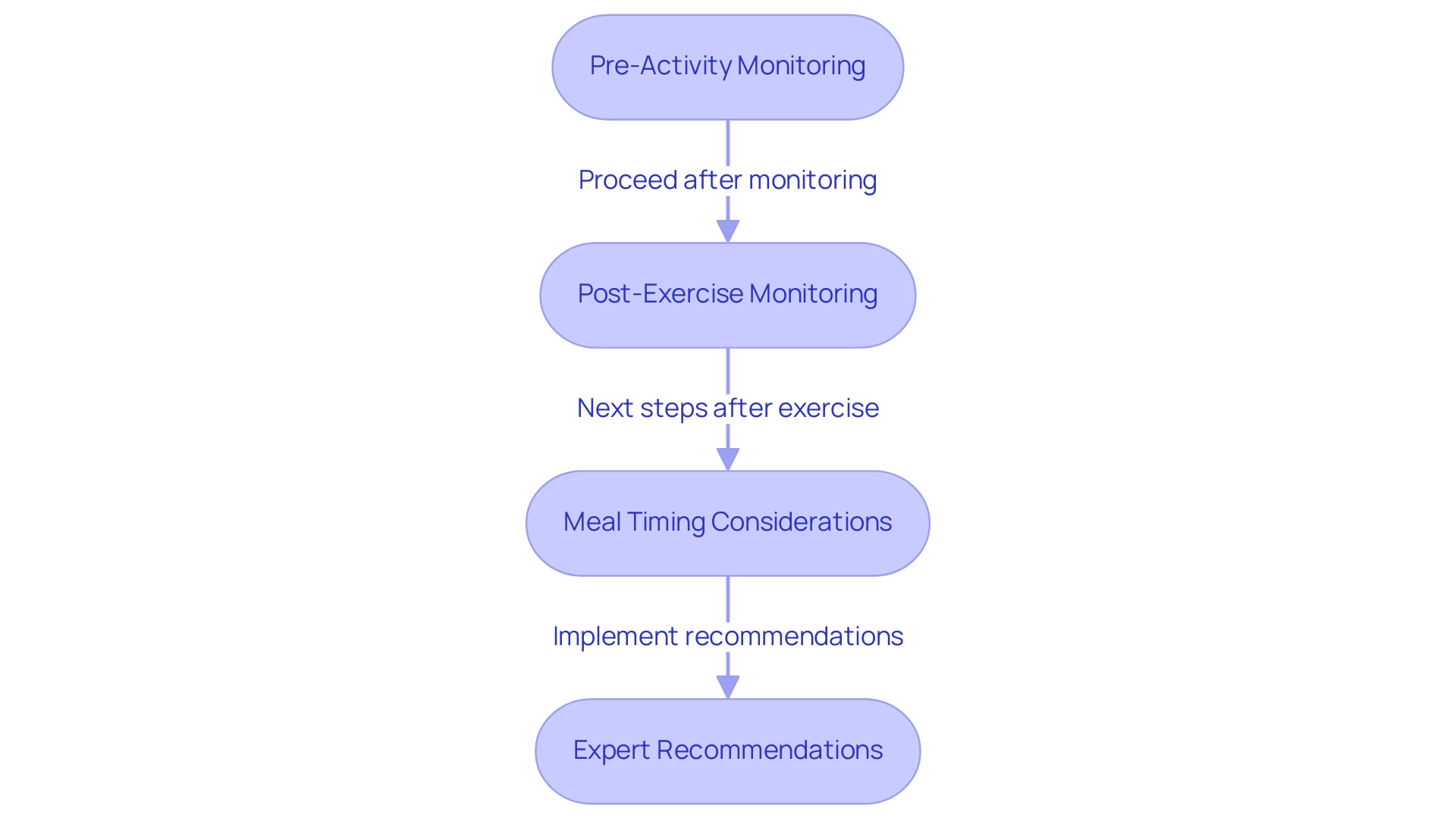
Timing Your Exercise for Optimal Blood Sugar Control
Scheduling your physical activity can significantly impact your glucose management, making it vital to approach your workouts with a thoughtful strategy.
- Pre-Activity Monitoring: It’s important to check your glucose levels before starting your workout. If your levels are too low, a light snack can help prevent hypoglycemia, ensuring you have the energy needed for your routine. Did you know that engaging in 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week can reduce the occurrence of diabetes by 46%? This highlights how crucial regular physical activity is in managing glucose levels. Consider starting a walking regimen as outlined in the Integrative Wellness Center’s manual, which encourages assessing your fitness status and setting realistic goals.
- Post-Exercise Monitoring: After exercising, tracking your glucose readings is essential, as they can drop significantly. Monitoring your levels every 1-2 hours post-exercise allows you to respond quickly to any changes. Implementing strategies to prevent exercise-induced hypoglycemia—like adjusting insulin doses or carbohydrate intake—is vital for safely integrating physical activity into your diabetes management. The American Diabetes Association notes that individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes face a two to six-fold increase in morbidity and early mortality from cardiovascular disease, underscoring the importance of diligent glucose management during exercise.
- Meal Timing Considerations: Aim to schedule your workouts about 1-3 hours after meals, when glucose levels are typically higher. This timing can help prevent postprandial spikes and provide a more stable energy source for your workouts. Keeping a record of your glucose levels in relation to your workout times can help you identify trends and refine your routine. Embracing an outdoor lifestyle in San Marcos, CA, by exploring local parks and trails can also enhance your physical activity experience and overall wellness.
- Expert Recommendations: Understanding how your body responds to physical activity is crucial. Adjusting your insulin or carbohydrate intake based on your exercise routine can further optimize your glucose management. Additionally, insights from case studies on exercise-induced hypoglycemia emphasize the importance of careful glucose management before, during, and after physical activity. By prioritizing personalized care and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals like Dr. Jason Shumard, you can take charge of your health and enhance your overall well-being.
Incorporating these practices into your routine not only empowers you to manage your diabetes effectively but also nurtures a proactive approach to your health journey, supported by community wellness programs and a balanced diet rich in local produce.
The Hormonal Response: Why Exercise Can Spike Blood Sugar
During exercise, the body undergoes a complex hormonal reaction that significantly influences glucose concentrations. It’s essential to understand these dynamics for effective management of type 2 diabetes, particularly when monitoring blood sugar levels after exercise. Integrative functional medicine strategies that emphasize holistic health can play a vital role in this process.
- Adrenaline: Released during intense physical activity, adrenaline prompts the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. This can lead to short-term increases in glucose concentrations, especially noticeable in after-exercise blood sugar levels during high-intensity workouts. Many patients find that spikes in after-exercise blood sugar levels can be significant, particularly for those with insulin resistance. This underscores the importance of personalized guidance from experts like Dr. Jason Shumard.
- Cortisol: Often referred to as the stress hormone, cortisol is released during prolonged or high-intensity physical activity. It can elevate blood sugar levels, potentially negating the benefits of exercise on insulin sensitivity, particularly concerning after-exercise blood sugar levels. This effect is especially pronounced for individuals who engage in extended periods of strenuous activity, highlighting the need to monitor after-exercise blood sugar levels. Integrating stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and yoga, into diabetes care can be beneficial.
- Insulin Sensitivity: While regular physical activity is known to enhance insulin sensitivity over time, immediate hormonal responses can sometimes create a temporary counterbalance to after-exercise blood sugar levels. For instance, during the HART-D trial, it was observed that concurrent training significantly reduced HbA1c levels by -0.34% compared to the control group. This emphasizes the importance of organized physical activity routines in achieving improved health outcomes for patients, particularly in the supportive environment of San Marcos, CA.
Management Strategies:
- Monitor Your Body’s Responses: Pay close attention to how your body reacts to different intensities of exercise. This awareness can help you predict fluctuations in glucose levels and adjust your strategy in response to after-exercise blood sugar levels.
- Adjust Carbohydrate Intake: Based on the intensity and duration of your workouts, consider modifying your carbohydrate intake or insulin dosage. Engaging in moderate-intensity aerobic activity has been shown to enhance mood and cognitive function, which can indirectly assist in managing after-exercise blood sugar levels.
- Utilize Expert Insights: Leverage the knowledge gained from case studies that highlight the role of physical activity in managing glucose levels. For instance, regular moderate-intensity aerobic activity not only aids in glycemic control but also supports after-exercise blood sugar management, while providing mental health benefits that are crucial for overall well-being. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.”
- Integrate Customized Nutrition Plans: Collaborate with healthcare experts to create tailored nutrition plans that enhance your physical activity and support glucose management. Targeted supplements may also be beneficial in optimizing your health outcomes.
- Engage with Community Wellness Programs: Explore local community wellness programs in San Marcos that focus on diabetes education, nutrition, and fitness. These programs can provide invaluable support and resources tailored to your needs.
By comprehending the hormonal reactions to physical activity and applying these management techniques, individuals can more effectively navigate the complexities of glucose regulation. This leads to improved after-exercise blood sugar levels, enhanced health outcomes, and a stronger sense of empowerment in their diabetes management journey.
Practical Strategies for Managing Blood Sugar After Exercise
To effectively manage blood sugar levels after exercise, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. Have you ever noticed how dehydration can lead to increased glucose levels? It’s essential to drink plenty of water before, during, and after your workout. In 2025, studies indicate that proper hydration significantly helps in maintaining stable glucose levels, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Embracing the outdoor lifestyle in San Marcos, CA, allows for enjoyable hydration opportunities, such as drinking infused water or herbal teas while exercising in the area’s beautiful parks and trails.
- Nutrition: Post-exercise nutrition plays a vital role in recovery and glucose stabilization. Aim to consume a balanced snack that includes both carbohydrates and protein within 30 minutes after exercise, as blood sugar levels can be affected. This combination aids in restoring energy reserves and assists in regulating glucose levels. Many individuals find that prioritizing post-workout nutrition leads to improved blood sugar levels along with enhanced overall health. Incorporating local produce from San Marcos, such as avocados and berries, into your post-exercise meals can enhance nutritional value and support diabetes management.
Monitoring your glucose readings is crucial to comprehend your body’s distinct reactions after exercise. This practice enables prompt modifications to your management strategy, ensuring that you sustain ideal glucose concentrations. Engaging with community wellness programs in San Marcos can provide additional support and resources for effective monitoring and management.
- Structured Walking Program: To initiate a walking program, assess your current fitness status and establish realistic goals, such as committing to a daily walk of 10-15 minutes. Gradually increase both the duration and frequency of your walks over time. Tracking your progress using a journal or an app can help maintain motivation and allow you to celebrate your achievements along the way.
Additional Tips:
- Keep fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice, readily available for quick recovery if your blood sugar drops too low.
- Include a gradual cool-down phase following intense workouts to assist in stabilizing glucose concentrations, as sudden stopping of activity can result in fluctuations in glucose.
It’s important to recognize that women with type 2 diabetes often face unique challenges, including a more pronounced limitation in cardiorespiratory fitness compared to men. Therefore, tailored strategies are essential for effective management. By concentrating on hydration, nutrition, monitoring, and an organized walking regimen, individuals with type 2 diabetes can effectively regulate their after-exercise blood sugar levels, leading to enhanced health and well-being.
As Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” This holistic approach, along with the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, supports a comprehensive management plan for type 2 diabetes.
Personalizing Your Approach: Tailoring Exercise to Your Blood Sugar Needs
Customizing your physical activity method is crucial for managing after-exercise blood sugar levels and ensuring efficient glucose control in people with type 2 diabetes. It’s important to recognize that everyone’s body responds differently to exercise. Here are some important strategies to consider:
- Evaluate Personal Reactions: Regularly observe how different forms of physical activity affect your glucose levels. This self-assessment will help you identify which activities yield the best results for your body. For example, many people find that aerobic activities such as walking or cycling reduce their glucose levels more effectively than strength training.
- Consult Professionals: Collaborate with healthcare providers or diabetes educators to develop a personalized fitness plan tailored to your specific health status and objectives. Their expertise can guide you in selecting appropriate activities and setting realistic targets. With the rise of artificial intelligence platforms, personalized health programs can now analyze your genetics and lifestyle habits, further enhancing your fitness strategy.
- Adjust as Needed: Flexibility is crucial. Be ready to adjust your workout schedule according to daily glucose levels and general well-being. For instance, if you notice that your blood sugar levels increase after a specific workout session, consider modifying the intensity or length of that activity.
Personalization Strategies:
- Try different forms of physical activity, such as resistance training, yoga, or even leisure pursuits like pickleball, which has experienced a rise in popularity with 36.5 million participants in the U.S. This trend indicates an increasing enthusiasm for outdoor fitness activities that can be enjoyable and advantageous for managing after-exercise blood sugar levels.
- Consider aspects such as the time of day, meal timing, and stress when organizing your workouts. Research indicates that 34.3% of Americans diagnosed with diabetes are physically inactive, highlighting the need for tailored approaches that encourage regular activity. The U.S. allocates around $379.9 billion for diabetes management, underscoring the significance of effective physical activity strategies.
Real-Life Examples:
- Consider a patient who incorporated functional fitness into their routine, focusing on movements that mimic everyday activities. This method not only enhanced their strength and balance but also resulted in a notable decrease in their HbA1c values, showcasing the efficacy of tailored fitness programs. Dr. Jason Shumard’s holistic approach, as exemplified in his transformative 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, empowers individuals to reclaim their health and improve their quality of life.
- This groundbreaking program is helping thousands stabilize their glucose levels without a dependency on insulin and prescription drugs, alleviating anxiety about potential complications and enhancing overall energy levels. By understanding and tailoring your exercise regimen to your unique needs, you can achieve better blood sugar control and enhance your overall health. The commitment to personalized care, as exemplified by Dr. Jason Shumard’s methodologies, fosters an environment where patients can thrive.
Conclusion
Incorporating exercise into the management of type 2 diabetes offers a wonderful opportunity for individuals to take charge of their health. It’s essential to understand how different types of physical activity can influence blood sugar levels, allowing individuals to customize their routines for optimal glucose management. Aerobic exercises, resistance training, and anaerobic workouts each present unique benefits and challenges that can significantly impact insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake.
It’s important to recognize that the timing of exercise plays a crucial role in blood sugar control. By monitoring levels before, during, and after physical activity, individuals can make informed decisions about their routines, ensuring both safety and effectiveness. Many patients find that personalized strategies, which take into account individual responses to exercise, can enhance their outcomes, leading to improved health and well-being.
Ultimately, embracing a holistic approach that combines exercise with proper nutrition, community support, and education empowers individuals to reclaim their health. By engaging with the insights and strategies outlined in this article, those living with type 2 diabetes can navigate their health journeys with confidence and purpose. Connecting with local resources and wellness programs, such as those in San Marcos, CA, fosters a supportive environment that encourages sustained lifestyle changes and better management of blood sugar levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does physical activity affect glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes?
Physical activity encourages muscles to require additional glucose for energy, leading to a reduction in glucose concentration. This effect can last for several hours after exercise.
Why is it important to monitor glucose levels during physical activity?
Careful observation of glucose levels before, during, and after workouts is crucial to mitigate the risks of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, ensuring a secure and productive workout experience.
What are the benefits of consistent physical activity for individuals with type 2 diabetes?
Consistent physical activity improves glucose absorption by muscles and enhances insulin sensitivity, which is vital for maintaining stable glucose levels.
What role does the community of San Marcos play in promoting physical activity for diabetes management?
San Marcos offers beautiful parks and trails that provide an ideal setting for regular physical activity, encouraging individuals to incorporate exercise into their daily routines.
How does sedentary behavior relate to the risk of developing type 2 diabetes?
Statistics indicate that every additional hour of sedentary activity beyond eight hours per day correlates with a 1% increase in the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
What is the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, and how does it help participants?
The program focuses on education, tailored care, and organized physical activity components, helping participants improve their glucose levels and encouraging an outdoor lifestyle for better health.
What types of exercise are beneficial for managing blood sugar levels?
Aerobic exercises (like walking and cycling) generally reduce blood sugar levels, while anaerobic exercises (like HIIT and weightlifting) may cause temporary spikes. Resistance training is beneficial for building muscle mass and improving insulin sensitivity over time.
How can aerobic exercise impact postprandial hyperglycemia?
Combining aerobic activity with pharmacologic therapies can lead to a notable reduction in postprandial hyperglycemia, enhancing diabetes management.
What should individuals consider when incorporating resistance training into their routine?
While resistance training is beneficial for long-term glucose control, it may cause short-term elevations in blood sugar levels. It’s important to balance it with cardiovascular activities and monitor blood sugar levels closely.
What is the significance of a personalized approach to physical activity in diabetes management?
Understanding how different types of physical activity affect individual health profiles allows for customized management strategies, which are crucial for effective diabetes control.