Overview
This article highlights the crucial steps for accurately converting A1C levels to blood sugar readings, an essential aspect of effective diabetes management.
It’s important to recognize that understanding this conversion can significantly empower individuals to track their blood sugar levels more accurately. This, in turn, facilitates better health outcomes.
Many patients find that by familiarizing themselves with the conversion formula, they can monitor their A1C levels in relation to their daily glucose management more effectively.
This understanding not only aids in tracking but also supports a healthier lifestyle.
Introduction
In the journey of managing diabetes, understanding the A1C test is essential for maintaining your health. This important blood test measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, providing valuable insights into your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It’s vital to recognize that clear thresholds define normal, prediabetes, and diabetes. Your A1C results not only serve as a benchmark for treatment effectiveness but also act as a warning signal for potential complications.
Many patients find that as the prevalence of elevated A1C levels increases among adults, the significance of regular monitoring and informed management strategies becomes clearer. By delving into the complexities of A1C testing, learning how to convert these results to estimated average glucose, and identifying common pitfalls in interpretation, you can empower yourself to take proactive steps toward better health outcomes and an enhanced quality of life. Remember, every small step you take can lead to significant improvements in your well-being.
Understand A1C and Its Role in Diabetes Management
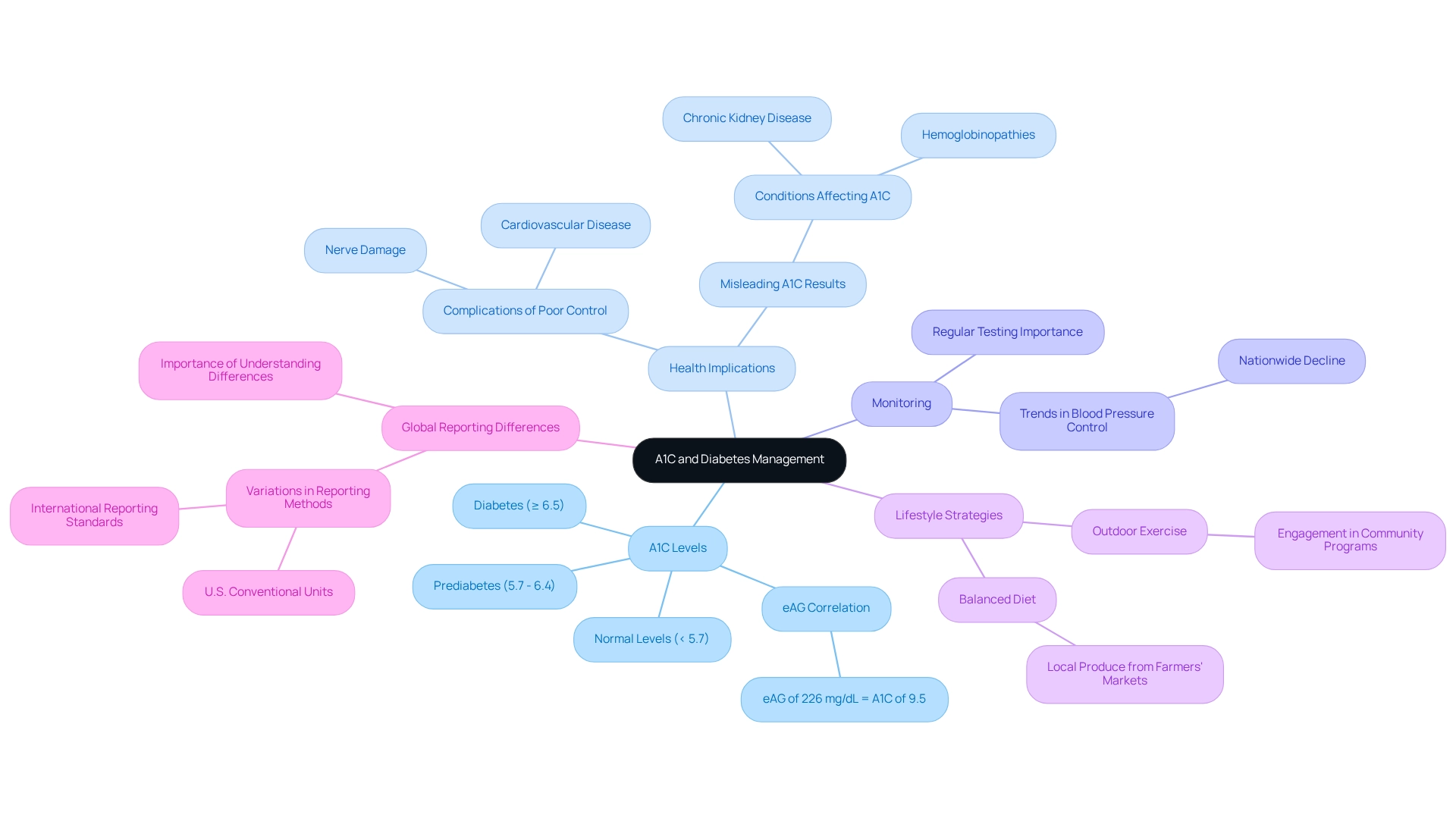
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in your blood, reflecting your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. Understanding this test is crucial for managing your blood sugar and the A1C to sugar conversion effectively. Normal A1C levels are under 5.7%. If your levels fall between 5.7% and 6.4%, it indicates prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms the condition. It’s important to recognize that comprehending your A1C results is essential for both you and your healthcare provider to evaluate the effectiveness of your management plan and make necessary adjustments. Regular monitoring of A1C to sugar conversion is essential in preventing complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease and nerve damage.
Many patients find that staying informed about their A1C levels empowers them to take proactive steps toward better health outcomes. Recent studies reveal that a significant number of adults in the U.S. with high blood sugar have A1C readings exceeding 6.5%, which underscores the need for consistent monitoring and management. Furthermore, an estimated average glucose (eAG) of 226 mg/dL corresponds to an A1C of 9.5%, illustrating the link between A1C values and the A1C to sugar conversion.
Expert opinions emphasize that conditions like chronic kidney disease and hemoglobinopathies can lead to misleading A1C results, making accurate testing and interpretation crucial. Moreover, the decline in blood pressure regulation across the nation reflects broader trends affecting adults with diabetes, highlighting the importance of considering all health indicators in your management strategies.
To enhance your diabetes management, consider integrating holistic lifestyle strategies. Engaging in regular outdoor exercise in San Marcos, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce from farmers’ markets, and participating in community wellness programs can provide valuable support and resources. These approaches not only promote better blood sugar control through A1C to sugar conversion but also contribute to your overall well-being.
Additionally, grasping global differences in hemoglobin A1C reporting is vital for interpreting your results accurately, as various countries may use different methods for reporting these values. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and by staying informed, you can embrace a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Follow the Steps to Convert A1C to Blood Sugar Levels
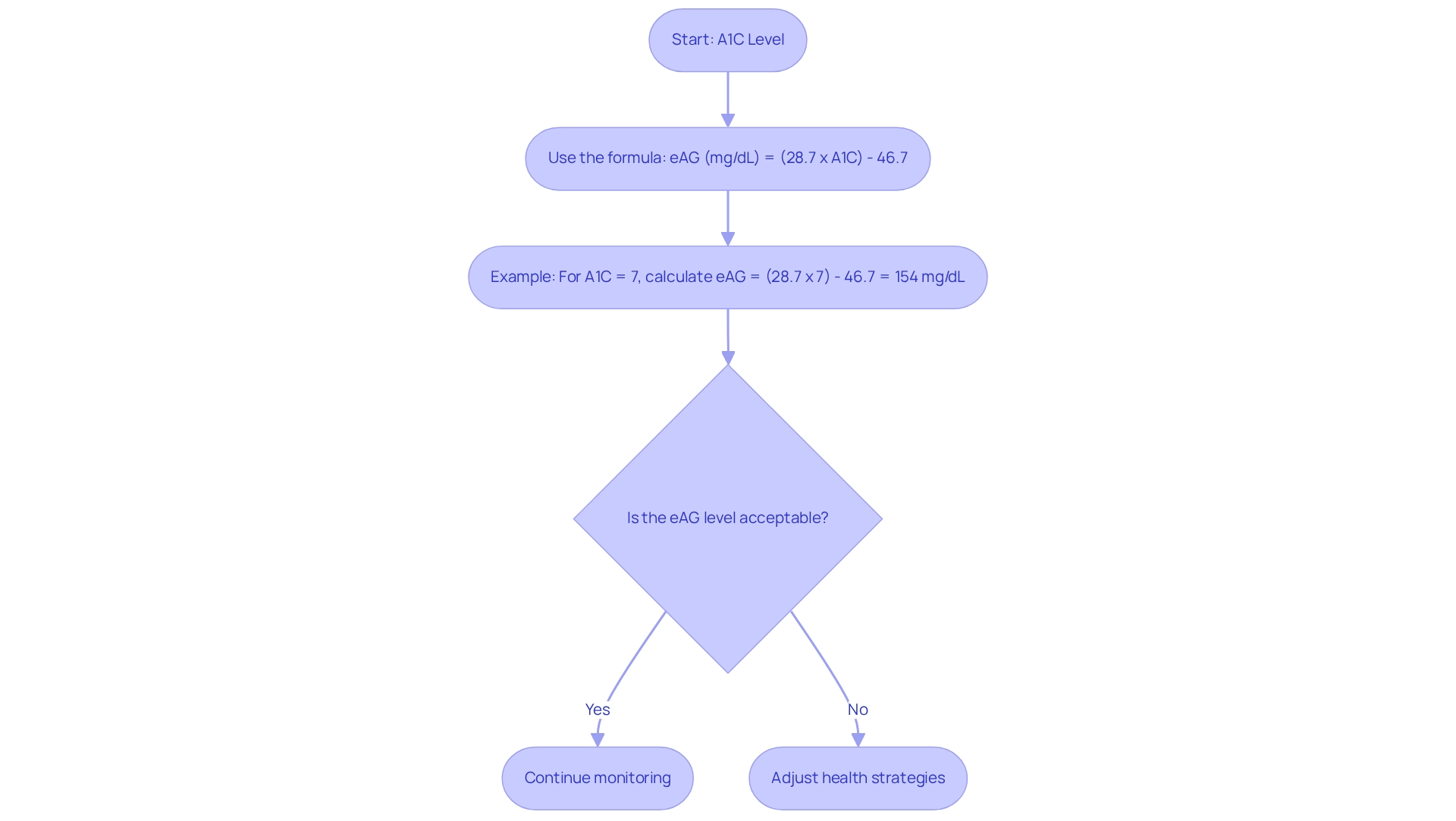
Converting your A1C percentage to estimated average glucose (eAG) levels is an important step in managing your health. You can use the formula:
eAG (mg/dL) = (28.7 x A1C) – 46.7.
For example, if your A1C is 7%, the calculation would be:
eAG = (28.7 x 7) – 46.7 = 154 mg/dL.
This means that an A1C of 7% corresponds to an average glucose level of about 154 mg/dL. Many patients find online calculators on trusted health websites helpful for simplifying this process. Understanding the A1C to sugar conversion is crucial because it connects your A1C results to the daily sugar readings you track at home, ultimately leading to better management of your condition.
Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes that addressing elevated blood sugar levels promptly can help prevent complications. With over 7.2 million cases of diabetes reported in Germany as of 2014, the importance of understanding A1C to sugar conversion cannot be overstated.
Alongside these conversions, implementing effective strategies for monitoring your progress and setting realistic goals can significantly enhance your health management. Have you considered using various tracking methods such as fitness apps, journals, or pedometers to keep an eye on your daily activities and blood sugar levels? For instance, you might set a SMART goal to lower your A1C by 0.5% over the next three months, while tracking your daily steps with a pedometer and logging your meals in a journal. Regularly reviewing your progress not only fosters accountability but also allows for adjustments based on your evolving health needs.
Dr. Shumard’s approach, illustrated in the case study titled “Challenging Traditional Healthcare,” shows how his center attracts patients seeking effective solutions to chronic health issues. By grasping these conversions and actively monitoring your progress, you can take proactive steps toward effectively managing your condition. Additionally, educators stress the significance of eAG in managing blood sugar levels, reinforcing the need for patients to be well-informed about their health metrics.
Troubleshoot Common Issues in A1C Conversion
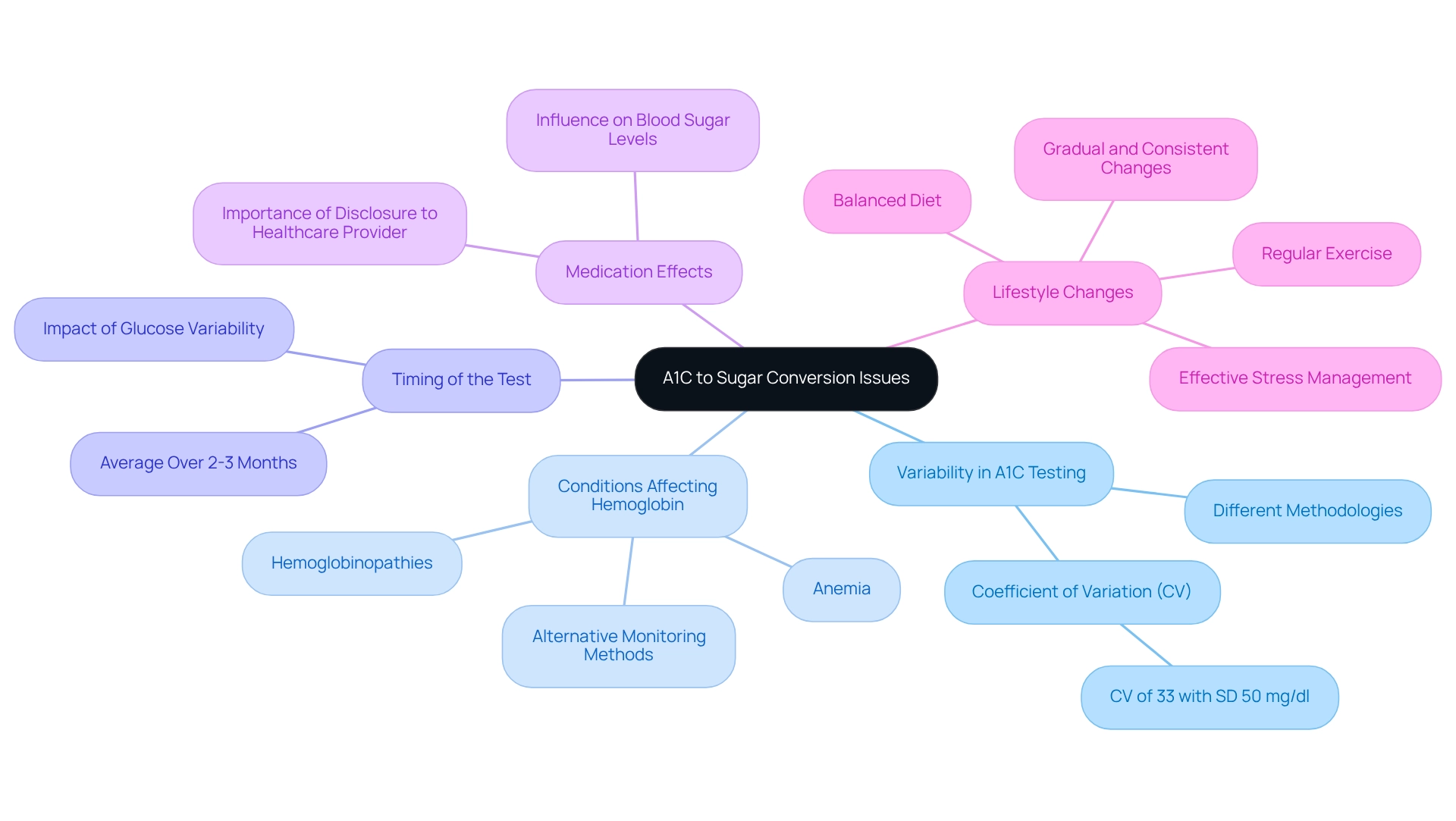
When considering the A1C to sugar conversion, it’s important to recognize that several factors can lead to inaccuracies:
-
Variability in A1C Testing: Different laboratories may use various methodologies for A1C testing, which can result in discrepancies in results. For instance, the coefficient of variation (CV) can be as high as 33% when the standard deviation is 50 mg/dl and the average glucose is 150 mg/dl. It’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to fully understand your specific test outcomes.
-
Conditions Affecting Hemoglobin: Medical conditions such as anemia or hemoglobinopathies can significantly impact A1C results. If you have any of these conditions, many patients find it helpful to discuss alternative monitoring methods with their doctor to ensure accurate diabetes management.
-
Timing of the Test: The A1C test reflects average glucose concentrations over the previous 2-3 months. If your glucose measurements have varied significantly during this time, your A1C may not accurately reflect your current control. Consistent tracking of daily glucose readings can offer a clearer view of your management.
-
Medication Effects: Certain medications can influence both blood sugar levels and A1C results. Always notify your healthcare provider about any medications you are using, as this information is crucial for precise interpretation of your results.
Incorporating lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and effective stress management can profoundly influence your management of blood sugar levels and lead to improved health outcomes. Grasping these elements is crucial for effectively interpreting A1C results and understanding the A1C to sugar conversion, which allows you to make informed choices regarding your health management. Remember, gradual and consistent changes are key to long-term success. For personalized guidance tailored to your unique needs, consider reaching out to Dr. Jason Shumard in San Marcos, CA. Our expert team is dedicated to helping you navigate your diabetes management journey with care and expertise. Schedule Now.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is fundamental for effective diabetes management. It provides crucial insights into average blood sugar levels over the past few months, helping to identify whether you fall within normal, prediabetic, or diabetic ranges. Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential not only for assessing the effectiveness of treatment plans but also for preventing complications that can arise from uncontrolled diabetes. It’s important to recognize that integrating holistic lifestyle strategies—such as a balanced diet and regular exercise—can significantly contribute to better health outcomes.
Many patients find that knowing how to convert A1C results into estimated average glucose levels is a valuable skill. This empowers you to relate lab results to daily blood sugar readings. Coupled with effective tracking methods, this understanding allows for proactive management of diabetes. However, it’s equally important to be aware of potential pitfalls in interpreting A1C results, including variability in testing methods and the influence of certain medical conditions and medications.
In conclusion, staying informed about your A1C levels and their implications fosters a proactive approach to diabetes management. By embracing regular monitoring, making informed lifestyle choices, and understanding the nuances of A1C testing, you can significantly enhance your quality of life and mitigate the risks associated with diabetes. Remember, every step you take toward better management is a step toward a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and what does it measure?
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in your blood, reflecting your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
What are the normal A1C levels and what do different ranges indicate?
Normal A1C levels are under 5.7%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms diabetes.
Why is understanding A1C results important?
Understanding A1C results is essential for both you and your healthcare provider to evaluate the effectiveness of your management plan and make necessary adjustments.
How does regular monitoring of A1C to sugar conversion help with diabetes management?
Regular monitoring of A1C to sugar conversion is crucial in preventing complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease and nerve damage.
What do recent studies indicate about adults in the U.S. and A1C levels?
Recent studies reveal that a significant number of adults in the U.S. with high blood sugar have A1C readings exceeding 6.5%, highlighting the need for consistent monitoring and management.
What is the estimated average glucose (eAG) corresponding to an A1C of 9.5%?
An estimated average glucose (eAG) of 226 mg/dL corresponds to an A1C of 9.5%.
What factors can lead to misleading A1C results?
Conditions like chronic kidney disease and hemoglobinopathies can lead to misleading A1C results, making accurate testing and interpretation crucial.
How can lifestyle strategies enhance diabetes management?
Integrating holistic lifestyle strategies, such as regular outdoor exercise, a balanced diet rich in local produce, and participation in community wellness programs, can support better blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Why is it important to understand global differences in hemoglobin A1C reporting?
Understanding global differences in hemoglobin A1C reporting is vital for accurately interpreting your results, as various countries may use different methods for reporting these values.