Overview
Understanding your fasting blood sugar levels, particularly a reading of 144 mg/dL, is crucial for effective diabetes management, as it indicates a state of prediabetes and the need for lifestyle modifications. The article emphasizes that consistent monitoring and proactive strategies—such as dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress management—are essential for controlling blood sugar levels and preventing complications associated with elevated glucose concentrations.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding and monitoring fasting blood sugar levels is paramount for individuals navigating the complexities of type 2 diabetes. A fasting blood glucose reading of 144 mg/dL serves as a critical indicator, suggesting that while levels are not alarmingly high, they exceed the normal range and warrant immediate attention.
Regular monitoring empowers individuals to recognize patterns in their blood sugar fluctuations, enabling timely interventions and informed discussions with healthcare providers. This proactive approach not only enhances personal health management but also plays a vital role in preventing the long-term complications associated with elevated glucose levels, such as cardiovascular disease and neuropathy.
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, particularly among younger populations, adopting effective strategies for blood sugar control has never been more essential. This article delves into the importance of monitoring fasting blood sugar levels, explores effective management strategies, and emphasizes the necessity of a comprehensive support system in the journey toward optimal health.
The Importance of Monitoring Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Observing fasting glucose readings is a basic practice for individuals controlling type 2 diabetes. A reading of 144 fasting blood sugar mg/dL, while not excessively high, indicates that glucose concentrations are above the normal range of 70-99 mg/dL. Consistent observation allows people to notice trends in their glucose readings, recognize possible spikes, and apply essential modifications to their management strategies.
This understanding not only aids in personal health management but also fosters informed discussions with healthcare providers regarding tailored treatment strategies and lifestyle modifications. Moreover, consistent monitoring is vital for preventing complications commonly associated with prolonged elevated glucose amounts, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease. Recent studies highlight that a substantial percentage of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes—around 80.6%—show increased pressure readings, further stressing the necessity for proactive management of fasting glucose.
People with high glucose face around twice the risk of coronary heart disease compared to those without, emphasizing the essential requirement for monitoring glucose concentrations. As Dr. Shaye Kivity emphasizes, keeping glucose levels within normal ranges can reduce the independent risk factors for coronary disease, highlighting the significance of incorporating careful glucose monitoring into management protocols. Additionally, the increasing occurrence of the condition among children and adolescents, with an estimated 18,169 diagnosed with type 1 and 5,293 with type 2 during 2017-2018, underscores the urgency of effective blood sugar management strategies.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we adopt a holistic approach to managing the condition that addresses root causes, empowering patients to reverse type 2 through personalized care and comprehensive insights into treatment options. Our success stories, such as those of patients who have significantly improved their health by following our holistic regimens, demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods. We understand that managing diabetes can be anxiety-inducing; thus, our approach also includes support systems aimed at alleviating these concerns, ensuring that our patients feel empowered and informed throughout their journey.
Effective Strategies for Managing Elevated Blood Sugar Levels
To effectively handle increased glucose concentrations, especially for Type 2 Diabetes patients, it is essential to employ a range of evidence-supported tactics:
- Dietary Adjustments: Prioritize a balanced diet that incorporates whole foods, including a diverse array of vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is essential to limit refined sugars and processed carbohydrates, as these can lead to significant spikes in blood sugar levels. According to recent research, ‘Active and effective dietary education may prevent the onset of this condition and its complications,’ highlighting the importance of informed dietary choices. Additionally, understanding insulin resistance and its implications can empower patients to make more effective dietary adjustments. The occurrence of type 2 condition has significantly increased across all racial and ethnic groups from 2002 to 2018, emphasizing the urgency of these dietary changes.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week. Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming improve insulin sensitivity and lead to reduced glucose amounts, establishing regular physical exercise as a fundamental aspect of successful diabetes control.
- Monitor Carbohydrate Intake: Implement carbohydrate counting or structured meal planning to manage glucose levels effectively. Understanding the glycemic index of foods can further enable individuals to make informed dietary choices that promote stable glucose regulation.
- Stay Hydrated: Consuming adequate water throughout the day assists the kidneys in flushing out excess glucose through urine, promoting better glycemic control.
- Medication Management: For those prescribed medications, adherence to the prescribed regimen is vital. Frequent discussions with healthcare professionals enable prompt modifications based on personal glucose measurements and overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Incorporating stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can mitigate the adverse effects of stress on blood sugar levels. This aspect of care is critical, given that stress can exacerbate insulin resistance, making stress management an integral part of comprehensive management for this condition.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule consistent appointments with healthcare professionals to monitor and evaluate your overall health. Regular check-ups enable timely adjustments to your management plan, ensuring it aligns with your health goals.
- Addressing Anxiety: It’s important to acknowledge the anxiety that often accompanies managing diabetes-related health. Many patients report feeling overwhelmed by the potential complications of their condition. Engaging in support groups or speaking with a mental health professional can provide valuable emotional support and coping strategies, which can significantly enhance individuals’ ability to manage fasting blood sugar levels while promoting overall health and well-being. The prevalence of complications such as foot infections—reported at a rate of 10.4% among Type 2 patients—underscores the importance of proactive and effective management approaches that address the root causes of the condition. As one patient shared, ‘Since I began implementing these strategies, I feel more in control of my health and less anxious about my condition.
Understanding the Implications of a 144 mg/dL Reading
A 144 fasting blood sugar measurement of 144 mg/dL suggests prediabetes, a crucial condition where blood glucose amounts surpass normal ranges but do not yet meet the criteria for a blood sugar disorder diagnosis. This measurement suggests suboptimal functioning of the body’s insulin response, which can have serious implications if left unaddressed. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we begin by reassessing the origin of your condition.
From that point, we can tackle health at the foundational aspect using a comprehensive regimen designed to reverse the condition. Studies show that:
- 70.8% of U.S. adults diagnosed with this condition have systolic pressure readings of 140 mmHg or above, highlighting a significant connection between increased glucose concentrations and cardiovascular risks.
- 80.6% of adults with diagnosed conditions related to diabetes have a systolic pressure of 130 mmHg or greater or are on medication for elevated pressure, further highlighting the cardiovascular risks linked to inadequate glucose management.
Persisting in sustaining such high glucose concentrations can accelerate the advancement to type 2 condition, which is especially troubling considering the rising occurrence rates among all racial and ethnic categories from 2002 to 2018. Non-Hispanic Black children and adolescents exhibit the highest incidence among these demographics. Thus, it is crucial to regard a reading of 144 fasting blood sugar with importance and adopt lifestyle modifications aimed at lowering glucose levels.
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring progress and adapting management strategies accordingly. As noted by experts in the field, including Mary R. Rooney, ‘Continuing and expanding global surveillance efforts, such as the WHO STEPS surveys, can help to provide data to fill this gap.’ Proactive measures, rooted in holistic health strategies, are vital to prevent the development of microvascular complications associated with prediabetes, as highlighted in the case study on microvascular complications in prediabetes, underscoring the necessity of early intervention and consistent monitoring.
Additionally, addressing the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of your disease is crucial for overall health and well-being.
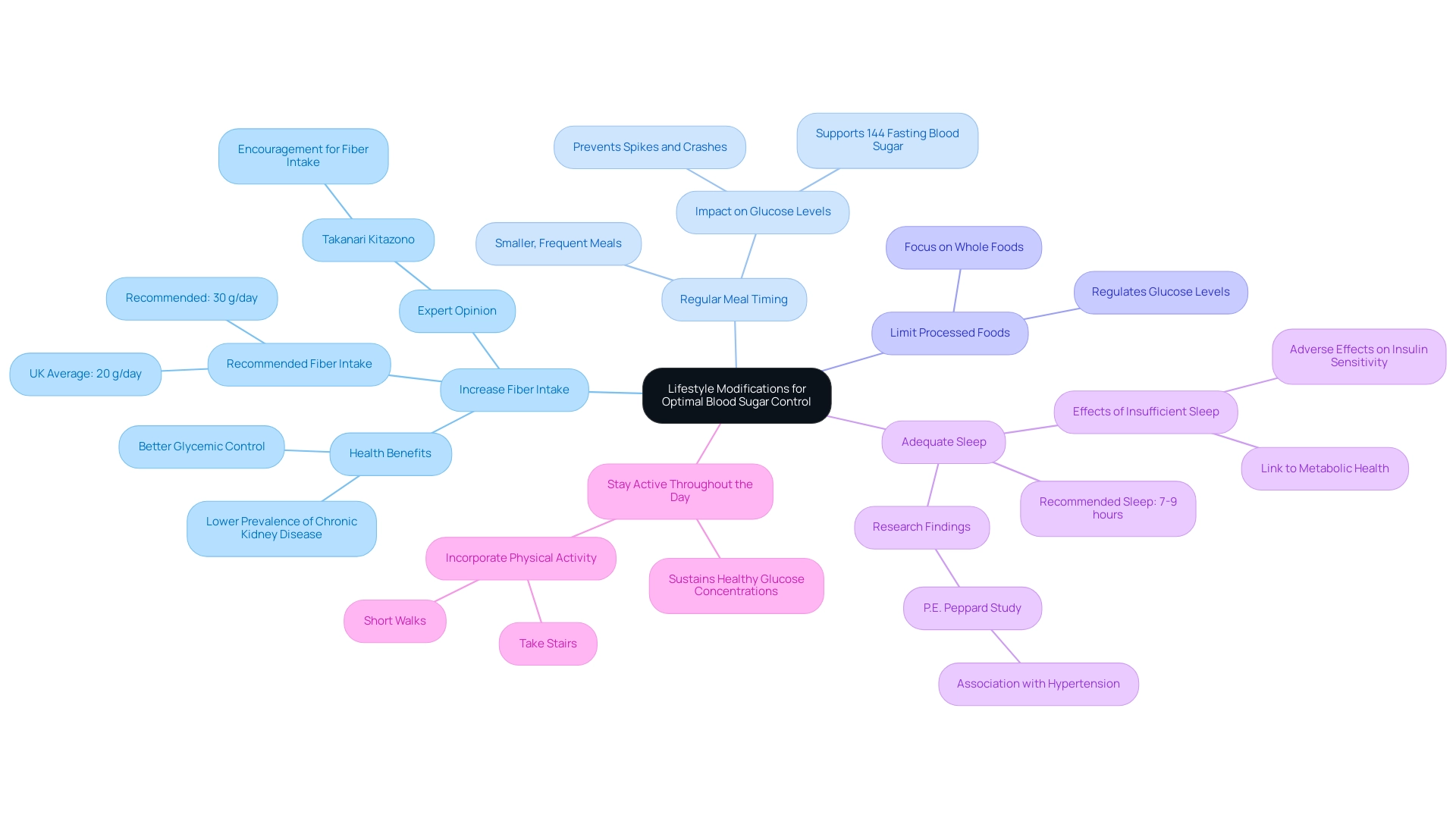
Lifestyle Modifications for Optimal Blood Sugar Control
To optimize blood sugar control and embrace a holistic approach to diabetes management, consider implementing the following lifestyle modifications, which can help alleviate the anxiety surrounding diabetes complications:
- Increase Fiber Intake: It is essential to incorporate more fiber-rich foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, beans, and whole grains. Research shows that in the United Kingdom, the average fiber consumption is only around 20 g per day, which is below the suggested 30 g. Higher dietary fiber has been associated with better glycemic control and more favorable cardiovascular risk factors, especially in individuals with type 2. A study titled “Dietary Fiber and Type 2 Diabetes in Japan” assessed 4,399 patients and found that higher dietary fiber intake was associated with better glycemic control and a lower prevalence of chronic kidney disease. Takanari Kitazono emphasizes that diabetic patients should be encouraged to consume more dietary fiber in daily life.
- Regular Meal Timing: Creating a schedule of smaller, more frequent meals during the day can assist in keeping consistent glucose amounts. This approach may prevent spikes and crashes, ultimately contributing to better overall glucose management, which is crucial for achieving a 144 fasting blood sugar. Statistics indicate that meal timing can significantly influence glucose levels, making it a vital component for maintaining a 144 fasting blood sugar in diabetes management.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reducing the consumption of processed and sugary items is crucial for effective management of 144 fasting blood sugar. Concentrating on whole, unprocessed foods not only aids in regulating glucose levels but also promotes overall health and wellness, enabling patients to take charge of their well-being.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring that you get 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night is crucial, as insufficient sleep can adversely affect insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Current research has shown associations between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension, led by P.E. Peppard, which further links sleep quality to metabolic health. Enhancing sleep quality can therefore have a significant impact on regulating glucose amounts, ultimately helping to achieve a healthy 144 fasting blood sugar.
- Stay active throughout the day: Including physical activity in your daily routine can greatly assist in sustaining healthy glucose concentrations, which may help achieve a 144 fasting blood sugar. Simple actions, such as taking the stairs or going for short walks, can make a considerable difference in your overall health outcomes, contributing to the empowerment of your health journey.
Additionally, consider exploring lesser-known strategies that can further enhance your health and potentially reverse your condition, as these can provide new avenues for managing it effectively.
The Role of Regular Health Screenings
Creating effective meal strategies for diabetes control is crucial for sustaining balanced glucose concentrations, especially for individuals with Type 2 diabetes. A holistic approach starts by re-evaluating the origins of your condition, allowing for a more thorough understanding of health at a foundational aspect. This process can also help reduce the anxiety that accompanies worries surrounding potential complications of your disease.
Routine health evaluations are essential in this process, particularly for individuals with 144 fasting blood sugar readings near 144 mg/dL. Significantly, over 80% of Americans with prediabetes do not recognize their risk for type 2 diabetes, highlighting the importance of proactive health measures to avert disease advancement.
Key strategies for regulating glucose amounts include:
- Incorporating Low Glycemic Index Foods: Focus on foods that possess a low glycemic index to assist in stabilizing glucose concentrations over time.
- Balanced Macronutrient Distribution: Ensure meals contain a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats to support overall health and energy levels.
- Frequent, Smaller Meals: Consuming smaller portions more often can help prevent spikes in glucose levels and sustain energy throughout the day.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of blood sugar levels to understand how different foods affect your body and adjust meal plans accordingly.
- Consulting with Healthcare Providers: Engage with dietitians or nutritionists who can assist in creating personalized meal plans that reflect your health needs and lifestyle.
By addressing these essential components, patients can empower themselves in their management journey. As Leslie Faith M. Taub expresses, identifying and managing this condition effectively has a positive impact on health, applicable not only to those affected but particularly crucial in contexts such as gestational cases to ensure favorable outcomes for both mother and child.
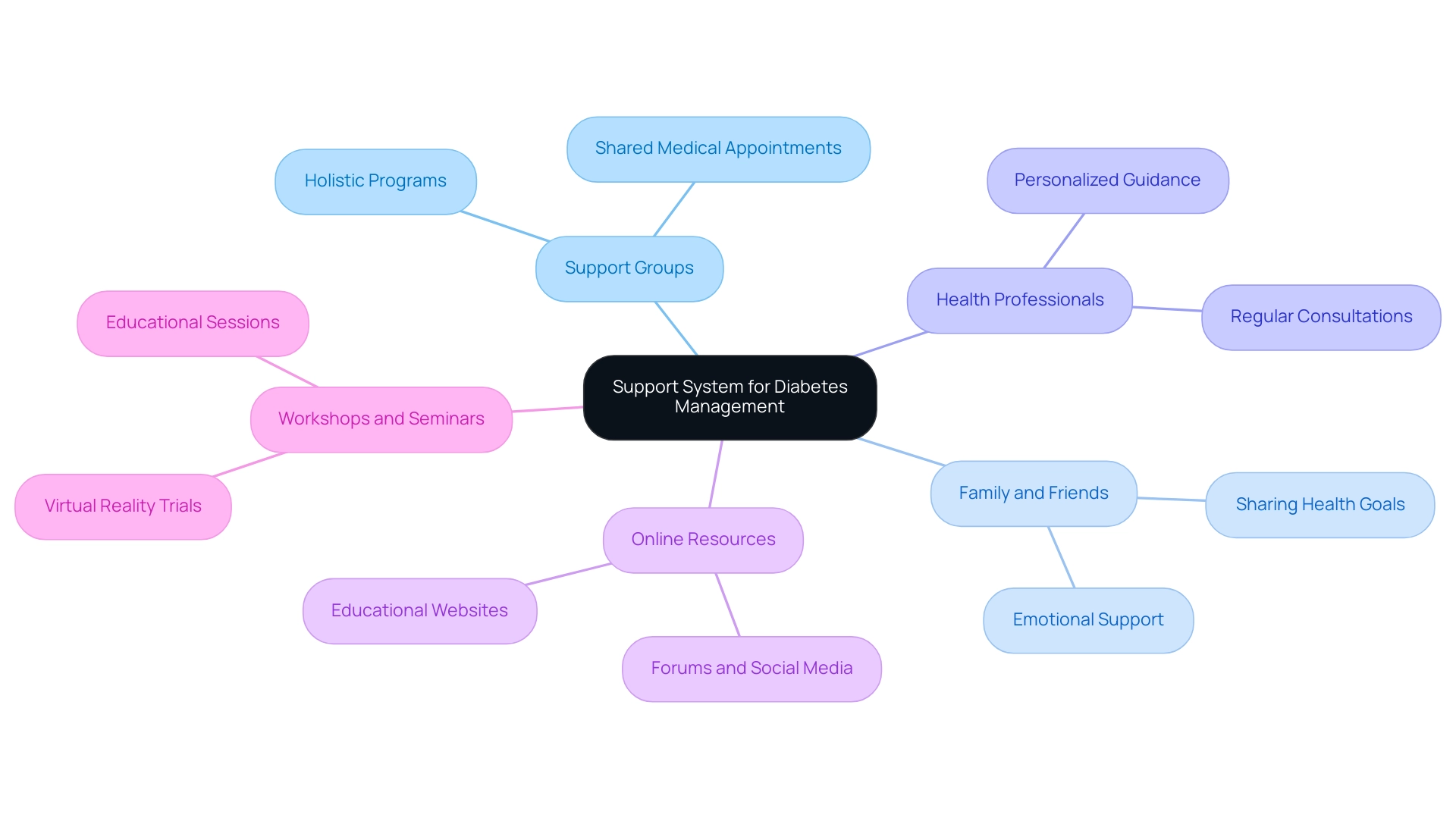
Building a Support System for Diabetes Management
Creating a robust support system is essential for individuals dealing with this condition. Consider the following methods to enhance your support network:
- Join Support Groups: Engaging with others who share similar experiences can offer invaluable encouragement and practical advice. Studies indicate that participation in shared medical appointments (SMAs) significantly contributes to improved health outcomes, with all three reviewed studies showing significant reductions in HbA1c values. A notable example includes M.L., a patient who, after 10 years of managing diabetes, engaged with a holistic program that emphasized personal care. M.L. successfully lost 55 lbs, reduced their A1C from 9.1 to 5.7, and saw their fasting glucose levels drop from 133 to 85. Furthermore, M.L.’s regular MD cut their blood pressure medications in half, illustrating the comprehensive benefits of a holistic approach.
- Involve Family and Friends: Openly sharing your health goals and daily challenges with family and friends fosters a supportive environment. Research indicates that family participation in care can lead to improved management outcomes and emotional support.
- Engage with Health Professionals: Regular consultations with healthcare providers, dietitians, and educators on blood sugar management are essential for personalized guidance and accountability. Their expertise can help you navigate the complexities of managing this condition effectively.
- Utilize Online Resources: Online forums, social media groups, and educational websites provide additional platforms for support and information. These digital resources can help you connect with a broader community and access a wealth of knowledge.
- Participate in Workshops and Seminars: Attending educational sessions enhances your understanding of the condition and inspires motivation to adhere to lifestyle changes. Recent developments, such as a trial comparing in-person chronic condition SMAs to virtual reality-augmented appointments, have shown significant improvements in HbA1c among participants, indicating that both methods are effective in supporting management of the condition.
A robust support network not only bolsters emotional well-being but also reinforces adherence to lifestyle modifications and monitoring practices crucial for managing fasting blood sugar levels. As Dr. Gary Levenston advises, “Certainly, if you or your loved ones are overwhelmed to the point that your health, functioning, or emotional wellbeing are compromised, it is important to seek the services of a licensed mental health professional.” Addressing the root causes of diabetes can also help alleviate anxiety surrounding potential complications, making it essential to seek assistance for maintaining both health and emotional stability.
Conclusion
Monitoring fasting blood sugar levels is a crucial component of effective diabetes management, particularly for those with readings around 144 mg/dL, which indicate prediabetes. This state requires immediate attention and proactive measures to prevent progression to type 2 diabetes and associated complications. Regular monitoring not only helps individuals understand their blood sugar patterns but also fosters informed discussions with healthcare providers about personalized management plans.
Adopting effective strategies, such as:
- Dietary adjustments
- Regular physical activity
- Stress management
can significantly improve blood sugar control. Incorporating whole foods, maintaining hydration, and managing carbohydrate intake are essential practices that empower individuals to take charge of their health. Additionally, building a robust support system and engaging in regular health screenings play pivotal roles in sustaining long-term wellness.
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, particularly among younger populations, the importance of these management strategies cannot be overstated. Taking proactive steps today can lead to improved health outcomes and a diminished risk of serious complications in the future. By prioritizing regular monitoring and lifestyle changes, individuals can navigate their diabetes journey with confidence and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is monitoring fasting glucose readings important for individuals with type 2 diabetes?
Monitoring fasting glucose readings helps individuals notice trends, recognize spikes, and make necessary adjustments to their management strategies. It is crucial for personal health management and for discussions with healthcare providers about tailored treatment options.
What is considered a normal range for fasting blood sugar levels?
The normal range for fasting blood sugar levels is between 70-99 mg/dL. A reading of 144 mg/dL indicates that glucose concentrations are above this normal range.
What are the potential complications of prolonged elevated glucose levels?
Prolonged elevated glucose levels can lead to complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
What percentage of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes show increased pressure readings?
Approximately 80.6% of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes show increased pressure readings.
How does high glucose affect the risk of coronary heart disease?
Individuals with high glucose levels face about twice the risk of coronary heart disease compared to those without, making glucose monitoring essential.
What approach does the Integrative Wellness Center take towards managing type 2 diabetes?
The Integrative Wellness Center adopts a holistic approach that addresses root causes and empowers patients to reverse type 2 diabetes through personalized care and comprehensive treatment insights.
What dietary adjustments are recommended for managing increased glucose concentrations?
Recommended dietary adjustments include prioritizing whole foods, limiting refined sugars and processed carbohydrates, and understanding insulin resistance to make informed dietary choices.
How much physical activity is suggested for effective diabetes management?
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week is suggested to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose levels.
What role does hydration play in glucose management?
Staying hydrated helps the kidneys flush out excess glucose through urine, promoting better glycemic control.
Why is medication management important for diabetes patients?
Adherence to prescribed medication regimens is vital for effective management, and regular discussions with healthcare professionals allow for timely adjustments based on glucose measurements and overall health.
How can stress management impact blood sugar levels?
Incorporating stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can help mitigate the adverse effects of stress on blood sugar levels, as stress can worsen insulin resistance.
What is the importance of regular check-ups for diabetes management?
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals enable timely adjustments to the management plan, ensuring it aligns with health goals and overall well-being.
How can addressing anxiety benefit individuals managing diabetes?
Acknowledging and addressing anxiety through support groups or mental health professionals can provide emotional support and coping strategies, enhancing individuals’ ability to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.