Overview
The article focuses on the A1C ADA guidelines for optimal diabetes management, emphasizing the importance of individualized A1C targets based on personal health factors. It supports this by detailing how tailored A1C goals can lead to better health outcomes and reduce complications, highlighting the necessity of regular monitoring, lifestyle changes, and personalized care to effectively manage diabetes.
Introduction
Understanding the A1C test is essential for effective diabetes management, as it serves as a key indicator of blood glucose control over time. This test measures the average blood sugar levels from the past two to three months, providing critical insights that can shape treatment strategies and lifestyle adjustments.
With the rising prevalence of diabetes, especially among specific demographics, the importance of regular A1C monitoring cannot be overstated. The implications of A1C levels extend far beyond mere numbers; they are directly linked to serious health risks and complications.
This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, the American Diabetes Association’s recommendations for optimal A1C targets, and the personalized approaches necessary for managing diabetes effectively. Through a comprehensive examination of A1C levels and their health implications, readers will gain valuable knowledge to empower their diabetes management journey.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Cornerstone of Diabetes Management
The A1C test, commonly referred to as hemoglobin A1C or glycated hemoglobin, is a vital diagnostic tool that measures average blood glucose levels over a span of two to three months. Conducted through a straightforward blood draw, results are reported as a percentage, with higher values indicating inadequate blood sugar control and an increased risk of diabetes-related complications. For individuals managing type 2 blood sugar issues, understanding the A1C test in accordance with the A1C ADA guidelines is crucial, as it provides a comprehensive overview of glucose control and informs necessary treatment decisions and lifestyle modifications.
At the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego, Dr. Shumard emphasizes personalized care tailored to each patient’s needs, empowering them to reverse type 2 conditions through holistic approaches. Recent studies suggest that maintaining an optimal A1C measurement in accordance with the A1C ADA guidelines is vital to decreasing the occurrence of severe complications, highlighting the test’s significance in efficient management of blood sugar. Notably, the incidence rate of diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar among Hispanic adults stands at 6.1 per 1,000, highlighting the need for targeted management strategies in this demographic.
Furthermore, research demonstrates a strong correlation between A1C values and average glucose, with a correlation coefficient of 0.92 (Nathan et al.). The ‘Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC)’ case study demonstrates how tracking A1C readings in accordance with the A1C ADA guidelines can result in better health outcomes for adults with the condition, highlighting the importance of routine A1C testing in effectively managing the illness and reducing anxiety about possible complications. By understanding their A1C results, individuals can feel more in control of their health, reducing worry about the risks of complications and allowing for informed discussions about treatment options that can lead to better management of their condition.
ADA Guidelines for A1C Targets: Key Recommendations for Optimal Management
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) generally advises that most adults with diabetes adhere to the A1C ADA guidelines to maintain an A1C measurement below 7%. However, these targets should be tailored to individual circumstances, considering factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of additional medical conditions. For certain individuals, particularly those who are younger or in better health, a more stringent target of less than 6.5% may be appropriate.
In contrast, older adults with declining cognitive or functional status might be advised to aim for an A1C level of less than 8% to balance the benefits of glycemic control against potential risks. This tailored approach is essential in reducing long-term complications while following the A1C ADA guidelines and honoring the health preferences of each individual. The Integrative Wellness Center emphasizes holistic care and education, which empowers individuals by addressing their concerns and reducing anxiety about developing traumatic and debilitating complications related to blood sugar.
As noted by Rachel Brunner, PharmD, BCPS, ‘The information presented is current as of February 23, 2024. This information is intended as an educational piece and should not be used as the sole source for clinical decision-making.’ Furthermore, with 357,069 views, this article underscores the relevance of these recommendations.
Recent assessments of self-management knowledge among older adults with this condition highlight the need for evaluating their understanding of treatment and health literacy at the onset of care, which facilitates effective and individualized management strategies. This is further supported by the case study titled ‘Assessment of Self-Management Knowledge,’ emphasizing the importance of such evaluations. Furthermore, the Integrative Wellness Center periodically evaluates advanced insulin delivery technologies for older adults with diminishing cognitive or functional abilities to ensure that management strategies are suitably customized, thereby empowering individuals and reducing their concerns about complications.
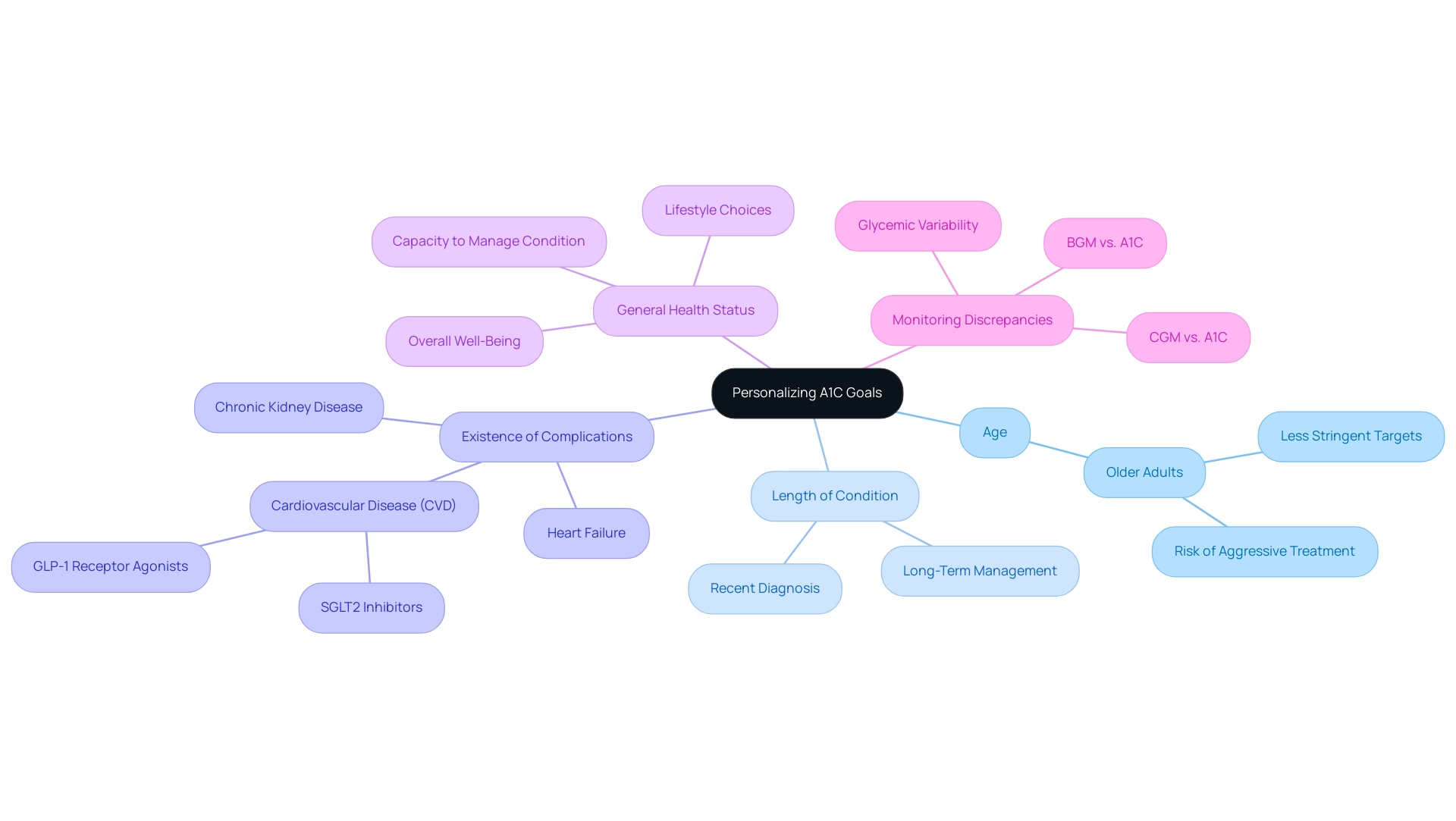
Personalizing A1C Goals: Factors to Consider for Individualized Care
Setting individualized A1C targets according to the A1C ADA guidelines is a complex procedure that requires thoughtful evaluation of different aspects, including the individual’s:
- Age
- Length of condition
- Existence of complications
- General health status
For example, older adults or those with a complex medical history may benefit from less stringent A1C targets, as aggressive treatment could pose significant risks. Furthermore, comprehending the individual’s preferences, lifestyle choices, and capacity to effectively manage their condition is essential in this process.
This personalized method not only promotes attainable A1C goals according to the A1C ADA guidelines but also harmonizes with a comprehensive plan that tackles the underlying factors of the condition, thereby enhancing well-being and potentially reducing the worry that comes with complications. Recent findings suggest that the inclusion of SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1 receptor agonists is advisable for individuals with established cardiovascular disease (CVD), chronic kidney disease, or heart failure, regardless of their current A1C values. Furthermore, it is important to recognize that discordant results between blood glucose monitoring (BGM) or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and A1C can arise from various conditions or glycemic variability, complicating the goal-setting process.
A study presented at the American College of Clinical Pharmacy Virtual Poster Symposium highlighted these complexities, emphasizing the need for a nuanced approach to A1C targets according to the A1C ADA guidelines. As mentioned by David O Meltzer, ‘Personalized care is crucial in managing health conditions, as it enables customized approaches that take into account the distinct situations of every individual.’ This evidence emphasizes the need for a comprehensive approach in managing blood sugar that prioritizes both A1C readings and the broader health context of the patient, integrating holistic methodologies for a more effective treatment pathway.
We begin by reassessing the origin of your diabetes, which is essential in tackling health at the root.
The Health Implications of A1C Levels: Risks and Complications
Poorly managed A1C values can precipitate a range of serious health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage
- Kidney failure
- Vision impairment
Elevated A1C levels are directly linked to vascular and nerve damage, significantly increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Research indicates that chronic hyperglycemia can result in conditions such as diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy, further complicating diabetic health status.
Alarmingly, a hospitalization rate for hypoglycemia has been reported at 2.2 per 1,000 adults with the condition, underscoring the risks associated with inadequate A1C management. According to the case study titled ‘ABCs of Diabetes Management,’ only 11.1% of individuals with the condition meet all established criteria for A1C, blood pressure, cholesterol, and smoking cessation, revealing the challenges faced in achieving comprehensive management.
The necessity of regular monitoring and management of A1C levels is emphasized by the observation that following the A1C ADA guidelines and measuring their stability within individualized target ranges over time is a predictor of risk for major adverse events.
This highlights the critical importance of proactive measures to mitigate complications and enhance overall health among individuals with this condition, especially through the holistic care and education provided at the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego. To empower patients further, the Integrative Wellness Center offers specific treatment options, including:
- Personalized dietary plans
- Exercise regimens
- Stress management techniques
These strategies not only assist in managing A1C values but also seek to reduce anxiety regarding the onset of traumatic and debilitating complications, promoting a sense of tranquility and control over one’s health.
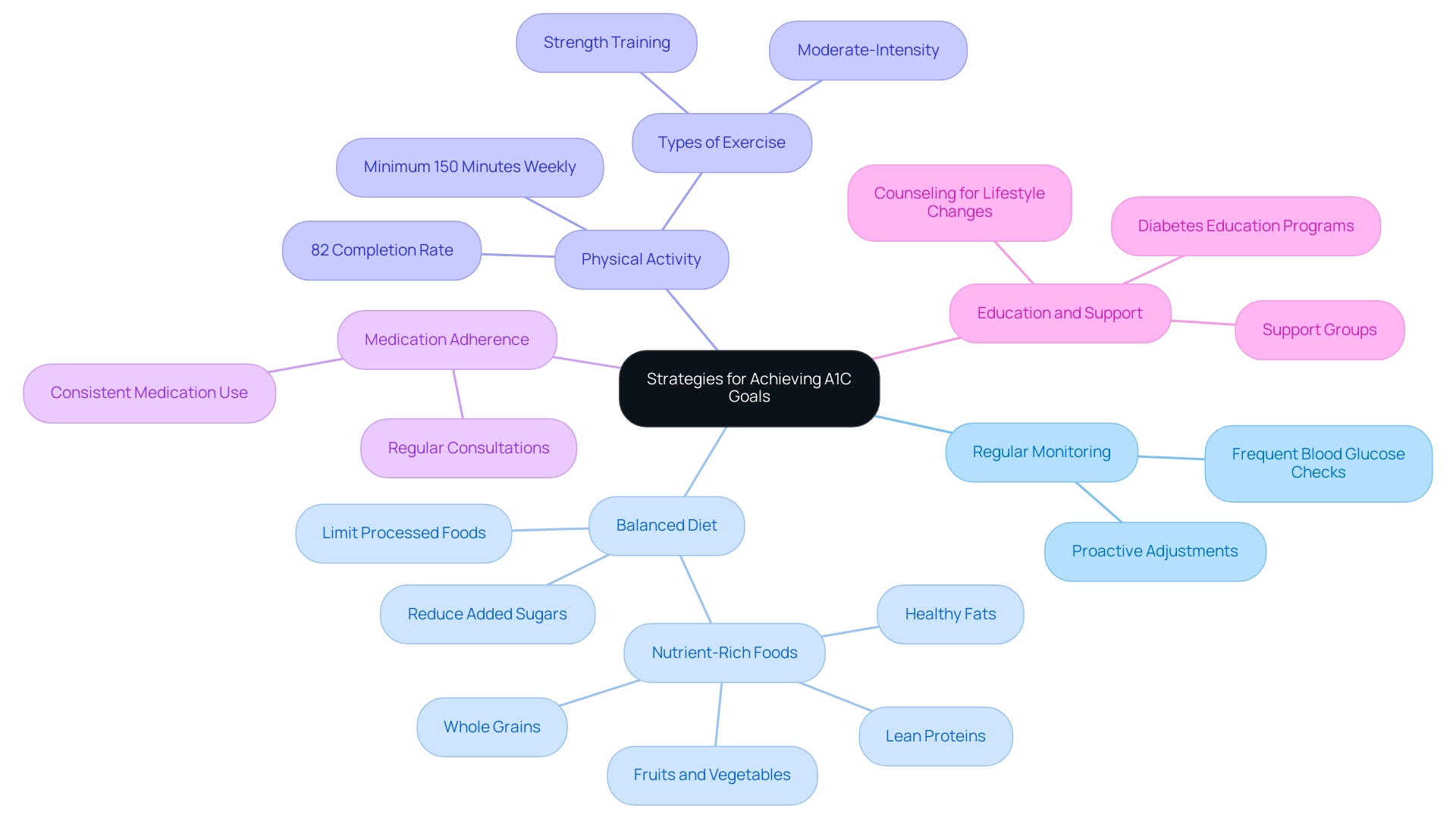
Strategies for Achieving A1C Goals: Practical Tips and Tools
To effectively reach and maintain A1C goals, individuals must adopt a comprehensive strategy that aligns with a1c ada guidelines and encompasses several key components:
-
Regular Monitoring: Frequent blood glucose checks are essential for recognizing patterns and making necessary adjustments. This practice enables individuals to respond proactively to fluctuations in their levels.
-
Balanced Diet: A nutrient-rich diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables is crucial. It is equally important to limit processed foods and added sugars, which can adversely affect glycemic control.
-
Physical Activity: Engaging in a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly is recommended to enhance insulin sensitivity and assist with weight management. A recent study indicated that participants completed 82% of their prescribed exercise sessions over 12 months, highlighting the potential for successful engagement in physical activity.
As noted,
Exercise is a cornerstone of therapy for diabetes-related conditions.
-
Medication Adherence: Consistently following prescribed medications is vital. Regular consultations with healthcare providers can ensure that any necessary adjustments are made to optimize treatment efficacy.
-
Education and Support: Involvement in diabetes education programs and support groups can provide valuable information and motivation, fostering a supportive environment for individuals facing similar challenges.
The significance of lifestyle changes is emphasized by the case study titled ‘Discussion on Lifestyle Modification Impact,’ which examined the relationship between lifestyle changes and glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes who declined further medication. This study found that simple educational interventions on diet and exercise led to significant improvements in glycemic control, suggesting that counseling can motivate patients to adopt healthier lifestyles. By adopting a holistic approach to managing the condition and addressing its root causes, individuals can improve their ability to reach and maintain target A1C levels as outlined in the a1c ada guidelines.
Additionally, addressing the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of diabetes is crucial for emotional well-being. We encourage you to learn more about our holistic regimens at the Integrative Wellness Center, where we focus on empowering your health through comprehensive support. This information is supported by research from institutions such as the Center of Inflammation and Metabolism and the Center for Physical Activity Research at the University of Copenhagen.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing A1C levels is fundamental for individuals living with diabetes. The A1C test serves as a crucial tool in monitoring average blood glucose levels over time, providing insights that guide treatment strategies and lifestyle changes. Adhering to the American Diabetes Association’s recommendations for personalized A1C targets is essential, as these targets vary based on individual health circumstances, age, and the presence of other medical conditions.
Moreover, the health implications associated with poorly managed A1C levels cannot be overlooked. Elevated A1C levels are linked to severe complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney failure
This underscores the necessity for regular monitoring and proactive management. By implementing strategies such as:
- Regular blood glucose checks
- Maintaining a balanced diet
- Engaging in physical activity
- Adhering to prescribed medications
individuals can significantly improve their A1C levels and overall health.
Ultimately, personalized care that addresses both A1C levels and the unique circumstances of each patient is vital. Empowering individuals through education, support, and tailored treatment plans not only fosters better diabetes management but also alleviates the anxiety associated with potential complications. Embracing a holistic approach to diabetes care is key to achieving optimal health outcomes and enhancing quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as hemoglobin A1C or glycated hemoglobin, measures average blood glucose levels over two to three months. It is crucial for assessing blood sugar control and informing treatment decisions, especially for individuals managing type 2 diabetes.
How are A1C test results reported?
A1C results are reported as a percentage, with higher values indicating poorer blood sugar control and a greater risk of diabetes-related complications.
What are the A1C ADA guidelines for adults with diabetes?
The American Diabetes Association recommends that most adults with diabetes maintain an A1C measurement below 7%. However, this target may vary based on individual circumstances such as age and overall health.
What is the significance of maintaining optimal A1C levels?
Maintaining optimal A1C levels is vital for reducing the occurrence of severe complications associated with diabetes, as highlighted by recent studies.
How does the A1C test correlate with average glucose levels?
Research shows a strong correlation between A1C values and average glucose levels, with a correlation coefficient of 0.92.
What tailored A1C targets might be recommended for different individuals?
Younger individuals or those in better health may aim for an A1C level of less than 6.5%, while older adults with declining cognitive or functional status may be advised to aim for less than 8%.
How does the Integrative Wellness Center approach A1C management?
The Integrative Wellness Center emphasizes personalized care and holistic approaches, empowering patients to manage their type 2 diabetes effectively and reduce anxiety about complications.
What role does patient education play in managing diabetes?
Patient education is essential for empowering individuals to understand their A1C results, which helps reduce anxiety about complications and facilitates informed discussions about treatment options.
Why is it important to evaluate self-management knowledge in older adults with diabetes?
Assessing self-management knowledge among older adults is important to ensure effective and individualized management strategies, as highlighted by case studies on health literacy.
What is the relevance of the information presented in the article?
The information is intended for educational purposes and reflects current guidelines as of February 23, 2024. It emphasizes the importance of tailored A1C targets and personalized care in managing diabetes.