Overview
A 4.7 A1C level indicates excellent blood sugar control, which is crucial for reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. The article emphasizes that maintaining this level requires a commitment to a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and adherence to prescribed medications, supported by evidence of lifestyle changes leading to improved health outcomes.
Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is crucial for effective diabetes management, particularly for individuals striving to maintain optimal blood sugar control. An A1C level of 4.7% is indicative of well-managed glucose levels, falling comfortably within the normal range. This benchmark not only reflects successful lifestyle choices but also underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to health that includes:
- Balanced nutrition
- Regular physical activity
- Consistent monitoring of health indicators
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, awareness of how to achieve and sustain healthy A1C levels becomes increasingly essential. This article delves into the significance of A1C levels, dietary strategies, the role of physical activity, and the necessity of regular monitoring, providing valuable insights for those navigating the complexities of diabetes management.
Understanding the Significance of a 4.7 A1C Level
An A1C measurement of 4.7 a1c is considered to be within the normal range, signifying that an individual’s average blood glucose readings over the past three months have been effectively controlled. According to the National Center for Health Statistics, estimates for undiagnosed conditions are based on:
- An 8- to 24-hour fasting plasma glucose greater than or equal to 126 mg/dL
- Hemoglobin A1c greater than or equal to 6.5% in a participant who reported never receiving a diagnosis from a healthcare provider.
Readings below 5.7% are classified as normal, while values ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, and amounts of 6.5% or higher are diagnostic for diabetes.
Thus, achieving a 4.7 a1c indicates outstanding control of blood sugar, which is crucial in reducing the risk of complications related to diabetes. Maintaining this optimal level requires a commitment to:
- A balanced diet
- Regular physical activity
- Strict adherence to any prescribed medication regimens
Recent studies emphasize that effective control of blood sugar levels is connected to lifestyle choices, reinforcing the need for ongoing education and support.
For instance, a case study from the Integrative Wellness Center showcases how a patient successfully reduced their A1C from 8.2% to 5.6% through a personalized meal plan, regular exercise, and participation in community wellness programs. This comprehensive approach, as outlined in the case study titled ‘Guiding Principles for Diabetes Management,’ emphasizes the importance of community wellness programs and educational resources to empower patients. Furthermore, Recommendation 5.51 encourages sleep wellness routines and practices, emphasizing the comprehensive strategies crucial for effective control of blood sugar.
Integrating vegetable-rich dishes into your diet not only supports blood sugar regulation but also enhances overall health, making it a crucial component of a diabetes-friendly meal plan. Lifestyle changes such as incorporating more whole foods, managing stress through mindfulness practices, and engaging in regular physical activity are vital strategies that can lead to significant improvements in controlling blood sugar levels.
A1C Levels and Their Role in Diabetes Management
A1C measurements are crucial in the management of blood sugar, acting as a primary indicator of a person’s glucose control over time. Health experts generally set A1C targets customized to each patient’s health goals, with a commonly recognized aim for many adults with high blood sugar being to keep an A1C reading under 7%. Achieving this target requires a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Dietary adjustments
- Regular physical activity
- Diligent monitoring of blood glucose levels
Importantly, adopting a holistic regimen that re-examines the root causes of diabetes and incorporates personalized meal plans tailored to a person’s culture, preferences, and personal goals can significantly enhance quality of life and nutritional status for individuals with diabetes. This approach not only addresses physical well-being but also aims to alleviate the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of the disease. For those managing an A1C level of 4.7, it is essential to persist with these healthy practices to ensure sustained glucose control.
Frequent discussions with healthcare professionals are essential, as they enable the personalization of plans that address individual wellness needs and lifestyle preferences. Lifestyle interventions have proven beneficial for older adults, as evidenced by the Look AHEAD trial, which showed reductions in multimorbidity and improvements in physical function and quality of life. Updated recommendations emphasize the need to deintensify therapy for older adults, particularly those on hypoglycemia-causing medications, ensuring that care is aligned with their specific needs.
According to Chuck Henderson, the chief executive officer of the American Diabetes Association, ‘At the ADA, we are focused on improving the quality of care for anyone who lives with this condition, prediabetes, or who is at risk of developing it.’ This highlights the significance of a well-informed and coordinated healthcare team in achieving optimal A1C readings and overall management of blood sugar, challenging traditional treatment myths and promoting an integrative approach that addresses wellness at the root.
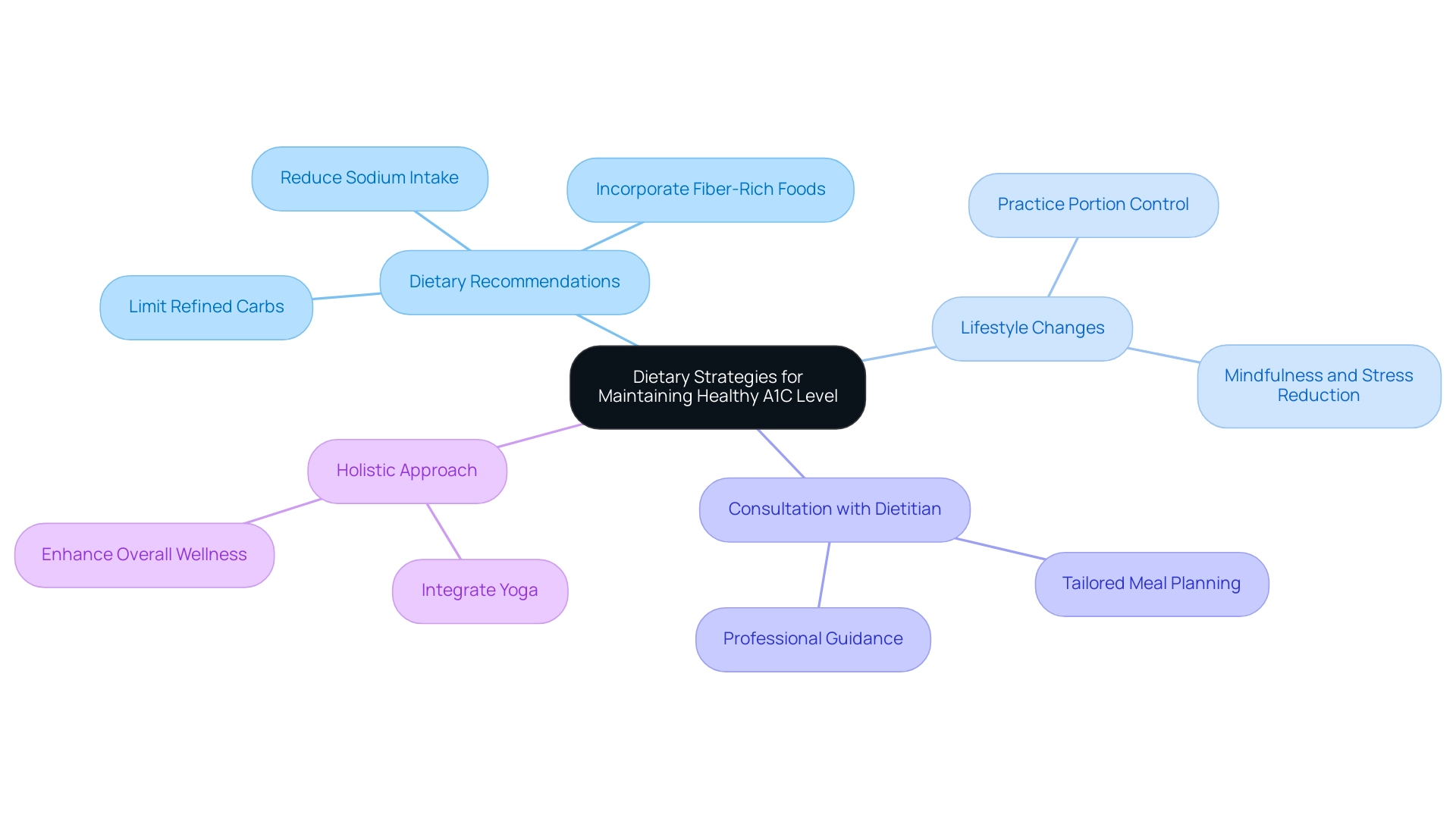
Dietary Strategies for Maintaining a Healthy A1C Level
To maintain a healthy level of 4.7 a1c and reverse the condition, it is essential to follow a balanced diet that emphasizes whole foods, incorporating an abundance of vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. This comprehensive method starts by reassessing the origin of your condition and tackling health at the foundational aspect. Many patients experience anxiety surrounding potential complications of the disease, which can be alleviated through informed dietary choices and lifestyle changes.
- Limiting refined carbohydrates and sugars is essential, as these can lead to significant spikes in blood glucose.
- Incorporating fiber-rich foods, such as legumes and whole grains, enhances insulin sensitivity and supports the integrative approach to managing blood sugar.
- According to a study published in the British Journal of Nutrition (2007), dietary modifications can significantly impact 4.7 a1c levels, highlighting the importance of a well-rounded diet.
Recent guidelines suggest that individuals with this condition should also aim to reduce sodium intake to a maximum of 2,300 mg per day, as many exceed this limit, adversely affecting glycemic control. A case study has shown that reducing sodium intake, along with lifestyle modifications, can improve glycemic and lipid control. Practicing portion control and mindfulness while eating further aids in blood sugar regulation.
For tailored meal planning that aligns with your diabetes management objectives, consulting with a registered dietitian is highly recommended. This professional guidance can provide specific strategies reflecting current dietary recommendations for maintaining optimal levels of 4.7 a1c while empowering you on your wellness journey. Furthermore, integrating a holistic routine that incorporates stress-reduction methods, like mindfulness or yoga, can enhance your overall wellness.
The Importance of Regular Physical Activity
Managing type 2 effectively requires a holistic approach that begins by re-examining the source of your condition. Participating in consistent physical activity is essential, but it should be paired with a considerate meal plan that addresses well-being at the root level. You have 150 minutes of exercise left to meet this week, emphasizing the importance of prioritizing physical activity alongside dietary choices.
The recommended target is a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week, which can include activities such as:
- Brisk walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
Moreover, including strength training workouts at least twice a week improves insulin sensitivity, promotes general wellness, and offers anti-inflammatory benefits essential for managing type 2. Integrating movement into your daily routine can also be effective; consider using stairs instead of elevators or taking walks during breaks.
It’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program to ensure it aligns with your individual health status. As highlighted by Ann L. Albright, PhD, RD from the Division of Diabetes Translation at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, incorporating physical activity into daily life is a crucial element of successful health care for those with diabetes. This holistic approach not only helps in managing blood sugar but also tackles the anxiety that can accompany concerns about possible complications of your condition.
A structured approach to exercise, as supported by the Look AHEAD trial, observed improvements in quality of life and reductions in depressive symptoms among participants with increased physical activity, highlighting the psychological benefits of exercise. By following these guidelines and adopting a comprehensive routine, individuals can make substantial progress in their condition while also easing the emotional burdens linked to it.
Monitoring Your A1C Levels and Health Indicators
Incorporating 4.7 a1c monitoring into your diabetes management plan is essential for effective control of the condition. The American Diabetes Association recommends that patients with stable blood sugar should check their A1C measurements, particularly the 4.7 a1c level, at least twice a year. However, for those requiring medication adjustments or lifestyle changes, more frequent assessments are recommended.
As Roopa Naik observes, ‘Regular monitoring of A1C readings, specifically targeting 4.7 a1c, is crucial for understanding long-term glycemic control and making informed treatment decisions.’ The importance of A1C, especially the 4.7 a1c level, as a long-term indicator of glycemic control cannot be overstated; it reflects average blood sugar levels over the preceding three months, making it a crucial metric in managing the condition. Furthermore, a holistic approach involves examining underlying factors contributing to your condition, allowing for targeted interventions that empower your health.
This process involves re-evaluating the origin of your condition, which can assist in reducing the anxiety that comes with the concern about possible complications of the illness. The ongoing use of personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) in hospitalized individuals with diabetes is highlighted, ensuring that patients receive the most accurate and timely information regarding their glucose readings. Beyond A1C, monitoring other wellness indicators, such as blood pressure and cholesterol readings, is vital for comprehensive care.
Recent recommendations stress the need to deintensify therapy for older adults, especially those on medications that may cause hypoglycemia. Specific methods, such as dietary adjustments and exercise regimens, can address wellness at the root level, promoting overall well-being. Utilizing diabetes monitoring applications or journals can facilitate the recording of these measurements, allowing for trend observation over time.
Regular consultations with your healthcare provider are equally important, as they provide opportunities to evaluate overall health, address insulin resistance, and make necessary adjustments to your management plan.
Conclusion
Maintaining an A1C level of 4.7% is a clear indication of effective diabetes management and reflects a commitment to healthy lifestyle choices. Achieving this benchmark requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses:
- Balanced nutrition
- Regular physical activity
- Diligent monitoring of health indicators
By prioritizing whole foods, engaging in consistent exercise, and utilizing tools for tracking progress, individuals can significantly enhance their blood sugar control and overall well-being.
The importance of dietary strategies cannot be overstated. A balanced diet rich in:
- Vegetables
- Lean proteins
- Whole grains
While limiting refined sugars and sodium, is essential for sustaining healthy A1C levels. Coupled with regular physical activity, these lifestyle changes can alleviate anxiety surrounding diabetes management and foster a proactive approach to health. Additionally, ongoing education and support are vital, as they empower individuals to make informed choices and adapt their management plans as needed.
Ultimately, the journey to effective diabetes management hinges on a holistic strategy that addresses both physical and emotional health. Regular consultations with healthcare providers, combined with the monitoring of A1C levels and other health indicators, ensure that individuals remain on track toward achieving their health goals. By embracing this comprehensive approach, those living with diabetes can take significant steps toward a healthier future, minimizing the risk of complications and enhancing their quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does an A1C measurement of 4.7 signify?
An A1C measurement of 4.7 is considered within the normal range, indicating that an individual’s average blood glucose readings over the past three months have been effectively controlled.
What are the classifications of A1C levels?
A1C levels are classified as follows: Below 5.7% is normal, 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher is diagnostic for diabetes.
What lifestyle changes are recommended to maintain an optimal A1C level?
To maintain an optimal A1C level, it is important to commit to a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and strictly adhere to any prescribed medication regimens.
How are A1C targets determined for individuals?
A1C targets are customized to each patient’s health goals, with a common aim for many adults with high blood sugar being to keep an A1C reading under 7%.
What holistic approaches can enhance the management of diabetes?
A holistic approach includes dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, diligent monitoring of blood glucose levels, and personalized meal plans that consider a person’s culture, preferences, and personal goals.
Why are frequent discussions with healthcare professionals important?
Frequent discussions with healthcare professionals are essential for personalizing plans that address individual wellness needs and lifestyle preferences, ensuring optimal management of blood sugar.
What evidence supports the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions for diabetes management?
The Look AHEAD trial provides evidence that lifestyle interventions can reduce multimorbidity and improve physical function and quality of life for older adults.
What is the significance of community wellness programs in diabetes management?
Community wellness programs and educational resources empower patients and play a crucial role in effective blood sugar control, as highlighted in various case studies.
How can integrating vegetable-rich dishes into the diet benefit individuals with diabetes?
Incorporating vegetable-rich dishes supports blood sugar regulation and enhances overall health, making it a vital component of a diabetes-friendly meal plan.
What is the role of the American Diabetes Association in diabetes care?
The American Diabetes Association focuses on improving the quality of care for individuals living with diabetes, prediabetes, or those at risk, promoting a well-informed and coordinated healthcare approach.