Overview
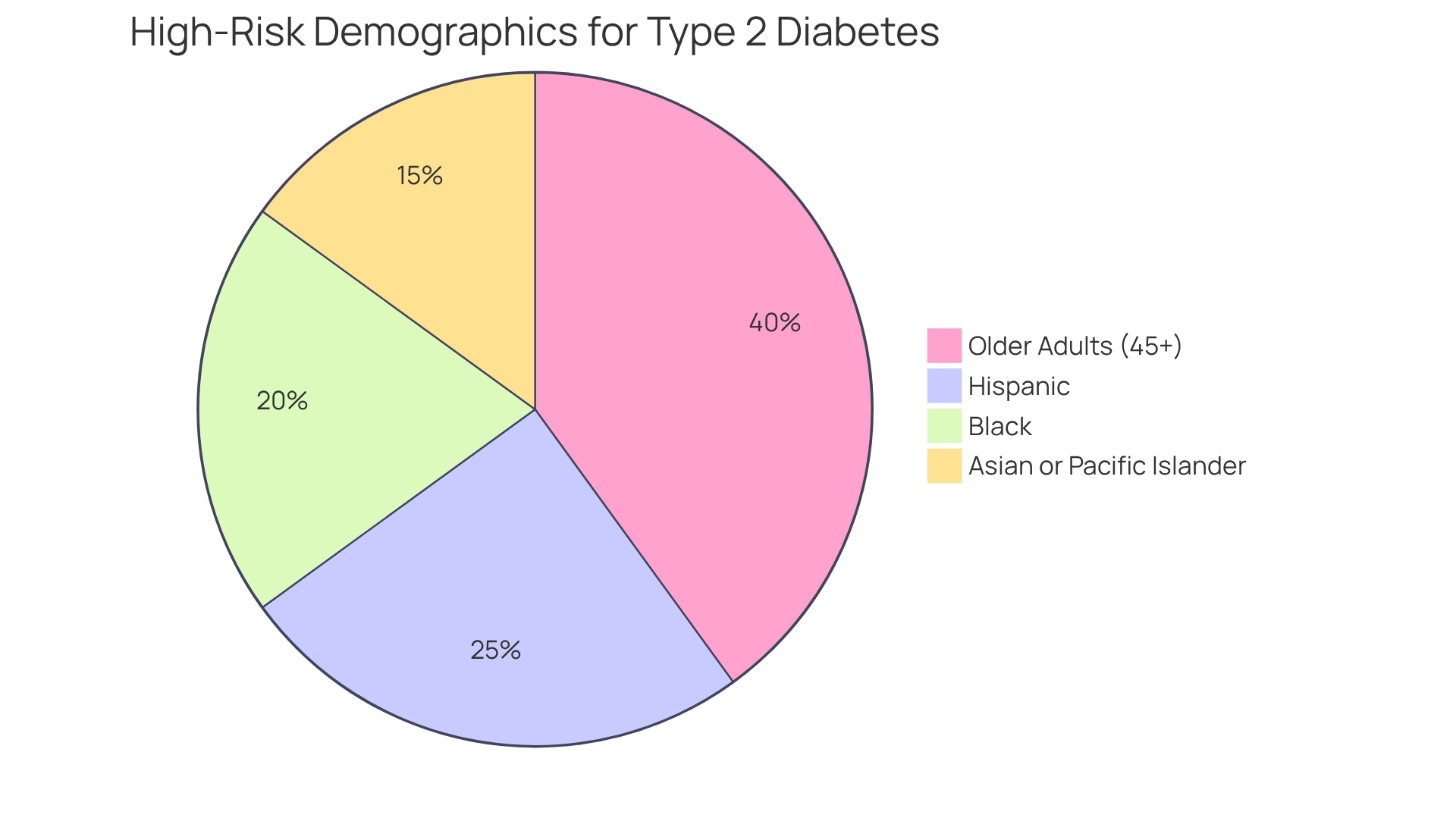
It’s important to recognize that certain populations are at a heightened risk for type 2 diabetes, particularly older adults aged 45 and above, along with racial and ethnic minorities, including Hispanic, Black, and Asian or Pacific Islander communities. These groups often face challenges related to lifestyle factors such as obesity and poor dietary habits. Many individuals may feel overwhelmed by these statistics, but understanding them is the first step toward change.
Addressing the unique needs of these demographics is crucial for developing effective public health initiatives. By focusing on their specific risk factors, we can create targeted programs that resonate with their experiences and challenges. This compassionate approach not only acknowledges their struggles but also fosters a supportive environment where healthier choices become attainable.
Let’s work together to combat the rising incidence of this chronic condition. By taking small, meaningful steps, we can empower ourselves and our communities to embrace a healthier lifestyle. Remember, every journey begins with a single step, and you are not alone in this endeavor.
Introduction
Type 2 diabetes is more than just a chronic metabolic disorder; it’s a challenge that millions face every day. As this condition spreads rapidly, affecting countless individuals around the globe, it’s essential to recognize the emotional and physical toll it can take. Characterized by insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels, Type 2 diabetes often stems from lifestyle choices and demographic factors. If left unmanaged, it can lead to serious health complications.
It’s important to acknowledge the struggles that many patients endure. With alarming statistics indicating a steady rise in prevalence, understanding the nuances of Type 2 diabetes is crucial for identifying those at risk. By exploring the multifaceted nature of this condition—from genetics and environment to community engagement and personalized care—we can uncover not only the challenges but also the proactive measures that can help combat its spread.
Many patients find that fostering awareness and empowering individuals can lead to significant improvements in health outcomes. As healthcare providers and communities work together, the potential for positive change becomes increasingly attainable. Let’s join hands in this journey toward healthier living, supporting one another every step of the way.
Define Type 2 Diabetes: Understanding the Condition
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition that many individuals face, characterized by insulin resistance and a relative deficiency of insulin. This leads to increased blood glucose levels, which can be concerning. Unlike insulin-dependent conditions that are primarily autoimmune disorders, non-insulin-dependent issues tend to progress slowly and are significantly influenced by lifestyle choices, including nutrition and exercise. It’s important to recognize that this condition poses serious risks to well-being, resulting in complications such as:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage
- Kidney dysfunction
- Vision problems
Current statistics reveal a troubling trend: the incidence of type 2 diabetes has been consistently rising, with a yearly increase of 4.8% in the U.S. from 2002 to 2012. By 2025, it is estimated that millions will be affected, underscoring the urgent need for effective prevention strategies. Alarmingly, around 73,000 lower-limb amputations were performed on diabetics aged 20 and older, highlighting the serious consequences of uncontrolled blood sugar levels. The healthcare system faces additional challenges, with:
- 7,000 errors in medication administration
- 80,000 infections contracted in hospitals
This emphasizes the necessity for careful management of blood sugar levels.
Many patients find that living with this condition can also impact their mental health, as individuals with type 2 diabetes are twice as likely to experience depression compared to those without it. The World Health Organization has noted that in developing nations, more than half of all diabetes cases remain undiagnosed, complicating efforts to tackle this growing epidemic and highlighting the need to understand what populations are now at the greatest risk for type 2 diabetes. Recent studies highlight the importance of education and management strategies; effectively regulating blood glucose levels can significantly reduce the likelihood of complications. By promoting awareness and offering resources, healthcare providers can empower individuals to manage their health and mitigate the challenges associated with this chronic condition.
Dr. Jason Shumard’s holistic approach at the Integrative Wellness Center in San Diego is a wonderful example of this empowerment. His focus on personalized functional medicine strategies, including tailored nutrition and lifestyle modifications, is truly inspiring. The center’s commitment to challenging the conventional healthcare status quo and providing lasting solutions within the San Diego community illustrates the proactive approach needed to manage this condition effectively. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are supportive resources available to help you thrive.
Identify High-Risk Populations: Demographics and Lifestyle Factors
Recent research emphasizes that specific groups are at a significantly higher likelihood of developing type 2 sugar intolerance. It is crucial to identify what populations are now at the greatest risk for type 2 diabetes, especially older adults aged 45 and above, as well as racial and ethnic minorities including Hispanic, Black, and Asian or Pacific Islander communities. Lifestyle factors significantly contribute to this risk. Many individuals in these populations face challenges with obesity, sedentary behavior, and poor dietary habits, prompting the inquiry of what populations are now at the greatest risk for type 2 diabetes?
Current statistics indicate that roughly 11.1% of the worldwide adult population is living with the disease, with many unaware of their condition. This can be alarming. For instance, the incidence ratio of end-stage renal disease among Non-Hispanic Black individuals compared to Non-Hispanic White individuals is 3.6, highlighting the disparities in medical outcomes that exist.
Public health initiatives aimed at addressing diabetes-related issues in minority communities are essential. They seek to tackle these disparities through education and access to resources. However, traditional treatments for this condition often fail to address the underlying issues, potentially exacerbating insulin resistance.
Many patients find that understanding what populations are now at the greatest risk for type 2 diabetes, along with these demographics and lifestyle elements, is crucial for creating targeted public initiatives that can greatly lower the occurrence of the disease. Research forecasts that by 2050, more than 1.3 billion individuals will be living with this condition, underscoring the urgent need for effective strategies to combat this growing epidemic.
Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program exemplifies a transformative approach. Many patients have reported significant enhancements in their well-being. For instance, one patient shared, “After participating in the program, I lost 55 lbs, reduced my A1C from 9.1 to 5.7, and experienced a substantial decrease in my reliance on medications.” As Dr. Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.
Examine Risk Factors: Genetics, Environment, and Lifestyle Choices
The contributing elements for developing type 2 sugar-related illness are complex and interrelated. It’s important to recognize that genetic tendency plays a major role; individuals with a family background of blood sugar issues face an increased likelihood, with roughly 100 genetic locations identified that account for 10% to 15% of this tendency. Additionally, environmental factors, such as access to nutritious foods and opportunities for physical activity, further influence a person’s health profile. Lifestyle choices, particularly diet, exercise, and weight management, are essential in determining the probability of developing type 2 health issues. Obesity, for instance, is a significant contributing factor, accounting for almost 60% of cases.
Many patients find that incorporating expert insights can be incredibly helpful. Nutritionists emphasize the significance of eating habits in preventing blood sugar issues. For example, increasing the consumption of green vegetables has been linked to weight loss, which can greatly lower the chances of developing diabetes. A case study on behavior changes highlights practical measures individuals can adopt to reduce their risk, such as increasing physical activity, embracing a healthier diet, and achieving gradual weight loss. This reinforces the notion that it is never too late to initiate positive changes for better health.
Dr. Jason Shumard, D.C., with his expertise in functional medicine, underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to addressing these factors. Understanding these varied threat factors is vital for developing effective prevention strategies, particularly in identifying what populations are now at the greatest risk for type 2 diabetes as its occurrence continues to rise. By addressing genetic, environmental, and lifestyle components, individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate their risk and improve their overall well-being. Participating in a structured walking regimen, starting with daily strolls of just 10-15 minutes, can be a practical step toward enhancing well-being and vitality.
Discuss Implications: Health Management and Preventive Strategies
The consequences of condition 2 extend far beyond personal health; they significantly affect our healthcare systems and economies. It’s important to recognize that effective management of this condition requires a multifaceted approach. This includes:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Medical interventions
- Consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels
Many patients in San Marcos, CA, find that adopting local lifestyle changes—like utilizing the area’s parks and trails for regular exercise, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, and participating in community wellness programs—can lead to meaningful improvements in health management, prompting the question of what populations are now at the greatest risk for type 2 diabetes, as preventive approaches such as encouraging nutritious diets, boosting physical activity, and supporting weight reduction have been shown to significantly lower this risk.
For instance, initiatives like the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) have demonstrated that lifestyle modifications can reduce the risk of developing the condition by up to 58%. Furthermore, a systematic review highlights the importance of addressing underlying health issues rather than merely managing symptoms, reinforcing the need for comprehensive care, particularly when considering what populations are now at the greatest risk for type 2 diabetes, given the staggering economic burden.
By prioritizing effective management strategies, we not only improve patient outcomes but also alleviate pressure on our healthcare systems. By embracing prevention and management through personalized functional medicine approaches, we can mitigate the impact of this growing epidemic and foster healthier communities together. Remember, every small step you take towards a healthier lifestyle counts, and you’re not alone on this journey.
Conclusion
The rising prevalence of type 2 diabetes highlights a significant public health challenge that urgently needs our attention. This chronic condition, marked by insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels, not only leads to serious health complications but also creates emotional and economic burdens for individuals and healthcare systems. It’s important to recognize that understanding the multifaceted nature of type 2 diabetes—considering genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors—is essential for effective prevention and management strategies.
Identifying high-risk populations, particularly older adults and racial minorities, is crucial for tailoring public health initiatives and providing necessary resources. Many patients find that by fostering awareness and implementing targeted interventions, communities can empower individuals to take charge of their health. Programs like Dr. Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset exemplify how personalized approaches can lead to tangible improvements in health outcomes, emphasizing the importance of addressing underlying issues rather than merely treating symptoms.
Ultimately, a proactive, community-driven approach to managing type 2 diabetes can pave the way for healthier living. By promoting lifestyle changes, encouraging regular physical activity, and focusing on balanced nutrition, the potential for positive change becomes increasingly attainable. As society rallies together to combat this epidemic, the collective effort can lead to improved quality of life and a reduction in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes, ensuring a healthier future for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition characterized by insulin resistance and a relative deficiency of insulin, leading to increased blood glucose levels.
How does Type 2 diabetes differ from insulin-dependent diabetes?
Unlike insulin-dependent diabetes, which is primarily an autoimmune disorder, Type 2 diabetes tends to progress slowly and is significantly influenced by lifestyle choices such as nutrition and exercise.
What are some serious complications associated with Type 2 diabetes?
Serious complications of Type 2 diabetes include cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney dysfunction, and vision problems.
What is the current trend in the incidence of Type 2 diabetes in the U.S.?
The incidence of Type 2 diabetes has been consistently rising, with a yearly increase of 4.8% in the U.S. from 2002 to 2012. It is estimated that millions will be affected by 2025.
What alarming statistics are associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels in diabetics?
Around 73,000 lower-limb amputations were performed on diabetics aged 20 and older, and the healthcare system faces challenges such as 7,000 errors in medication administration and 80,000 infections contracted in hospitals.
How does Type 2 diabetes impact mental health?
Individuals with Type 2 diabetes are twice as likely to experience depression compared to those without the condition.
What is the situation regarding undiagnosed diabetes cases in developing nations?
The World Health Organization has noted that in developing nations, more than half of all diabetes cases remain undiagnosed, complicating efforts to address the epidemic.
What strategies can help manage Type 2 diabetes effectively?
Education and management strategies that effectively regulate blood glucose levels can significantly reduce the likelihood of complications. Promoting awareness and providing resources are essential for empowering individuals to manage their health.
What approach does Dr. Jason Shumard take at the Integrative Wellness Center?
Dr. Jason Shumard focuses on personalized functional medicine strategies, including tailored nutrition and lifestyle modifications, to empower individuals in managing their health and mitigating challenges associated with Type 2 diabetes.