Overview
The article provides an in-depth tutorial on the American Diabetes Association (ADA) prediabetes guidelines, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle modifications, diagnostic criteria, and community support in managing prediabetes. It highlights that effective management through diet, exercise, and regular monitoring can significantly reduce the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes, as evidenced by statistics and success stories illustrating the impact of these guidelines on individual health outcomes.
Introduction
The rising prevalence of prediabetes represents a critical public health challenge, with over 84 million adults in the United States currently affected. This condition, marked by elevated blood glucose levels that fall short of a diabetes diagnosis, serves as a crucial warning sign for individuals at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Alarmingly, awareness of prediabetes varies widely among different racial and ethnic groups, highlighting a pressing need for targeted health education and outreach.
Fortunately, with the right lifestyle modifications, prediabetes can often be reversed, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention.
This article delves into the definition, diagnostic criteria, and management guidelines for prediabetes, providing valuable insights into effective strategies for prevention and lifestyle changes that can significantly improve health outcomes.
Understanding Prediabetes: Definition and Importance
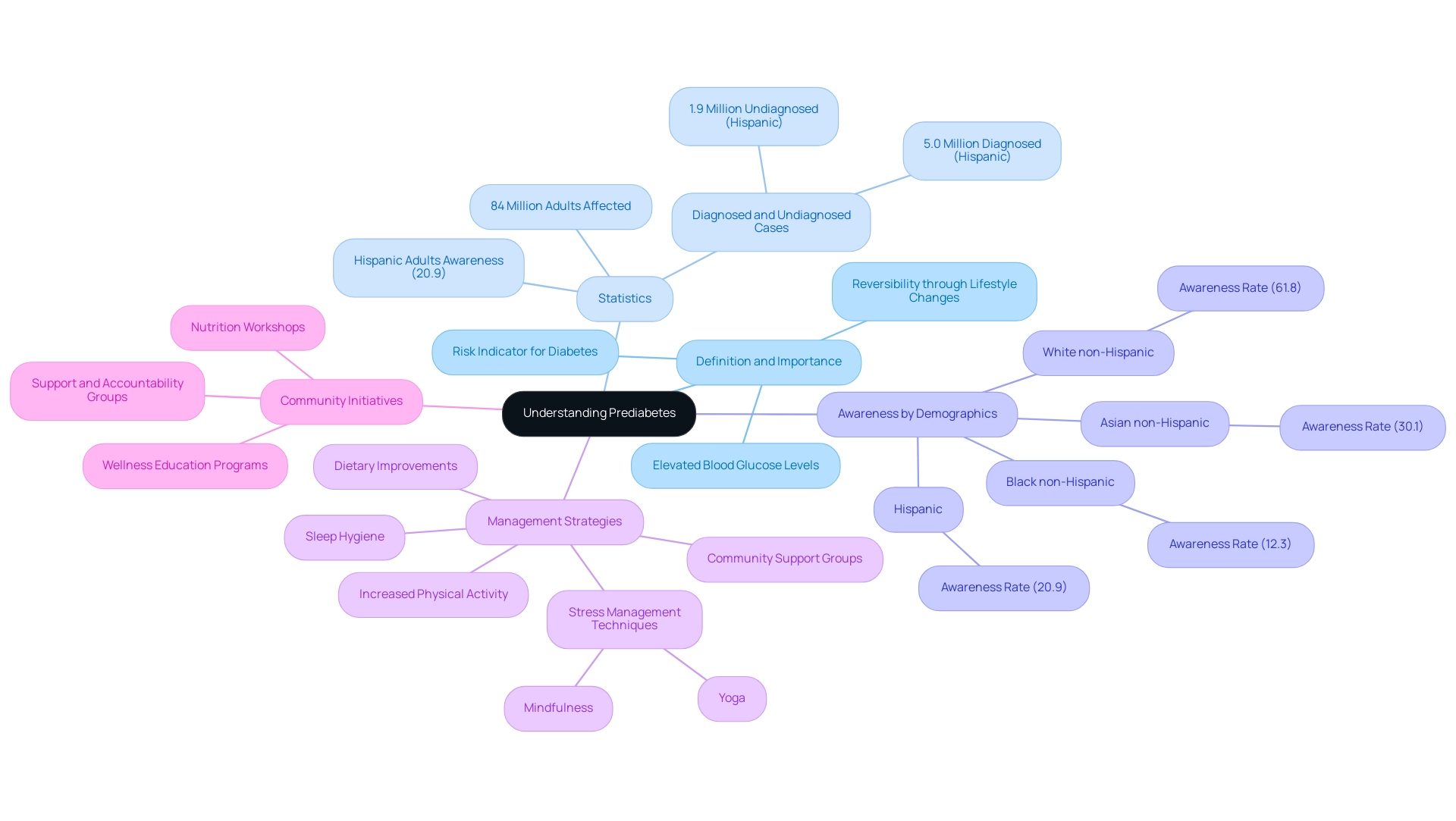
Prediabetes is a significant health condition defined by elevated blood glucose levels that are not high enough for a diagnosis of type 2. This stage serves as a critical indicator of a heightened risk for developing diabetes, as outlined in the ADA prediabetes guidelines, and its associated complications. Current data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicates that more than 84 million adults in the United States are living with elevated blood sugar levels.
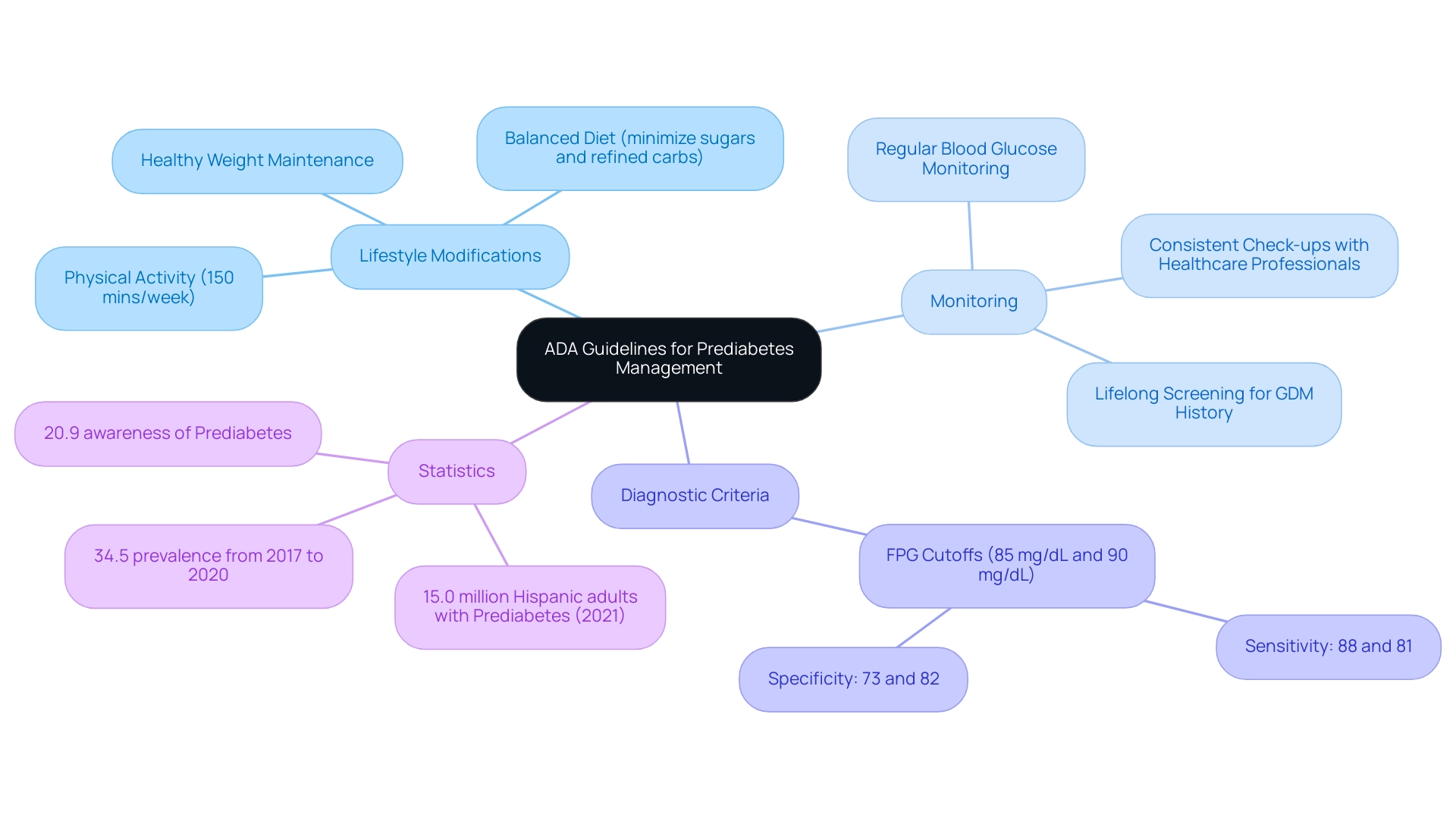
Alarmingly, awareness of glucose intolerance varies significantly among racial and ethnic groups; during the 2017-2020 period, only 20.9% of Hispanic adults were aware of their condition, compared to:
- 61.8% of White non-Hispanics
- 12.3% of Black non-Hispanics
- 30.1% of Asian non-Hispanics
Among Hispanic individuals, there are 5.0 million diagnosed diabetes cases and 1.9 million undiagnosed cases, highlighting the need for enhanced wellness education and outreach efforts. Fortunately, this condition is often reversible through targeted lifestyle changes that align with the ADA prediabetes guidelines, including improved diet and increased physical activity.
Community wellness initiatives concentrating on education, nutrition, and support play a vital role in empowering individuals to manage their wellbeing effectively. Identifying the indicators of insulin resistance is essential, as prompt action can avert advancement to more serious conditions and greatly improve overall health results, as outlined in ADA prediabetes guidelines. To aid in this, consider these four lesser-known power-plays:
- Incorporating stress management techniques such as mindfulness or yoga
- Prioritizing sleep hygiene
- Utilizing whole grains for better blood sugar control
- Engaging in community support groups for motivation and accountability
Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H., states, “The age-adjusted prevalence of total and diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar has risen steadily over the years,” emphasizing the importance of early detection and comprehensive management following ADA prediabetes guidelines for at-risk individuals.
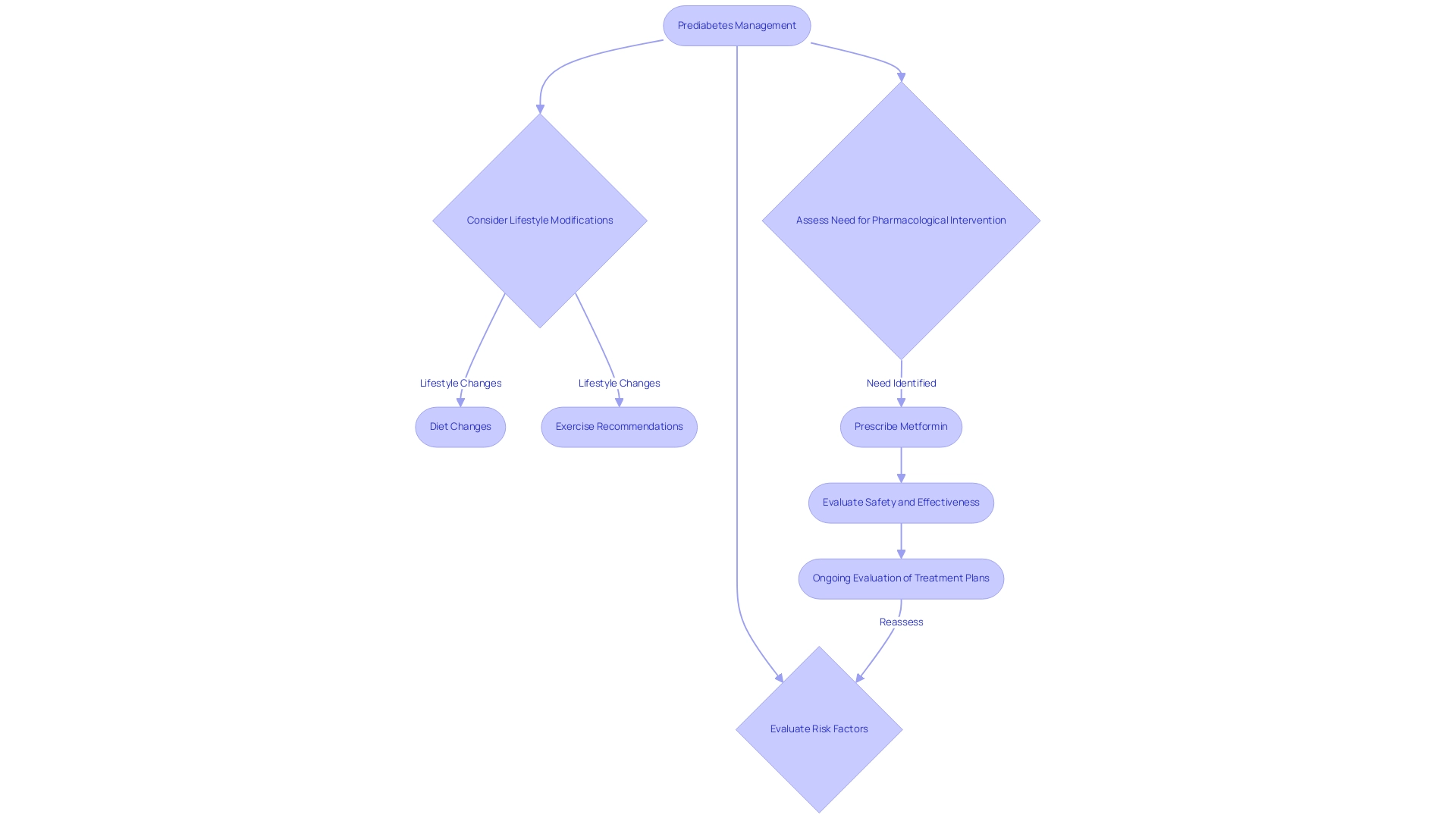
Key ADA Guidelines for Prediabetes Management
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) outlines essential recommendations for individuals diagnosed with prediabetes, particularly emphasizing the critical role of lifestyle modifications as per the ADA prediabetes guidelines. Their guidelines advocate for engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity weekly and adopting a balanced diet that minimizes refined carbohydrates and sugars. These strategies are essential, particularly for regulating blood sugar levels during pregnancy in accordance with ADA prediabetes guidelines to avoid gestational complications.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for effective management. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is advised according to ADA prediabetes guidelines, with the organization stressing the importance of personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs. The ADA further recommends consistent check-ups with healthcare professionals to assess progress and adjust management strategies as necessary.
Significantly, the ADA emphasizes the dangers of conventional treatments, which can present serious risks to individuals, highlighting the necessity for a comprehensive approach to reversing this condition by tackling root causes and empowering patient wellness at the Integrative Wellness Center. This includes re-examining the source of the condition to mitigate the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications. Regular screening is also vital; for instance, individuals with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) should have lifelong screenings every three years to facilitate early detection and management of diabetes, significantly reducing long-term health risks.
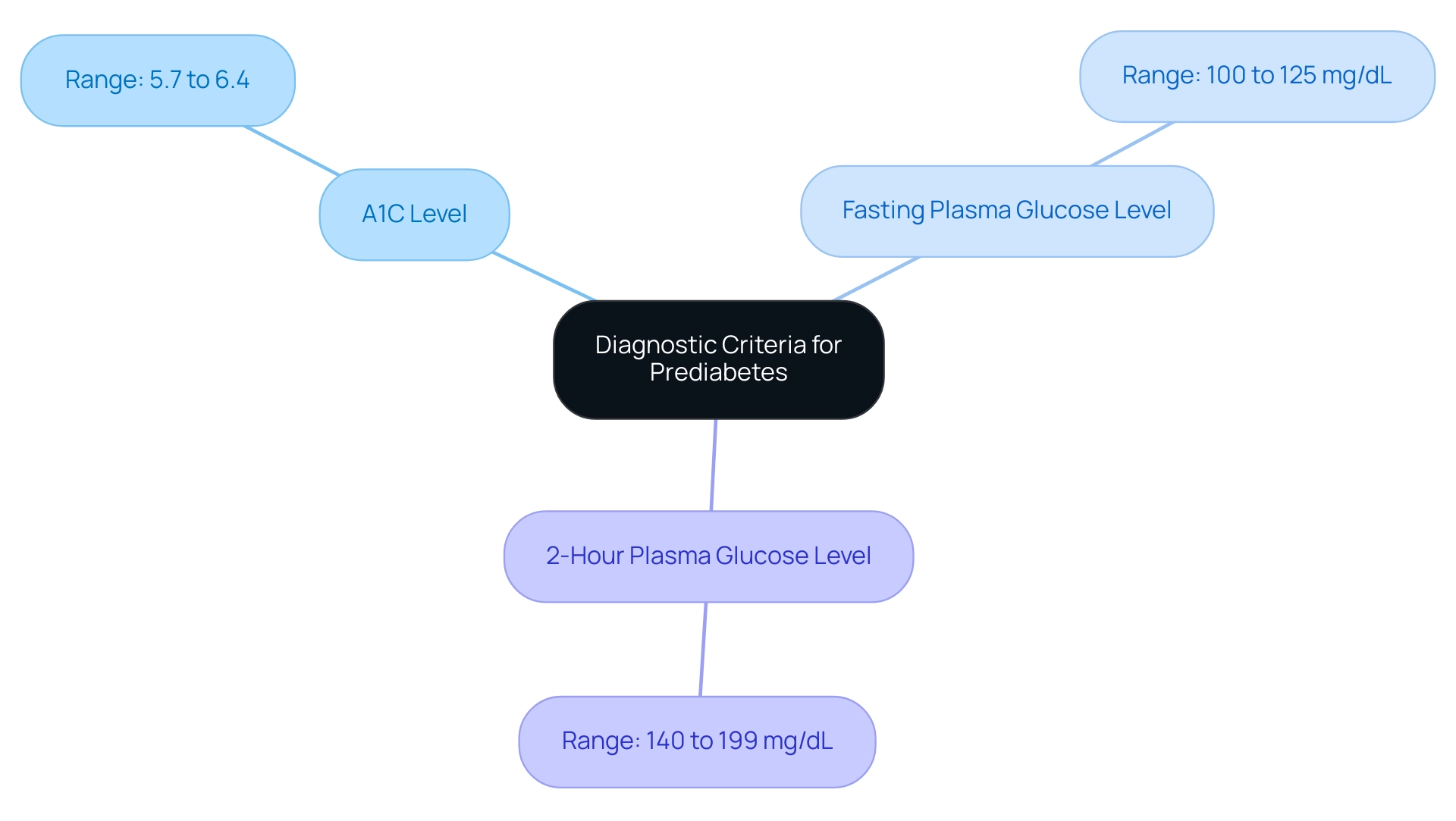
This aligns with the ADA prediabetes guidelines that indicate FPG cutoffs of 85 mg/dL and 90 mg/dL had sensitivities of 88% and 81%, and specificities of 73% and 82%, respectively, enhancing the understanding of diagnostic criteria. Recent statistics revealed that approximately 15.0 million Hispanic adults were diagnosed with a condition preceding diabetes in 2021, showcasing a 34.5% prevalence from 2017 to 2020 with only 20.9% awareness. The ADA Professional Practice Committee states, “There remains strong consensus that establishing a uniform approach to diagnosing GDM will benefit people with GDM, caregivers, and policymakers.”
These figures emphasize the urgent need for effective lifestyle interventions as part of the ADA prediabetes guidelines for managing elevated blood sugar levels.
Diagnostic Criteria for Prediabetes: What You Need to Know
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) outlines clear diagnostic criteria for the condition preceding diabetes according to the ADA prediabetes guidelines, which include:
- An A1C level ranging from 5.7% to 6.4%
- A fasting plasma glucose level between 100 to 125 mg/dL
- A 2-hour plasma glucose level between 140 to 199 mg/dL as measured during an oral glucose tolerance test.
It is imperative for healthcare professionals to familiarize themselves with these criteria to effectively identify individuals at risk. Awareness of these markers is crucial, as it allows for timely interventions that can significantly impact patient outcomes.
According to recent statistics, the occurrence of elevated blood sugar levels continues to increase, with an estimated 29.4 million adults identified with this condition in the U.S. in 2021, emphasizing the need for vigilance in screening and diagnosis. Moreover, while the ADA prediabetes guidelines emphasize lifestyle changes through better nutrition and heightened physical activity as the primary approach for preventing the progression from prediabetes to this condition, it is crucial to comprehend the underlying causes for long-term management.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we begin by re-evaluating the origin of your condition, empowering individuals like M.L., who, after engaging in our program, lost 55 lbs and significantly enhanced their A1C levels from 9.1 to 5.7 within eight months.
M.L.’s journey reflects not only a physical transformation but also a reduction in the anxiety and worry surrounding the potential complications of diabetes. Transformative success stories like this demonstrate the effectiveness of addressing underlying concerns rather than simply treating symptoms.
By recognizing and acting on these diagnostic indicators and integrating personalized care, healthcare providers play a vital role in supporting individuals’ health and facilitating necessary lifestyle changes.
Lifestyle Modifications: The ADA’s Recommendations for Prevention
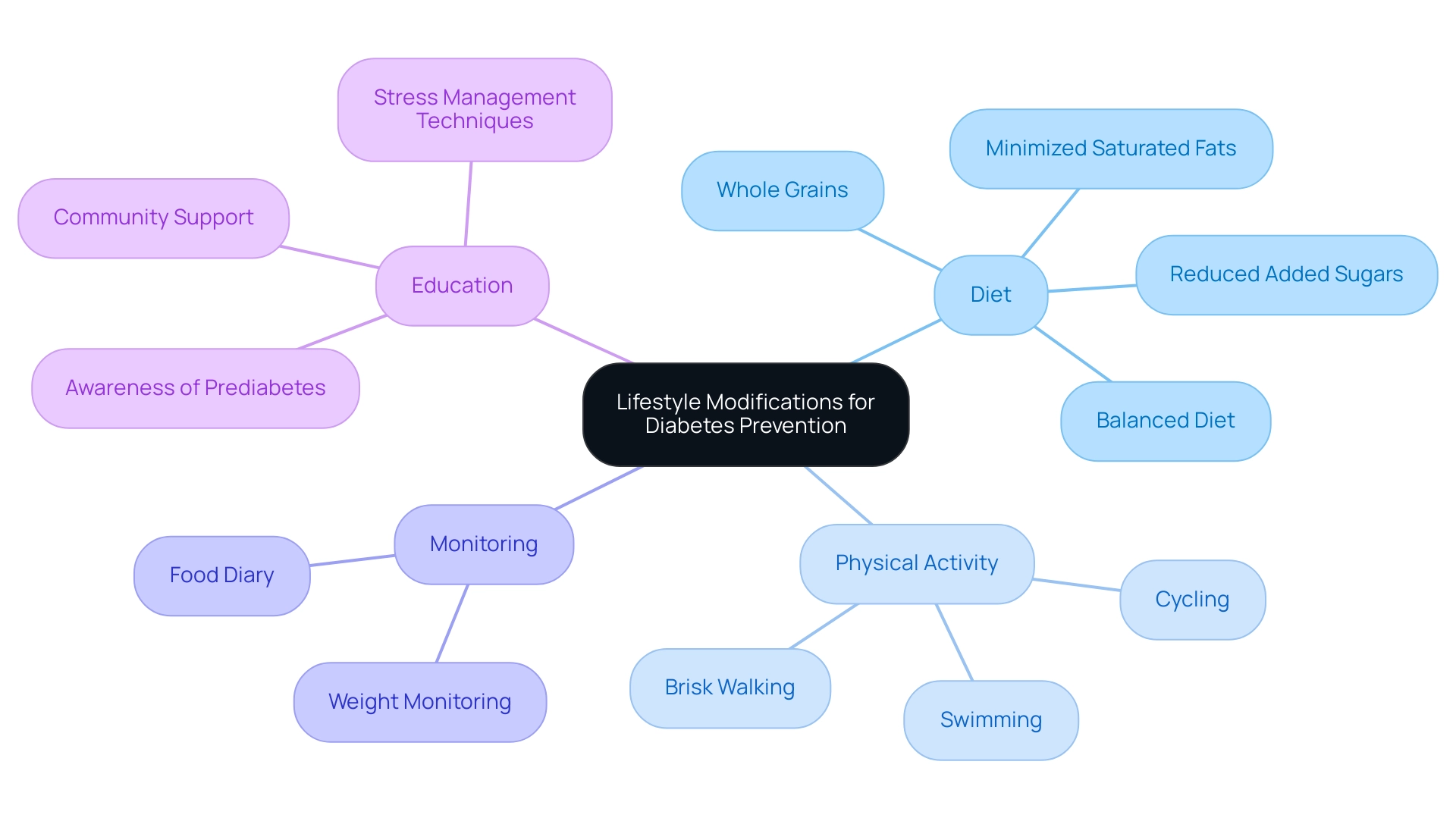
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) emphasizes the critical role of lifestyle modifications in preventing type 2 diabetes, particularly in accordance with the ADA prediabetes guidelines for individuals diagnosed with prediabetes. Individuals at the Integrative Wellness Center have shared transformative experiences, such as one individual who reported significant improvements in their blood sugar levels after adopting a functional medicine approach that emphasized comprehensive lifestyle changes. Key recommendations include:
- Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet
- Focusing on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins
- Minimizing saturated fats and added sugars
For example, another patient noted that integrating more whole grains into their meals helped them feel fuller and more energized. Research, including the PREDIMED study, indicates that type 2 conditions can be prevented even without significant weight loss through the Mediterranean diet, which has demonstrated risk reductions of 30% to 50% in high-risk populations. Moreover, the alarming statistic of approximately 16.8 million emergency department visits related to this condition in 2020 underscores the urgency of these lifestyle changes.
Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, is equally vital in maintaining a healthy weight and managing diabetes effectively. One patient shared their success in incorporating daily walks into their routine, which not only helped manage their weight but also improved their overall mood. Monitoring weight and keeping a food diary are practical strategies that enhance accountability and facilitate informed dietary choices.
Recent statistics show that awareness of elevated blood sugar levels among Hispanic adults was only 20.9% from 2017 to 2020, highlighting the need for increased education and lifestyle changes to combat the rising prevalence of diabetes-related complications. Nutrition specialists emphasize that ‘incorporating these lifestyle changes is essential for effective management of prediabetic conditions as outlined in the ADA prediabetes guidelines and can significantly reduce the risk of advancement to type 2 diabetes.’ The Integrative Wellness Center encourages patients to explore lesser-known strategies, such as stress management techniques and community support, to further enhance their wellness journey.
Pharmacological Approaches in Prediabetes Management
According to the ADA prediabetes guidelines, pharmacological interventions should be considered for individuals with prediabetes who are at an elevated risk of progressing to type 2, especially when lifestyle modifications alone do not yield sufficient results. However, at the Integrative Wellness Center, we promote a comprehensive approach that re-evaluates the origin of your condition and tackles wellness at the fundamental level. This approach not only aims to enhance physical well-being but also helps alleviate the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of your disease.
Metformin, a widely recognized oral medication used primarily for managing type 2 diabetes, may be prescribed to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels. Yet, it is crucial to consider the dangers of solely relying on traditional treatments. Healthcare providers must carefully assess each individual’s unique circumstances, integrating insights on insulin resistance and personal health goals to determine the most suitable treatment options.
This customized method is crucial for enhancing health outcomes and effectively managing prediabetes according to ADA prediabetes guidelines. Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of Metformin in postponing the onset of type 2 conditions in high-risk groups, but it is also crucial to equip individuals with knowledge and resources for lifestyle changes. Additionally, endocrinologists emphasize the need for ongoing evaluation of treatment plans to adapt to changes in patient circumstances, including potential cost-related barriers to medication adherence.
As highlighted, the total direct and indirect estimated costs of diagnosed diabetes in the United States reached $413 billion in 2022, reflecting the growing economic burden of diabetes on the healthcare system and society. Furthermore, awareness gaps exist, particularly among Hispanic adults—20.9% of whom were aware of their prediabetes. Lastly, as noted by the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, individuals who have experienced DKA should not be treated with SGLT inhibition, emphasizing the importance of safety considerations in pharmacological management.
Maintaining a patient-centered focus in pharmacological management is crucial, ensuring that interventions align with the patient’s health goals and lifestyle, as well as integrating a holistic regimen that supports overall well-being.
Conclusion
The rising prevalence of prediabetes is a significant public health concern, affecting millions of adults across the United States. Understanding the condition, its diagnostic criteria, and the vital lifestyle modifications recommended by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) is crucial for effective management and prevention of type 2 diabetes. Awareness of prediabetes varies among different demographic groups, emphasizing the urgent need for targeted health education and outreach to empower individuals to recognize and address this critical health issue.
Lifestyle changes play a pivotal role in reversing prediabetes. Emphasizing a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and monitoring health markers are essential strategies that can lead to improved outcomes. The ADA’s guidelines advocate for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly and highlight the importance of maintaining a healthy weight. Furthermore, addressing the root causes of prediabetes through a holistic approach can significantly enhance patient outcomes and reduce associated health risks.
While pharmacological interventions such as Metformin are available for those at high risk, they should complement, not replace, lifestyle modifications. The focus must remain on empowering patients with knowledge and resources to take proactive steps in managing their health. As awareness increases and education spreads, individuals can better navigate their health journeys, ultimately lowering the risk of progression to type 2 diabetes and improving overall well-being. The time for action is now; early detection and intervention can make a profound difference in the fight against prediabetes and its complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is prediabetes?
Prediabetes is a health condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels that are not high enough for a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. It indicates a heightened risk for developing diabetes and its associated complications.
How many adults in the United States are affected by elevated blood sugar levels?
Current data from the CDC indicates that more than 84 million adults in the United States are living with elevated blood sugar levels.
What are the awareness levels of glucose intolerance among different racial and ethnic groups?
Awareness of glucose intolerance varies significantly, with only 20.9% of Hispanic adults aware of their condition, compared to 61.8% of White non-Hispanics, 12.3% of Black non-Hispanics, and 30.1% of Asian non-Hispanics.
What is the estimated number of diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes cases among Hispanic individuals?
Among Hispanic individuals, there are approximately 5.0 million diagnosed diabetes cases and 1.9 million undiagnosed cases.
Can prediabetes be reversed, and if so, how?
Yes, prediabetes is often reversible through targeted lifestyle changes that include improved diet and increased physical activity, as recommended by the ADA prediabetes guidelines.
What role do community wellness initiatives play in managing prediabetes?
Community wellness initiatives focusing on education, nutrition, and support are vital in empowering individuals to manage their wellbeing effectively.
What are some strategies for managing prediabetes?
Strategies include incorporating stress management techniques, prioritizing sleep hygiene, utilizing whole grains for better blood sugar control, and engaging in community support groups for motivation and accountability.
What recommendations does the ADA provide for individuals diagnosed with prediabetes?
The ADA recommends engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity weekly, adopting a balanced diet low in refined carbohydrates and sugars, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels.
Why is regular screening important for those with a history of gestational diabetes?
Regular screening is crucial for individuals with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) to facilitate early detection and management of diabetes, which can significantly reduce long-term health risks.
What are the diagnostic criteria for prediabetes according to the ADA?
The ADA prediabetes guidelines indicate fasting plasma glucose (FPG) cutoffs of 85 mg/dL and 90 mg/dL, with sensitivities of 88% and 81%, and specificities of 73% and 82%, respectively.