Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management requires a multifaceted approach, with the A1C test serving as a pivotal tool in this journey. This test provides crucial insights into average blood glucose levels over the past few months, guiding individuals and healthcare providers in formulating effective management strategies. By understanding the significance of A1C results, patients can take proactive steps to mitigate complications and enhance their overall health.
The article delves into essential strategies for achieving and maintaining an optimal A1C level, including:
- Dietary modifications
- Regular physical activity
- The importance of a supportive healthcare network
Additionally, it emphasizes the role of meal planning and stress management in promoting a holistic approach to diabetes care. Through informed decisions and consistent efforts, individuals can empower themselves to navigate their health journey with confidence and clarity.
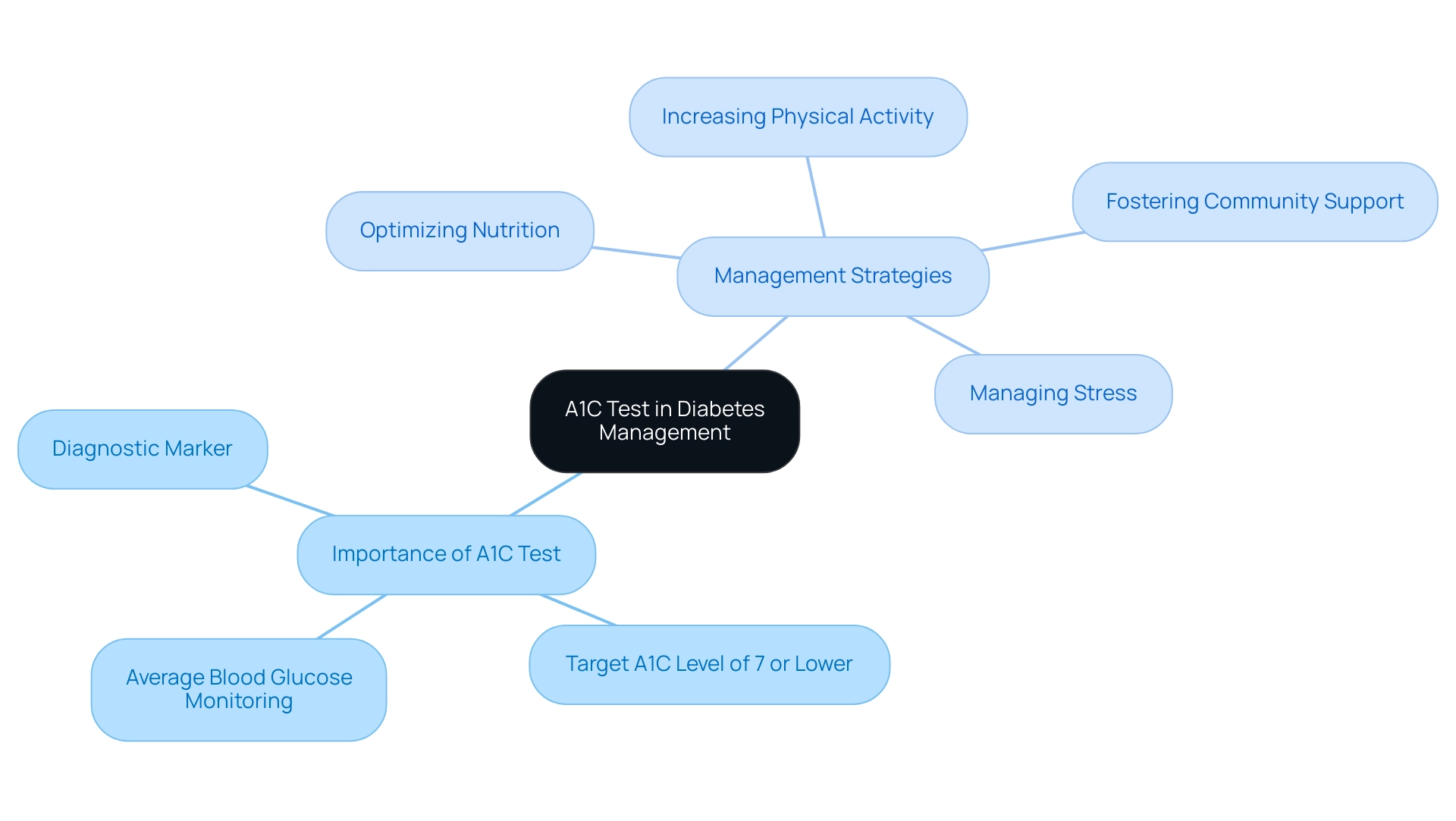
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key to Diabetes Management
The A1C test is an essential tool for evaluating average blood glucose readings over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. For adults diagnosed with the condition, a target A1C of 7 or lower is typically recommended to mitigate the risk of complications associated with it. Understanding your A1C results is vital, as it empowers you and your healthcare team to formulate a more effective management strategy for your condition.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize holistic care, addressing root causes and offering education to enhance patient health. Our approach includes four essential strategies:
- Optimizing nutrition
- Increasing physical activity
- Managing stress
- Fostering community support
Routine testing, generally conducted every three to six months, is essential for tracking your progress and fine-tuning your treatment plan as necessary.
Familiarizing yourself with the A1C testing procedure and being aware of various factors that can influence your results, such as recent illnesses or adjustments in medication, is also important. Recent studies have indicated that an increased A1C measurement can act as a useful marker for diagnosing the condition, especially when supported by strict glucose standards. In 2021, it was reported that approximately 15.0 million Hispanic adults had prediabetes, with a prediabetes percentage of 34.5% and only 20.9% being aware of their condition.
This emphasizes the essential function of A1C testing in early identification and management, as prompt intervention can greatly diminish the advancement to type 2, of which 10.2% of a population sample developed new cases over a six-year span. Moreover, it is recommended that an elevated A1C or fasting glucose be confirmed on a second occasion to enhance diagnostic accuracy, as emphasized in recent case studies. As stated by experts, ‘In conclusion, we found that A1C level was effective and convenient for screening,’ underscoring the test’s significance in managing the condition effectively and empowering patients through informed health decisions.
By concentrating on these strategies, patients can strive to remove concern about developing traumatic and debilitating complications related to their condition.
Effective Strategies for Achieving an A1C of 7
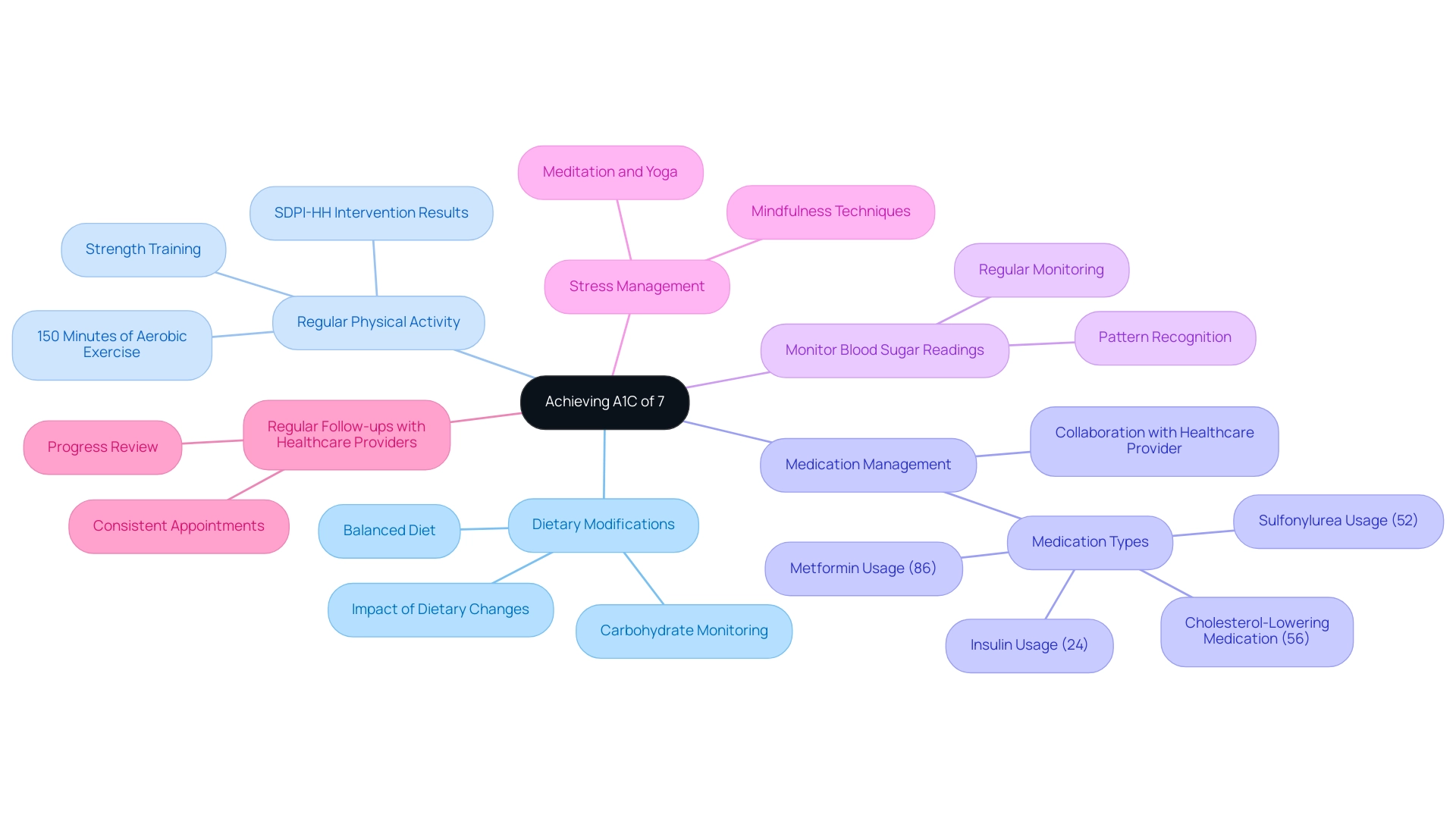
To achieve and maintain an A1C of 7%, individuals should consider implementing the following comprehensive strategies rooted in a holistic understanding of diabetes management, while also addressing the anxiety that may accompany concerns about potential complications of the disease:
-
Dietary Modifications:
- Prioritize a balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Monitoring carbohydrate consumption is essential; carbohydrate counting can be an effective approach for managing blood sugar.
- Recent studies indicate that dietary changes have a significant impact on A1C measurements, with participants in intervention programs showing marked improvements.
- This holistic approach emphasizes re-examining the source of diabetes through informed dietary choices.
-
Regular Physical Activity:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, complemented by strength training exercises on at least two days.
- Participating in consistent physical exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps to reduce blood sugar amounts.
- The Special Diabetes Program for Indians-Healthy Heart (SDPI-HH) intervention demonstrated that participants who increased their physical activity and adopted healthier eating habits experienced a significant reduction in their HbA1c values, particularly among women, showcasing how lifestyle changes can empower patients.
-
Medication Management:
- Collaborate closely with your healthcare provider to ensure that your medication regimen is tailored to your specific needs.
- This may involve oral medications, insulin therapy, or other injectable treatments.
- According to recent findings, 86% of participants in low-fat diet groups utilized Metformin, 52% were on Sulfonylurea, 24% used Insulin, and 56% were on cholesterol-lowering medication.
- Dr. Jong Ryeal Hahm emphasizes, “Effective control of blood sugar often requires a multifaceted approach, including medication customized to individual patient needs.”
-
Monitor Blood Sugar Readings:
- Regularly checking blood glucose readings is essential to understanding how various foods, activities, and medications influence your A1C.
- Maintaining a detailed record can assist in recognizing patterns and directing essential modifications in your strategy, emphasizing the significance of self-empowerment in health care.
-
Stress Management:
- Managing stress is vital, as elevated stress levels can adversely affect blood sugar control.
- Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga into your daily routine to promote better overall well-being.
- This aspect emphasizes the integrative strategy of addressing mental health alongside physical health in the context of blood sugar regulation.
-
Regular Follow-ups with Healthcare Providers:
- Schedule consistent appointments with your healthcare team to review your progress, address any challenges, and make adjustments to your care plan as needed.
- Regular check-ins are essential to staying on track toward achieving an A1C of 7, ensuring that you receive ongoing support and guidance throughout your health management journey.
- This collaborative aspect emphasizes the importance of healthcare partnerships in reversing the condition.
Additionally, it’s important to note that participants in the study had lived with the condition for an average of 4.6 ± 6.5 years, providing context for the experience level of individuals managing their health. This holistic method not only tackles the physical elements of the condition but also the emotional issues, promoting a thorough comprehension of wellness management.
Incorporating Meal Planning into Your Routine
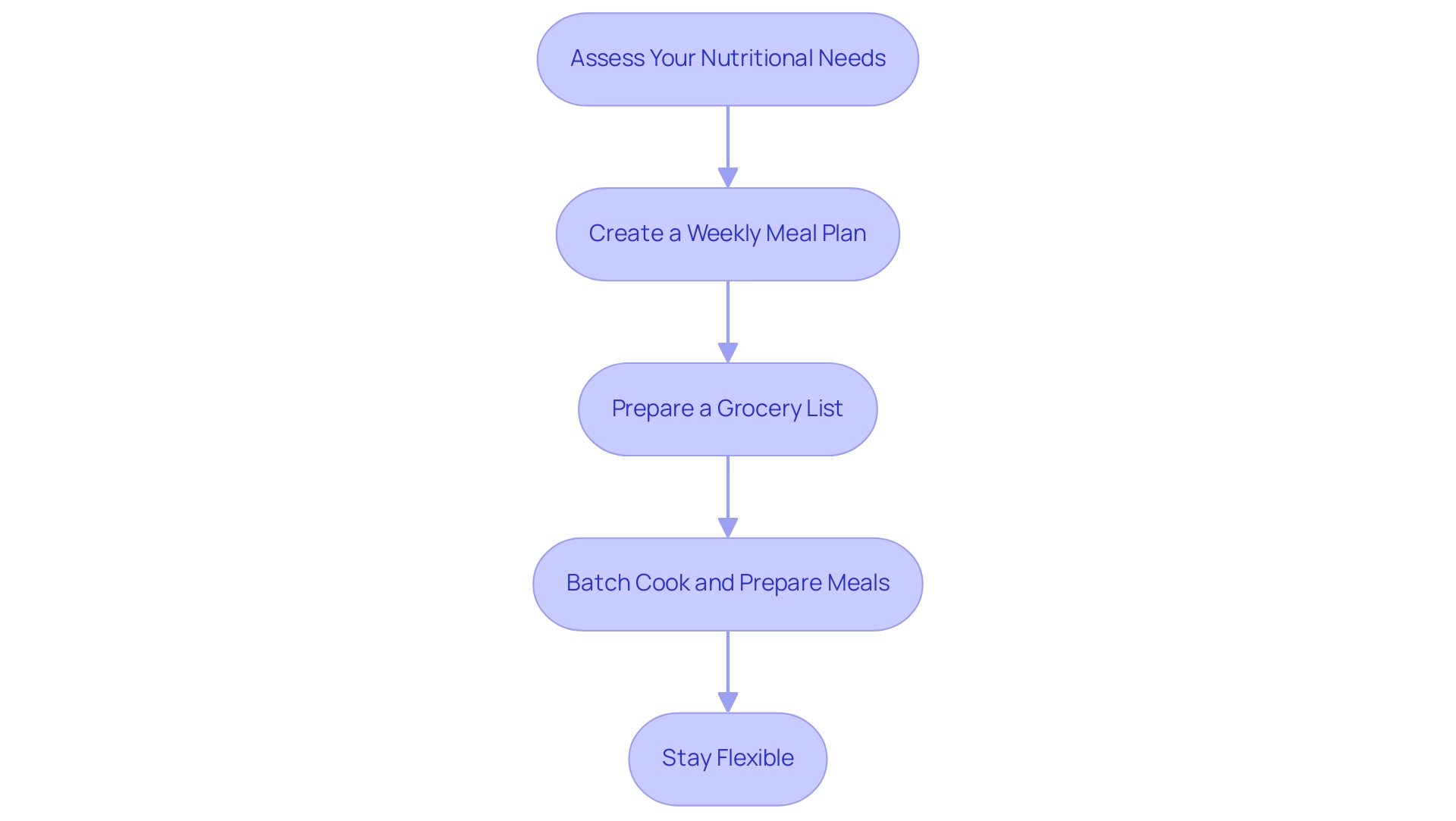
To seamlessly integrate meal planning into your routine and effectively manage your condition, consider the following structured steps, all aimed at empowering you to eliminate anxiety over complications:
-
Assess Your Nutritional Needs:
Begin by consulting with a registered dietitian who can help you identify your specific dietary requirements based on your health status and lifestyle. This evaluation is essential in customizing a strategy that addresses your specific needs and enhances your overall well-being through a comprehensive approach to health management.
-
Create a Weekly Meal Plan:
Allocate time each week to develop a comprehensive meal plan. Aim for a diverse array of foods to ensure you receive all essential nutrients while carefully managing your carbohydrate intake. Recent trends indicate that 19.0% of women engage in meal planning compared to 11.3% of men, highlighting the growing recognition of its importance.
According to the NutriNet-Sante study, meal planning practices significantly contribute to healthier eating habits, thus reducing concern about potential health complications and promoting peace of mind.
-
Prepare a Grocery List:
Once your meal plan is in place, prepare a detailed grocery list. This practice not only helps you avoid impulse purchases but also ensures that you have all necessary ingredients readily available, facilitating adherence to your dietary goals and providing you with a sense of control over your health.
-
Batch Cook and Prepare Meals:
Dedicate specific periods for batch cooking meals and preparing healthy snacks. This strategy can significantly reduce the temptation to make unhealthy food choices when time limitations occur, thereby supporting your overall wellness objectives. As highlighted by Joseph, assistant professor at The Ohio State University College of Medicine, effective meal preparation is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and promoting a proactive attitude towards well-being, ultimately easing worries about complications.
-
Stay Flexible:
While adhering to a meal plan is beneficial, it is equally important to remain flexible. Allow for adjustments to accommodate unexpected events or cravings while still striving to meet your overall dietary goals. As highlighted in the study on food agency among Diabetes Prevention Program participants, confidence in cooking and meal preparation is vital for maintaining healthy eating habits.
Participants showed strong food autonomy, highlighting the significance of cooking abilities in the control of blood sugar and strengthening your ability to take charge of your well-being.
By adhering to these steps, you can improve your meal planning techniques, ultimately resulting in better blood sugar regulation, enhanced wellness outcomes, and a greater sense of tranquility concerning your condition, which can help you achieve an a1c of 7, in line with the comprehensive care approach promoted at the Integrative Wellness Center.
Understanding the Role of Physical Activity
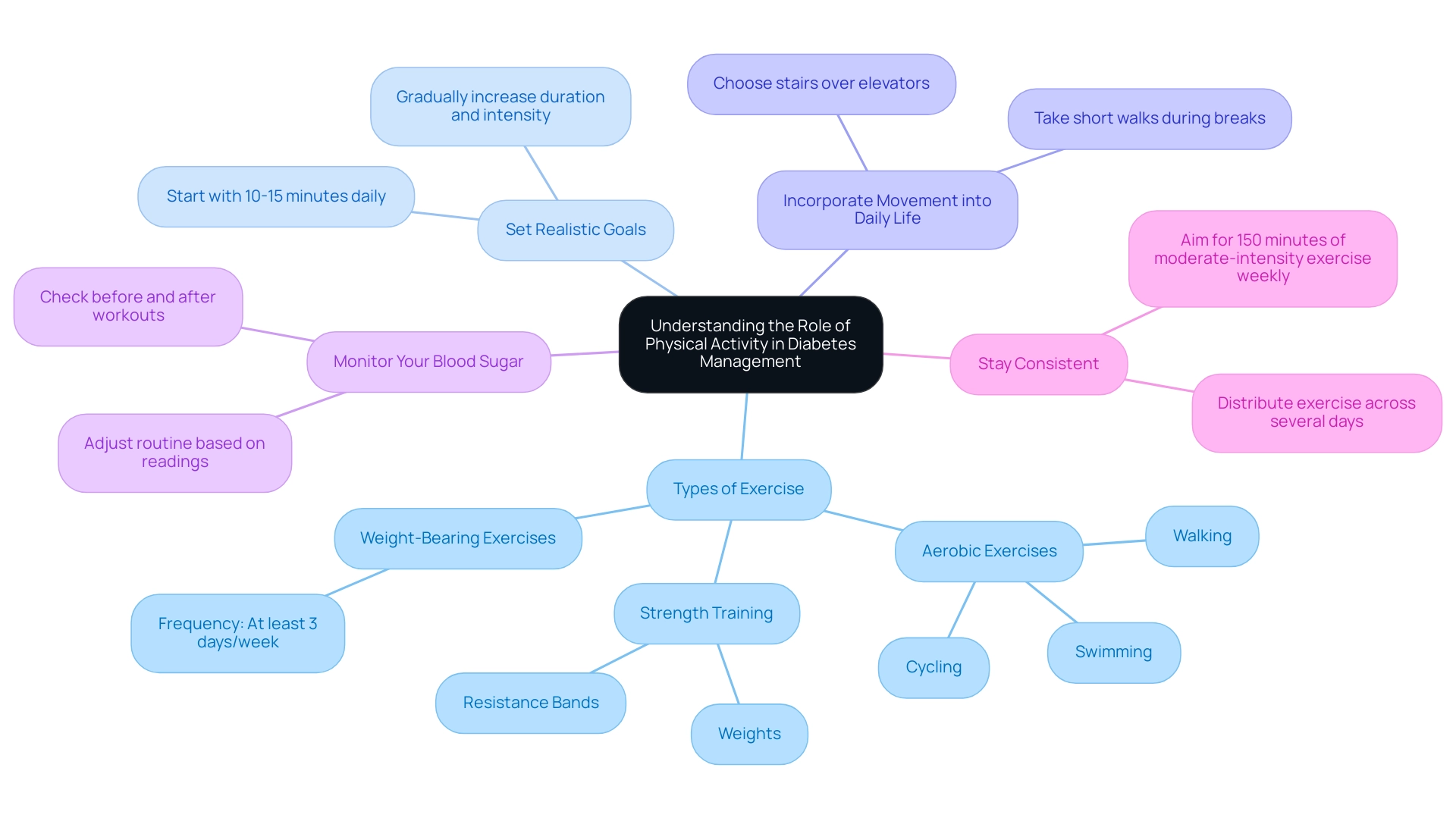
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management, offering numerous benefits for individuals living with this condition. Here are several critical considerations:
- Types of Exercise: It is essential to incorporate a balanced mix of aerobic exercises, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, alongside strength training with weights or resistance bands. Both types of exercise have been demonstrated to effectively manage insulin resistance and enhance overall wellness metrics. Additionally, it is important to include weight-bearing exercise at least three days per week, especially for children and adolescents, to strengthen bones and support overall health.
- Set Realistic Goals: Initiate your fitness journey with achievable targets, such as walking for 10-15 minutes daily. Gradually increase the duration and intensity of your workouts as your fitness state evolves, aligning with the latest Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, which suggest tailored modifications for individuals with diabetes.
- Incorporate Movement into Daily Life: Look for opportunities to increase your physical activity throughout the day. Simple changes, such as choosing stairs over elevators or taking short walks during breaks, can significantly boost your overall activity.
- Monitor Your Blood Sugar: It is crucial to observe how exercise affects your blood glucose readings. Regularly check your blood sugar before and after workouts to gain insights into your body’s responses and adjust your routine accordingly.
- Stay Consistent: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week, distributed across several days. Consistency is essential for achieving and maintaining a1c of 7, as demonstrated by recent case studies emphasizing the link between regular exercise and enhanced management of the condition.
As Ann L. Albright, PhD, RD, from the Division of Diabetes Translation at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, emphasizes, “Embracing physical activity not only enhances physical condition but can also positively influence mental well-being and quality of life for individuals with type 2 conditions.” By committing to a structured exercise regimen, individuals can take significant strides toward improved wellness outcomes.
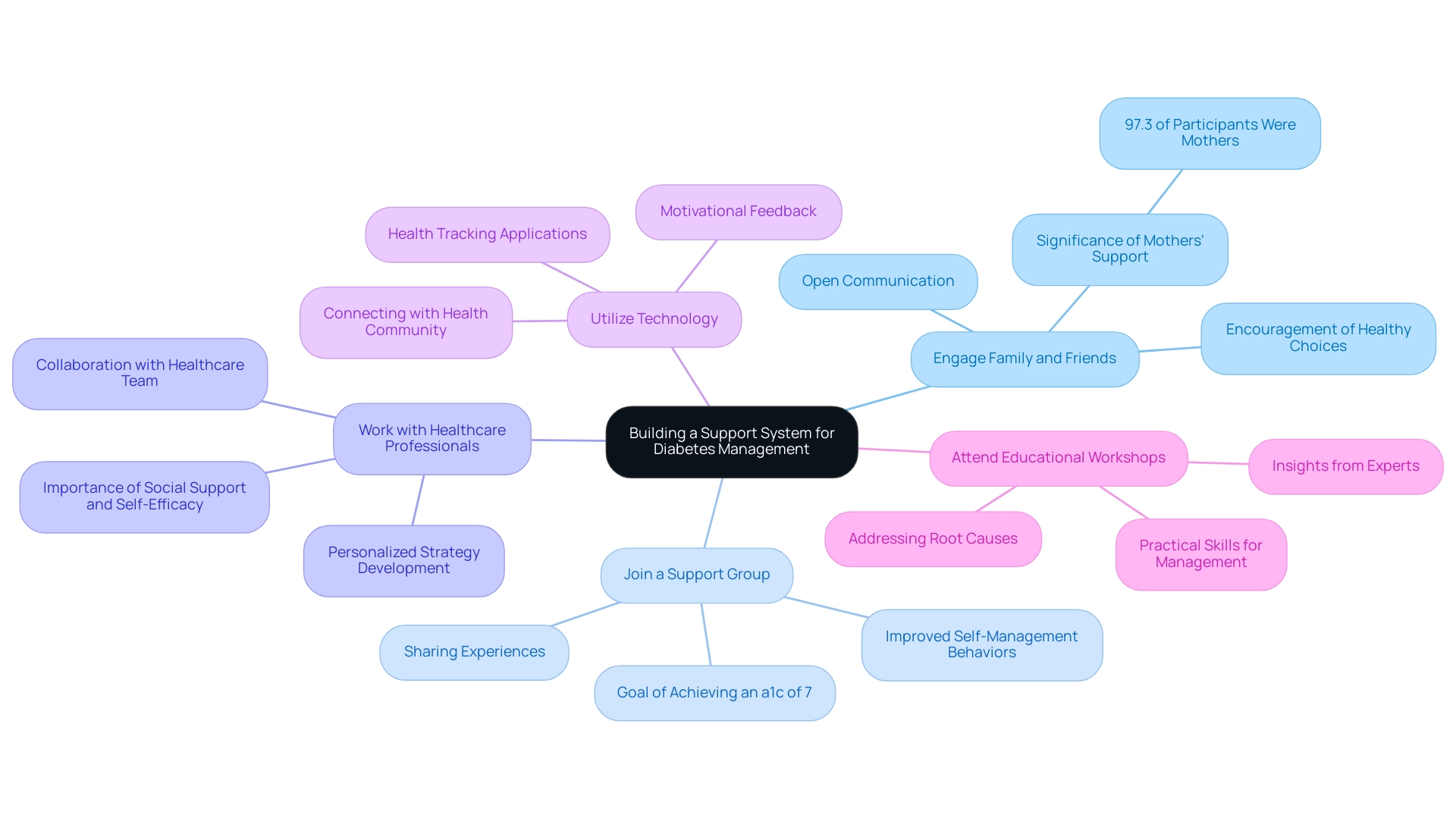
Building a Support System
Establishing a robust support system is essential for navigating the complexities of managing the condition, especially when aiming to eliminate anxiety over potential complications. A key element of this journey entails reassessing the origin of your condition, which can greatly affect your overall well-being. Research published in Clinical Therapeutics in 2011 highlights that adherence to treatment for the condition is closely linked to clinical and economic outcomes, reinforcing the critical role of support systems.
Here are several strategies to enhance your journey:
- Engage Family and Friends: Openly communicate your health goals with family and friends, encouraging them to partake in healthier lifestyle choices alongside you. Given that 97.3% of participants in relevant studies were mothers, the involvement of family, especially mothers, can significantly enhance management outcomes, reinforcing the need for their support and engagement.
- Join a Support Group: Actively seek out local or online support groups to help manage blood sugar conditions and achieve an a1c of 7. These communities provide a platform for sharing experiences, challenges, and triumphs, creating an environment of understanding and encouragement, while also empowering patients through education. Statistics have shown that participation in support groups can lead to improved self-management behaviors among patients, particularly those aiming for an a1c of 7.
- Work with Healthcare Professionals: Collaborate closely with a team of healthcare providers, including physicians, dietitians, and educators focused on managing blood sugar to achieve an a1c of 7. Together, you can create a personalized strategy that addresses your unique circumstances and health objectives. Insights from experts highlight that the impact of social support, along with self-efficacy in managing the condition and resilience, is vital for effective control to maintain an a1c of 7.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage health condition tracking applications to monitor your progress and connect with others in the health community. These tools can facilitate extra support and offer motivational feedback, enhancing your overall efforts and challenging common health myths.
- Attend Educational Workshops: Participate in workshops or seminars focused on managing diabetes-related conditions to achieve an a1c of 7. These events provide valuable insights and motivation from experts in the field, equipping you with practical skills to better manage your condition and achieve an a1c of 7 while addressing the issue at its core. Furthermore, think about integrating a comprehensive routine that tackles not only the symptoms but the root causes of the condition, which can further improve your wellness journey.
Moreover, case studies demonstrate the varied outcomes concerning social support’s direct effect on self-management, highlighting the importance of personal initiative alongside support systems. Remember, building a support system not only aids in managing diabetes but also fosters a sense of community and shared purpose, empowering you to take control of your health.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing diabetes is a multifaceted journey, with the A1C test playing a critical role in assessing average blood glucose levels and guiding effective treatment strategies. By aiming for an optimal A1C level of 7% or lower, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. This article has outlined essential strategies such as:
- Dietary modifications
- Regular physical activity
- Medication management
- The importance of monitoring blood sugar levels
All of these contribute to effective diabetes management.
Incorporating meal planning and stress management techniques further empowers individuals to take charge of their health. Establishing a robust support system through family, friends, healthcare professionals, and community groups enhances the chances of success in achieving diabetes management goals. By fostering an environment of support and education, individuals are better equipped to navigate the challenges of diabetes with confidence.
Ultimately, the journey toward effective diabetes management is not a solitary one. It requires informed decision-making, consistent effort, and a holistic approach that addresses both physical and emotional health. By implementing these strategies and prioritizing regular check-ups, individuals can work towards maintaining healthy A1C levels, leading to improved overall health and a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test evaluates average blood glucose readings over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. It is important for individuals with diabetes as it helps in formulating effective management strategies and mitigating the risk of complications.
What is the recommended target A1C level for adults with diabetes?
A target A1C of 7% or lower is typically recommended for adults diagnosed with diabetes.
How often should A1C testing be conducted?
Routine A1C testing is generally conducted every three to six months to track progress and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
What factors can influence A1C test results?
Factors that can influence A1C results include recent illnesses or adjustments in medication.
What strategies can help achieve and maintain an A1C of 7%?
Strategies include dietary modifications, regular physical activity, medication management, monitoring blood sugar readings, stress management, and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers.
What dietary modifications are recommended for managing A1C levels?
Recommended dietary modifications include prioritizing a balanced diet with whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables, as well as monitoring carbohydrate consumption.
How much physical activity is recommended for individuals aiming to manage their A1C?
Individuals should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, along with strength training exercises on at least two days.
Why is medication management important in controlling blood sugar levels?
Medication management is important because it ensures that the treatment regimen is tailored to individual needs, which may include oral medications, insulin therapy, or other injectable treatments.
How can monitoring blood sugar readings assist in diabetes management?
Regularly checking blood glucose readings helps individuals understand how various foods, activities, and medications influence their A1C, allowing for necessary modifications in their management strategy.
What role does stress management play in diabetes management?
Managing stress is vital because elevated stress levels can adversely affect blood sugar control. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can promote better overall well-being.
Why are regular follow-ups with healthcare providers essential?
Regular follow-ups are essential to review progress, address challenges, and make adjustments to care plans, ensuring ongoing support and guidance in managing diabetes effectively.