Overview
The article outlines effective strategies to lower A1C levels from 6.9 to healthier ranges through dietary changes, regular exercise, stress management, and robust support systems. It emphasizes that a holistic approach—incorporating whole foods, consistent physical activity, mindfulness practices, and community support—can significantly enhance glucose control and overall well-being, thereby addressing the complexities of diabetes management.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses:
- Dietary choices
- Physical activity
- Stress management
- Support systems
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, effective strategies for lowering A1C levels have become more critical than ever. This article delves into:
- Essential nutritional practices
- The pivotal role of regular exercise
- The impact of stress on blood sugar control
It emphasizes the importance of monitoring and support networks. By adopting these evidence-based strategies, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their condition and improving their overall health.
Revamping Your Diet: Key Nutritional Strategies to Lower A1C
To effectively lower your A1C levels and embrace a holistic approach to diabetes management, consider implementing the following dietary strategies while also addressing the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of your disease:
- Focus on Whole Foods: Emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods—such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins—is crucial. These foods generally possess a reduced glycemic index and offer vital nutrients that assist in preventing substantial increases in sugar concentrations, fitting with a comprehensive approach that tackles the underlying factors of the condition.
- Monitor Carbohydrate Intake: It is essential to be aware of carbohydrate consumption. Favor complex carbohydrates, which are digested more slowly, thereby aiding in the maintenance of stable glucose levels. This approach is especially pertinent given the recent findings that highlight the prevalence of diagnosed diabetes at 10.1%, indicating a need for effective dietary management at the Integrative Wellness Center.
- Incorporate Fiber-Rich Foods: Foods high in fiber, such as legumes, nuts, and seeds, can significantly aid in slowing digestion and enhancing sugar control. It is advisable to aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day, as this has been shown to enhance overall glucose metabolism and empower patients in their health journey.
- Limit Sugary Beverages: Replacing sugary drinks with water, herbal teas, or other low-calorie options can assist in reducing overall calorie intake and avert sudden spikes in glucose. This strategy aligns with the need for dietary changes that support sugar management, reinforcing the holistic approach to reversing the condition.
- Plan Balanced Meals: Strive to create balanced meals that combine carbohydrates with proteins and healthy fats. This combination not only encourages fullness but also aids in maintaining steady blood sugar, further bolstering the continuous efforts to stabilize the prevalence rates of blood sugar issues, which have remained constant at 14.3% from August 2021 to August 2023.
Maggie Wilkin, Director of Research and Evaluation for the Public Health Institute’s Center for Wellness and Nutrition, emphasizes the importance of such dietary strategies, stating, “The study’s findings support policies to have health insurers cover ‘food as medicine’ programs.” By adopting these nutritional strategies within a holistic framework, including the concept of ‘food as medicine,’ individuals can effectively manage their A1C readings, ideally reaching an A1C 6.9, and improve their overall health, especially in light of the recent findings indicating a stabilization in diabetes prevalence rates.
The Role of Regular Exercise in Reducing A1C Levels
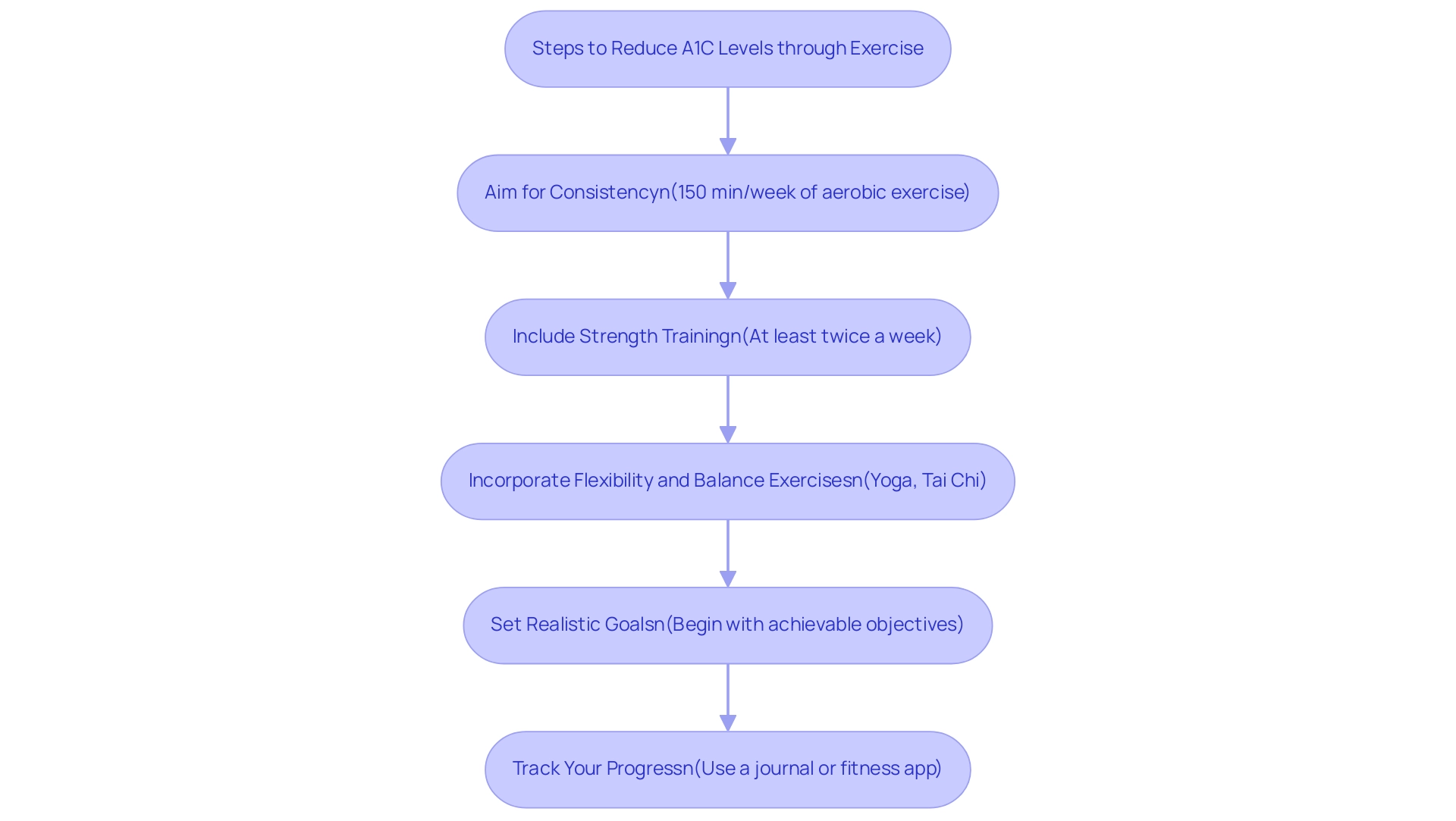
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine can significantly affect your a1c 6.9 levels. Here are some essential recommendations:
-
Aim for Consistency: Strive for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Consistency is essential, as studies show that aerobic exercise of 40–60 minutes per session can significantly enhance glucose levels, with a standardized mean difference of d = −0.59 (95% CI: −0.71 to −0.46, p < 0.05). A meta-analysis by Palta P et al. highlights the positive correlation between regular aerobic exercise and improved glucose management.
-
Include Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week. Increasing muscle mass can enhance insulin sensitivity, which is essential for effective glucose management.
Experts emphasize the benefits of strength training, noting that it plays a critical role in enhancing metabolic health. It’s important to note that while hyperglycemia can be worsened by exercise in type 1 diabetic individuals who are insulin deficient and ketotic, very few persons with type 2 diabetes develop such a profound degree of insulin deficiency.
-
Incorporate Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Activities such as yoga or tai chi enhance flexibility while also promoting relaxation and stress reduction.
These factors are significant, as stress can adversely affect glucose levels.
-
Set Realistic Goals: Begin with achievable objectives and progressively increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. This strategy not only helps maintain motivation but also reduces the risk of injury.
-
Track Your Progress: Utilize a journal or fitness app to log your physical activity, which can enhance accountability and help you observe improvements in both your fitness and a1c 6.9 levels. This practice aligns with the latest recommendations from the 2018 update of the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, which offers tailored advice for individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Furthermore, a meta-analysis on exercise in pregnant women indicated that exercise enhanced blood glucose regulation and cardiorespiratory fitness, demonstrating the extensive advantages of physical activity.
By following these guidelines, you can actively strive towards managing your A1C values, aiming for an a1c 6.9, through regular exercise.
Understanding the Impact of Stress on A1C Levels
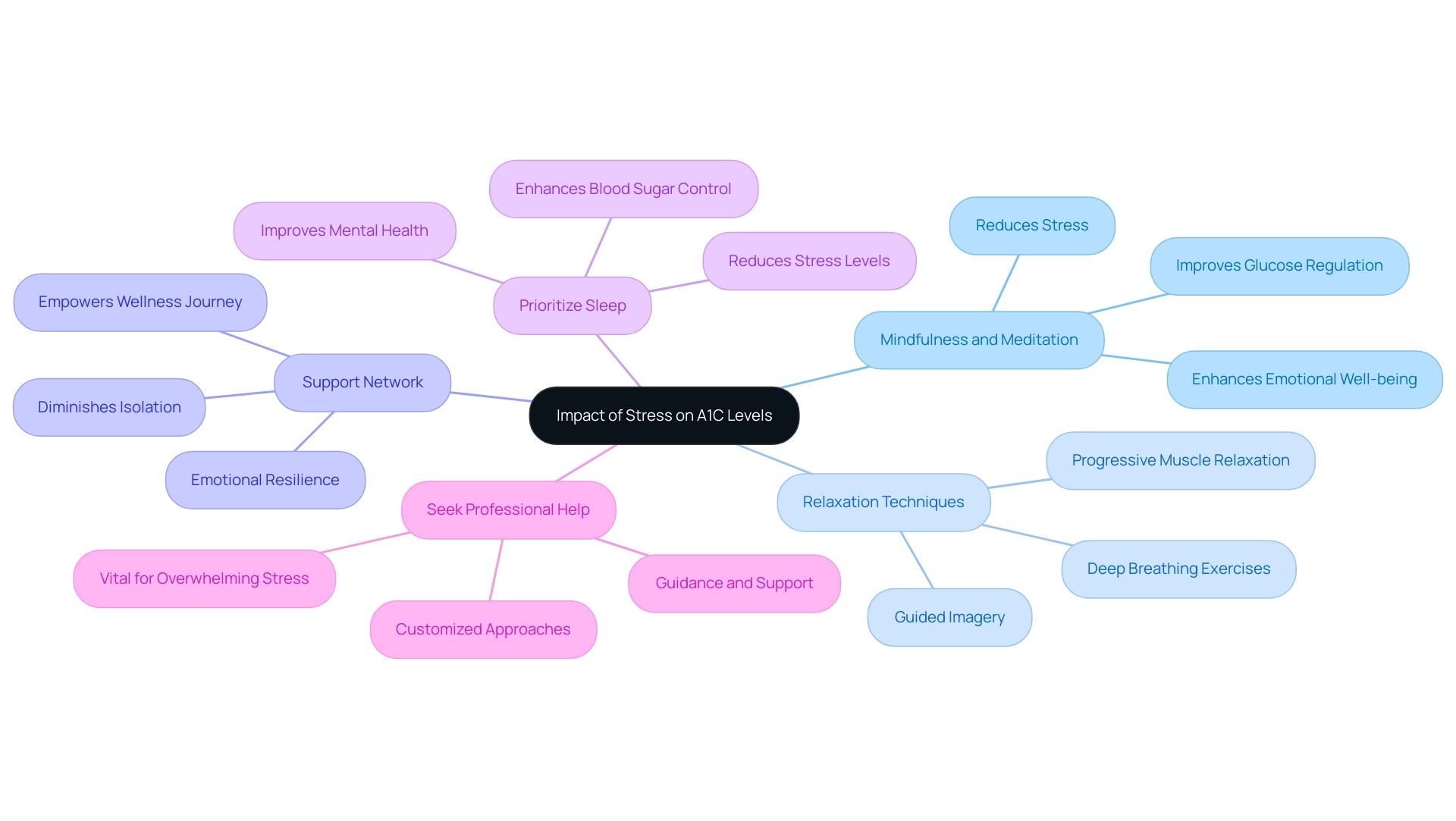
Handling stress is essential for maintaining healthy A1C readings, particularly for individuals navigating the challenges associated with an A1C 6.9. According to Fisher L., ‘this paper provides one of the first and clearest definitions of the construct of ‘diabetes distress,’ which is important to differentiate from general stress, particularly when evaluating associations with glycemic control in clinical practice.’ At the Integrative Wellness Center, we empower patients to eliminate anxiety over health complications through holistic care and education.
We begin by re-evaluating the origin of your condition, addressing health at the root level. Here are several effective strategies to consider:
-
Practice Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness meditation techniques can significantly reduce stress and enhance emotional well-being.
Studies suggest that such methods may result in better glucose regulation, rendering them a useful instrument in the control of health conditions related to insulin. Findings from the ACCORD and VADT studies suggest that glycemic goals and pharmacologic treatments may need adjustment to minimize hypoglycemic events, underscoring the importance of stress management in achieving optimal diabetes care.
-
Engage in Relaxation Techniques: Incorporating activities such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery can effectively alleviate stress.
These techniques assist in soothing the mind and body, which is crucial for sustaining stable glucose amounts. A case study on stress-induced hyperglycemia in patients with atrial fibrillation emphasized how unresolved stress responses can elevate glucose concentrations and insulin resistance, highlighting the necessity for effective stress management.
-
Establish a Support Network: Connecting with friends, family, or support groups allows individuals to share their experiences and feelings, diminishing feelings of isolation and stress.
A robust support system is vital for emotional resilience and overall health, empowering patients to take charge of their wellness journey.
-
Prioritize Sleep: Ensuring adequate sleep each night is critical, as poor sleep quality is linked to increased stress levels and can adversely affect blood sugar control.
Prioritizing restful sleep can significantly improve both mental and physical health.
-
Seek Professional Help if Needed: If stress becomes overwhelming, it is advisable to consult a mental health professional for guidance and support.
Effective stress control is a vital aspect of health care for individuals with diabetes, particularly those aiming for an A1C 6.9 level, and expert support can offer customized approaches to improve well-being. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we are dedicated to addressing the root causes of diabetes, empowering you towards better health and reversing type 2 diabetes.
LEARN MORE about our holistic services and how we can support your journey.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring and Adjustments
To effectively reduce your A1C figures and ease the stress that frequently comes with concerns about possible complications of your condition, regular monitoring of your glucose is essential, along with necessary modifications to your care plan:
- Track Your Glucose Levels: Regular use of a glucose meter allows you to check your sugar levels at various times throughout the day. This practice helps you identify patterns and make informed decisions about your diet and activity levels.
- Review Your A1C Regularly: It is vital to schedule A1C tests to monitor levels such as A1C 6.9 with your healthcare provider at recommended intervals. As noted in recent findings, about 35,000 deaths were reported among non-diagnosed individuals under 25 in 2022, which emphasizes the importance of tests that include the A1C 6.9 measurement in providing a comprehensive overview of your glucose control over the past three months and enabling timely adjustments to your management plan as needed.
- Adjust Your Plan as Necessary: Based on your monitoring results, be prepared to modify your dietary choices, exercise routine, or medication regimen. The prevalence of undiagnosed conditions related to blood sugar rises significantly with age, as demonstrated in the case study on the occurrence of undiagnosed issues by age group, suggesting that modifications may be required to attain optimal blood sugar management. Engaging with a holistic approach that addresses the root causes of the condition, including re-examining its source, can empower you to make more effective changes in your health journey.
- Engage with Healthcare Professionals: Regular consultations with your healthcare team are essential. They can provide valuable insights, suggest customized strategies based on a holistic wellness perspective, and assist you in your health journey. Their expertise can assist you in navigating the complexities of insulin resistance and challenge common misconceptions about treatment.
- Educate Yourself: Staying updated on the newest developments and recommendations in blood sugar control through trustworthy sources enables you to make knowledgeable choices about your health. This proactive method is especially crucial as socioeconomic factors also contribute—such as in North Dakota, where the highest occurrence rate of 19% is among individuals earning under $15,000, emphasizing the essential need for awareness and education in effectively managing the condition.
By adopting these strategies and taking a comprehensive viewpoint, you can significantly impact your A1C 6.9 levels and overall management of the illness while alleviating the stress associated with handling your situation.
Incorporating Support Systems into Your Diabetes Management Plan
Creating a strong support system is essential for effectively managing the condition and achieving an A1C of 6.9. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we empower patients to eliminate anxiety about complications related to blood sugar through holistic care and education, helping them find peace in their lives. Here are several strategies to consider:
- Join a Support Group for Diabetes: Connecting with individuals who encounter comparable obstacles can provide priceless motivation and useful guidance for controlling the condition. According to a recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) involving 324 individuals with prediabetes, increased physical activity was observed at 8 weeks due to supportive text messages, highlighting the positive impact of support groups on achieving an A1C 6.9 and improving health outcomes, ultimately reducing worries about complications.
- Engage Family and Friends: Actively involve your loved ones in your health journey. By sharing your health goals, you can encourage them to support your efforts, whether it’s through accountability or joining you in healthy activities. The American Diabetes Association emphasizes the importance of this support, recommending that families choose water over nutritive and non-nutritive sweetened beverages to promote better health choices, fostering a supportive environment that alleviates anxiety.
- Collaborate with a Health Coach: A certified health coach can offer customized advice, encouragement, and responsibility, improving your condition oversight experience. This professional support can be particularly beneficial in navigating the complexities of lifestyle changes and medication adjustments, addressing root causes for better patient health and promoting a sense of calm and control.
- Utilize Online Resources: Leverage online platforms, including forums and social media groups, to connect with others and share experiences. These resources can provide a sense of community and access to a wealth of knowledge and support, crucial for empowering patients and reducing feelings of isolation and anxiety.
- Participate in Community Events: Attend local health awareness events or health fairs to expand your network and learn from others in your community. Engaging in these activities not only increases your knowledge but also fosters connections that can enhance your support system. A case study exploring the social factors that contribute to diabetes management emphasizes the need for innovative care delivery models to mitigate health disparities, underscoring the value of participating in community initiatives that promote peace of mind.
Conclusion
Implementing effective strategies for managing diabetes is essential for lowering A1C levels and enhancing overall health. A comprehensive approach that includes:
- Nutritional practices
- Regular exercise
- Stress management
- Robust support systems
can empower individuals to take control of their condition. By focusing on whole foods, monitoring carbohydrate intake, and incorporating fiber-rich options, dietary choices can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, including aerobic and strength training exercises, plays a vital role in improving insulin sensitivity and facilitating better blood glucose control.
Moreover, understanding the psychological aspects of diabetes management, such as stress and anxiety, is crucial. Mindfulness practices, relaxation techniques, and establishing a support network contribute to emotional well-being and help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Consistent monitoring of blood glucose and A1C levels, along with regular consultations with healthcare professionals, ensure that adjustments to management plans can be made as necessary.
Ultimately, embracing a holistic approach to diabetes management not only aids in lowering A1C levels but also fosters a sense of empowerment and resilience. By prioritizing:
- Nutrition
- Exercise
- Stress management
- Community support
individuals can navigate the complexities of diabetes more effectively, leading to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life. Taking proactive steps today can pave the way for a healthier tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What dietary strategies can help lower A1C levels?
Effective dietary strategies include focusing on whole foods, monitoring carbohydrate intake, incorporating fiber-rich foods, limiting sugary beverages, and planning balanced meals.
Why is it important to focus on whole foods?
Whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins have a reduced glycemic index and provide vital nutrients that help prevent significant increases in sugar concentrations.
How should one manage carbohydrate intake?
It is essential to be aware of carbohydrate consumption and to favor complex carbohydrates, which are digested more slowly and help maintain stable glucose levels.
What role does fiber play in diabetes management?
Foods high in fiber, such as legumes, nuts, and seeds, help slow digestion and enhance sugar control. It is recommended to aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day for better glucose metabolism.
How can limiting sugary beverages impact A1C levels?
Replacing sugary drinks with water, herbal teas, or low-calorie options can reduce overall calorie intake and prevent sudden spikes in glucose, supporting sugar management.
What does a balanced meal consist of?
A balanced meal should combine carbohydrates with proteins and healthy fats to encourage fullness and maintain steady blood sugar levels.
How much exercise is recommended for managing A1C levels?
It is recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, along with strength training exercises at least twice a week.
What are the benefits of strength training for diabetes management?
Strength training increases muscle mass, which enhances insulin sensitivity, crucial for effective glucose management.
How can flexibility and balance exercises help with diabetes?
Activities such as yoga or tai chi promote relaxation and stress reduction, which can positively influence glucose levels.
What is the importance of setting realistic exercise goals?
Setting achievable objectives helps maintain motivation and reduces the risk of injury while progressively increasing workout intensity and duration.
How can tracking physical activity contribute to A1C management?
Using a journal or fitness app to log physical activity enhances accountability and helps observe improvements in fitness and A1C levels.