Overview
Healthy sugar alternatives for tea include natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit, which provide sweetness without the adverse effects of traditional sugars and are particularly beneficial for individuals managing diabetes. The article emphasizes that these alternatives can enhance flavor while supporting glycemic control, making them safer dietary choices for those looking to reduce sugar intake and improve overall health.
Introduction
As the quest for healthier lifestyles continues to gain momentum, the search for sugar alternatives in tea has become increasingly relevant. With rising awareness about the impacts of sugar on health, consumers are exploring options that allow them to enjoy their favorite beverages without compromising their well-being.
The market for sugar substitutes has expanded significantly, reflecting a shift in consumer preferences towards natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit, which offer the sweetness of sugar without the associated health risks.
This article delves into the various alternatives available, their health benefits, potential drawbacks, and practical tips for incorporating them into tea. Understanding these options is essential for individuals looking to manage their sugar intake and enhance their overall health.
Exploring Healthy Sugar Alternatives for Tea
The demand for healthy sugar alternatives for tea has surged as individuals increasingly aim to lower their sweetener consumption while still enjoying flavorful beverages. In 2019, the market for artificial substitutes generated a revenue of 17,750.43 million U.S. dollars, highlighting the increasing interest in alternatives. These alternatives not only accommodate various health requirements but also appeal to a broad spectrum of tea drinkers.
A significant instance is Tate & Lyle’s TASTEVA SOL, a new stevia sweetener introduced in July 2023, improving their portfolio with a cleaner taste profile and providing manufacturers a high-performance sweetening option that effectively lowers sweetness levels in various food and beverage applications. As the market for sweetener alternatives continues to expand, understanding the healthy sugar alternatives for tea is imperative for consumers, especially those managing type 2 diabetes. Each substitute possesses distinct characteristics and potential advantages, which will be examined in detail in the following sections.
This knowledge empowers consumers to make informed choices that align with their health objectives, thereby enhancing their overall well-being. Moreover, searching for eateries that offer vibrant, nutrient-rich vegetable-based meals can greatly aid in regulating blood levels. These meals not only provide essential nutrients but also offer a satisfying way to meet dietary needs.
Incorporating such dishes into your diet emphasizes the connection between nutrition and diabetes management. As Kamari noted, ‘Cracker versatility and variety should play a bigger role in snacking, yet chips top the list,’ indicating that opportunities exist for brands to tap into flavor, texture, and pairings, which can also extend to the realm of sweeteners in beverages.
Top Natural Sweeteners for Your Tea: Stevia, Honey, and More
A variety of healthy sugar alternatives for tea are frequently suggested as better options than traditional sweeteners, especially for those managing type 2 diabetes. Stevia, derived from the foliage of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, is especially preferred because of its zero-calorie content and extraordinary sweetness—being 200 to 400 times sweeter than regular table sweetener. Although the FDA has not approved raw stevia for use, it considers high-purity extracts to be generally regarded as safe, making it a reliable option for those managing blood sugar levels.
This is essential, as traditional treatments for diabetes can pose significant risks, including potential life-threatening complications, particularly for individuals dealing with insulin resistance. Monk fruit substitute, another natural alternative, contains 0.5 grams of carbohydrates per teaspoon and is celebrated for its unique flavor profile and zero-calorie content. Each of these sweeteners can serve as healthy sugar alternatives for tea, enhancing its flavor without the adverse effects linked to excessive sweetener consumption, making them appropriate options for individuals looking to improve their well-being.
Moreover, a case study shows that monk fruit and stevia are typically safe for individuals with diabetes, although consumers should verify labels for added sweeteners or carbohydrates. Moreover, recent research indicates that older individuals who frequently drink green tea may encounter fewer brain lesions associated with dementia, suggesting that incorporating healthy sugar alternatives for tea can improve the tea experience while potentially aiding cognitive function. By opting for these natural alternatives, individuals can make safer dietary choices that align with an integrative approach to managing diabetes and mitigating the risks associated with traditional treatments.
Health Benefits and Considerations of Sugar Substitutes
Using healthy sugar alternatives for tea offers considerable benefits, particularly for people controlling diabetes or those aiming to reduce their overall sweet consumption. Transformative patient experiences at the Integrative Wellness Center emphasize how dietary changes, including the use of natural substitutes like stevia and monk fruit, can lead to improved glycemic control and overall health. For example, one patient revealed how transitioning to monk fruit as a substitute assisted them in reducing their blood glucose levels considerably, enabling them to savor their favorite teas without concern.
Recent statistics reveal that middle-aged adults aged 51-60 consume approximately 15-21 teaspoons of added sweetener daily, while older adults aged 60 and above consume around 14-20 teaspoons, underscoring the significance of substitutes in reducing overall sweetener intake. Healthy sugar alternatives for tea are especially advantageous as they do not lead to spikes in blood glucose levels, rendering them perfect for glycemic control. Additionally, xylitol, a common sweetener alternative, provides approximately 40% fewer calories than traditional sucrose, aiding in weight management efforts.
It is crucial, however, to consider personal tolerance to these additives, as some individuals may experience digestive discomfort or adverse reactions. As Trishita Deb, a market research and consulting analyst in healthcare, observes:
The selection of sweetener should correspond with personal wellness requirements and preferences.
Furthermore, research on the association between artificial substitutes and cancer risk has produced mixed results, but recent systematic reviews found no significant correlation between artificial substance consumption and cancer risk, affirming the safety of approved alternatives.
Consulting with a healthcare provider can provide personalized guidance, helping individuals select the most suitable options for their specific circumstances. Overall, the advantages linked to using healthy sugar alternatives for tea, especially in the context of diabetes management, remain a focal point of interest and research in 2024, reflecting changing consumer trends in food and beverage purchases.
Understanding the Drawbacks of Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial additives, including aspartame and sucralose, provide a calorie-free choice for enhancing beverages like tea; however, their use is accompanied by significant controversy. Research has indicated potential links between artificial substitutes and a range of health issues, particularly metabolic disorders and digestive problems. For example, the research titled ‘Conclusions on Artificial Substances and T2D Risk’ highlighted positive associations between certain artificial substances and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, specifically noting concerns regarding aspartame and acesulfame-K.
The findings support a decrease in sugary flavors in diets instead of endorsing these additives as safe options. Furthermore, many individuals report that artificial alternatives often leave a distinct aftertaste, which may deter their use. Considering the scientific statement from the American Heart Association and the American Diabetes Association, which addresses the current usage and wellness viewpoints of non-nutritive alternatives, it becomes evident that consumers should treat these choices with care.
Ketura Persellin from the EWG aptly stated, ‘But, they say, it does make reducing the intake of artificial additives a viable option for individuals who want to try to lower their risk of developing these medical issues,’ emphasizing the need for careful consideration of risks. It is essential for consumers, particularly those with underlying health conditions, to evaluate these factors when considering the inclusion of artificial alternatives into their diets, especially in light of ongoing controversies surrounding aspartame and sucralose.
How to Use Sugar Alternatives in Your Tea
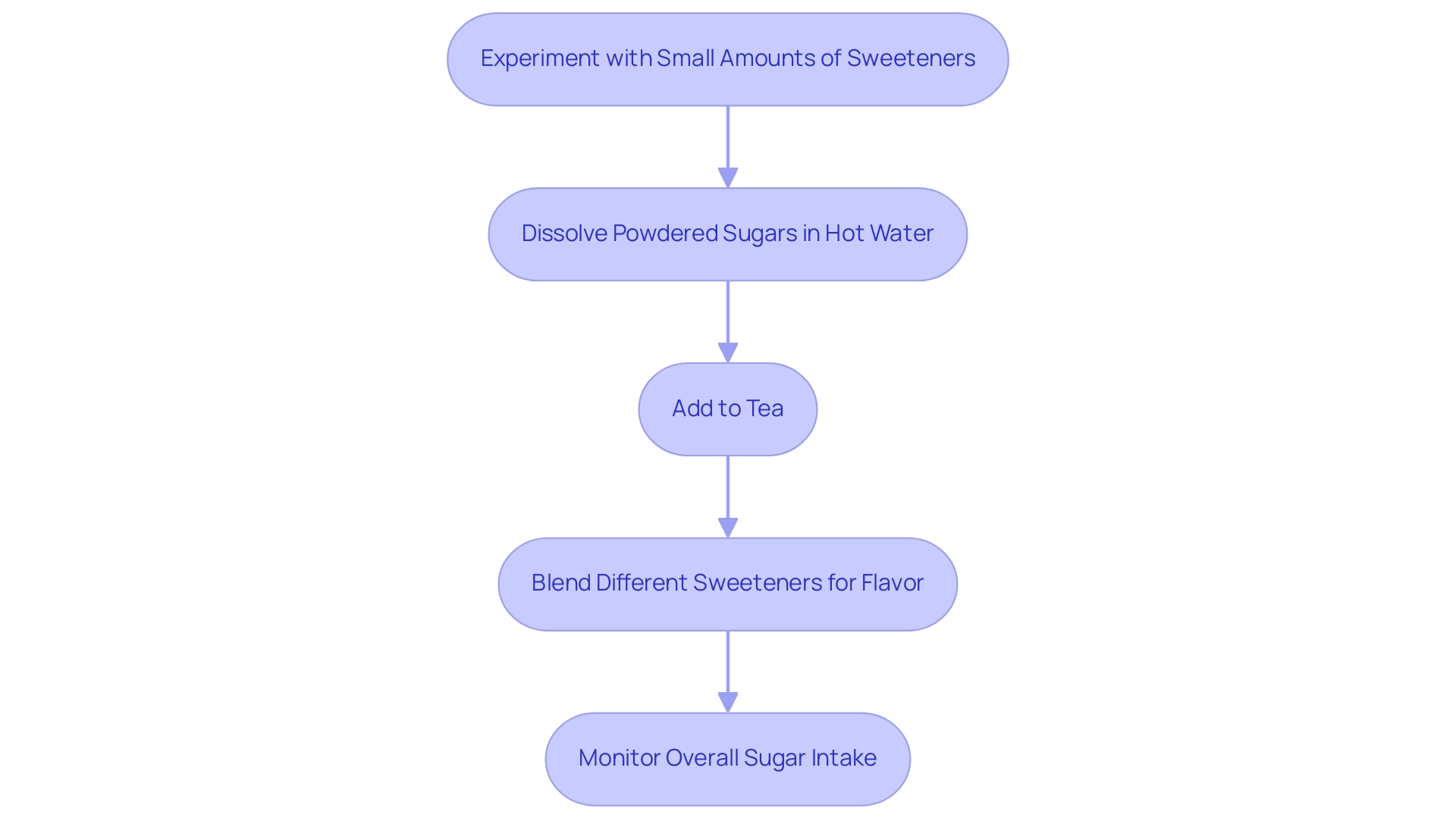
Incorporating sugar alternatives into tea can be both straightforward and enjoyable. Begin by experimenting with small amounts of sugar alternatives such as stevia or honey to identify the balance that best suits your taste preferences. For powdered sugars, it is advisable to dissolve them in a small amount of hot water prior to adding them to your tea, as this ensures even distribution throughout the beverage.
Additionally, consider blending different sweeteners to craft a distinct flavor profile. For example, a combination of honey and a touch of stevia can enhance sweetness while respecting the tea’s inherent flavors. It is crucial to remain vigilant about your overall sugar intake, especially considering that current scientific evidence suggests that replacing sugar-sweetened beverages with diet soft drinks does not prevent disease.
Furthermore, findings from a study titled ‘Knowledge Related to Wellness and Beverage Intake‘ indicate that increased wellness knowledge may not always correlate with reduced beverage consumption, reinforcing the need for practical strategies like these. As Ritchie et al. noted regarding beverage policies, there is a significant impact when healthier options are made readily available, which can also apply to sweetening tea.
By adhering to these best practices, you can enjoy a flavorful cup of tea that aligns with your health goals.
Conclusion
Exploring sugar alternatives for tea reveals a wealth of options that cater to health-conscious consumers. The growing interest in natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit highlights their potential to enhance flavor without the adverse effects of sugar. These alternatives not only support individuals managing diabetes but also contribute to overall well-being by promoting better glycemic control and reducing excessive sugar intake.
While the benefits of natural sweeteners are clear, it is equally important to be aware of the drawbacks associated with artificial sweeteners. Concerns regarding metabolic disorders and digestive issues necessitate a cautious approach to their use. Understanding the potential risks allows consumers to make informed choices that align with their health needs.
Incorporating sugar alternatives into tea can be a straightforward process, enhancing the beverage experience while maintaining health goals. By experimenting with different sweeteners and blending techniques, individuals can enjoy flavorful teas without compromising their dietary objectives. With the right knowledge and approach, the transition to healthier sweetening options can be both enjoyable and beneficial, paving the way for a more health-conscious lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why has the demand for healthy sugar alternatives for tea increased?
The demand has surged as individuals aim to lower their sweetener consumption while still enjoying flavorful beverages, particularly as more people manage health conditions like type 2 diabetes.
What was the revenue of the artificial sweetener market in 2019?
In 2019, the market for artificial substitutes generated a revenue of 17,750.43 million U.S. dollars.
What is TASTEVA SOL and when was it introduced?
TASTEVA SOL is a new stevia sweetener introduced by Tate & Lyle in July 2023, known for its cleaner taste profile and high-performance sweetening option that lowers sweetness levels in various food and beverage applications.
What are some characteristics of stevia as a sugar alternative?
Stevia, derived from the Stevia rebaudiana plant, is preferred for its zero-calorie content and extraordinary sweetness—being 200 to 400 times sweeter than regular table sugar. High-purity extracts of stevia are considered generally regarded as safe by the FDA.
What are the benefits of using monk fruit as a sugar alternative?
Monk fruit contains 0.5 grams of carbohydrates per teaspoon and is celebrated for its unique flavor profile and zero-calorie content, making it a healthy option for sweetening tea.
How do these sugar alternatives benefit individuals managing diabetes?
Both stevia and monk fruit are typically safe for individuals with diabetes, as they enhance the flavor of tea without the adverse effects linked to excessive sweetener consumption.
What potential cognitive benefits are associated with drinking green tea?
Recent research suggests that older individuals who frequently drink green tea may encounter fewer brain lesions associated with dementia, indicating that incorporating healthy sugar alternatives for tea can enhance the tea experience while potentially aiding cognitive function.
What should consumers be cautious about when choosing sugar alternatives?
Consumers should verify labels for added sweeteners or carbohydrates to ensure that the alternatives they choose align with their dietary needs, especially for those managing blood sugar levels.