Overview
Managing diabetes can be a challenging journey, and understanding the tools available is crucial. This article explores the key differences between A1C and average glucose measurements, shedding light on their unique roles in your health management. A1C offers a reliable overview of blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, helping you see the bigger picture of your long-term control.
On the other hand, average glucose readings provide immediate insights into your daily fluctuations. This real-time information empowers you to make informed decisions about your health management strategies. It’s important to recognize that both measurements serve vital purposes, and together, they can guide you toward a healthier lifestyle.
Many patients find that combining these insights helps them feel more in control of their diabetes. By understanding how these measurements work, you can take proactive steps in your health journey. Remember, you are not alone in this; support is available, and taking action today can lead to a brighter tomorrow.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, it’s important to recognize that understanding the intricacies of blood glucose metrics can feel overwhelming. Many patients struggle with this journey, yet grasping these concepts is paramount for achieving optimal health outcomes. Two critical measures—A1C and average glucose—serve distinct yet complementary roles. A1C provides a long-term snapshot of blood sugar control, while average glucose offers immediate insights into daily fluctuations.
As diabetes affects millions and healthcare costs soar, mastering these metrics is not just beneficial, but essential for effective self-management. It’s natural to feel uncertain, but by learning about these measurements, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions. This knowledge can ultimately help you reclaim your well-being, transforming your health journey into one of hope and resilience.
As you navigate your path, remember that you are not alone. Understanding the interplay between A1C and average glucose can guide you towards a healthier future. You have the strength to take charge of your health, and with the right tools, you can thrive.
Define A1C and Average Glucose: Key Metrics in Diabetes Management
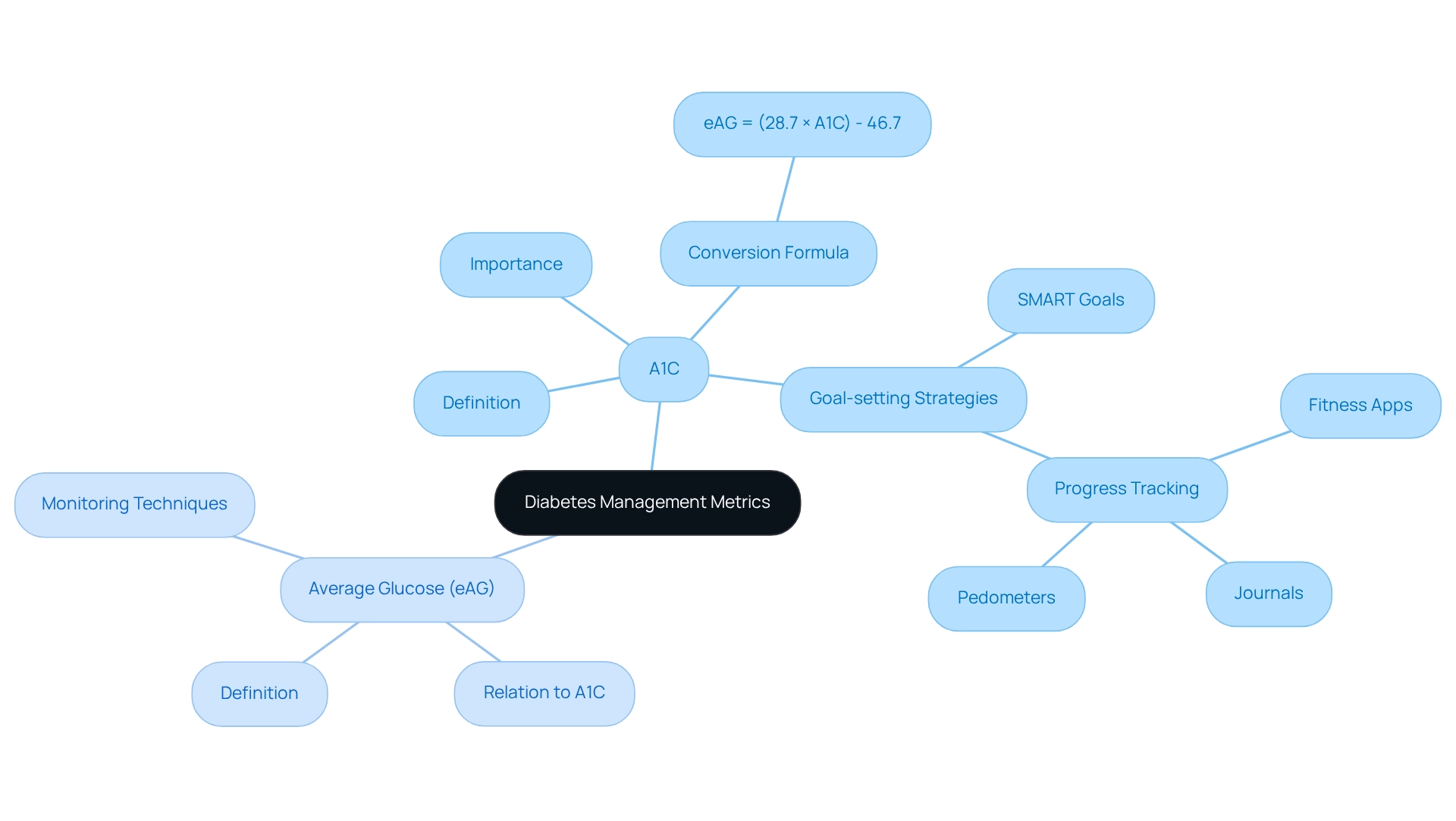
A1C, or hemoglobin A1C, is a vital blood test that helps you understand your typical blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, allowing for comparison in A1C vs average glucose, expressed as a percentage. For example, an A1C of 7% indicates that 7% of hemoglobin molecules are glycated, reflecting elevated blood sugar levels. This metric is crucial for assessing long-term blood sugar management in individuals with diabetes.
On the other hand, mean blood sugar—often referred to as estimated mean blood sugar (eAG)—translates A1C results into a more relatable format, typically measured in mg/dL. The conversion formula is:
eAG = (28.7 × A1C) - 46.7
This calculation provides a daily average of blood sugar levels, helping you connect your A1C results with your daily monitoring practices, and understanding the relationship between A1C vs average glucose is essential for effective diabetes management. Regularly monitoring these metrics is particularly important, especially considering that 8.0% of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes have a non-HDL level of 190 mg/dL or higher, which can complicate diabetes management. Additionally, typical medical costs for individuals with diagnosed diabetes are 2.6 times greater than for those without, underscoring the financial implications of effectively managing A1C vs average glucose levels.
To enhance your management strategies, consider adopting structured goal-setting methods, such as SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. For instance, you might aim to reduce your A1C by a certain percentage within a defined timeframe or gradually increase your daily physical activity. Utilizing tracking methods like fitness apps, journals, and pedometers can further support this journey. However, it’s important to recognize that there can be systematic negative relationships between goal achievement and goal difficulty, highlighting the need for appropriately challenging goals. Regularly reviewing your progress not only fosters accountability but also allows you to adapt your goals in response to changing health conditions.
By providing you with actionable insights and practical resources, the Integrative Wellness Center creates a nurturing environment where you can reclaim your health and well-being. This emphasizes the importance of understanding and managing A1C and average sugar levels, guiding you toward a healthier future.
Explore the Importance of A1C and Average Glucose in Diabetes Care
A1C plays a crucial role in diagnosing diabetes and evaluating long-term glucose control, especially when comparing A1C vs average glucose, serving as a benchmark for healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of an individual’s diabetes management plan. It’s important to recognize that regular A1C testing reveals trends in blood sugar control, enabling timely adjustments to treatment strategies. In fact, research suggests that consistent monitoring of A1C levels can significantly enhance outcomes for individuals, as it enables proactive management of diabetes.
Transformative experiences at Dr. Jason Shumard‘s Functional Medicine Center highlight the effectiveness of this approach. One individual shared, “I lost 55 lbs. My A1C started at 9.1 after 8 months; it is now 5.7.” Another noted, “I feel so much better… I lost a lot of weight, have more energy, and feel great. I am not depressed anymore and I don’t need my meds anymore!” These testimonials underscore the potential for holistic care to reverse the effects of type 2 diabetes and enhance overall well-being. The personal attention from Dr. Shumard and the cleansing program were pivotal in these transformations.
Many patients find that typical blood sugar provides a clearer perspective on daily sugar levels, enabling them to comprehend how their everyday behaviors—like food choices and exercise—affect their overall sugar management. By carefully tracking typical blood sugar levels, individuals can make educated choices about their daily management plans, which is essential for attaining improved health results. Recent advancements in diabetes management, including continuous glucose monitoring, have further improved the ability to track average glucose levels, motivating individuals to take greater responsibility for their health.
The significance of A1C vs average glucose in diabetes management is emphasized by expert views, which underscore its role in guiding treatment choices and enhancing education for individuals. Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By offering individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where people can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to enhanced quality of life and decreased dependence on conventional medical interventions.” Case studies have indicated that individuals who actively participate in tracking both A1C and mean sugar levels, particularly in the context of A1C vs average glucose, achieve more positive diabetes management results. Furthermore, statistics indicate that the median county-level incidence of diagnosed diabetes was 9.7 per 1,000 people in 2004 and decreased to 9.0 per 1,000 people in 2020, highlighting the ongoing need for effective management strategies.
As the landscape of diabetes care evolves, understanding the relationship of A1C vs average glucose remains crucial for effective healthcare and long-term health management. The findings largely reflect treatment and control in individuals with type 2 diabetes, reinforcing the significance of these metrics in managing the condition.
Compare A1C and Average Glucose: Calculation, Interpretation, and Clinical Relevance
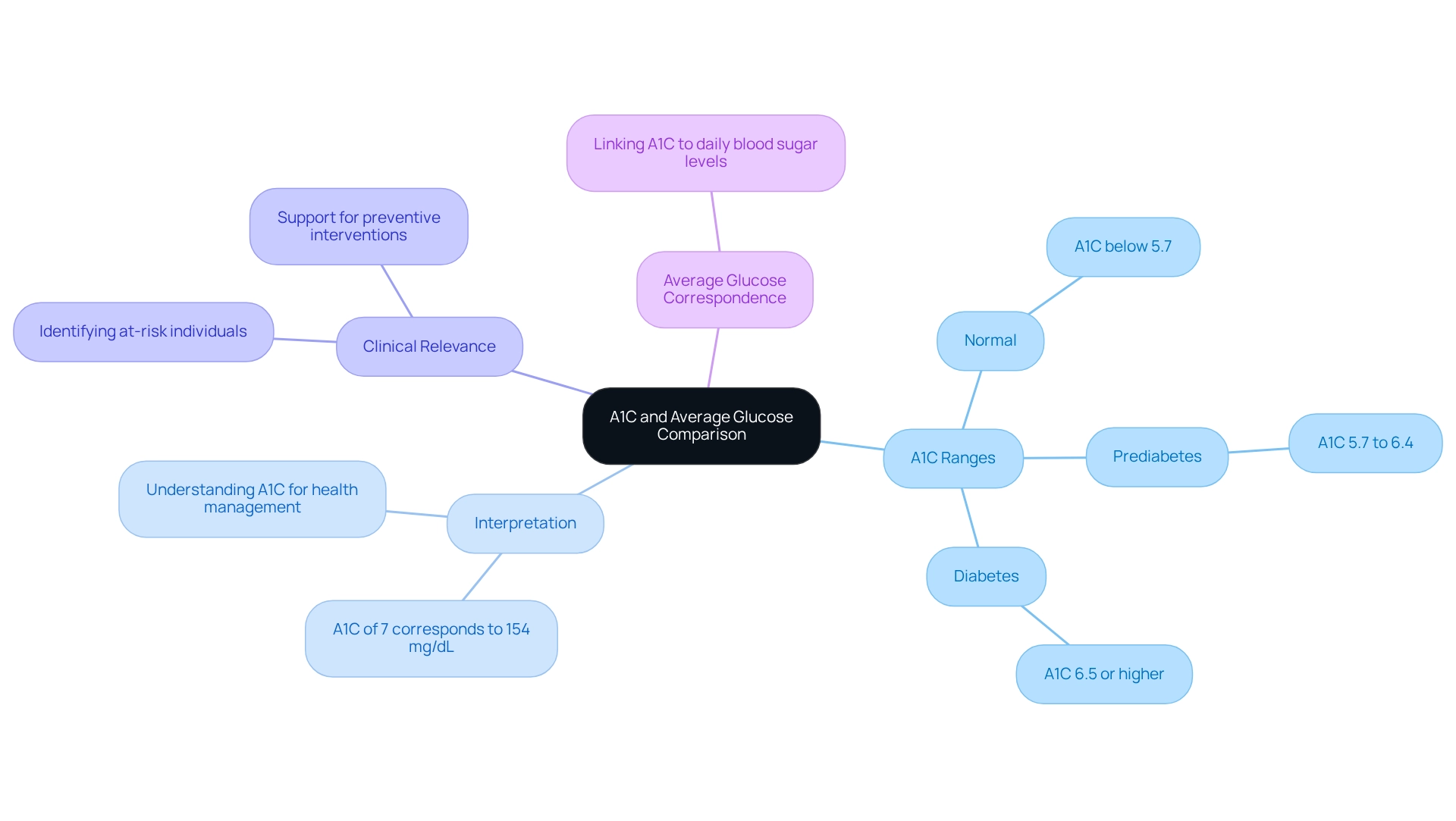
The A1C test, obtained from a blood sample, indicates typical blood sugar levels over the last two to three months. Understanding this test can feel overwhelming, but it’s essential for managing your health. Here’s a simple breakdown of what the A1C results mean:
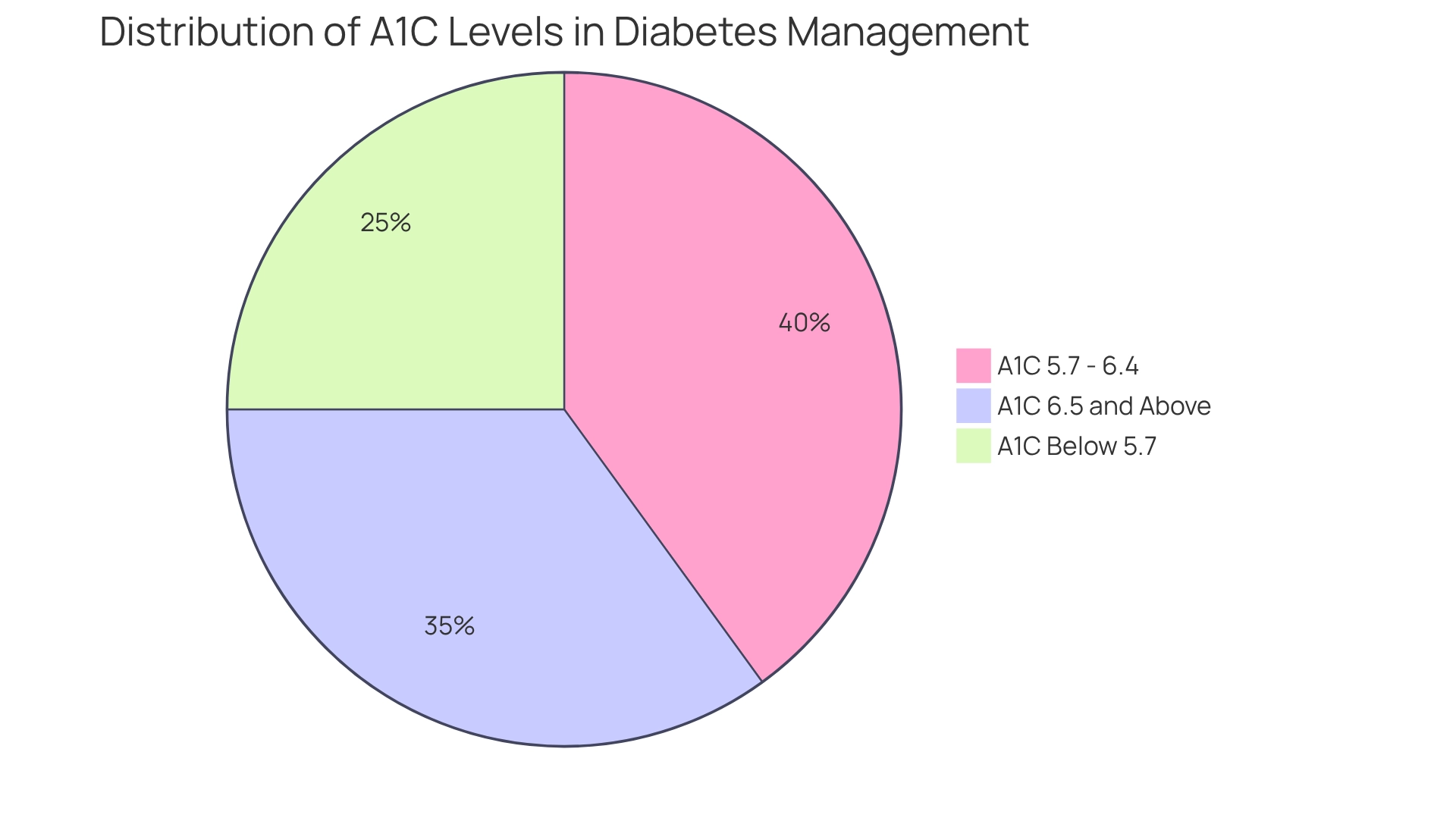
- An A1C below 5.7% is considered normal.
- A range of 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes.
- An A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diabetes diagnosis.
Many patients find it helpful to understand the differences in A1C vs average glucose by relating their A1C results to daily blood sugar levels. For instance, an A1C of 7% corresponds to an estimated blood sugar level of roughly 154 mg/dL. This perspective can make the numbers feel more tangible and understandable.
Clinically, the A1C test serves as a vital tool for long-term tracking of diabetes control, while typical blood sugar levels assist in daily decision-making regarding diet and medication. This dual approach provides a comprehensive understanding of sugar regulation, making the comparison of A1C vs average glucose essential and complementary in diabetes care.
Recent findings highlight the importance of A1C in identifying individuals at risk, which supports preventive interventions. With 13.2% of the population affected by diabetes from 2017 to 2020, grasping these metrics is crucial for effective management and improved health outcomes.
As diabetes continues to rise, especially among vulnerable populations, the clinical relevance of A1C vs average glucose measurements becomes increasingly significant. The results from a case study on public health implications of diabetes risk emphasize the necessity of using A1C as a tool for identifying those at risk. This aligns with the initiatives at Integrative Wellness Center to promote education and empowerment. Dr. Jason Shumard stresses the importance of personalized functional medicine approaches, stating, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, we foster an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” This commitment to safe, effective, and lasting solutions for chronic illnesses, including tailored nutrition and lifestyle changes, is essential for effective diabetes management. If you’re interested in learning more about how Dr. Shumard can help you restore your health, please call Integrative Wellness Center at 858-564-7081.
Evaluate the Pros and Cons of A1C and Average Glucose Measurements
Evaluate the Pros and Cons of A1C and Average Glucose Measurements
Pros and Cons of A1C Measurements
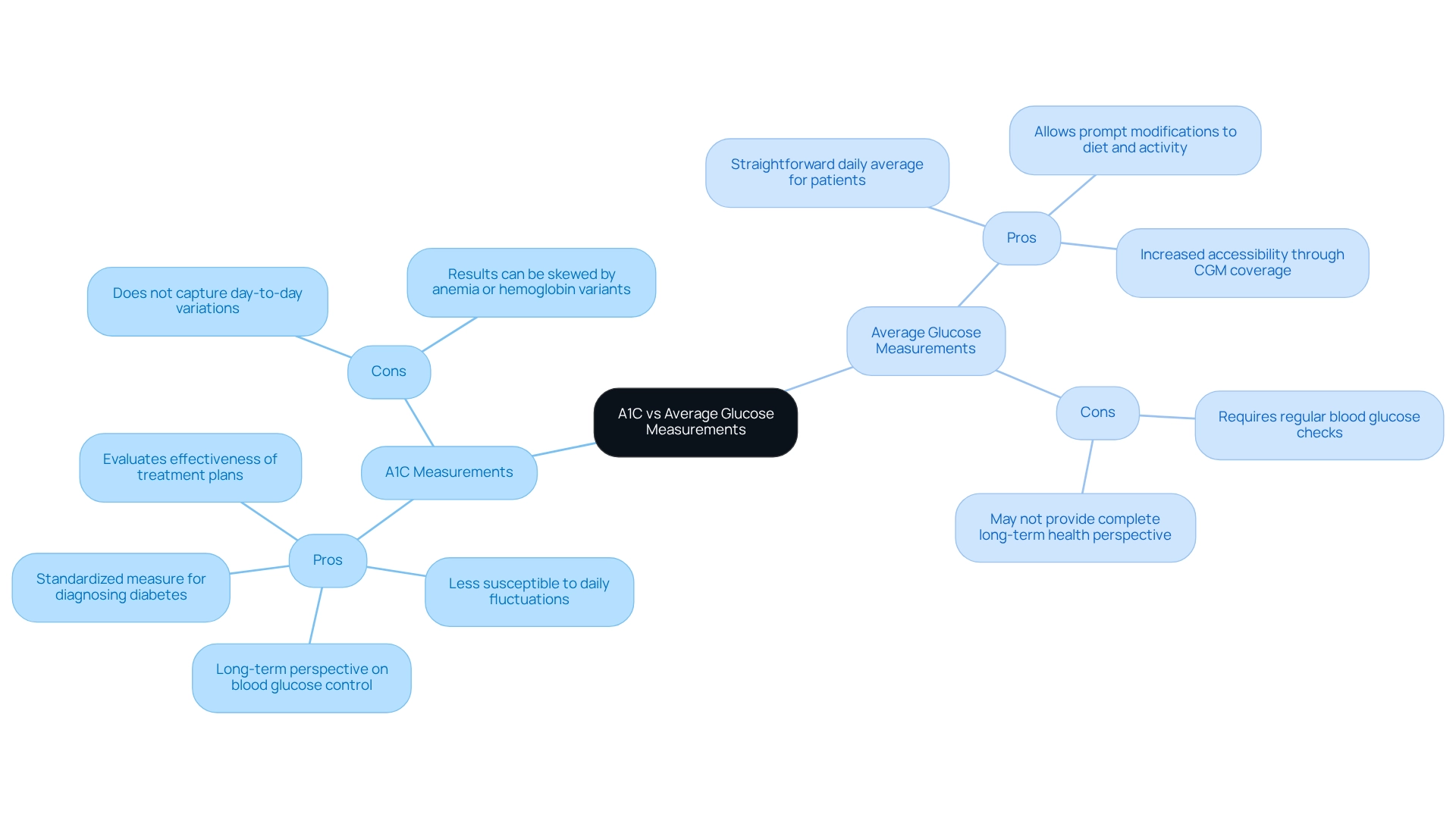
Pros:
- A1C provides a long-term perspective on blood glucose control, reflecting average levels over the past two to three months.
- It is less susceptible to daily fluctuations, making it a reliable metric for assessing overall diabetes management.
- A1C is instrumental in diagnosing diabetes and evaluating the effectiveness of treatment plans, offering a standardized measure that is widely accepted in clinical practice.
Cons:
- A1C does not capture day-to-day variations in blood glucose, which can be critical for immediate management decisions.
- Factors such as anemia or hemoglobin variants can skew results, potentially leading to misinterpretations of an individual’s glycemic control.
Pros and Cons of Average Glucose Measurements
Pros:
- Average glucose readings provide a straightforward daily average that patients can easily understand, facilitating better self-management.
- This approach permits prompt modifications to nutrition and physical activity, enabling individuals to react to their blood sugar levels instantly.
- The growing variety of health plans offering ongoing blood sugar monitoring (CGM) coverage emphasizes the changing environment of diabetes management, enhancing accessibility for individuals.
Cons:
- Effective average glucose monitoring necessitates regular blood glucose checks, which can be burdensome for some patients.
- While beneficial for daily oversight, typical blood sugar readings may not deliver the complete perspective that A1C vs average glucose provides for long-term health results.
It’s important to recognize that integrating comprehensive lifestyle approaches can greatly influence the accuracy of both A1C and average sugar assessments. Engaging in regular outdoor exercise, such as hiking or walking in San Marcos, enhances insulin sensitivity and improves overall blood sugar control. Additionally, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, like avocados and berries, supports better glycemic management. Many patients find that community wellness initiatives, like those provided by local health organizations, offer vital assistance and resources, aiding them in understanding how to interpret their blood sugar readings in relation to their daily activities and dietary choices.
In a recent case study titled “Conclusion on CGM Efficacy,” it was found that CGM is linked to improved HbA1c and time in range results compared to traditional self-monitoring blood sugar (SMBG) methods. This highlights the benefits of average sugar measurements in offering prompt feedback for diabetes management.
Furthermore, specialist panelists have observed that the pharmacy channel assists individuals who cannot receive delivery from durable medical equipment (DME) providers, especially for those encountering access difficulties due to diverse situations.
Consistently examining blood sugar information can assist individuals in recognizing ‘Bright Spots’ and ‘Landmines’ in their management, improving their capacity to make informed choices regarding their care.
In conclusion, the comparison of A1C vs average glucose measurements is crucial for long-term monitoring and diagnosis, while average glucose readings play a vital role in daily management and immediate feedback. Understanding the strengths and limitations of both methods, alongside holistic lifestyle strategies, can help patients make informed decisions about their diabetes care.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of A1C and average glucose is essential for effective diabetes management. It’s important to recognize that A1C serves as a vital long-term measure, reflecting average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, while average glucose provides immediate insights into daily fluctuations. Together, these metrics empower you to make informed decisions about your health, allowing for proactive adjustments to treatment plans and lifestyle changes.
Many patients find that the significance of these measurements is underscored by their role in improving outcomes. Regular monitoring not only aids in diagnosing diabetes but also facilitates the identification of trends that inform clinical decisions. As evidenced by transformative patient experiences, committing to understanding and managing these metrics can lead to remarkable improvements in health and well-being.
Ultimately, the journey toward optimal diabetes management is one of empowerment and resilience. By leveraging the strengths of both A1C and average glucose measurements, you can take charge of your health and work towards better outcomes. This holistic approach, combined with personalized support and actionable insights, fosters an environment where you can reclaim your health, paving the way for a brighter and healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is A1C and why is it important?
A1C, or hemoglobin A1C, is a blood test that indicates average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is expressed as a percentage and is crucial for assessing long-term blood sugar management in individuals with diabetes.
How is mean blood sugar related to A1C?
Mean blood sugar, or estimated mean blood sugar (eAG), translates A1C results into a more relatable format measured in mg/dL. The conversion formula is eAG = (28.7 × A1C) – 46.7, which helps connect A1C results with daily blood sugar monitoring.
Why is it important to monitor A1C and average glucose levels?
Regular monitoring of A1C and average glucose levels is essential for effective diabetes management. It helps individuals understand their blood sugar control and make necessary adjustments to their management strategies.
What are the financial implications of managing A1C levels in diabetes?
Individuals diagnosed with diabetes typically incur medical costs that are 2.6 times greater than those without diabetes, highlighting the financial importance of effectively managing A1C and average glucose levels.
What strategies can help in managing A1C levels?
Strategies include adopting structured goal-setting methods like SMART goals (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound), utilizing tracking methods such as fitness apps and journals, and regularly reviewing progress to adapt goals as needed.
What does the statistic about U.S. adults with diabetes and non-HDL levels indicate?
About 8.0% of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes have a non-HDL level of 190 mg/dL or higher, which can complicate diabetes management and underscores the importance of monitoring blood sugar levels effectively.