Overview
Understanding the A1C definition of diabetes is crucial for anyone navigating this condition. Did you know that an A1C level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes? Meanwhile, levels between 5.7% and 6.4% signal prediabetes. It’s important to recognize that these numbers can feel overwhelming, but they are essential for effective management.
The A1C test offers a reliable assessment of your average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. Many patients find that this insight enables them to monitor their health more effectively and develop tailored treatment strategies. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; there are ways to take control and improve your well-being.
By focusing on your A1C levels, you can take proactive steps toward a healthier life. If you’re feeling uncertain or anxious, consider reaching out for support. Programs like the 30-Day Diabetes Reset can provide you with the guidance and encouragement needed to navigate this path with confidence.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, it’s important to recognize that understanding the A1C test is a pivotal component in diagnosing and monitoring this chronic condition. This essential diagnostic tool measures average blood glucose levels over the previous two to three months, providing crucial insights into your blood sugar control. As diabetes and prediabetes continue to pose significant public health challenges, the A1C test serves not only as a reliable indicator for diagnosis but also plays a vital role in shaping personalized treatment strategies.
Many patients find that with a growing emphasis on holistic approaches to health, integrating A1C testing into comprehensive diabetes care programs empowers them to take charge of their health. This fosters informed decisions and improved outcomes. This article delves into the intricacies of the A1C test, its implications for diabetes management, and the transformative potential of lifestyle modifications in achieving optimal health. Together, we can navigate this journey toward better health and well-being.
Understanding A1C: The Key Metric in Diabetes Diagnosis
The A1C test, officially known as the hemoglobin A1C test, is a crucial tool for understanding diabetes. It assesses your average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, providing a clear picture of how well your blood sugar has been managed. This test is particularly important for diagnosing conditions related to blood sugar regulation, as it aligns with the A1C definition of diabetes. Results are expressed as a percentage, indicating the proportion of hemoglobin molecules that have glucose attached.
When we look at the A1C definition of diabetes, an elevated percentage signals poorer blood sugar control. This makes it an essential metric not only for diagnosis but also for ongoing management of the condition.
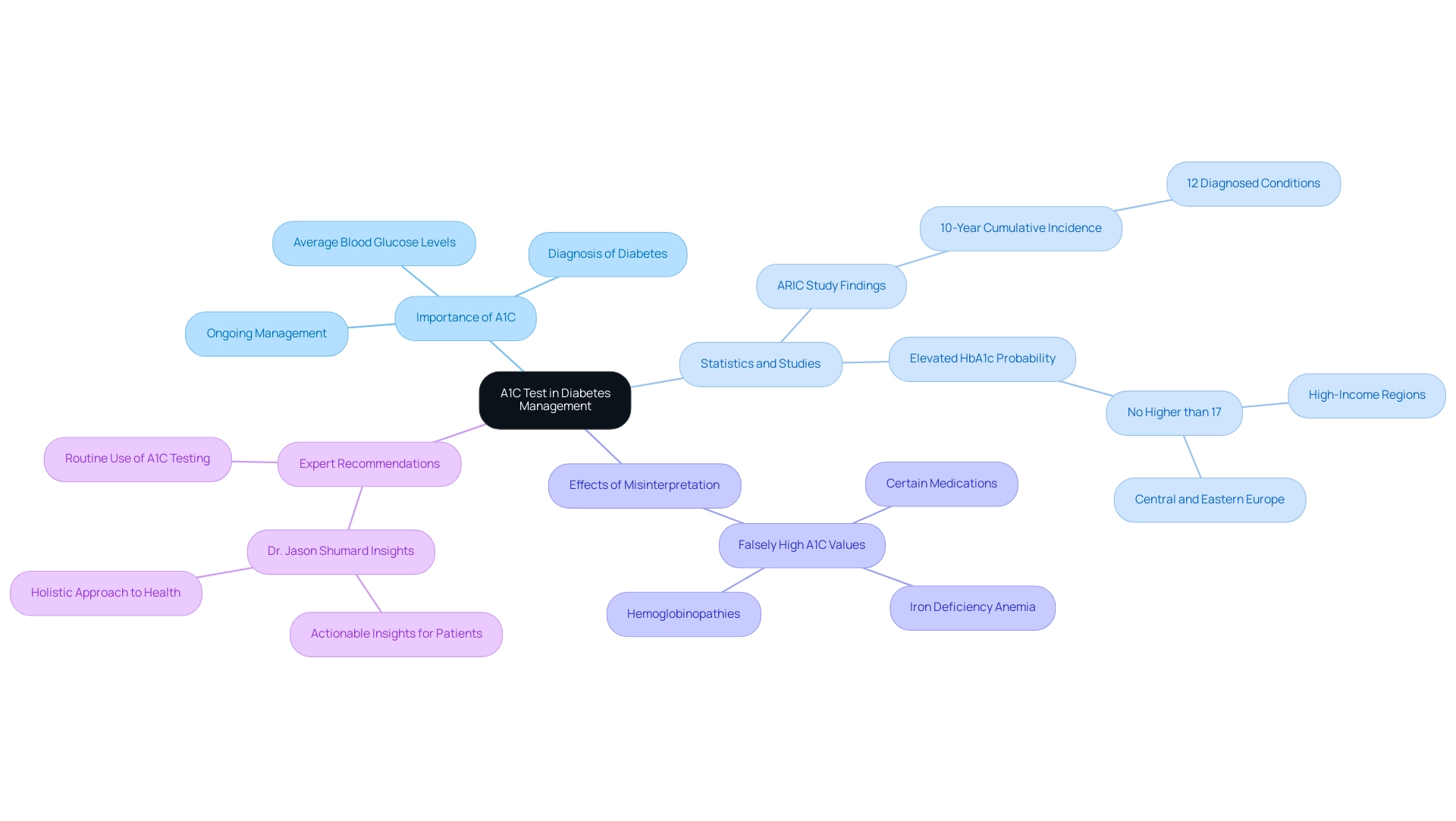
Recent studies underscore the importance of the A1C test in accurately identifying diabetes. For example, the ARIC study revealed varying effectiveness in classifying new cases of diabetes, showing a 10-year cumulative incidence of diagnosed conditions at 12%. This highlights the test’s role in assessing diabetes risk and the necessity of using both A1C and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) for accurate diagnosis, especially in low-resource settings where misdiagnosis can have serious health implications. Understanding the A1C definition of diabetes is vital in these contexts.
Current statistics show that the likelihood of having elevated HbA1c levels is relatively low—no higher than 17%—in high-income regions and central and eastern Europe for individuals of the same age and FPG level. This data reinforces the reliability of the A1C test in these populations. However, it’s important to recognize that falsely high A1C values can arise due to conditions like iron deficiency anemia, hemoglobinopathies, and certain medications, complicating the interpretation of results. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective care and management strategies.
Experts emphasize the significance of A1C testing in managing glucose levels. Endocrinologists advocate for the routine use of the A1C definition of diabetes, as it not only aids in diagnosis but also serves as a vital indicator for monitoring long-term glucose control. Dr. Jason Shumard highlights, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where people can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.”
This aligns beautifully with the holistic approach championed by Dr. Shumard and his Integrative Wellness Center, particularly through the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program. By incorporating the A1C test into this program, patients are empowered to take charge of their health, make informed decisions about their treatment options, and effectively manage their condition. This approach also addresses the pressing safety concerns associated with traditional hospital care, fostering a supportive environment for everyone involved.
Defining Diabetes and Prediabetes: A Foundation for A1C Understanding
Diabetes is a chronic condition that can feel overwhelming, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to the body’s struggle to produce or effectively use insulin. On the other hand, prediabetes serves as an important warning signal; blood sugar readings are elevated beyond normal but not high enough to be classified as a serious condition. According to the American Diabetes Association, a diagnosis of diabetes is made when a person has an A1C level of 6.5% or higher, while prediabetes is indicated by an A1C level ranging from 5.7% to 6.4%. Understanding the A1C definition of diabetes is essential for managing blood sugar effectively.
As of 2025, blood sugar disorders and prediabetes continue to be significant public health concerns in the United States, affecting millions of lives. Recent statistics reveal a sharp increase in the prevalence of these conditions, with the excess medical costs per person rising from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022. This alarming trend underscores the urgent need for effective screening and intervention strategies.
A case study focusing on public awareness and screening for diabetes highlights the critical importance of early detection. Many individuals remain undiagnosed, despite the rising prevalence of the disease. The introduction of new screening guidelines aims to identify a larger percentage of undiagnosed cases, enabling timely intervention and management.
This commitment to addressing these challenges is echoed in Dr. Jason Shumard’s work at the Integrative Wellness Center. His innovative methodologies and patient education initiatives, particularly the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, have transformed the lives of many individuals on their health journeys.
The connection between A1C measurements and the A1C definition of diabetes is vital. A1C testing provides a reliable assessment of average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, which is crucial for understanding diabetes and diagnosing related conditions. Expert insights emphasize that grasping the A1C definition of diabetes is essential for effective management and prevention strategies.
As Dr. Shumard puts it, “By offering individuals actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center cultivates an environment where people can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.”
Testimonials from participants in the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program highlight its success:
- ‘I lost 55 lbs. My A1C started at 9.1, and after 8 months, it is now 5.7. Fasting glucose was at 133 and now it is at 85.’
- Another individual shared, “I feel so much better, and going through the cleanse helped in so many ways. I lost a lot of weight, have more energy, and feel great. I am not depressed anymore, and I don’t need my meds anymore!”
In summary, understanding the meanings of diabetes and prediabetes, along with the A1C definition of diabetes, is vital for individuals navigating their health journeys. By fostering awareness and encouraging proactive screening, we can better address the challenges posed by these chronic conditions, empowering patients to take control of their health through functional medicine approaches. To learn more about how Dr. Shumard can help you restore your health and get your life back, call the Integrative Wellness Center at 858-564-7081 or register for the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program today!
Diagnostic Criteria for Diabetes: The Role of A1C Testing
The A1C test plays a vital role in understanding diabetes, serving as a key tool for diagnosis alongside fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT). According to the American Diabetes Association, a diagnosis of diabetes is confirmed when an A1C measurement reaches 6.5% or greater on two separate occasions. For those at risk of developing blood sugar issues, an A1C measurement between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, highlighting the importance of taking proactive health measures.
One of the significant benefits of the A1C test is its convenience; it doesn’t require fasting and reflects average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. This broader perspective allows healthcare providers and individuals to make informed choices about managing and treating diabetes. A recent study in India, involving over 1,150 individuals aged 40 and older, revealed that 20.7% met the criteria for prediabetes, while 14.6% were diagnosed with diabetes, underscoring the prevalence of these conditions.
Additionally, the A1C definition of diabetes can be expressed through estimated Average Glucose (eAG), which offers relatable context for typical blood glucose readings, even though it may differ from home meter results. This dual reporting enhances patient understanding and engagement in their health management.
As we look toward 2025, updates in diagnostic criteria for A1C testing are evolving, which are crucial for grasping the A1C definition of diabetes and reflect advancements in blood sugar management. New methods for diagnosing this condition are being explored, with experts emphasizing the importance of accurate and timely diagnosis to prevent complications. The A1C definition of diabetes remains a cornerstone in this effort, providing a reliable measure that, when compared to fasting plasma glucose and OGTT, offers a more comprehensive view of long-term glucose control.
Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes that ‘dedication to client education and empowerment, combined with innovative methodologies, offers a unique value proposition in the healthcare landscape.’ This philosophy resonates with the importance of understanding the A1C definition of diabetes for effective management. By equipping individuals with knowledge about the A1C definition of diabetes and its implications for their health, they can take proactive steps toward reclaiming their well-being.
Incorporating effective strategies for tracking progress, such as setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can significantly enhance blood sugar management. For instance, patients might aim to reduce their A1C values by a certain percentage within a set timeframe or gradually increase their physical activity. Utilizing tracking methods like fitness apps, journals, and pedometers can further support this journey.
Regularly reviewing progress not only fosters accountability but also allows for the adaptation of goals in response to changing health conditions. Understanding the A1C definition of diabetes is essential for effective management, particularly in relation to Dr. Shumard’s holistic approach to health, which emphasizes personalized care and education. It is also crucial to recognize that the A1C definition of diabetes indicates that A1C test results should be confirmed through repeat testing to ensure accurate diagnosis and management of the condition.
The A1C Test Explained: Measurement and Methodology
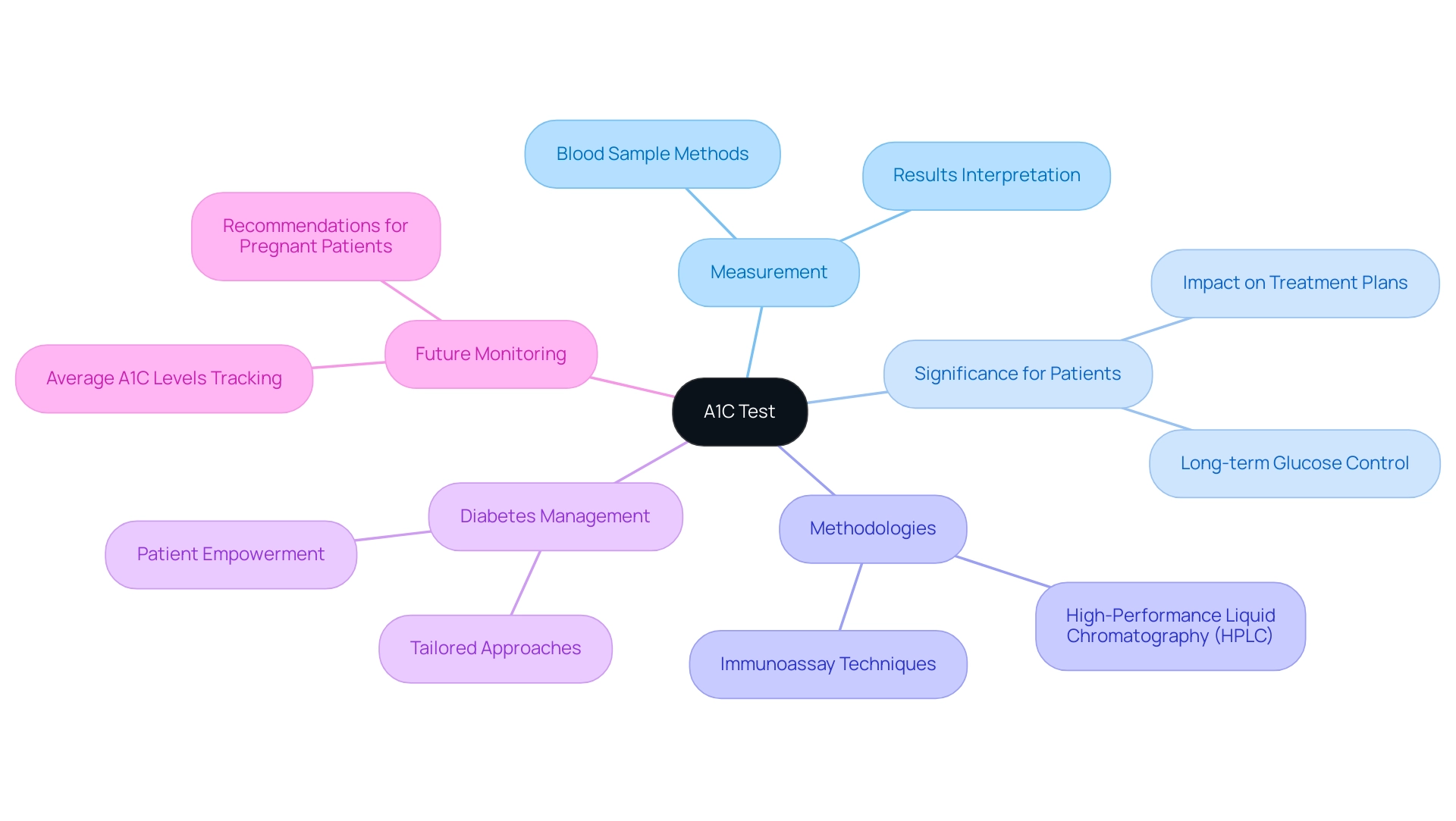
The A1C test is a vital diagnostic tool that measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in the blood, indicating how much glucose has been attached to hemoglobin over time. Typically, this test is conducted using a blood sample drawn from a vein or via a finger prick, with results expressed as a percentage. It’s important to recognize that normal A1C values are regarded as being below 5.7%.
By reflecting average blood glucose readings over the prior two to three months, the A1C test offers a more stable and comprehensive measure than daily blood sugar tests. This makes it essential for both diagnosing the condition and monitoring ongoing management, providing reassurance to those navigating their health journey.
Looking ahead to 2025, average A1C levels in the general population will be closely monitored, as healthcare providers emphasize the significance of maintaining optimal levels to prevent complications related to blood sugar issues. For instance, many patients with Type 1 diabetes who are pregnant are advised to aim for an A1C of 6.5% or lower throughout their pregnancy, minimizing risks to both mother and child.
The importance of effective management of diabetes is underscored by the fact that it was the eighth leading cause of death in the United States in 2021, with 103,294 death certificates citing it as the underlying cause. Additionally, the total estimated costs of diagnosed metabolic disorders in the U.S. in 2022 reached $413 billion, highlighting the economic burden of this chronic condition.
At Dr. Jason Shumard’s Integrative Wellness Center, founded in 2005, the methodology for conducting the A1C test is complemented by personalized functional medicine strategies that empower patients to take control of their health. Dr. Shumard, with nearly 20 years of experience, emphasizes the importance of tailored approaches to managing blood sugar conditions. Laboratories employ various techniques to ensure accuracy and reliability, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and immunoassay techniques, which yield consistent results across different populations.
Many patients find that the choice of methodology can significantly impact the interpretation of results, underscoring the need for standardized practices in A1C measurement. Real-world examples illustrate the significance of the A1C definition of diabetes in managing the condition. For instance, an individual with an A1C level of 8% may require adjustments in their treatment plan, while another with a level of 5.5% may be effectively managing their condition. Such interpretations are crucial for tailoring individual care plans, particularly in a holistic approach like that of Dr. Shumard, which focuses on empowering individuals with knowledge and tools to reclaim their health.
As Dr. Shumard states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where people can reclaim their health and well-being.”
Overall, the A1C definition of diabetes serves as a cornerstone in managing blood sugar, providing essential insights into long-term glucose control and guiding treatment decisions. As advancements in testing methodologies continue to evolve, the accuracy and effectiveness of A1C testing will play an increasingly vital role in managing blood sugar levels and improving health outcomes. Furthermore, testimonials from patients underscore the life-changing outcomes achieved through the program, emphasizing the empowerment they feel in taking control of their health through structured goal-setting and progress tracking.
To learn more about how Dr. Shumard and the Integrative Wellness Center can assist you in managing your condition, call us today!
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do the Numbers Mean?
A1C results are classified into specific ranges that reflect an individual’s health condition. An A1C value below 5.7% is considered normal, while readings between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes. A result of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of this condition.
For those managing diabetes, the target A1C value is typically set below 7%. This threshold is crucial, as it is associated with a reduced risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease and neuropathy. It’s important to recognize that achieving this goal can feel overwhelming, but it is a vital step toward better health.
Understanding the A1C definition of diabetes and its thresholds is essential for both individuals and healthcare providers. It facilitates the establishment of realistic treatment goals and enables effective monitoring of progress. For instance, a patient with an A1C of 8% may need to adjust their treatment plan to better manage their blood sugar. Many patients find that small, consistent changes can lead to significant improvements over time.
Current guidelines emphasize the importance of individualized A1C goals. These goals may vary based on factors such as age, duration of diabetes, and the presence of other health conditions. Recent statistics indicate that achieving an A1C below 7% can significantly lower the risk of diabetes-related complications, reinforcing the need for proactive management strategies. Have you considered how your own goals align with these recommendations?
Moreover, it is essential to interpret A1C results in the context of other health indicators. Certain conditions, such as severe anemia, kidney failure, liver disease, and specific medications, can skew A1C results, leading to potential misinterpretations. Therefore, healthcare providers often consider a comprehensive approach that includes regular monitoring of blood glucose readings alongside A1C assessments.
In practice, many individuals have shared their experiences regarding A1C management. For example, individuals participating in Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program at the Integrative Wellness Center have reported significant improvements in their A1C levels. They attribute their success to the program’s focus on education, personalized care, and structured goal-setting. Patients are encouraged to utilize various tracking methods, including fitness apps and journals, to monitor their progress effectively.
As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By offering individuals actionable insights and practical tools, the center cultivates an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to enhanced quality of life and diminished dependence on conventional medical interventions.” This holistic approach empowers patients to take control of their health, ultimately leading to better outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
A1C Levels and Diabetes Management: Setting Goals and Making Adjustments
Effective diabetes management is rooted in the regular monitoring of A1C values, serving as a critical indicator for treatment decisions. It’s important to recognize that when A1C values exceed the target range, healthcare providers typically recommend a multifaceted approach. This may include:
- Medication adjustments
- Dietary modifications
- Increased physical activity
For instance, if a patient’s A1C consistently registers above 7%, a provider might advocate for more intensive lifestyle changes or a reevaluation of medication to enhance glycemic control.
Many patients find that real-world examples demonstrate the positive impact of lifestyle changes on A1C values. Those who adopt a balanced diet rich in whole foods and engage in regular physical activity often see significant improvements in their A1C readings. A case study from 2020 highlighted the variability in diabetes incidence across U.S. counties, with rates ranging from 2.2 to 53.5 per 1,000 people. This underscores the need for localized health strategies that can effectively address diabetes prevalence and inform public health initiatives.
Current recommendations regarding the A1C definition of diabetes emphasize the importance of personalized treatment goals. In 2025, healthcare providers are encouraged to collaborate with individuals to establish individualized A1C targets that reflect their unique health circumstances and lifestyle. This personalized approach not only fosters better adherence to treatment plans but also empowers individuals to take an active role in their health management.
Statistics indicate that tracking A1C readings is a frequent activity among individuals with this condition, with many undergoing testing at least twice annually. Notably, from 2012 to 2022, excess medical costs per person linked to the condition increased from $10,179 to $12,022, highlighting the financial impact of the illness and the importance of effective management strategies. Expert guidance from diabetes management specialists indicates that treatment adjustments based on A1C levels should be customized to each individual’s specific needs, ensuring that strategies are both effective and sustainable.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize the importance of tracking progress and setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. By utilizing various tracking methods such as fitness apps, which can log daily activity and provide insights into step counts, and journals that allow individuals to reflect on their dietary choices and physical activity, users can monitor their progress effectively. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By offering individuals actionable insights and practical tools, the center cultivates an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to enhanced quality of life and diminished dependence on conventional medical interventions.”
This method not only fosters a sense of accomplishment but also keeps individuals engaged in health management, enabling them to transform their health journeys. If you’re ready to take control of your health, contact us today to learn more about how we can support you in achieving your health goals.
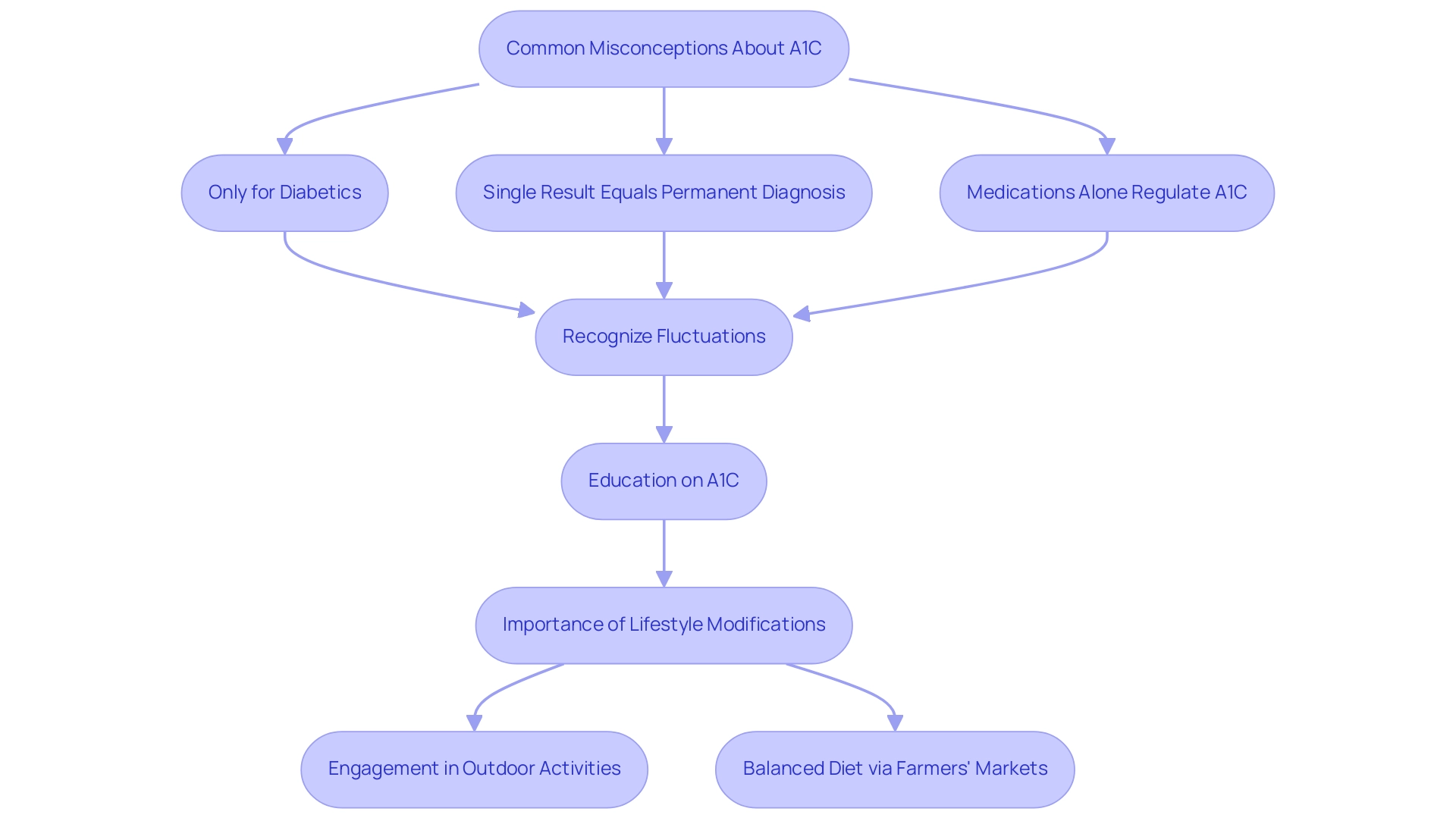
Common Misconceptions About A1C: What Patients Should Know
Misunderstandings surrounding the A1C test are common among patients. Many believe it applies only to those diagnosed with diabetes or think that a single elevated result means a permanent diagnosis. It’s important to recognize that A1C values can fluctuate due to various factors, including stress, illness, and dietary changes. Furthermore, some individuals mistakenly assume that medication alone can regulate their A1C values, overlooking the crucial role of lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise.
In San Marcos, CA, embracing a holistic lifestyle is essential for effective diabetes management. Many patients find that participating in consistent outdoor activities, like hiking at Lake San Marcos or strolling along the paths at Discovery Lake, not only enhances physical fitness but also promotes mental wellness. This balance is vital for regulating blood sugar. Additionally, the vibrant local farmers’ markets offer access to fresh, nutritious produce, including avocados and berries, which can help regulate A1C levels and support overall health.
Statistics reveal that individuals relying on oral medications often have a distorted view of their condition, with an odds ratio of 4.7 for believing these effects are confined. This highlights the urgent need for comprehensive education on the significance of A1C testing and its implications for diabetes management, as discussed in recent conversations about diabetes education.
Real-world examples from Dr. Jason Shumard’s practice illustrate the transformative impact of client education. Through the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, individuals gain insights into the factors influencing their A1C levels, which aligns with the understanding of diabetes. This empowers them to take charge of their health. Testimonials from participants underscore the importance of grasping the A1C definition and integrating lifestyle changes into their management plans.
One participant shared, “I lost 55 lbs. My A1C started at 9.1, and after 8 months, it is now 5.7,” highlighting the effectiveness of personalized functional medicine approaches.
Dr. Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” Addressing misconceptions about blood sugar regulation is vital for nurturing a proactive approach to care. Effective management of diabetes requires frequent daily blood glucose monitoring and attention to lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress management.
By equipping patients with accurate information and practical tools, healthcare providers can help individuals navigate their conditions more effectively. This ultimately leads to improved health outcomes and a greater quality of life. Additionally, participating in community wellness programs in San Marcos can offer invaluable support for managing type 2 conditions, providing resources tailored to individual needs.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting A1C: A Holistic Approach to Diabetes Management
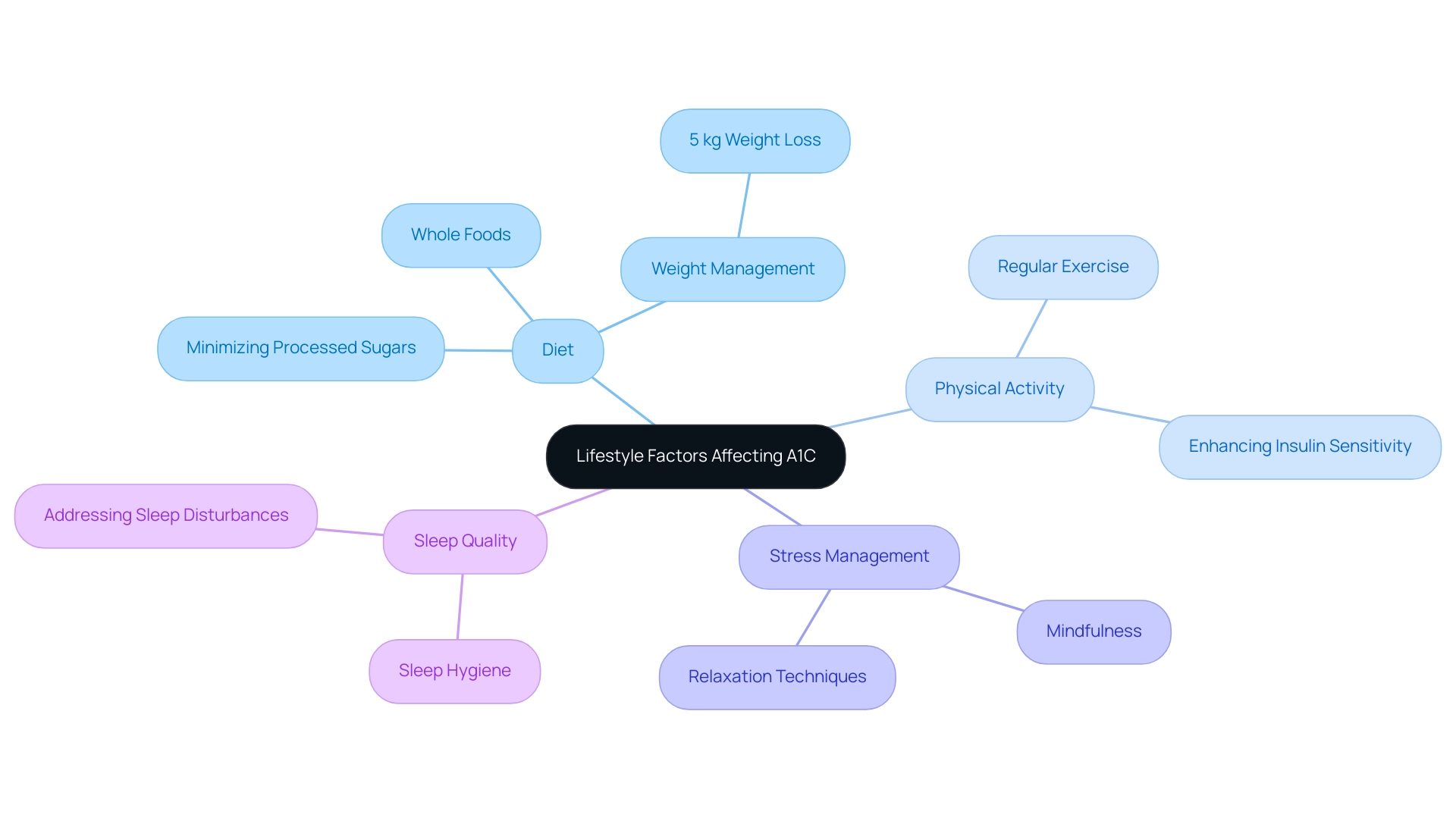
Lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, stress management, and sleep quality are essential in shaping the A1C definition of diabetes. It’s important to recognize that a balanced diet, particularly one rich in whole foods, can significantly impact blood sugar control. For instance, studies show that a modest weight loss of just 5 kg can lead to a remarkable 58% reduction in diabetes incidence. This underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy weight through thoughtful dietary choices in the context of A1C management.
At Integrative Wellness Center, we understand the unique challenges each individual faces. We emphasize personalized nutrition plans tailored to individual needs, which are foundational in functional medicine. These plans focus on nutrient-rich foods designed to stabilize blood sugar and enhance metabolic function, ultimately promoting overall health. Transformative patient experiences, such as those shared by Ed, highlight how our compassionate approach can lead to positive change.
Many patients find that participating in Dr. Jason Shumard‘s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program can be life-changing. Ed, for example, reported significant improvements in his health, including a reduction in A1C numbers from 9.1 to 5.7 and a weight loss of 55 lbs. His story exemplifies how personalized care can lead to remarkable outcomes.
Regular physical activity is another key component of diabetes management. It enhances insulin sensitivity, which is vital for effective blood sugar regulation. Engaging in regular exercise not only aids in lowering A1C values but also boosts overall well-being. Furthermore, effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, can help mitigate the adverse effects of stress on blood sugar, promoting a more stable A1C.
The influence of diet and exercise on A1C levels is crucial for understanding the A1C definition of diabetes and managing the condition. Nutritionists emphasize that incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods while minimizing processed sugars can lead to significant improvements in A1C readings. Real-world examples illustrate how individuals adopting a holistic approach—addressing not just dietary habits but also physical activity and mental health—experience enhanced quality of life and improved control of their condition.
Dr. Jason Shumard highlights, “What sets the Integrative Wellness Center apart is its holistic approach to health, focusing on personalized care and education rather than just symptom management.”
Recent findings show that behavioral factors, including sedentary lifestyles and sleep disturbances, are linked to a heightened risk of diabetes, regardless of other health issues. This reinforces the need for a comprehensive strategy that encompasses all aspects of lifestyle. By focusing on these factors, individuals can achieve A1C levels that align with the A1C definition of diabetes, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.
The center’s commitment to personalized care and education exemplifies how addressing lifestyle factors can lead to significant improvements in diabetes management. We invite you to take that first step toward a healthier life.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is essential for effective diabetes management. It provides crucial insights into average blood glucose levels over time. This diagnostic tool not only aids in diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes but also plays a significant role in ongoing management strategies. By recognizing the importance of A1C levels, patients can make informed decisions about their health. They can embrace lifestyle modifications that lead to improved outcomes.
The article highlights the transformative potential of personalized care and education in diabetes management. Through programs like the 30-Day Diabetes Reset, individuals are empowered to take control of their health. This empowerment often leads to significant improvements in A1C levels and overall well-being. It’s important to recognize that holistic approaches—addressing diet, physical activity, stress management, and sleep quality—underscore the multifaceted nature of diabetes care.
Ultimately, fostering awareness and understanding of A1C testing can reshape the landscape of diabetes management. Many patients find that by equipping themselves with the knowledge and tools necessary to interpret their A1C results, they can implement effective lifestyle changes. Healthcare providers play a vital role in helping individuals navigate their health journeys with confidence. The integration of A1C testing within comprehensive care strategies paves the way for better health outcomes and a higher quality of life for those living with diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, measures average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. It is crucial for diagnosing diabetes and assessing blood sugar management, as it indicates the percentage of hemoglobin molecules with glucose attached.
How is diabetes defined in relation to A1C levels?
According to the American Diabetes Association, diabetes is diagnosed when a person has an A1C level of 6.5% or higher. Prediabetes is indicated by an A1C level between 5.7% and 6.4%.
What role does the A1C test play in diabetes management?
The A1C test is essential for both diagnosing diabetes and ongoing management of the condition. It helps monitor long-term glucose control and provides actionable insights for individuals managing their health.
What are the recent statistics regarding A1C levels and diabetes prevalence?
Recent studies show that the likelihood of elevated HbA1c levels is low in high-income regions, with no more than 17% of individuals having elevated levels for the same age and fasting plasma glucose. The prevalence of blood sugar disorders and prediabetes is increasing, with medical costs per person rising from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022.
What factors can affect A1C test results?
Conditions such as iron deficiency anemia, hemoglobinopathies, and certain medications can lead to falsely high A1C values, which complicates the interpretation of results.
How does Dr. Jason Shumard’s approach relate to the A1C test?
Dr. Shumard emphasizes the significance of A1C testing in managing glucose levels. His Integrative Wellness Center incorporates the A1C test into programs like the 30-Day Diabetes Reset, empowering patients to take charge of their health and make informed treatment decisions.
What is the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program?
The 30-Day Diabetes Reset program is an initiative at the Integrative Wellness Center designed to help individuals manage their diabetes more effectively. It incorporates A1C testing and provides practical tools and insights for improving health and reducing reliance on conventional medical interventions.
What testimonials have participants shared about the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program?
Participants have reported significant health improvements, such as weight loss and reduced A1C levels. For example, one individual lost 55 pounds and reduced their A1C from 9.1 to 5.7, while another mentioned increased energy and improved mental health.