Overview
This article seeks to understand the incidence of type 2 diabetes by examining key trends and contributing factors.
It’s important to recognize that the rising incidence is primarily driven by lifestyle choices, such as obesity and sedentary behavior, along with genetic predispositions.
These elements collectively pose significant challenges to public health.
Many people find that acknowledging these factors is the first step toward making meaningful changes.
Therefore, targeted prevention strategies are essential to support individuals in their journey toward healthier living.
Introduction
The rising tide of type 2 diabetes presents a formidable challenge to global health, affecting nearly 589 million adults today. It’s important to recognize that as the prevalence of this chronic condition continues to escalate, many individuals may feel overwhelmed and uncertain about their health. Understanding the underlying trends and contributing factors becomes crucial for developing effective public health strategies.
What drives this alarming increase?
How can individuals and communities take proactive steps to combat it?
Exploring these questions not only reveals the complexities of type 2 diabetes but also offers actionable insights that can empower healthier lifestyles and improve overall well-being. Together, we can navigate this journey toward better health.
Define Type 2 Diabetes: An Overview
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder that many individuals face, primarily characterized by insulin resistance and a relative deficiency in insulin production, influencing the incidence of type 2 diabetes. It’s important to recognize that, unlike Type 1 diabetes, where the pancreas fails to generate insulin, those with Type 2 can produce insulin. However, their bodies do not use it efficiently. This dysfunction can lead to elevated blood glucose levels, which, if not addressed, may result in serious medical issues such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and vision loss.
Common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
The substantial public health challenge posed by type 2 diabetes is highlighted by the incidence of type 2 diabetes among around 589 million adults aged 20-79 currently living with this condition. Many patients find that understanding its mechanisms and management strategies can empower them in their journey toward better health. It is particularly concerning because this condition is largely preventable and, in some cases, potentially reversible if identified and managed early.
Moreover, the incidence of type 2 diabetes accounts for 96.0% of diabetes cases globally, emphasizing its widespread nature. Alarmingly, over 4 in 10 individuals with the illness are unaware they have it. This underscores the need for increased awareness and early diagnosis. By fostering understanding and encouraging proactive management, we can support those affected in leading healthier lives. Remember, taking steps towards awareness and early intervention can make a significant difference.
Importance of Incidence Statistics in Public Health
Understanding incidence statistics is crucial for public wellness, especially when it comes to type 2 diabetes. These statistics provide valuable insights into how many new cases arise in specific populations over time. It’s important to recognize that by analyzing these trends, we can better evaluate the effectiveness of public health initiatives and allocate resources where they are most needed.
For instance, if we see an increase in the incidence of type 2 diabetes, it may indicate a pressing need for enhanced prevention programs or additional funding for diabetes education. Many patients find that having access to the right information can make a significant difference in their lives. By grasping these patterns, health authorities can implement targeted strategies to effectively combat the growing epidemic of blood sugar issues.
Ultimately, these statistics are not just numbers; they represent real people facing challenges. By understanding the data, we can work together to create a healthier future, ensuring that everyone has the support they need to thrive.
Current Trends and Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Incidence
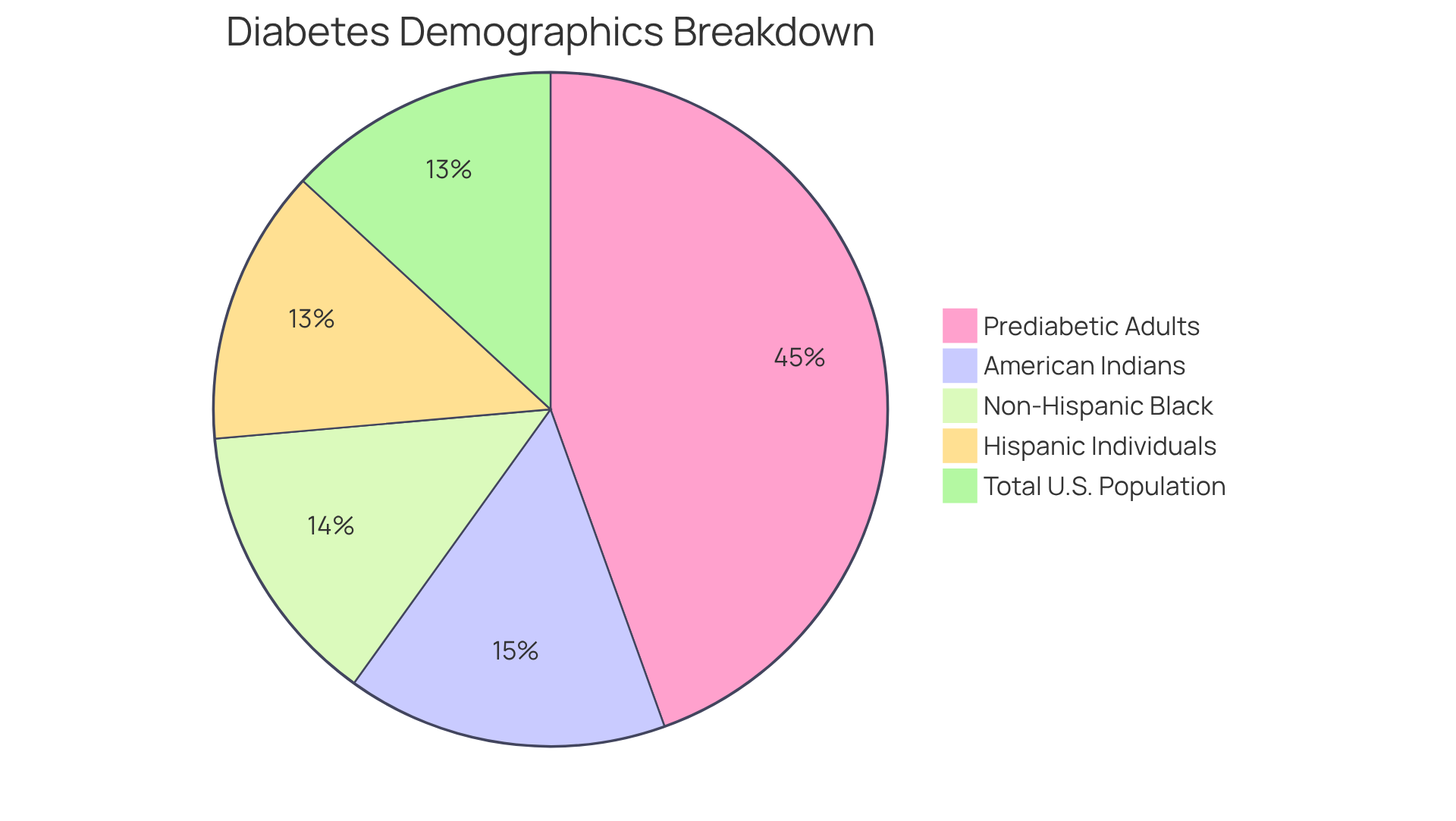
Recent studies indicate a troubling worldwide rise in the incidence of type 2 diabetes. It’s important to recognize that the CDC states the incidence of type 2 diabetes affects over 38.4 million Americans, accounting for roughly 11.6% of the population. This condition, which includes the incidence of type 2 diabetes, represents approximately 90-95% of all cases, with its prevalence significantly higher among older individuals and ethnic minorities. For instance, American Indians and Alaska Natives show the highest diagnosed rates of diabetes-related conditions at 13.6%, followed closely by non-Hispanic Black individuals at 12.1% and Hispanic individuals at 11.7%.
Many patients find that factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and poor dietary habits significantly contribute to the increasing incidence of type 2 diabetes. The increase in prediabetes is also worrisome as it reflects the rising incidence of type 2 diabetes, with almost 97.6 million U.S. adults identified as prediabetic in 2021. This signifies an elevated risk for the incidence of type 2 diabetes, and it’s crucial to address these challenges with compassion and understanding.
The economic impact of diagnosed conditions in the U.S. was assessed at $412.9 billion in 2022, emphasizing the urgency of tackling this public wellness crisis. Understanding these statistics is vital for formulating effective public health strategies aimed at the prevention and management of the incidence of type 2 diabetes, particularly in high-risk demographics. By acknowledging these struggles, we can work together to foster healthier lifestyles and support those affected.
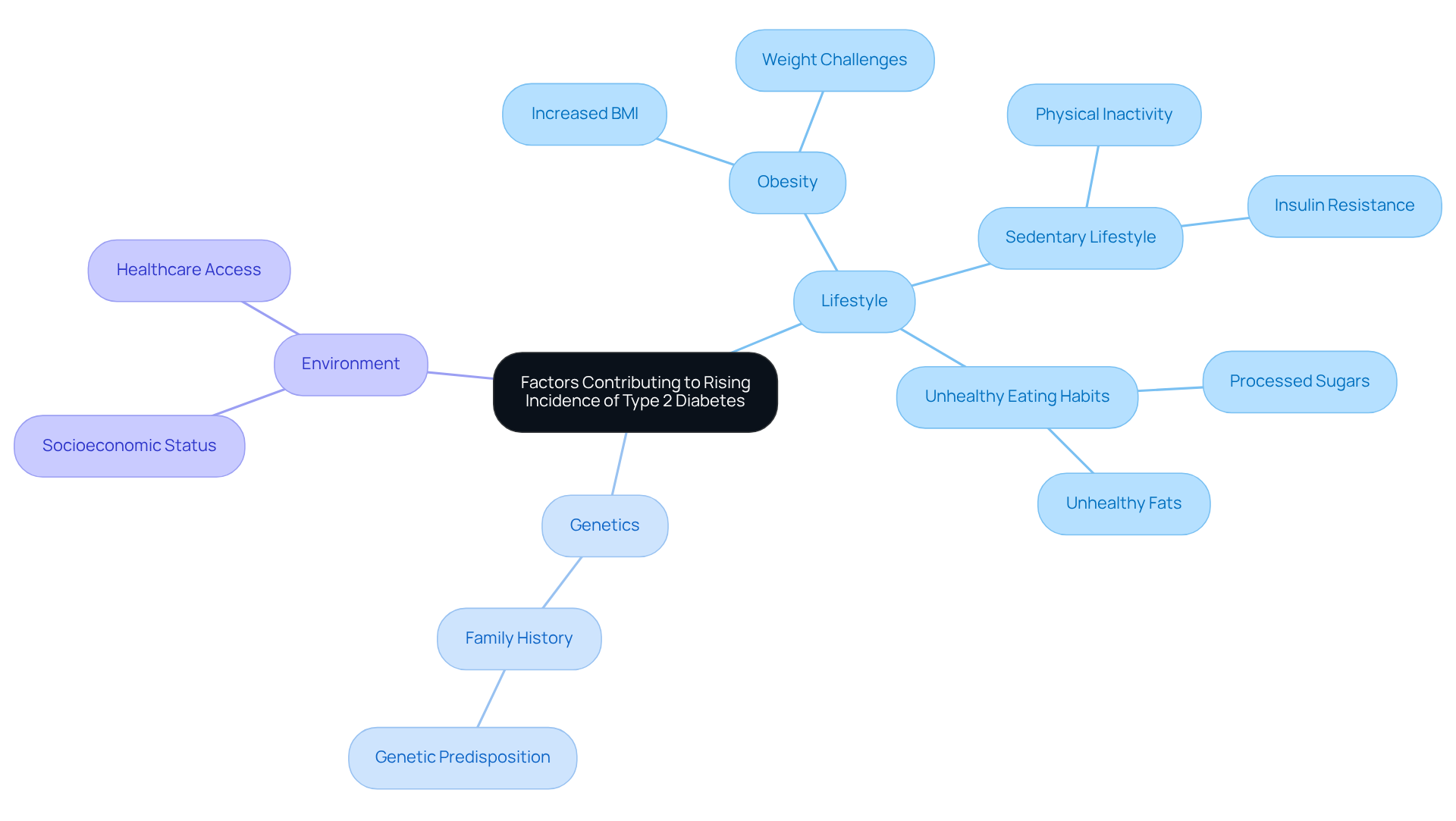
Factors Contributing to the Rising Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes
The overwhelming feeling regarding the rising incidence of type 2 diabetes is influenced by a complex interplay of lifestyle, genetic, and environmental elements. Many individuals are struggling with obesity, with nearly two-thirds of those who face weight challenges experiencing an incidence of type 2 diabetes. Since 1990, the significant increase in adult obesity rates has more than doubled, contributing to the incidence of type 2 diabetes and the diabetes epidemic. It’s important to recognize that sedentary lifestyles further exacerbate the incidence of type 2 diabetes, as physical inactivity can lead to insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels. Unhealthy eating habits, particularly those high in processed sugars and unhealthy fats, raise the incidence of type 2 diabetes.
Genetic predisposition is another essential factor to consider; individuals with a family history of diabetes are at a significantly elevated risk for the incidence of type 2 diabetes. Studies suggest that as body mass index (BMI) increases, the incidence of type 2 diabetes can rise from 7% to a staggering 70%. Additionally, the global incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) accounts for over 90% of cases, underscoring its prevalence. Environmental factors, such as socioeconomic status and access to healthcare, also play a crucial role in determining the incidence of type 2 diabetes and its related conditions.
To address the growing trend of health issues related to blood sugar, it is vital to introduce community education programs and encourage lifestyle changes to reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes. Many patients find that making informed dietary choices and participating in regular physical activity can help decrease the incidence of type 2 diabetes. These strategies can empower individuals to promote a healthier lifestyle, ultimately reducing the incidence of type 2 diabetes. The International Diabetes Federation reports that 11.1% of the adult population is living with diabetes, with projections indicating that this number could rise to 853 million adults by 2050. This alarming trend highlights the urgent need for comprehensive prevention measures and community support to address the increasing incidence of type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion
The rising incidence of type 2 diabetes represents a critical public health challenge that demands our immediate attention. This chronic metabolic disorder, primarily characterized by insulin resistance, affects millions globally and poses significant health risks if left unmanaged. It’s essential to understand the intricacies of type 2 diabetes, as this not only emphasizes the importance of awareness but also highlights the potential for prevention and early intervention.
Many individuals may feel overwhelmed by the alarming trends, including the increasing prevalence of obesity and sedentary lifestyles, which significantly contribute to the rising incidence of type 2 diabetes. It’s important to recognize that genetic predisposition and socioeconomic factors also play a crucial role. Unfortunately, a substantial portion of the population remains unaware of their condition, underscoring the urgent need for improved education and access to healthcare resources.
Addressing the incidence of type 2 diabetes requires a collective effort that prioritizes community education, lifestyle changes, and proactive management strategies. By fostering a deeper understanding of the risk factors and promoting healthier choices, individuals can take meaningful steps towards reducing their risk. Remember, the time to act is now; together, we can combat the growing diabetes epidemic and pave the way for a healthier future for all. Let’s support one another on this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and a relative deficiency in insulin production, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
How does Type 2 diabetes differ from Type 1 diabetes?
Unlike Type 1 diabetes, where the pancreas fails to produce insulin, individuals with Type 2 diabetes can produce insulin but their bodies do not use it efficiently.
What are the common symptoms of Type 2 diabetes?
Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
How prevalent is Type 2 diabetes globally?
Type 2 diabetes accounts for 96.0% of diabetes cases worldwide, affecting approximately 589 million adults aged 20-79.
Why is Type 2 diabetes a public health concern?
It poses a substantial public health challenge due to its high incidence, potential complications like cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and vision loss, and the fact that many individuals are unaware they have the condition.
Can Type 2 diabetes be prevented or reversed?
Yes, Type 2 diabetes is largely preventable and, in some cases, potentially reversible if identified and managed early.
What is the importance of awareness and early diagnosis in Type 2 diabetes?
Increased awareness and early diagnosis are crucial because over 4 in 10 individuals with Type 2 diabetes are unaware they have it, and proactive management can lead to healthier lives.