Overview
The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to effectively use the A1C to glucose level chart to manage blood sugar levels and understand the implications of A1C test results. It emphasizes the importance of obtaining accurate A1C results, interpreting them against average blood glucose levels, and employing lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, to improve overall health and diabetes management.
Introduction
In the heart of San Marcos, CA, the A1C test stands as a pivotal tool in the management of diabetes, offering insights into average blood glucose levels over the past few months. This essential metric not only helps individuals understand their health better but also guides healthcare providers in tailoring effective treatment plans.
With A1C levels serving as indicators of diabetes control, the implications of these results are profound, influencing lifestyle choices and dietary habits. As communities increasingly emphasize holistic approaches to health, the integration of local resources, such as farmers’ markets and wellness programs, becomes crucial in supporting individuals on their journey toward better health outcomes.
This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, the relationship between A1C and daily blood glucose monitoring, and effective strategies for maintaining optimal glucose levels, all while fostering a supportive community environment.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance and Functionality
The A1C test functions as an essential marker of average blood glucose levels over the prior two to three months, and it helps in interpreting the A1C to glucose level chart for effective management in the vibrant community of San Marcos, CA. This test is essential for evaluating the efficacy of your treatment plan for blood sugar management. Understanding your A1C results empowers you and your healthcare provider to make informed decisions regarding your health.
According to expert Emily Eyth, ‘Hemoglobin A1c is a valuable tool in managing blood sugar conditions and other glycemic control disorders, but it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment to be effective.’ An A1C level below 5.7% is categorized as normal according to the A1C to glucose level chart, while levels from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, and levels of 6.5% or above signify a diagnosis of diabetes. Regular A1C testing is paramount for fine-tuning dietary and lifestyle modifications, especially when combined with a holistic approach that incorporates:
- A balanced diet rich in local produce such as avocados and berries
- Community support through wellness programs
- Regular exercise in San Marcos’s beautiful outdoor settings like hiking at Lake San Marcos or walking the trails at Discovery Lake
This comprehensive strategy ensures you stay on course toward better health outcomes. Furthermore, recent studies indicate that undiagnosed cases of this condition prevalence varies significantly:
- 1.6% in underweight or normal weight adults
- 2.8% in overweight adults
- 7.9% among those with obesity
This underscores the need for consistent monitoring and the role of A1C testing in identifying and managing diabetes effectively.
Additionally, there is a growing movement within the medical community to explore emerging methods for glycemic control, such as estimated average blood sugar and blood sugar time in range, which may provide a more accurate view of blood sugar averages and fluctuations. The data for these insights is grounded in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from August 2021 to August 2023.
The Connection Between A1C Levels and Blood Glucose Measurements
A1C values are presented as a percentage, indicating the ratio of hemoglobin molecules in the bloodstream that have sugar attached. For example, an A1C level of 6% corresponds with an average blood sugar level of approximately 126 mg/dL. This relationship is essential for individuals overseeing their condition, as it demonstrates how long-term sugar management aligns with daily blood sugar monitoring.
A higher A1C percentage signifies inadequate blood sugar management, while a lower percentage reflects improved control. According to recent findings, stable A1C levels between 5.6% and 7.6% (38-60 mmol/mol) are indicative of specific types of the condition, highlighting the relevance of this metric in treatment plans. To empower patients, effective strategies for progress tracking should be employed, such as utilizing management applications or journals to log daily glucose readings and set SMART goals.
For example, an individual might aim to increase their daily step count to 10,000 steps or extend their exercise duration by five minutes each week. This structured goal-setting can significantly enhance motivation and accountability for managing blood sugar. Holistic lifestyle strategies, particularly in community settings like San Marcos, CA, emphasize the importance of balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and stress management in improving A1C levels.
Participating in local wellness programs can offer invaluable support and resources tailored to managing health conditions, such as group exercise classes or nutrition workshops, fostering a sense of community and shared goals. Alternative biomarkers, such as fructosamine and glycated albumin, can also be utilized for monitoring glycemic control, providing additional insights for managing blood sugar. Using an A1C to glucose level chart is crucial in connecting these two essential measurements.
Furthermore, ongoing research emphasizes the significance of A1C levels in managing blood sugar. For example, in the context of pregnancy, individuals planning to conceive should be screened for undiagnosed prediabetes or diabetes, particularly those with risk factors. Prompt recognition and management of abnormal sugar metabolism may enhance pregnancy results.
Expert Vivian Fonseca states,
Translating the hemoglobin A1C assay,
underscoring the importance of understanding these correlations not only for individual management but also for informed clinical decisions. It is also essential to consider that if test results are discordant, the higher result should be repeated, and factors influencing A1C or sugar concentrations should be taken into account.
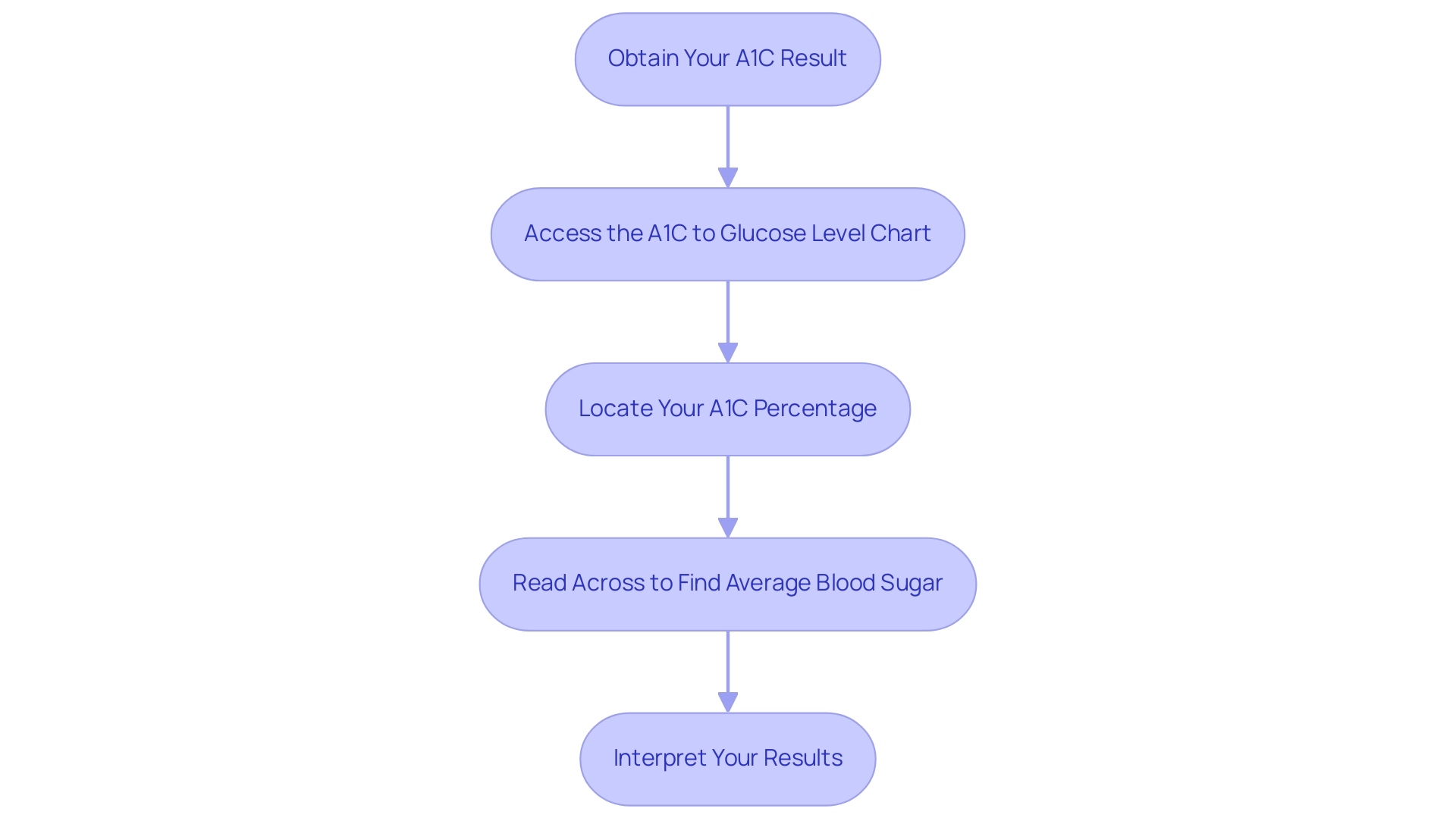
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the A1C to Glucose Level Chart
-
Obtain Your A1C Result: Begin by acquiring your most recent A1C test result from your healthcare provider, which will typically be displayed as a percentage. This measurement is essential for evaluating your long-term blood sugar control.
- Access the a1c to glucose level chart: Locate a reputable a1c to glucose level conversion chart, which can be found online or provided by your healthcare professional. This chart is a valuable resource for understanding your A1C in relation to the a1c to glucose level chart for your average blood sugar levels.
- Locate Your A1C Percentage: On the chart, identify the row corresponding to your A1C percentage. This step is crucial for making accurate comparisons with sugar levels.
- Read Across to Find Average Blood Sugar: After pinpointing your A1C percentage, move horizontally across the row to discover the associated average blood sugar level, typically denoted in mg/dL. This information offers insight into your sugar management.
- Interpret Your Results: Utilize these findings to evaluate how your long-term blood sugar control aligns with your daily monitoring practices. If you experience symptoms such as fatigue, unusual thirst, frequent urination, or blurred vision, it may indicate high blood glucose, while signs of low blood glucose include nervousness, confusion, and sweating. It’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to discuss any necessary adjustments to your management plan for blood sugar.
As highlighted by the Cleveland Clinic,
If you’re feeling overwhelmed with managing your condition, talk to your healthcare provider; they can offer support and guidance tailored to your individual needs.
To further empower your diabetes management, consider incorporating a walking program into your routine. Start by assessing your current fitness condition and setting realistic walking goals, such as committing to at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, like strolling through the scenic parks in San Marcos.
Furthermore, findings from the ADAG Study emphasize the connection between A1C and eAG, offering a scientific foundation for comprehending how your A1C results correspond to your average glucose amounts. Remember to include a balanced diet rich in local produce, such as avocados and berries, to support your overall health. Tracking your progress through a journal or app can enhance motivation and lead to sustained wellness and vitality. Consider joining local wellness groups or initiatives in San Marcos to further support your walking program and diabetes management.
Common Questions About A1C and Blood Glucose Levels
- What is a normal A1C value? Normal A1C readings are defined as below 5.7% according to the a1c to glucose level chart. Values between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest prediabetes, and according to the a1c to glucose level chart, an A1C of 6.5% or above is diagnostic for the condition. The importance of these levels is highlighted by recent findings, which show that within the prediabetes range, higher A1C levels can be examined using the a1c to glucose level chart, indicating an increased risk of developing the condition. As noted, ‘Within the prediabetes A1C range of 5.7 to 6.4 percent, the a1c to glucose level chart shows that the higher the A1C, the greater the risk of developing the condition.’ Additionally, historical data from 2009 indicates that the Medicare PPO A1C measure was 51.8, providing a concrete reference point for understanding A1C levels.
- How often should I check my A1C? For individuals managing diabetes, it is generally recommended to have the A1C tested at least twice a year. However, more regular testing may be required if there are alterations in treatment plans or if blood sugar measurements are not well-controlled as indicated by the a1c to glucose level chart.
- Does A1C reflect daily fluctuations? The A1C test does not capture daily fluctuations in blood glucose readings, which can be better understood with the a1c to glucose level chart. Rather, it offers an average of blood sugar readings from the previous two to three months, which can be compared using the a1c to glucose level chart to present a wider perspective on managing the condition.
- Can lifestyle changes affect my A1C? Absolutely. Adjustments in diet, exercise habits, and medication can significantly influence the values represented in the a1c to glucose level chart. In San Marcos, CA, adopting a holistic lifestyle that includes regular exercise in local parks and a diet rich in fresh produce from farmers’ markets can lead to substantial improvements in A1C results. Participating in community wellness programs and handling stress through activities like yoga further aids in effective health management. However, it’s crucial to understand that conventional treatments for blood sugar management can sometimes exacerbate insulin resistance, making it vital to explore holistic approaches. Ongoing clinical trials conducted by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) focus on how these lifestyle changes can enhance care and outcomes for individuals with blood sugar issues. Furthermore, maintaining hydration is crucial; consuming water or herbal teas can assist in regulating blood sugar effectively. Incorporating these lifestyle changes can profoundly impact managing Type 2 diabetes, as shown in the a1c to glucose level chart, leading to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
Effective Strategies for Lowering A1C Levels
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Prioritize a diet rich in whole foods, such as fresh vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. In San Marcos, CA, you can find vibrant farmers’ markets offering seasonal produce like avocados and berries, perfect for a diabetes-friendly diet. This method not only aids in stabilizing blood sugar amounts but also promotes overall well-being. Reducing processed sugars and refined carbohydrates is essential, as these can lead to spikes in blood glucose. Research has demonstrated that dietary choices significantly affect the a1c to glucose level chart, urging individuals to make informed food selections. In fact, with this condition being the eighth leading cause of death in the United States in 2021, managing A1C levels according to the a1c to glucose level chart has never been more critical. Traditional treatments often focus on symptom management through medications and insulin, which can come with side effects that may compromise long-term health. Understanding these drawbacks is crucial for making informed choices about diabetes management.
- Increase Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for managing blood sugar. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week; activities like brisk walking, hiking at Lake San Marcos, or cycling can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and aid in weight management. The beautiful San Marcos weather and scenic parks make outdoor exercise enjoyable year-round. Exercise not only helps reduce A1C values, as indicated by the a1c to glucose level chart, but also improves overall well-being.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly: Regularly tracking your blood sugar readings is vital for understanding how your body responds to different foods and activities. By recognizing patterns in your blood sugar levels, you can make necessary adjustments to your diet and lifestyle. This proactive approach empowers you to take control of your diabetes management effectively.
- Stay Hydrated: Maintaining proper hydration is often overlooked but plays a vital role in blood glucose management. Consuming ample water aids kidney function and assists in diluting excess sugar in the bloodstream, which contributes to improved overall health and potentially reduced A1C values as shown on an A1C to glucose level chart. Choose water or herbal teas instead of sugary beverages to aid in maintaining proper hydration without affecting blood sugar.
- Work with a Healthcare Provider: Collaborating with your healthcare provider is essential to developing a tailored management plan for your condition. Regular consultations can help you stay informed about the latest strategies for managing A1C levels and refer to the a1c to glucose level chart to adapt your approach based on your unique needs and progress. As highlighted by Nichola J. Davis, MD, MS, “our study shows that among overweight patients with type 2, there was no significant difference in the weight or A1C change in participants after a low-carbohydrate compared with a low-fat diet for 12 months.” This highlights the importance of personalized dietary strategies. For personalized support and guidance, consider contacting Dr. Jason Shumard in San Marcos, CA, who is committed to assisting you in managing your health journey with expertise. Additionally, engaging in community wellness programs available in San Marcos can provide invaluable support and resources tailored to managing diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding the significance of the A1C test is vital for effective diabetes management. This crucial metric not only reflects average blood glucose levels over the past few months but also serves as a guiding light for individuals and healthcare providers alike. With regular A1C testing, individuals can tailor their lifestyle and dietary choices to enhance their health outcomes, particularly when supported by local resources such as farmers’ markets and community wellness programs in San Marcos, CA.
The connection between A1C levels and daily blood glucose measurements reinforces the importance of consistent monitoring. By utilizing tools like the A1C to glucose level chart, individuals can gain clarity on their diabetes management and make informed decisions about their health. Incorporating effective strategies—such as adopting a balanced diet, increasing physical activity, and staying hydrated—can significantly lower A1C levels and improve overall well-being.
Ultimately, the journey toward better diabetes management is not taken alone. Engaging with healthcare providers and community initiatives fosters a supportive environment that empowers individuals to achieve their health goals. As awareness of the A1C test and its implications grows, so does the potential for improved health outcomes for those living with diabetes. Embracing a holistic approach, enriched by local resources and community support, is essential for navigating the complexities of diabetes management and achieving lasting wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test measures average blood glucose levels over the prior two to three months and is essential for evaluating the efficacy of treatment plans for blood sugar management. It helps individuals and healthcare providers make informed health decisions.
How are A1C levels categorized?
According to the A1C to glucose level chart, A1C levels are categorized as follows: below 5.7% is normal, 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, and 6.5% or above signifies a diagnosis of diabetes.
What lifestyle modifications can help manage A1C levels?
Effective management of A1C levels can be supported by a balanced diet rich in local produce, community support through wellness programs, and regular exercise in outdoor settings.
What is the prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes based on weight categories?
Recent studies show that undiagnosed diabetes prevalence varies: 1.6% in underweight or normal weight adults, 2.8% in overweight adults, and 7.9% among those with obesity.
What emerging methods are being explored for glycemic control?
The medical community is exploring methods such as estimated average blood sugar and blood sugar time in range, which may provide a more accurate view of blood sugar averages and fluctuations.
How does the A1C percentage relate to average blood sugar levels?
A1C values are presented as a percentage indicating the ratio of hemoglobin molecules with sugar attached. For instance, an A1C level of 6% corresponds to an average blood sugar level of approximately 126 mg/dL.
What strategies can help individuals monitor their blood sugar effectively?
Individuals can use management applications or journals to log daily glucose readings and set SMART goals, such as increasing daily step counts or extending exercise duration.
What role do local wellness programs play in managing health conditions?
Local wellness programs provide support and resources tailored to managing health conditions, such as group exercise classes and nutrition workshops, fostering community and shared goals.
Are there alternative biomarkers for monitoring glycemic control?
Yes, alternative biomarkers such as fructosamine and glycated albumin can be used alongside A1C testing to provide additional insights for managing blood sugar.
Why is it important to screen for prediabetes or diabetes in pregnancy?
Individuals planning to conceive should be screened for undiagnosed prediabetes or diabetes, especially those with risk factors, as prompt recognition and management of abnormal sugar metabolism may enhance pregnancy outcomes.