Overview
The article provides a comprehensive guide on creating a prediabetes diet PDF, emphasizing the importance of dietary management in controlling blood sugar levels and preventing the progression to diabetes. It outlines key dietary components, meal planning strategies, and the significance of physical activity, supported by evidence showing that these approaches can significantly enhance overall wellness and reduce health risks associated with prediabetes.
Introduction
In the face of rising prediabetes rates, understanding the crucial role of diet and lifestyle modifications is more important than ever. Prediabetes, marked by elevated blood sugar levels that do not yet qualify as diabetes, presents a significant opportunity for intervention through informed dietary choices and physical activity.
This article delves into practical strategies for managing prediabetes effectively, including:
- Crafting a personalized meal plan
- Incorporating regular exercise
By exploring the essential dietary components and lifestyle adjustments necessary for controlling blood sugar levels, readers will gain valuable insights into how to proactively navigate their health journey and reduce the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes.
Understanding Prediabetes: The Importance of Diet
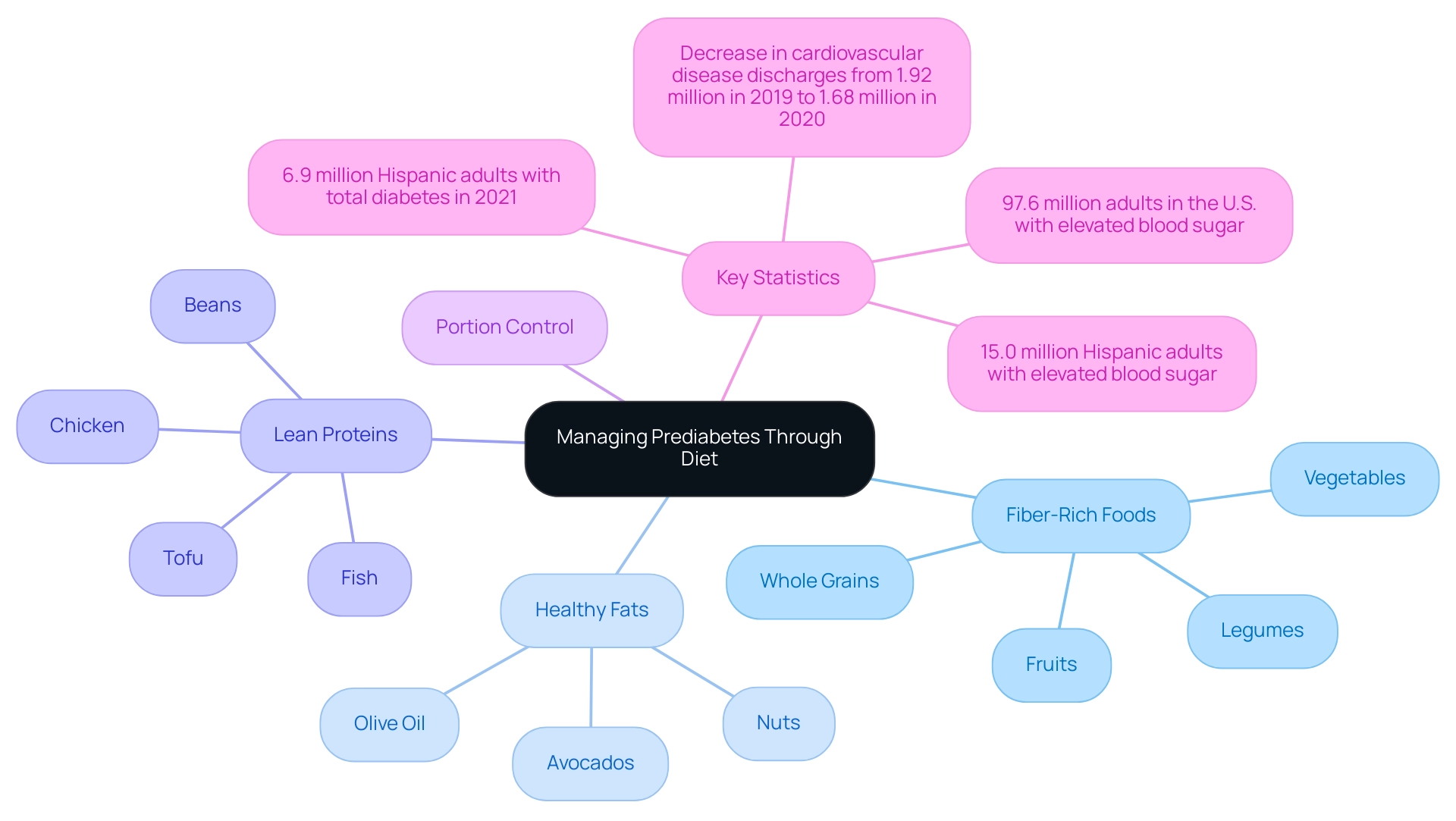
Prediabetes is defined by glucose levels that surpass normal ranges yet do not meet the criteria for type 2 metabolic disorder. Comprehending the role of diet, particularly as outlined in a prediabetes diet pdf, in managing this condition is crucial for effective wellness management. A well-balanced prediabetes diet pdf not only aids in regulating sugar levels but also reduces the risk of progressing to diabetes while enhancing overall wellness.
Key dietary components essential for managing blood sugar levels include:
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Incorporate whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables to enhance insulin sensitivity and slow digestion, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Fats: Choose sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil to support cardiovascular wellness and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Lean Proteins: Integrate options such as chicken, fish, beans, and tofu to preserve muscle mass and promote a feeling of fullness, which is vital in weight management.
- Portion Control: Remain vigilant about portion sizes to prevent overeating, which can lead to significant spikes in blood sugar.
By following the guidelines outlined in the prediabetes diet pdf, individuals can proactively manage their condition. Given that an estimated 15.0 million Hispanic adults had elevated blood sugar levels in 2021, with only 20.9% being aware of their condition, it is imperative to focus on dietary management within this demographic. Furthermore, the total figure of 97.6 million adults in the U.S. with elevated blood sugar highlights the importance of these dietary guidelines for public welfare and personal well-being.
Moreover, the reduction in discharges for significant cardiovascular illnesses from 1.92 million in 2019 to 1.68 million in 2020 emphasizes the wider wellness implications of managing prediabetic conditions through diet, connecting dietary choices to enhanced wellness results.
Step-by-Step Guide to Crafting Your Prediabetes Meal Plan
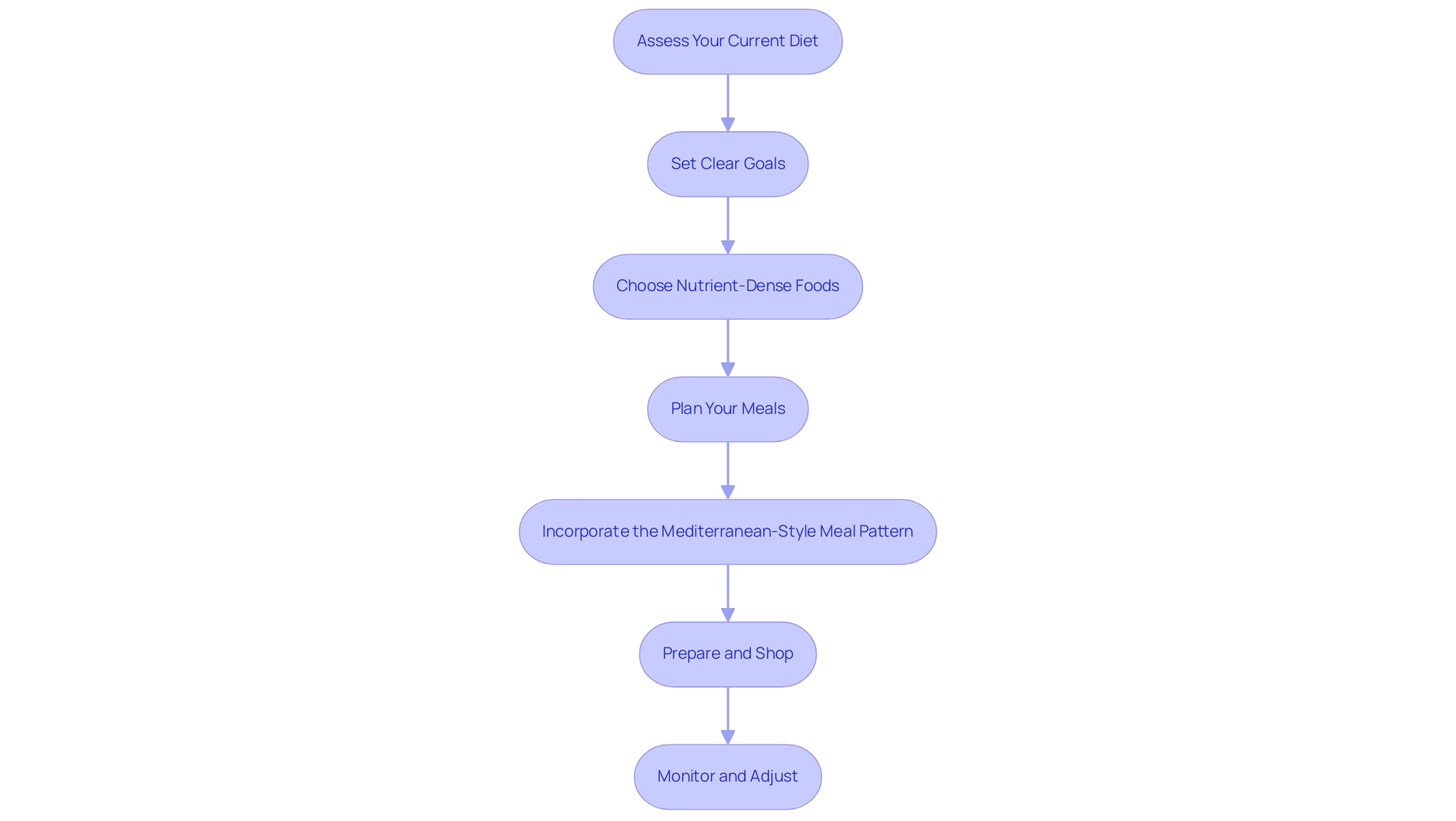
Developing a customized prediabetes meal plan necessitates various strategic steps that correspond with a comprehensive approach to managing the condition:
- Assess Your Current Diet: Initiate the process by meticulously tracking your eating habits over a week. Document what you consume, portion sizes, and your post-meal sensations. This thorough evaluation will illuminate areas that require enhancement and help address the root causes of your health concerns, potentially reducing the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding complications related to blood sugar.
- Set Clear Goals: Establish specific objectives for your meal plan. These goals may encompass weight loss, heightened energy levels, or enhanced sugar regulation. Tara Seymour, an advanced practice clinical dietitian and educator at Johns Hopkins, emphasizes the importance of goal-setting in this context, as it empowers patients to take charge of their health.
- Choose Nutrient-Dense Foods: Prioritize foods that are rich in essential nutrients while minimizing added sugars and unhealthy fats. Highlight whole foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, which have been demonstrated to aid in sugar management and fight insulin resistance.
- Plan Your Meals: Develop a structured weekly meal schedule that encompasses breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks. Each meal should maintain a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. For instance:
-
Breakfast: Oatmeal topped with berries and nuts.
-
Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens and vinaigrette.
-
Dinner: Baked salmon served with quinoa and steamed broccoli.
-
Snacks: Greek yogurt with a sprinkle of cinnamon or carrot sticks with hummus.
On the third day, consider increasing your daily intake to 2,000 calories by adding 2 Tbsp. of natural peanut butter to your apple at lunch and having ¼ cup of unsalted dry-roasted almonds with a small pear as an evening snack.
-
- Incorporate the Mediterranean-Style Meal Pattern: From the prediabetes diet pdf, as this meal pattern is beneficial for those looking to reduce diabetes risk and improve cardiovascular health. It includes plant-based foods, fish, olive oil, and limited red meat, contributing to lower A1C and triglyceride levels. This approach also helps address the dangers of traditional treatments by focusing on whole, nutrient-rich foods.
- Prepare and Shop: After finalizing your meal plan, create a comprehensive shopping list that includes all necessary ingredients. Meal prepping on weekends can be beneficial, ensuring you have healthy options readily available throughout the week.
- Monitor and Adjust: After a few weeks on your meal plan, assess how you feel and any changes in your sugar levels. Be prepared to adjust your plan as needed to better align with your goals. Even modest weight loss—ranging from 5% to 10%—can significantly lower A1C levels, providing a substantial benefit for those managing elevated blood sugar. Moreover, including a practice of walking for only 2 minutes after every meal can enhance sugar levels.
By following these measures and reassessing the origin of your diabetes, as suggested in the prediabetes diet pdf, you can create a sustainable meal strategy that effectively aids your journey in managing elevated glucose levels, promoting a comprehensive approach to your wellness while reducing the stress related to your condition.
Incorporating Physical Activity into Your Lifestyle
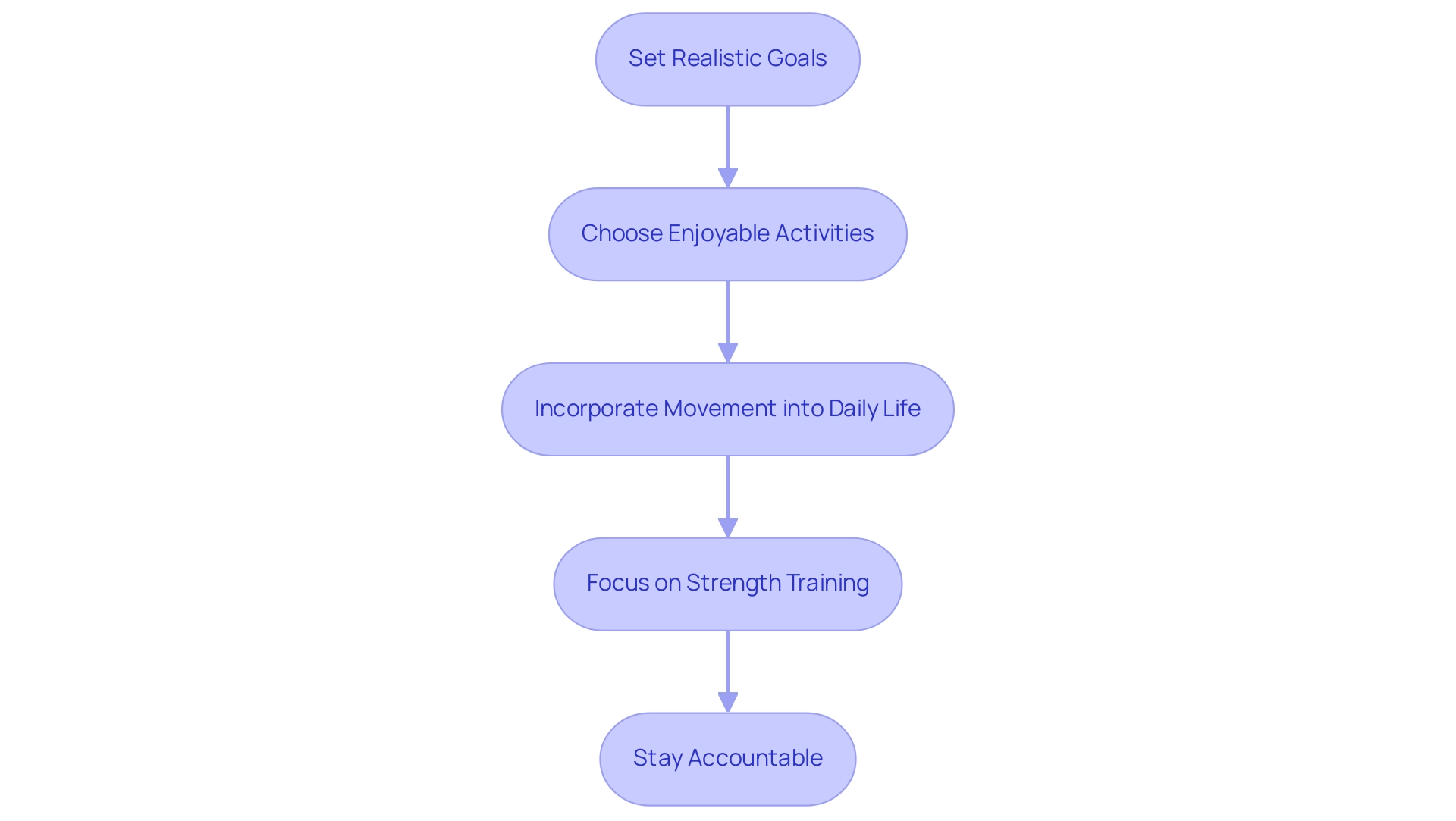
Incorporating physical activity into your daily routine can significantly improve your capability to manage prediabetes effectively. Here are several practical steps to consider:
-
Set Realistic Goals: Aim for a minimum of 175 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking or cycling.
This can be broken down into manageable sessions, for example, 35 minutes a day, five days a week. This approach aligns with findings from the Look AHEAD trial, where participants sought to lose more than 7% of their initial weight while increasing their physical activity levels.
-
Choose Enjoyable Activities: Engaging in exercises that you find enjoyable significantly boosts the likelihood of maintaining a consistent routine.
Options may include dancing, swimming, hiking, or participating in group fitness classes. The greater the enjoyment, the more sustainable your exercise habits will be.
-
Incorporate Movement into Daily Life: Identify opportunities to be active throughout your day.
Simple changes, such as opting for stairs over elevators, parking further away from your destination, or taking short walking breaks during your workday, can positively contribute to your activity levels.
-
Focus on Strength Training: Integrate strength training exercises at least two days a week.
This can involve bodyweight exercises, resistance bands, or light weights, all of which help build muscle and enhance insulin sensitivity.
Studies indicate that resistance exercise can lead to reduced fasting blood glucose levels, particularly when performed at higher volumes and intensities. According to the case study titled ‘Conclusions on Exercise and Diabetes,’ exercise is crucial for the prevention and control of insulin resistance and diabetes-related issues.
-
Stay Accountable: Consider partnering with a friend for workouts or joining a fitness class to maintain motivation.
Tracking your progress through fitness apps or journals can also provide a sense of accountability. As emphasized in recent studies, regular exercise is crucial for optimal well-being in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus, necessitating precautions to ensure safety.
By incorporating these physical activity strategies into your lifestyle, you can strengthen your dietary efforts and improve your overall wellness. As noted by expert D.G.-G., ‘the evidence supports that tailored physical activity programs can address individual necessities and preferences, tackling one of the greatest public health challenges of the 21st century.
Monitoring Your Progress and Making Adjustments
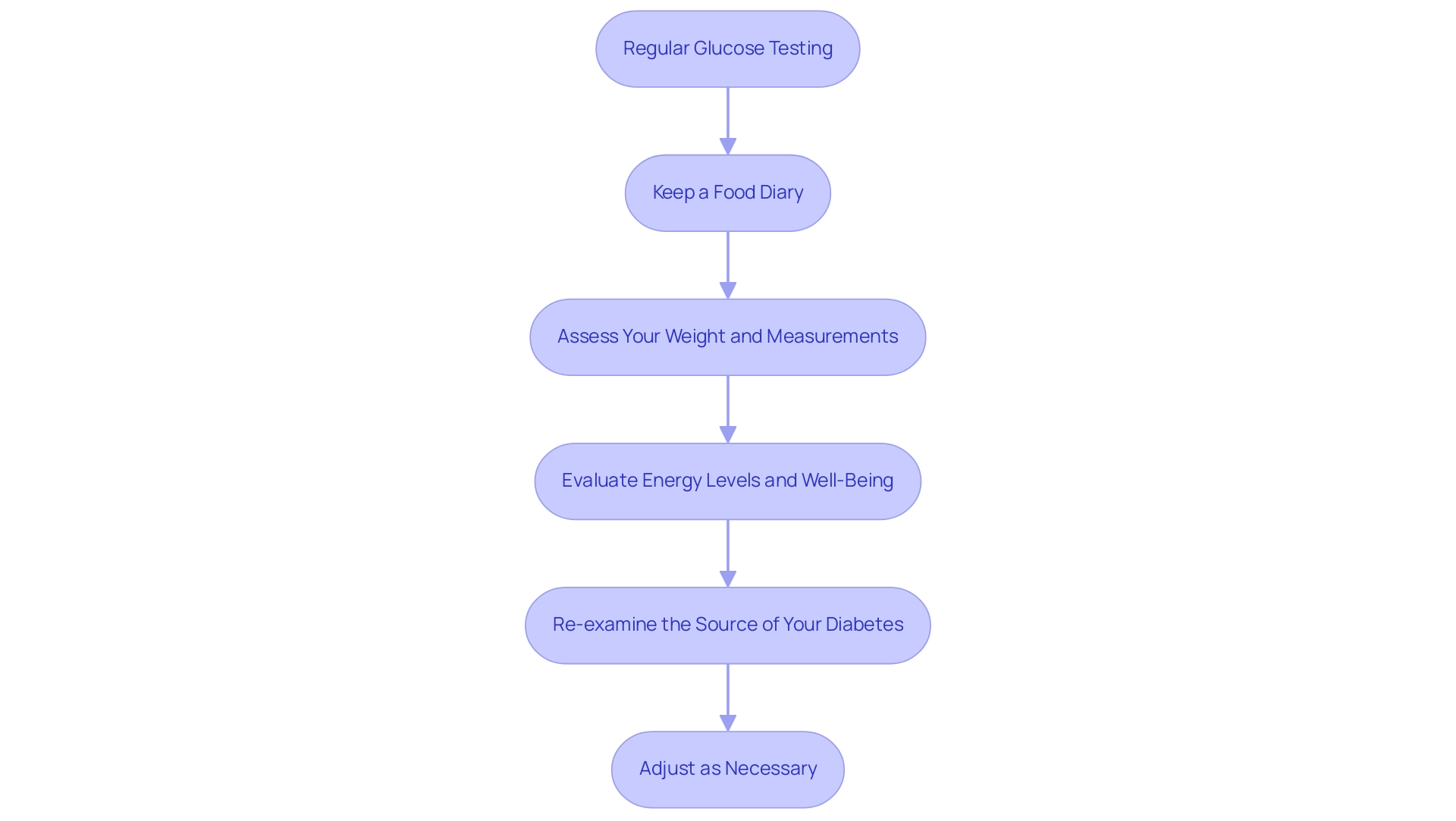
Monitoring your progress is crucial for determining the effectiveness of your diabetes management plan, particularly when approached holistically. This process can also help alleviate the anxiety that accompanies concerns about potential complications of your disease. Here are structured steps to assist you in tracking your progress:
- Regular Glucose Testing: Work together with your healthcare provider to create a consistent timetable for glucose testing. Regular monitoring allows you to understand how dietary and lifestyle modifications from a prediabetes diet pdf influence your glucose levels. Statistics indicate that only 34.9% of participants with stroke engage in glucose testing, highlighting a gap in proactive management that you can bridge by taking a comprehensive approach to your health.
- Keep a Food Diary: Maintain a detailed record of your meals, snacks, and any symptoms that arise. This practice can reveal patterns and triggers significantly affecting your sugar levels. Recent studies have demonstrated that food diaries improve blood sugar monitoring, rendering them a valuable resource in managing blood sugar levels, particularly within a holistic approach that takes overall health into account.
- Assess Your Weight and Measurements: Regularly monitor your weight and body measurements. Evidence indicates that a gradual weight reduction of 5-10% can significantly enhance insulin sensitivity, decreasing the likelihood of advancing from elevated blood sugar levels to a more severe condition by as much as 70% through lifestyle modifications. These lifestyle changes, guided by a holistic dietary approach outlined in the prediabetes diet pdf, are essential for preventing the transition from prediabetes to diabetes.
- Evaluate Energy Levels and Well-Being: Remain attuned to your physical and emotional state. Noticeable increases in energy and improvements in mood can serve as positive indicators of successful dietary and lifestyle alterations. Understanding the socioeconomic and psychological determinants of self-care related to the condition, as highlighted in Walker et al.’s 2014 study, provides a broader context for your management efforts, reinforcing the importance of a holistic understanding of health.
- Re-examine the Source of Your Diabetes: Consider how your lifestyle, diet, and emotional well-being contribute to the root causes of your diabetes. Engaging with your healthcare provider or a nutritionist can help you understand these underlying factors and address them effectively.
- Adjust as Necessary: If your glucose levels remain unchanged or if you do not feel at your best, it may be time to reassess your meal plan and exercise regimen. Engage in discussions with your healthcare provider or a nutritionist to make informed adjustments that align with your wellness goals. Recall, research suggests a connection between consistently high blood glucose levels and greater risks for negative outcomes, highlighting the necessity of effective monitoring within a comprehensive framework.
By carefully tracking your progress and embracing a comprehensive approach, you can maintain focus on your management plan, reduce anxiety related to possible complications, and make necessary adjustments to enhance your results.
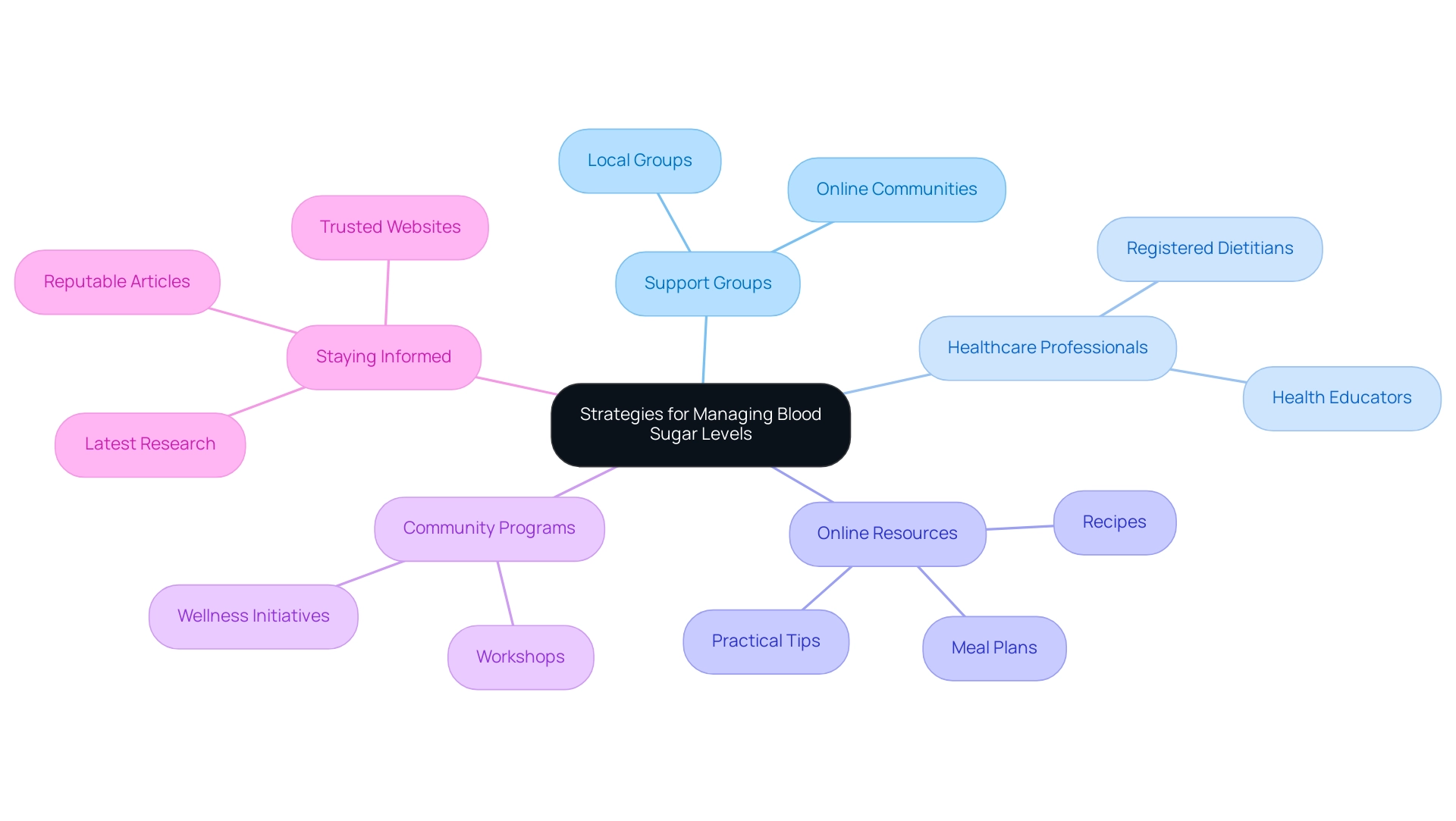
Seeking Support and Resources
Managing elevated blood sugar levels can present significant challenges; however, embracing a holistic approach can markedly enhance your journey toward effective management and eliminate worry about developing traumatic and debilitating diabetes complications. Below are strategic avenues to explore for support and resources, focusing on addressing root causes and empowering your well-being:
- Join Support Groups: Engage with local or online support groups tailored for individuals with prediabetes. These communities provide a platform for sharing experiences and strategies, fostering motivation and accountability among participants. Evidence indicates that community support worker and peer leader programs produce favorable results, especially for Latino adults dealing with blood sugar issues, emphasizing the importance of collective assistance in addressing common misconceptions.
- Work with a Healthcare Professional: Consulting with a registered dietitian, health educator, or healthcare provider can offer invaluable personalized guidance. Expert opinions emphasize the advantages of working with dietitians, who can create customized meal plans that address personal wellness requirements, ultimately aiding in better control of blood sugar levels and empowering patients to remove concerns about complications related to their condition. It is essential to re-examine the source of your diabetes to address well-being at the root level.
- Utilize Online Resources: Numerous organizations offer extensive resources, including meal plans, recipes, and practical tips for managing elevated blood sugar levels, which can often be found in a prediabetes diet pdf. Websites like the American Diabetes Association provide excellent information for individuals dealing with prediabetes, including a prediabetes diet pdf that promotes a deeper understanding of comprehensive wellness practices.
- Engage in Community Programs: Actively participate in local wellness initiatives or workshops focused on managing blood sugar levels. Many communities provide free or low-cost resources aimed at enhancing well-being outcomes, making these programs accessible to a broad audience and reinforcing the significance of collective wellness in the fight against diabetes.
- Stay Informed: Keeping abreast of the latest research and developments in diabetes care is crucial. Engaging with books, reputable articles, and trusted websites can deepen your understanding and empower you to make informed health decisions, fostering a proactive approach to your health.
By proactively seeking support and leveraging available resources, you can significantly enhance your capacity to manage prediabetes effectively. The recent trial titled ‘Using Peer Support to Aid in Prevention and Treatment in Prediabetes (UPSTART)’ has shown promising results, indicating good acceptance for structured support systems, which could lead to improved patient engagement. Additionally, a study on A1c and weight outcomes revealed that participants showed notable reductions in A1c levels and weight over time, with both peer support and usual care approaches demonstrating effectiveness. Notably, the Patient Activation Measure (PAM13) mean score at baseline was 68.4, reflecting the importance of patient engagement in effective management strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing prediabetes is a proactive journey that can significantly improve health outcomes. By focusing on diet and lifestyle modifications, individuals can effectively regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes. Key dietary strategies include:
- Incorporating fiber-rich foods
- Including healthy fats
- Adding lean proteins
- Being mindful of portion sizes
Crafting a personalized meal plan that emphasizes nutrient-dense foods and adheres to a Mediterranean-style meal pattern can further enhance these efforts.
In addition to dietary changes, regular physical activity plays a vital role in managing prediabetes. Recommended strategies include:
- Setting achievable exercise goals
- Engaging in enjoyable activities
- Incorporating movement into daily routines
These practices can foster consistency and improve overall health. Strength training, in particular, has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, making it an essential component of a balanced approach to diabetes management.
Monitoring progress through regular blood sugar testing, maintaining a food diary, and assessing physical and emotional well-being is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of these strategies. Adjustments to the meal plan or exercise regimen may be necessary to align with health goals. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, joining support groups, and utilizing online resources can provide additional guidance and accountability.
Ultimately, taking charge of prediabetes through informed dietary choices, consistent physical activity, and ongoing support empowers individuals to navigate their health journey confidently. By implementing these strategies, one can not only manage prediabetes effectively but also enhance overall quality of life and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is prediabetes?
Prediabetes is defined by glucose levels that exceed normal ranges but do not meet the criteria for type 2 diabetes.
How can diet help manage prediabetes?
A well-balanced diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of progressing to diabetes, and enhance overall wellness.
What are the key dietary components for managing blood sugar levels?
Key dietary components include fiber-rich foods, healthy fats, lean proteins, and portion control.
Why are fiber-rich foods important for prediabetes?
Fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, enhance insulin sensitivity and slow digestion, helping to stabilize blood sugar levels.
How do healthy fats contribute to blood sugar management?
Healthy fats, like those from avocados, nuts, and olive oil, support cardiovascular health and help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
What role do lean proteins play in a prediabetes diet?
Lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, beans, and tofu, help preserve muscle mass and promote a feeling of fullness, which is vital for weight management.
Why is portion control essential for individuals with prediabetes?
Monitoring portion sizes is crucial to prevent overeating, which can lead to significant spikes in blood sugar levels.
What steps are involved in developing a customized prediabetes meal plan?
Steps include assessing your current diet, setting clear goals, choosing nutrient-dense foods, planning meals, incorporating a Mediterranean-style meal pattern, preparing and shopping, and monitoring and adjusting the plan as needed.
How can tracking your diet help in managing prediabetes?
Tracking your eating habits helps identify areas for improvement and addresses the root causes of health concerns, potentially reducing anxiety about blood sugar complications.
What is the Mediterranean-style meal pattern?
This meal pattern emphasizes plant-based foods, fish, olive oil, and limited red meat, contributing to lower A1C and triglyceride levels while reducing diabetes risk.
How important is meal preparation in managing prediabetes?
Meal preparation is important as it ensures that healthy options are readily available throughout the week, making it easier to stick to the meal plan.
What should you do after a few weeks on your meal plan?
After a few weeks, assess how you feel and any changes in your sugar levels, and be prepared to adjust your plan to better align with your health goals.