Overview
The article provides a comprehensive tutorial on the American Diabetes A1C chart, emphasizing its critical role in monitoring long-term blood glucose levels for individuals with diabetes. It explains how understanding A1C levels can guide personalized treatment strategies and lifestyle changes, such as dietary adjustments and regular exercise, to improve health outcomes and manage diabetes effectively.
Introduction
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, serves as a cornerstone in the management of diabetes, providing critical insights into a patient’s average blood glucose levels over the preceding months.
For those living with type 2 diabetes, understanding this test is paramount, as it not only reflects long-term blood sugar control but also aids in tailoring personalized treatment plans.
The implications of A1C results extend beyond mere numbers; they signal the need for lifestyle adjustments and ongoing medical support.
This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, the interpretation of its results, and the various factors that can influence these levels. Additionally, it offers practical lifestyle changes to enhance A1C outcomes and emphasizes the importance of regular consultations with healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive diabetes management.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance and Purpose
The A1C test, formally known as the glycated hemoglobin test, is essential for assessing average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, especially for individuals with type 2. This assessment provides a comprehensive understanding of long-term blood sugar control and is essential for empowering patients through education and personalized care. Results are expressed as a percentage, indicating the proportion of glucose molecules attached to hemoglobin in the bloodstream.
A higher A1C percentage typically signifies suboptimal blood sugar control, increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications. For example, historical data from 1999 revealed a Monitoring Nephropathy rate of 36.0% for Commercial HMO, highlighting the ongoing difficulties in managing blood sugar levels. Regular A1C testing is indispensable for modifying treatment plans and achieving favorable health outcomes, echoing Roopa Naik’s assertion on its critical role in influencing treatment efficacy.
Most adults with this condition are generally advised to maintain an A1C level below 7%, although individual targets should be personalized based on specific health considerations. This customized method is essential, particularly considering recent discoveries that emphasize the necessity for effective management strategies. Along with A1C testing, implementing four lesser-known strategies—such as:
- Dietary adjustments
- Mindfulness practices
- Regular physical activity
- Community engagement
can significantly improve health and aid in reversing the condition.
Community wellness programs play a pivotal role in this process by providing education, nutrition support, and a sense of belonging, all of which empower patients to take control of their health. Furthermore, the A1C test is applicable during early pregnancy to check for undiagnosed conditions in at-risk women, as highlighted in the case study ‘A1C Test During Pregnancy,’ demonstrating the test’s relevance across various populations.
Interpreting A1C Levels: What Do They Mean for Your Health?
A1C levels are classified into distinct categories, each carrying significant implications for diabetes management:
- Normal range (below 5.7%): This range indicates no presence of diabetes and reflects effective blood sugar management practices. According to the American diabetes A1C chart, individuals in the prediabetes range (5.7% to 6.4%) face an elevated risk of progressing to Type 2. It is crucial for patients to implement lifestyle changes to mitigate this risk.
- Diabetes (6.5% or higher): An A1C reading of 6.5% or higher, as indicated on the American diabetes A1C chart, confirms a diagnosis of this condition, signaling an urgent need for management strategies.
Understanding these categories is vital as they inform treatment decisions and necessary lifestyle modifications based on the American diabetes A1C chart. According to Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics, the prevalence of total, diagnosed, and undiagnosed conditions related to blood sugar in adults has been a growing concern, particularly among those with lower income brackets, where the prevalence reaches 6.3% for men and 3.9% for women. This statistic underscores the importance of monitoring A1C levels across different demographics.
Moreover, our approach at the Integrative Wellness Center emphasizes addressing the root causes of this condition through a holistic regimen. By re-evaluating the elements leading to insulin resistance, we can enable patients to question conventional treatment misconceptions and adopt more effective approaches for reversing Type 2. This process also aims to alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications associated with the condition.
The case study titled ‘Trends in Diabetes Prevalence Over Time’ highlights that the age-adjusted prevalence of total and diagnosed health issues has increased from 1999-2000 to August 2021–August 2023, indicating a growing public health concern. Current guidelines emphasize that patients should engage in discussions with their healthcare providers regarding their A1C results and the American diabetes A1C chart to understand the potential complications of the condition. Such discussions assist in setting personalized objectives and action strategies focused on improving or sustaining optimal A1C values, emphasizing the significance of proactive diabetes management.
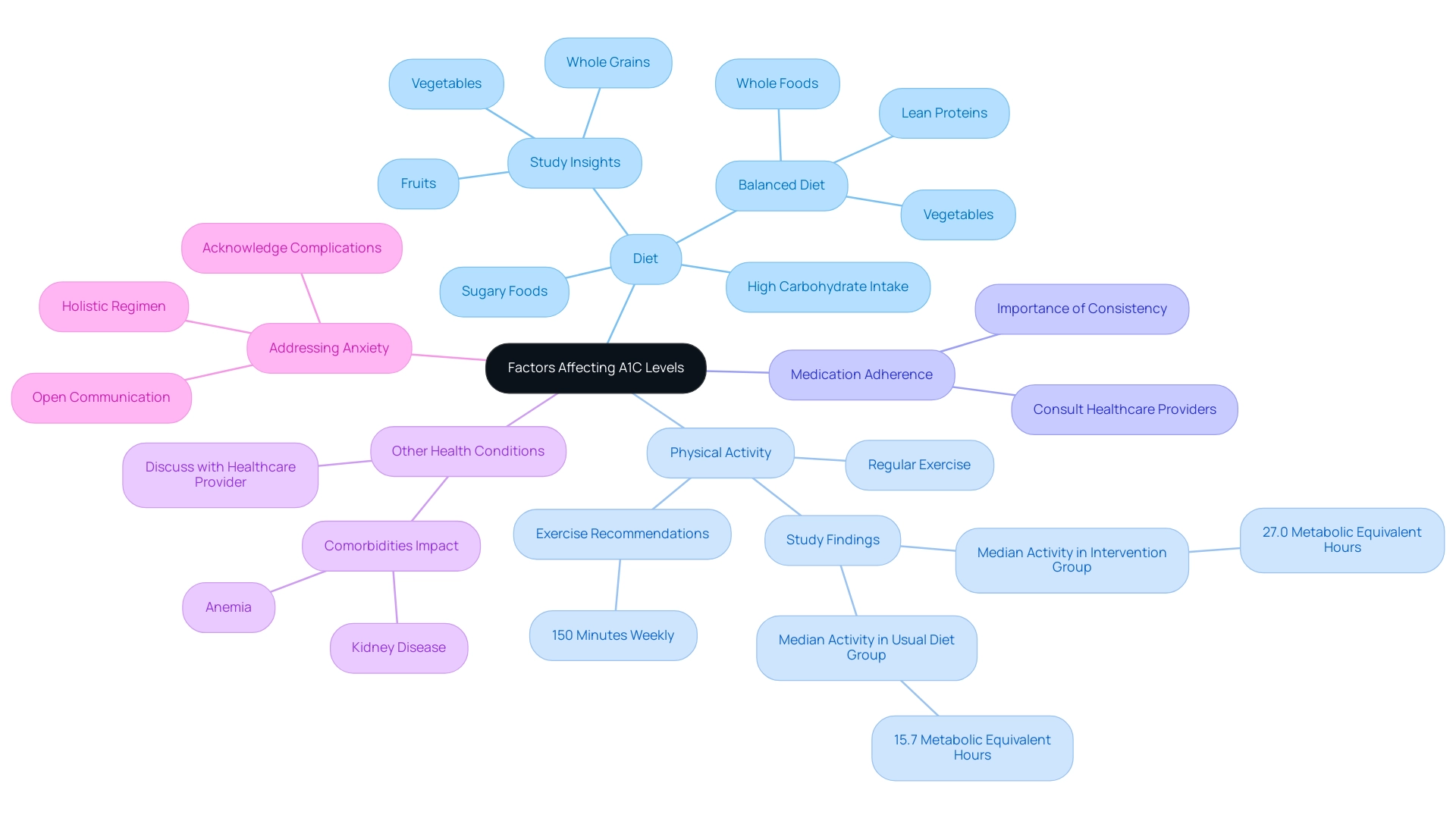
Factors Affecting A1C Levels: What to Consider
A variety of factors can significantly affect A1C measurements, which can be tracked using the American Diabetes A1C chart in individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. These include:
- Diet: A high intake of carbohydrates and sugary foods can elevate blood sugar levels, resulting in increased A1C readings. Emphasizing a balanced diet rich in whole foods, vegetables, and lean proteins is essential for effective management of blood sugar levels. Recent findings from the study titled “Diet Components Affecting T2D Risk” highlight that higher consumption of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables is associated with a reduced risk of Type 2 Diabetes, underscoring the importance of dietary choices in a holistic regimen. As Dr. Lydia A. Bazzano noted, dietary adjustments can play a crucial role in managing diabetes effectively.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise is vital for lowering blood sugar and enhancing insulin sensitivity. Research indicates that individuals who participated in structured exercise programs demonstrated improved A1C levels as shown on the American Diabetes A1C chart. Patients are encouraged to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, as this can significantly contribute to better blood glucose control. A recent study demonstrated that participants in an intervention group reached a median of 27.0 metabolic equivalent hours per week, in contrast to only 15.7 hours in the usual diet group, highlighting the effect of physical activity on managing blood sugar levels.
- Medication Adherence: Consistent adherence to prescribed medications for managing blood sugar levels is critical for maintaining optimal control. Missing doses can lead to spikes in blood glucose readings, which can adversely affect the results reflected in the American Diabetes A1C chart. Patients should prioritize their medication schedules and consult healthcare providers for any concerns regarding their treatment plans.
- Other Health Conditions: Comorbidities such as anemia or kidney disease can also affect A1C results. It is crucial for patients to discuss any underlying health issues with their healthcare provider to understand how these conditions may influence their A1C readings, as referenced in the American Diabetes A1C chart.
- Addressing Anxiety: It’s crucial to acknowledge that anxiety regarding the possible complications of this condition can affect overall health and care. By re-assessing the origin of your condition and addressing health at the foundational aspect through a holistic regimen, patients can decrease anxiety and take charge of their health journey. Maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals can help patients navigate these concerns effectively, ensuring comprehensive care and a more effective approach to reversing Type 2 Diabetes.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve A1C Levels: Practical Tips
To improve A1C values and promote a comprehensive approach to blood sugar care, adopting the following lifestyle changes is essential:
- Nutrition: Embrace a diet low in refined sugars and rich in fiber. Prioritize whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. The Mediterranean diet is frequently advised for its positive impact on blood sugar control. Despite the variability in eating patterns across Mediterranean countries, research suggests that adherence to this dietary approach may yield synergistic health benefits that surpass the individual qualities of its components. In fact, participants in studies adhering to this diet scored an average of 7.5 on a 10-point adherence scale, highlighting its effectiveness.
- Regular Monitoring: It is essential to consistently track blood sugar readings with the American diabetes A1C chart to understand how food intake, physical activity, and medication influence your A1C. This practice enables the identification of patterns and necessary adjustments for better management, aligning with the goal of addressing the condition at its root, much like the insights provided by the American diabetes A1C chart.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration supports kidney function by helping to flush out excess sugar through urine. Aim to consume at least eight glasses of water daily to assist in blood sugar regulation.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively affect blood sugar readings and contribute to anxiety surrounding potential complications of this condition. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness practices, yoga, or regular physical activity, can significantly help mitigate these effects, underscoring the importance of holistic health and alleviating anxiety.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Strive for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, as inadequate sleep can hinder insulin sensitivity and disrupt glucose metabolism. Ensuring good sleep hygiene is vital for maintaining optimal blood sugar. As Christopher Gardner, PhD, notes, ‘What is it about this diet that would be so compelling that you would give up some of those central tenets of health and nutrition?’. This question highlights the significance of grasping the motivations behind dietary changes, particularly for individuals dealing with blood sugar conditions.
- Re-examining the Source of Your Condition: By concentrating on the root causes of your health issue, we can implement a holistic regimen that not only addresses blood sugar levels but also empowers your overall well-being and alleviates anxiety about complications.
- Research Limitations: It is crucial to recognize that the insufficient number of trials restricts further subgroup analysis on specific indicators related to dietary interventions and their effectiveness in A1C control as referenced in the American diabetes A1C chart. By recognizing these limitations, we can better appreciate the complexities involved in reversing Type 2 conditions.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals: Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are fundamental to effective diabetes care, particularly at the Integrative Wellness Center, where a holistic approach is emphasized. These consultations facilitate several crucial aspects:
- Monitoring Progress: Systematic evaluations of A1C levels through the American diabetes A1C chart allow healthcare professionals to track a patient’s progress and determine whether treatment adjustments are necessary. Regular monitoring can offer insights into the effectiveness of current organizational strategies.
- Medication Management: Healthcare providers play a vital role in assessing the efficacy of prescribed medications. They can suggest alternatives or modifications to optimize treatment and address any concerns about side effects or interactions.
- Education and Support: Ongoing learning about blood sugar control, nutrition, and lifestyle modifications enables patients to assume an active part in their health.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, access to tailored resources and support from healthcare professionals enhances self-management skills and improves outcomes, allowing patients to eliminate anxiety over potential complications.
- Addressing Complications: Timely detection of potential diabetes-related complications is critical for improving patient outcomes. Regular consultations enable early intervention, significantly mitigating risks associated with the condition.
According to the American Diabetes Association, patients are advised to schedule follow-up appointments every three to six months, or as recommended by their healthcare provider, to ensure comprehensive management of their condition. Furthermore, the ADA recommends statin therapy for most adults with metabolic conditions, regardless of their specific lipid levels, based on their cardiovascular risk, highlighting the importance of cardiovascular health in managing these conditions. Additionally, normal eGFR levels, which range from 100 to 120 ml/min/1.73 m², are crucial for assessing kidney function, an essential aspect of care for these conditions.
A recent study titled ‘Conclusions on Diabetes Care Engagement’ highlighted that follow-up care and blood glucose monitoring among Chinese patients with type 2 conditions at moderate to high cardiovascular risk were suboptimal, indicating a clear need for tailored educational approaches to improve patient engagement and address disparities in care. This underscores the importance of regular healthcare consultations in managing diabetes effectively, as shown by the American diabetes A1C chart, particularly in underserved areas.
Conclusion
The A1C test serves as a critical tool in the ongoing management of type 2 diabetes, offering valuable insights into a patient’s average blood glucose levels over the preceding months. Understanding the significance of A1C results is essential for individuals living with diabetes, as these results not only reflect long-term blood sugar control but also guide personalized treatment strategies. The classification of A1C levels into normal, prediabetes, and diabetes categories provides a framework for making informed lifestyle changes and medical decisions, reinforcing the necessity of proactive engagement with healthcare providers.
Factors influencing A1C levels, such as diet, physical activity, and medication adherence, highlight the multifaceted nature of diabetes management. By adopting practical lifestyle modifications—ranging from nutritional adjustments to stress management—individuals can significantly enhance their A1C outcomes. The incorporation of community support and education further empowers patients, fostering a sense of belonging and shared responsibility in managing their health.
Regular consultations with healthcare professionals are indispensable for monitoring progress and addressing potential complications. These check-ups not only facilitate tailored treatment adjustments but also promote ongoing education and support, ultimately enhancing self-management skills. As diabetes prevalence continues to rise, the importance of understanding the A1C test and its implications cannot be overstated. By prioritizing comprehensive diabetes management strategies, individuals can take meaningful steps towards achieving better health outcomes and reducing the risks associated with this chronic condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, measures average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. It is crucial for assessing long-term blood sugar control, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes, and helps empower patients through education and personalized care.
How are A1C results expressed and what do they indicate?
A1C results are expressed as a percentage, representing the proportion of glucose molecules attached to hemoglobin in the bloodstream. A higher A1C percentage generally indicates suboptimal blood sugar control, increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
What A1C level is typically recommended for adults with type 2 diabetes?
Most adults with type 2 diabetes are advised to maintain an A1C level below 7%. However, individual targets should be personalized based on specific health considerations.
What additional strategies can improve health alongside A1C testing?
Along with A1C testing, strategies such as dietary adjustments, mindfulness practices, regular physical activity, and community engagement can significantly improve health and aid in reversing type 2 diabetes.
How does community wellness play a role in diabetes management?
Community wellness programs provide education, nutrition support, and a sense of belonging, empowering patients to take control of their health and effectively manage their diabetes.
Can the A1C test be used during pregnancy?
Yes, the A1C test is applicable during early pregnancy to check for undiagnosed conditions in at-risk women, demonstrating its relevance across various populations.
What are the A1C categories and their implications for diabetes management?
A1C categories include: Normal range (below 5.7%): Indicates no diabetes and effective blood sugar management. Prediabetes (5.7% to 6.4%): Indicates an elevated risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes, requiring lifestyle changes. Diabetes (6.5% or higher): Confirms a diagnosis of diabetes, signaling an urgent need for management strategies.
Why is it important to monitor A1C levels across different demographics?
Monitoring A1C levels is vital as it informs treatment decisions and necessary lifestyle modifications. The prevalence of blood sugar-related conditions varies among demographics, particularly among lower income brackets, highlighting the need for widespread monitoring.
What approach does the Integrative Wellness Center take towards diabetes management?
The Integrative Wellness Center emphasizes addressing the root causes of type 2 diabetes through a holistic regimen, enabling patients to question conventional treatment misconceptions and adopt more effective approaches for reversing the condition.
What should patients discuss with their healthcare providers regarding A1C results?
Patients should engage in discussions with their healthcare providers about their A1C results and the implications as outlined in the American diabetes A1C chart. This helps in setting personalized objectives and action strategies focused on improving or sustaining optimal A1C values.