Overview
Understanding diabetes management can be challenging, especially when it comes to interpreting different metrics. The article explores whether GMI (Glucose Management Indicator) is synonymous with A1C (hemoglobin A1c). While both are vital for managing diabetes, it’s important to recognize that they differ in their methodologies and implications.
GMI offers a real-time estimate of average glucose levels over a short period, providing immediate insights into your current state. In contrast, A1C reflects historical blood sugar levels over two to three months, giving a broader view of your glucose control. This distinction is crucial for tailoring treatment plans effectively.
Many patients find that understanding these differences can empower them to make informed decisions about their health. Studies have shown variability between the two measurements, highlighting the importance of discussing these results with your healthcare provider. By doing so, you can develop a more personalized approach to managing your diabetes, ultimately leading to a healthier lifestyle.
Introduction
Understanding diabetes management can feel overwhelming, especially with the many metrics available to monitor glucose levels. Among these, the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) and hemoglobin A1C (A1C) stand out. Each serves a unique purpose in tracking blood sugar control, and it’s important to recognize that they can provide different insights.
As healthcare providers and patients work together to optimize diabetes care, a common question arises: Are GMI and A1C interchangeable, or do they offer distinct insights that can enhance treatment strategies? Many patients find that exploring the nuances between these two metrics not only reveals their differences but also opens the door to a more comprehensive approach to diabetes management.
Define GMI: Understanding the Glucose Management Indicator
The Management Indicator for Sugar (GMI), which is gmi same as A1C, serves as a vital metric derived from continuous sugar monitoring (CGM) data to estimate an individual’s average hemoglobin A1c (A1C) level. It’s important to recognize that while A1C reflects blood sugar levels over an extended period, the question of is GMI same as A1C arises, as GMI provides a more immediate evaluation of sugar control. This feature is especially beneficial for individuals managing diabetes, as it allows for real-time insights into current glucose control. Calculated from the average glucose levels recorded by CGM devices over a typical 14-day period, GMI enables healthcare providers and patients to make informed treatment decisions more swiftly.
Many patients find that integrating GMI with personalized functional medicine strategies enhances their diabetes care. This approach focuses on individual health profiles through comprehensive assessments and diagnostic tests that aim to identify underlying issues. For instance, in San Marcos, CA, individuals can take advantage of local resources such as:
- Farmers’ markets for fresh produce
- Community wellness programs for support
- Outdoor activities that promote regular exercise
Furthermore, incorporating stress reduction techniques like mindfulness and yoga can significantly enhance blood sugar control. By doing so, GMI becomes a crucial element of a holistic strategy for managing type 2 diabetes, fostering a supportive environment for healthier living.
Compare GMI and A1C: Key Differences and Similarities
Managing diabetes can feel overwhelming at times, and understanding the tools available to you is crucial. In evaluating sugar management, it is important to understand whether GMI is the same as A1C, as both are essential metrics but differ significantly in their methodologies and implications. A1C measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, offering a historical perspective on your sugar management. In contrast, GMI provides a more immediate estimate, derived from real-time information gathered by continuous monitoring (CGM) devices. This responsiveness means GMI can quickly adapt to changes in your sugar control strategies, making it especially beneficial for those actively adjusting their treatment plans.
It’s important to recognize that recent studies show that while the question of whether GMI is the same as A1C can effectively predict A1C levels, discrepancies can occur. For example, only 11% of participants in one study demonstrated less than a 0.1 percentage point difference between their A1C and GMI results. This highlights the value of using both metrics together: A1C gives you a long-term view of glucose control, while GMI offers immediate feedback, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of your glucose oversight.
By focusing on both metrics, healthcare providers can better tailor treatment plans to meet your unique needs. Additionally, incorporating holistic health solutions, like engaging in outdoor activities and maintaining a balanced diet rich in local produce, can significantly enhance your diabetes control. Community wellness programs can also provide essential support and resources tailored to effectively managing diabetes. Remember, you’re not alone on this journey, and there are many avenues to explore for a healthier lifestyle.
Evaluate GMI’s Role in Diabetes Management: Accuracy and Clinical Implications
The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) plays a crucial role in diabetes management, providing a timely estimate of A1C levels that can help healthcare providers make informed treatment adjustments. It’s important to recognize that while research shows GMI is the same as A1C as a reliable indicator, individual differences in sugar metabolism may lead to discrepancies. For example, some patients with elevated sugar levels might find that GMI underestimates their A1C, which underscores the importance of using both metrics together for comprehensive monitoring.
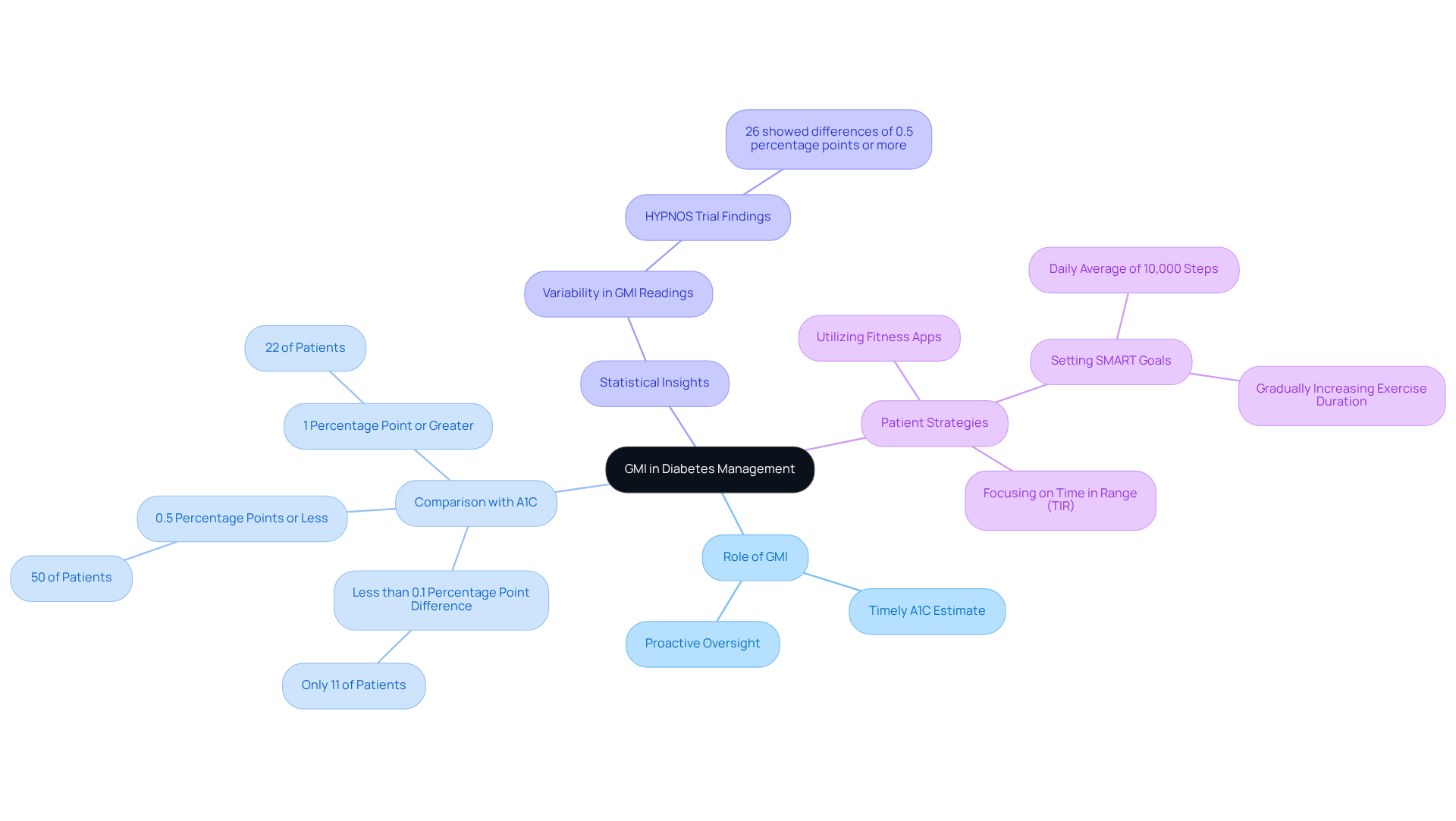
In clinical practice, GMI assists in identifying patterns in sugar regulation, fostering proactive diabetes oversight and reducing the risk of complications. A study involving 641 diabetes patients revealed that:
- Only 11% showed less than a 0.1 percentage point difference between GMI and A1C.
- 50% had differences of 0.5 percentage points or less.
- Additionally, 22% of participants experienced a difference of 1 percentage point or greater.
This variability highlights the significance of incorporating GMI into standard diabetes care, as it provides patients with practical insights into their blood sugar management.
Many patients find that the application of GMI in real-world settings can guide their treatment decisions effectively. For instance, during the HYPNOS trial, discrepancies between GMI readings from different continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) sensors were observed, with about 26% of participants showing differences of 0.5 percentage points or more. Such findings emphasize the need for healthcare providers to consider whether GMI is the same as A1C when assessing patient progress and adjusting treatment plans.
To further enhance diabetes control, patients are encouraged to adopt effective strategies for tracking their progress. Have you considered utilizing fitness apps, journals, or pedometers? Setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can significantly boost your focus and motivation. For example, you might aim to maintain a daily average of 10,000 steps or gradually increase your exercise duration. Regularly reviewing your progress not only fosters accountability but also allows you to adapt your goals in response to changing fitness levels. By utilizing GMI and emphasizing organized goal-setting, healthcare professionals can improve patient engagement and inspire a more proactive approach to diabetes care. Furthermore, focusing on Time in Range (TIR) is recommended for better diabetes outcomes, as it offers a more comprehensive view of glucose management.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) and A1C is essential for effective diabetes management. It’s important to recognize that while both metrics serve as critical tools for monitoring blood sugar levels, GMI offers a more immediate reflection of glucose control, derived from real-time data gathered through continuous glucose monitoring. This immediacy allows for timely adjustments in treatment strategies, making GMI a valuable asset for individuals managing diabetes.
Many patients find that the article highlights the key differences and similarities between GMI and A1C, emphasizing that while A1C provides a historical perspective on blood sugar levels over a two to three-month period, GMI captures current glucose trends. It underscores the importance of utilizing both metrics in tandem, as they complement each other to provide a comprehensive view of diabetes management. Incorporating holistic health strategies, such as engaging in local community resources and adopting mindful practices, further enhances the effectiveness of these metrics in improving overall health outcomes.
In conclusion, leveraging both GMI and A1C can empower individuals to take control of their diabetes management. By understanding how these indicators work together, patients and healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans more effectively. Embracing a proactive approach that includes regular monitoring, goal-setting, and lifestyle adjustments can lead to better health and a more fulfilling life. The journey of managing diabetes is complex, but with the right tools and support, it becomes a path towards improved well-being and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI)?
The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) is a metric derived from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data that estimates an individual’s average hemoglobin A1c (A1C) level, providing a more immediate evaluation of sugar control.
How does GMI compare to A1C?
While both GMI and A1C reflect blood sugar levels, A1C indicates levels over an extended period, whereas GMI offers real-time insights into current glucose control, making it especially beneficial for individuals managing diabetes.
How is GMI calculated?
GMI is calculated from the average glucose levels recorded by CGM devices over a typical 14-day period.
How can GMI assist in diabetes management?
GMI allows healthcare providers and patients to make informed treatment decisions more swiftly by providing immediate insights into glucose control.
What additional strategies can enhance diabetes care alongside GMI?
Integrating GMI with personalized functional medicine strategies, which include comprehensive assessments and diagnostic tests, can enhance diabetes care by identifying underlying health issues.
What local resources are available for diabetes management in San Marcos, CA?
In San Marcos, CA, individuals can access farmers’ markets for fresh produce, community wellness programs for support, and outdoor activities that promote regular exercise.
How can stress reduction techniques impact blood sugar control?
Incorporating stress reduction techniques like mindfulness and yoga can significantly enhance blood sugar control, contributing to overall diabetes management.