Overview
Understanding the effects of alcohol on blood sugar levels is crucial, especially for those managing diabetes. Have you ever noticed how a drink can change how you feel? Alcohol consumption can lead to significant fluctuations in glucose levels, which may pose risks like hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
It’s important to recognize that monitoring your blood sugar is essential. By making informed beverage choices and adhering to safe consumption guidelines, you can enjoy social occasions while effectively managing your diabetes.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and there are ways to navigate these challenges with care and support.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management can feel overwhelming, especially when it comes to enjoying a glass of wine or a cocktail during social occasions. It’s important to recognize that many individuals with diabetes want to partake in these moments without jeopardizing their health. Understanding the intricate relationship between alcohol and blood sugar levels is essential for making informed choices. Alcohol can significantly impact glucose metabolism, leading to fluctuations that may complicate diabetes management.
This article explores the effects of various types of alcoholic beverages, the potential risks associated with drinking, and practical guidelines for safe consumption. By empowering individuals with knowledge and strategies, it aims to foster a balanced lifestyle that prioritizes both enjoyment and health.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey—there are ways to enjoy life while managing your diabetes effectively.
The Connection Between Alcohol and Blood Sugar Levels
The impact of alcohol on blood sugar can significantly affect glucose levels, especially for those managing diabetes. When alcohol is consumed, ethanol is primarily metabolized by the liver, which prioritizes this process over glucose production. This shift can lead to a temporary drop in glucose levels, particularly when alcoholic beverages are consumed on an empty stomach. It’s important to recognize that understanding this effect is crucial for diabetics, as it allows them to anticipate and manage potential fluctuations in their glucose levels effectively.
Research shows that while moderate alcohol consumption may not directly cause diabetes, the effects of alcohol on blood sugar indicate that excessive intake can greatly increase the risk of developing the condition and complicate existing diabetes management. In fact, studies suggest that reducing or eliminating alcoholic beverages can lead to better blood sugar control, highlighting the importance of being mindful of the alcohol effect on blood sugar and reducing health complications for those at risk. Notably, statistics reveal that opioid overdose deaths involving spirits as a contributing factor rose by 41% in 2020, emphasizing the serious risks associated with excessive drinking.
As we look ahead to 2025, experts continue to stress the importance of caution for diabetics regarding ethanol-containing beverages. While there may be potential cardiovascular benefits to moderate consumption, these must be weighed against the risks of impaired glucose regulation. For instance, a case study titled ‘Alcohol Abuse and Diabetes Risk’ illustrates that although moderate consumption might not adversely affect glucose levels, the alcohol effect on blood sugar can significantly disrupt glucose regulation, leading to harmful health consequences.
Real-world experiences further underscore the relationship between beverage metabolism and diabetes management. Many patients who have moderated their alcohol intake report improved control over their blood sugar levels, which reinforces the significance of understanding the alcohol effect on blood sugar in managing diabetes. Dr. Jason Shumard’s innovative methodologies offer valuable insights and practical tools that empower patients to navigate their consumption in relation to their diabetes.
As Dr. Shumard wisely notes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” This holistic approach encourages patients to make informed choices about their beverage consumption, ultimately leading to better health outcomes. Additionally, integrating lifestyle strategies—such as engaging in regular outdoor exercise, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, and participating in community wellness programs—can further enhance diabetes management, creating a supportive environment for individuals in San Marcos, CA.
Types of Alcohol and Their Impact on Blood Sugar
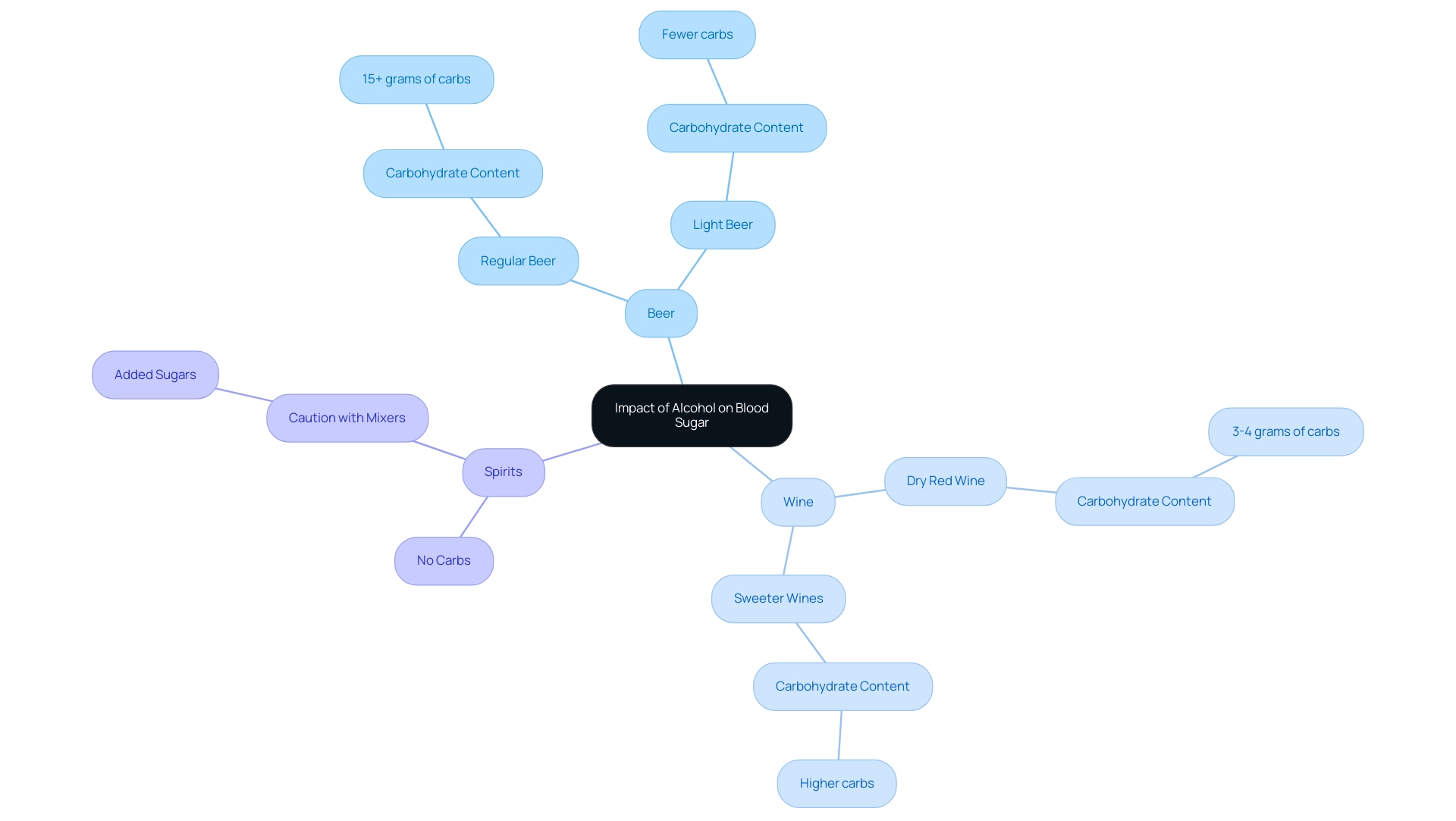
When it comes to regulating glucose levels, the impact of alcohol on blood sugar can vary greatly among different types of drinks. Understanding the carbohydrate content and how alcohol affects blood sugar is essential for individuals managing diabetes. Let’s take a closer look at how various alcoholic beverages can influence blood sugar:
- Beer: Regular beers often contain a high amount of carbohydrates, with some varieties having upwards of 15 grams of carbs per serving, which can lead to a significant rise in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, light beers usually have fewer carbohydrates, making them a more suitable choice for those concerned about the effects of alcohol on their blood sugar.
- Wine: Both red and white wines generally have less sweetness compared to sweeter wines and cocktails. For instance, a typical glass of dry red wine contains around 3-4 grams of carbs, making it a preferable option for diabetics who wish to enjoy a drink while being mindful of their blood sugar levels.
- Spirits: Distilled beverages like vodka, gin, and whiskey contain no carbohydrates, meaning they won’t directly affect blood glucose. However, it’s important to be cautious with mixers, as many can include added sugars that impact blood sugar levels. Choosing sugar-free mixers can help maintain stable glucose levels.
As we look ahead to 2025, it’s crucial for individuals with diabetes to stay vigilant about their beverage choices. Research shows that the effects of alcohol on blood sugar can lead to increased calorie intake and may cause individuals to forget their medications, complicating diabetes management. By arming oneself with strategies for responsible drinking, significant improvements in managing alcohol consumption can be achieved.
Real-life experiences illustrate that many individuals with diabetes successfully control their glucose levels while enjoying various alcoholic drinks. For example, one patient who opts for a glass of dry red wine during dinner reports stable glucose readings, while another who chooses a regular beer notices a significant increase. These stories underscore the importance of monitoring individual reactions to different beverages, especially regarding alcohol’s impact on blood sugar.
Ultimately, understanding the carbohydrate content in alcoholic beverages is vital due to its effect on blood sugar. For instance, a Tequila Sunrise (6.8 fl oz) contains about 23.84 grams of carbs, which can greatly affect glucose levels. By making informed choices and monitoring their intake, individuals with diabetes can enjoy social occasions without compromising their health.
As Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.” This holistic approach, coupled with community support and personalized guidance, empowers individuals to manage their diabetes effectively while enjoying the vibrant lifestyle that San Marcos offers. Engaging with local wellness programs and utilizing resources like farmers’ markets can further enhance these efforts, allowing individuals to incorporate fresh, local produce into their diets and connect with others on similar health journeys.
Risks of Alcohol Consumption for Diabetics
Diabetics face several significant risks when consuming alcohol, which can complicate their health management.
- Hypoglycemia: It’s important to recognize that alcohol consumption can lead to dangerously low blood sugar levels, especially when combined with diabetes medications like insulin. This risk is heightened if beverages containing ethanol are consumed on an empty stomach, as alcohol can inhibit gluconeogenesis, the process by which the liver produces glucose. Many patients have reported severe episodes of hypoglycemia due to beverage consumption, highlighting the need for vigilance and immediate intervention.
- Hyperglycemia: Conversely, excessive consumption of beverages can lead to increased glucose concentrations. This occurs because the alcohol effect on blood sugar can impair the body’s ability to regulate glucose effectively. A study involving 15,453 participants in Japan revealed that high beverage intake significantly increased the risk of type 2 diabetes in men with elevated fasting plasma glucose, underscoring the dual threat of such drinks on glucose levels.
- Medication Interactions: Many patients find that alcohol can disrupt the effectiveness of diabetes treatments, complicating glucose management. For instance, certain medications may have their effects diminished or altered when intoxicants are present, leading to unpredictable fluctuations in blood sugar. This interaction emphasizes the importance of closely monitoring beverage consumption.
- Real-World Examples: There are numerous documented incidents of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia related to beverage consumption among diabetics. Patients have shared experiences where a night of drinking led to severe hypoglycemia the following day, necessitating emergency assistance. These real-world cases serve as critical reminders of the potential dangers associated with alcoholic beverages, particularly regarding the alcohol effect on blood sugar.
- Expert Opinions: Specialists stress the necessity for diabetics to be careful with beverage intake. They suggest that individuals with diabetes seek advice from healthcare professionals to understand how beverages may influence their specific treatment plans and overall health. Dr. Jason Shumard advocates for patient education, stating, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life.”
- Statistics: Recent statistics indicate that the interaction between beverage consumption and body mass index (BMI) can significantly affect the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This interaction suggests that the impact of spirits is not uniform and varies based on individual health profiles. For example, the study titled “Impact of Beverage Consumption on Type 2 Diabetes Risk” found that heavy beverage intake significantly increased T2D risk in men with elevated fasting plasma glucose but had no significant effect on women or those with normal fasting plasma glucose, indicating the need for further research on gender-specific insights.
Understanding the alcohol effect on blood sugar is crucial for diabetics in making informed decisions about alcohol consumption, ensuring they can manage their condition effectively while maintaining their quality of life. Additionally, embracing a holistic lifestyle in San Marcos, CA, through balanced nutrition, regular exercise in the area’s beautiful parks, and community support can further enhance diabetes management and overall well-being.
How Alcohol Affects Glucose Metabolism
The effect of alcohol on blood sugar is significant, primarily because it obstructs gluconeogenesis—the liver’s way of generating glucose. This inhibition can lead to lower glucose levels, especially if someone hasn’t eaten before drinking. In fact, studies from 2025 reveal that around 20% of adults in the U.S. suffer from chronic pain, with many seeking relief through beverages as a form of self-medication.
This behavior complicates diabetes management, particularly for those with type 2 diabetes, who already face challenges in regulating their glucose levels. It’s important to recognize that alcohol can also impair insulin sensitivity, making it harder for the body to utilize glucose effectively. This issue is especially concerning for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as it can worsen existing problems with glucose metabolism. Real-world experiences show that even moderate alcohol consumption can lead to notable fluctuations in blood sugar levels, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and personalized nutrition plans.
While some studies have looked into the relationship between moderate alcohol consumption and potential heart health benefits, experts do not recommend it as a strategy for diabetes prevention. Responsible intake is crucial due to the potential harmful effects of alcohol on blood sugar and glucose metabolism. Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.”
In managing diabetes, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet is essential to prevent complications like coronary artery disease and to promote overall health. This dietary approach becomes particularly relevant when considering how alcohol affects blood sugar and glucose metabolism. Additionally, empowering patients through structured goal-setting and progress tracking can significantly enhance their engagement in managing their health.
For example, patients can set specific goals such as:
- Gradually reducing their alcohol intake
- Tracking their blood sugar levels after consuming beverages to better understand their effects
Many patients have shared their appreciation for the control they feel over their health after participating in educational programs that address these important issues, including the effects of substances on their diabetes management.
Guidelines for Safe Alcohol Consumption in Diabetics
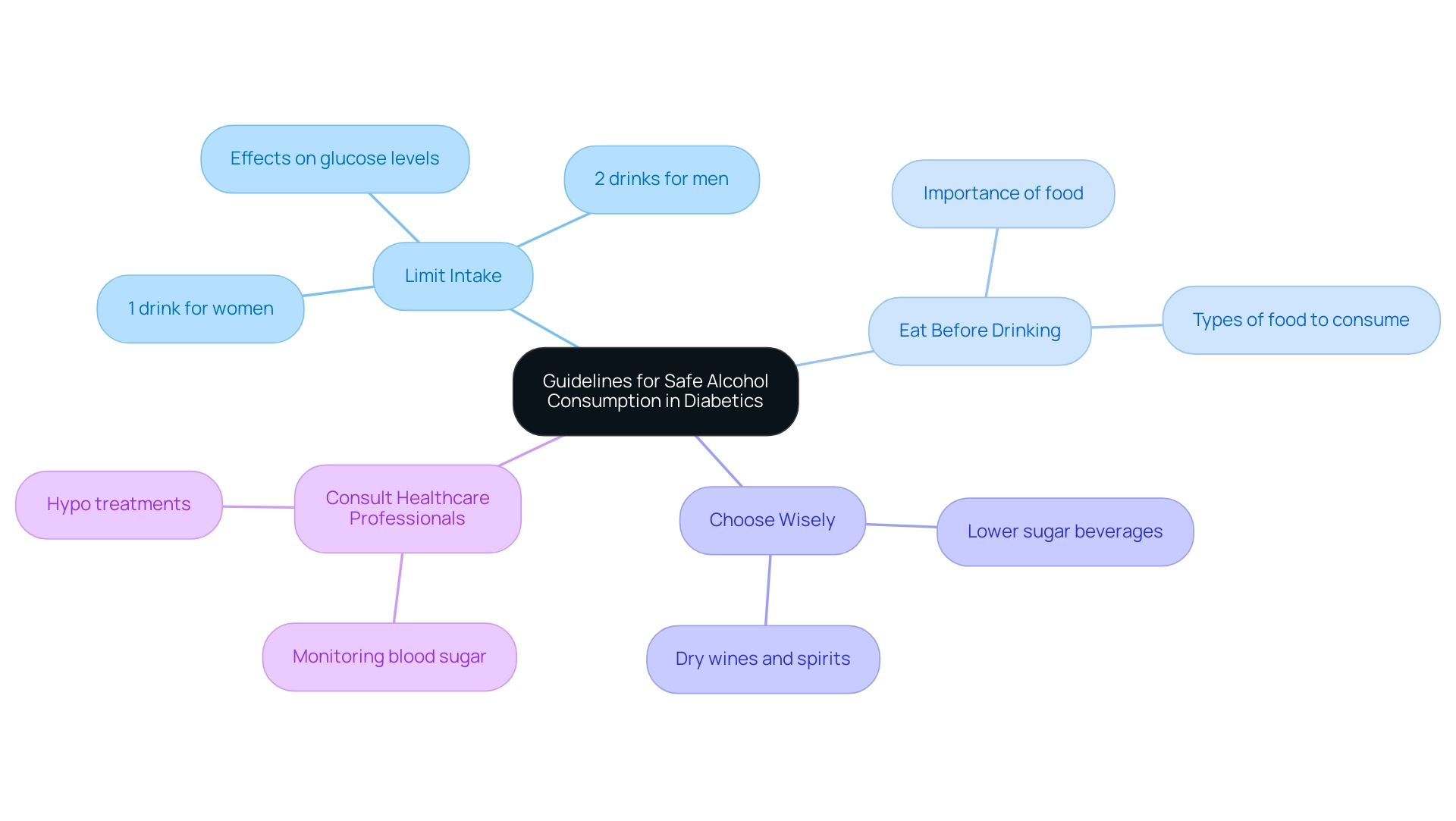
To consume alcohol safely, diabetics should consider the following guidelines:
- Limit Intake: It’s important for women to restrict their alcohol consumption to one drink per day, while men should not exceed two drinks. This moderation is crucial, as excessive beverages can lead to fluctuations in glucose levels, complicating diabetes management due to the impact of alcohol on blood sugar.
- Eat Before Drinking: Consuming food, especially carbohydrates, before or while drinking is essential. This practice helps stabilize glucose levels and reduces the risk of hypoglycemia, particularly given how alcohol affects blood sugar, especially on an empty stomach.
- Choose Wisely: Opt for beverages that are lower in sugar, such as dry wines or spirits mixed with sugar-free mixers. This choice can significantly reduce the risk of glucose spikes.
Recent statistics highlight the importance of safe beverage consumption guidelines for diabetics, as they can help prevent complications related to diabetes and the effects of alcohol on blood sugar. For instance, studies indicate that individuals with diabetes who follow these guidelines experience fewer instances of hypoglycemia and related health issues. In fact, those who adhere to these recommendations report a 30% reduction in hypoglycemic episodes, likely influenced by the alcohol’s effect on blood sugar, compared to those who do not.
Real-life examples further illustrate the significance of these guidelines. Many diabetic individuals have successfully integrated moderate beverage intake into their lifestyles by following these recommendations, aiding in their management of the alcohol’s impact on blood sugar and enhancing their overall health. One patient shared that after adhering to these guidelines, their A1C levels improved significantly, showcasing the effectiveness of moderation.
Expert opinions also underscore the need for personalized approaches to beverage consumption for diabetics. Healthcare professionals advocate for consistent blood sugar monitoring and ensuring that hypo treatments are readily available, especially during social occasions. This proactive strategy can help prevent adverse effects and ensure a safer drinking experience.
Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.”
Moreover, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential risks associated with beverage consumption, particularly regarding the alcohol’s effect on blood sugar. Heavy consumption of spirits can lead to neurological damage, and conditions like Wernicke’s encephalopathy, which can arise from thiamine deficiency, emphasize the importance of caution. This highlights the necessity for diabetics to closely monitor their beverage consumption and consult their healthcare team.
In summary, understanding and implementing safe beverage consumption guidelines is essential for diabetics. By following these recommendations, individuals can enjoy social occasions while maintaining their health and effectively managing their diabetes.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels While Drinking Alcohol
To effectively manage blood sugar levels while enjoying a drink, it’s essential to embrace holistic strategies that resonate with the vibrant lifestyle in San Marcos, CA.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Regularly checking your blood sugar levels before, during, and after drinking is a vital practice. This not only helps you understand how different types of spirits affect your blood sugar but also empowers you to take charge of your health. Did you know that around 30% of individuals with diabetes report fluctuations in their glucose readings after consuming alcohol? This highlights the importance of self-monitoring. Additionally, findings from the COMBINE Study revealed that individuals with higher baseline glucose levels were more likely to engage in heavy drinking, underscoring the need to consider how alcohol can impact your blood sugar for responsible consumption.
- Stay Hydrated: Remember to drink water alongside your alcoholic beverages. Staying hydrated can significantly mitigate the alcohol’s effects on your blood sugar, as dehydration may lead to increased glucose levels in your bloodstream. Research suggests that proper hydration stabilizes glucose concentrations, making it an indispensable part of responsible drinking. In San Marcos, why not infuse your water with local fruits for a refreshing twist?
- Have Snacks Ready: It’s wise to keep glucose tablets or healthy snacks nearby to counteract potential hypoglycemia. The alcohol effect on blood sugar can sometimes lead to low glucose levels, especially if you drink on an empty stomach. Having quick sources of glucose readily available can help prevent dangerous drops in your levels. Consider visiting local farmers’ markets to stock up on fresh, diabetes-friendly snacks like avocados and nuts.
- Incorporate Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes. In San Marcos, take advantage of the beautiful parks and trails for outdoor workouts. Activities like hiking at Lake San Marcos or strolling along the trails at Discovery Lake can enhance your insulin sensitivity and help regulate your glucose levels. Pairing exercise with mindful drinking can further support your health goals.
Real-world examples illustrate the importance of these strategies. Diabetic patients who actively monitor their blood sugar while drinking often express feeling more in control and less anxious about their health. One participant shared, “I always verify my measurements before heading out. It gives me peace of mind knowing I can enjoy a drink without risking my health.” Another participant noted, “Sometimes it can get messy [drinking] with the people my age; we’re all about 19–21, so we’re all still quite young and a little bit ambitious. Some nights, they’ll go right from the get-go, and they won’t remember anything the next morning.” This highlights the societal pressures young adults with diabetes face in managing their glucose levels while enjoying social occasions.
Expert opinions emphasize the necessity of understanding how alcohol affects blood sugar for diabetics. A recent analysis of the COMBINE Study indicated that those with higher baseline glucose levels were more inclined to engage in heavy drinking, suggesting a link between glucose management and drinking behavior. This reinforces the need for tailored medical interventions aimed at reducing alcohol consumption among individuals with diabetes.
By incorporating these strategies, you can enjoy social gatherings while prioritizing your health and well-being, supported by the community and resources available in San Marcos. For personalized guidance tailored to your unique needs, consider reaching out to Dr. Jason Shumard, who can offer expert advice on managing diabetes effectively.
The Importance of Monitoring Blood Sugar Around Alcohol Consumption
Supervising glucose measurements is crucial for individuals with diabetes, especially when enjoying beverages. It’s important to recognize that monitoring your blood sugar levels can make a significant difference in your health. Here are some key practices to follow:
- Check Before Drinking: Ensuring your blood sugar levels are within a safe range before consuming alcohol is vital. This initial check helps prevent potential spikes or drops that could lead to complications.
- Regular Checks: Throughout the evening, it’s essential to continue tracking your glucose readings, particularly if you’re having multiple drinks. Many patients find that spirits can have unpredictable impacts on glucose measurements, making continuous watchfulness critical.
- Post-Consumption Monitoring: Checking your glucose concentrations before going to bed is particularly important. Alcohol can influence glucose levels for several hours after intake, so this practice assists in managing overnight glucose amounts and reduces the risk of hypoglycemia.
To effectively monitor and improve your progress in managing glucose levels, consider utilizing various tracking methods, such as fitness applications, journals, and pedometers. Implementing SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can significantly boost your focus and motivation. For instance, you might establish a goal to keep your glucose levels within a particular range after consuming alcohol or to gradually decrease your intake over a month.
Research indicates that persistence in goal-setting can positively impact performance, demonstrating the effectiveness of structured goal-setting in health management. However, it’s essential to set appropriately challenging goals, as studies have shown that overly difficult goals can lead to frustration and hinder progress.
Real-life examples illustrate the importance of these practices. Many individuals with diabetes have reported considerable variations in their glucose readings after consuming alcohol, highlighting the necessity for vigilant observation. For example, a patient who frequently monitors their glucose levels before and after drinking has noticed a trend of elevated levels post-consumption, prompting them to adjust their intake accordingly.
These experiences resonate with the findings from Dr. Jason Shumard’s Functional Medicine Approach, where patients express gratitude for the empowerment they feel in taking control of their health through effective monitoring and education.
Statistics indicate that individuals with high beverage consumption face a 73% greater chance of developing diabetes, underscoring the significance of tracking glucose levels in relation to beverage intake. This statistic emphasizes the essential need for awareness in beverage consumption, as regular glucose tests can enable you to make informed choices regarding your health. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.”
Incorporating these monitoring practices not only enhances safety but also fosters a proactive approach to managing diabetes while enjoying social activities. By understanding how spirits impact glucose levels, you can regain your well-being and maintain a balanced lifestyle. Notably, the mean age of individuals in related studies was 43.71 ± 8.90 years, indicating that this demographic is particularly affected by the interaction between beverage consumption and diabetes management.
Key Takeaways for Diabetics on Alcohol Consumption
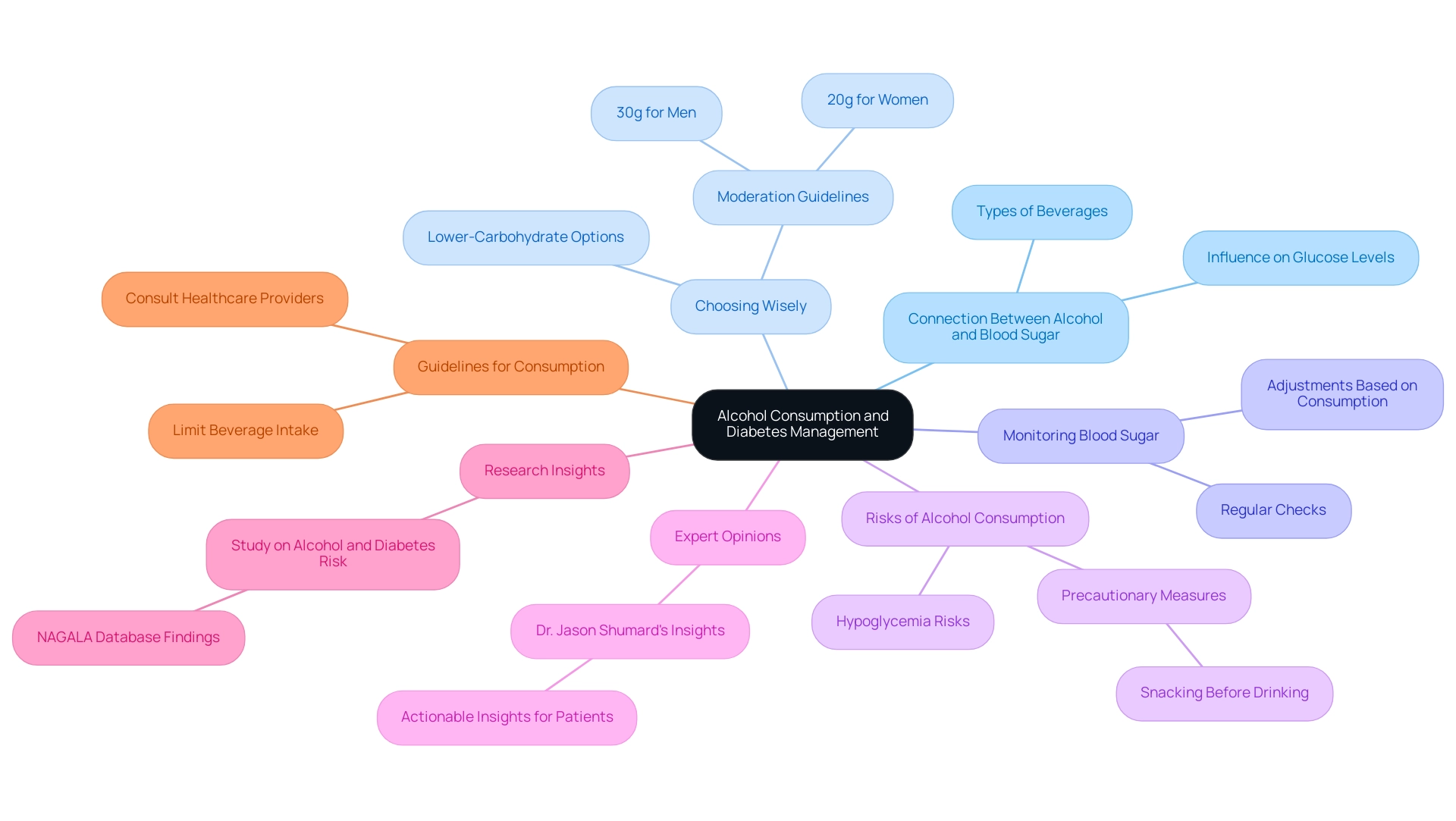
For individuals managing diabetes, understanding the relationship between beverage consumption and glucose levels is crucial. Let’s explore some key insights together:
- Connection Between Alcohol and Blood Sugar: Alcohol can significantly influence blood sugar levels, leading to fluctuations that may complicate diabetes management. It’s important to recognize how different types of beverages can affect your glucose levels.
- Choosing Wisely: Opt for lower-carbohydrate alcoholic options, such as dry wines or spirits mixed with soda water, to keep sweetener intake in check. Remember, moderation is key; consuming more than 30 grams per day for men and 20 grams for women can increase the risk of developing diabetes and exacerbate existing conditions.
- Monitoring your blood sugar is essential to understand how alcohol affects you. Regularly checking your glucose levels before, during, and after drinking can help you see how different beverages influence your individual responses, allowing for timely adjustments in your diabetes management.
- Be mindful of the potential risks associated with alcohol consumption, including hypoglycemia (low glucose) and its often subtle symptoms. Taking precautions, such as having a snack before drinking, can greatly help in managing these risks.
- Many individuals with diabetes have successfully navigated their beverage choices by following these guidelines. For instance, those who reserve alcohol for special occasions and choose lower-sugar options often report better control over their blood sugar levels, which can enhance their overall health.
- Expert Opinions: Healthcare professionals stress the importance of personalized care and education in diabetes management. Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” This underscores the commitment to empowering patients through education.
- Research Insights: A study titled “Beverage Consumption and Diabetes Risk” examines the relationship between excessive beverage intake and its effects on blood sugar, offering valuable insights into the risks associated with high consumption.
- Guidelines for Consumption: Current recommendations suggest that individuals with diabetes should limit their beverage intake due to its impact on blood sugar and always consult with healthcare providers to tailor guidelines to their specific health needs.
Incorporating these insights into your daily routine, while embracing the outdoor lifestyle and community support available in San Marcos, can help you navigate alcohol consumption more effectively. By focusing on balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management, you can prioritize your health while still enjoying social occasions.
Conclusion
Navigating alcohol consumption while managing diabetes can be challenging, and it’s important to understand how different beverages affect blood sugar levels. Alcohol has the potential to cause significant fluctuations in glucose, leading to risks such as hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Recognizing the carbohydrate content in various drinks is crucial. For example, many find that opting for dry wines or spirits mixed with sugar-free mixers can help mitigate these risks.
Establishing safe drinking guidelines is essential for diabetics. Limiting intake, ensuring food consumption before drinking, and regularly monitoring blood sugar levels can empower individuals to enjoy social occasions without compromising their health. Many patients share their success stories of integrating moderate alcohol consumption into their lives by adhering to these strategies, which often leads to improved diabetes management.
Ultimately, understanding the connection between alcohol and diabetes is vital for making informed choices. With personalized care, education, and community support, individuals can reclaim their health while enjoying a balanced lifestyle. By embracing these practices, managing diabetes effectively becomes a more attainable goal, allowing for enjoyment and well-being in social settings. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and with the right support, you can thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does alcohol consumption affect blood sugar levels, particularly for diabetics?
Alcohol consumption can lead to a temporary drop in glucose levels, especially when consumed on an empty stomach. This occurs because the liver prioritizes metabolizing ethanol over glucose production, which can complicate glucose management for diabetics.
Can moderate alcohol consumption cause diabetes?
While moderate alcohol consumption does not directly cause diabetes, excessive intake can significantly increase the risk of developing the condition and complicate diabetes management.
What benefits can result from reducing or eliminating alcohol intake for diabetics?
Reducing or eliminating alcoholic beverages can lead to better blood sugar control, which is crucial for managing diabetes and minimizing health complications.
What types of alcoholic beverages should diabetics be cautious about?
Diabetics should pay attention to the carbohydrate content in different alcoholic beverages. Regular beers can contain high amounts of carbohydrates, while light beers have fewer. Dry wines are generally lower in carbs compared to sweeter wines and cocktails. Spirits contain no carbohydrates but caution is needed with mixers that may have added sugars.
What are the carbohydrate contents of common alcoholic beverages?
Regular beers can have upwards of 15 grams of carbs per serving. Dry red wine typically contains about 3-4 grams of carbs per glass, while spirits like vodka, gin, and whiskey contain no carbs. For example, a Tequila Sunrise can have about 23.84 grams of carbs.
How can individuals with diabetes manage their alcohol consumption effectively?
Individuals can manage their alcohol consumption by being mindful of the carbohydrate content in beverages, monitoring their blood sugar levels, and choosing options like sugar-free mixers. Engaging in community wellness programs and incorporating a balanced diet can further support diabetes management.
What real-world experiences highlight the impact of alcohol on blood sugar management?
Many individuals with diabetes report improved control over their blood sugar levels when they moderate their alcohol intake. For instance, one patient experienced stable glucose readings with dry red wine, while another saw significant increases with regular beer.
What holistic approaches can support diabetes management alongside alcohol consumption?
Holistic approaches include providing actionable insights and practical tools for patients, engaging in regular exercise, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, and participating in community wellness programs to enhance overall health and diabetes management.