Overview
This article addresses the rising trends and implications of type 2 diabetes, a condition that increasingly affects individuals around the world. It’s important to recognize that the prevalence of this disease is growing, highlighting an urgent need for effective public health strategies. Many patients find themselves grappling with significant challenges, such as obesity and sedentary lifestyles, which are key risk factors in this epidemic.
Statistics reveal a troubling rise in diabetes cases, along with the economic burden it places on communities. These figures underscore the necessity for targeted interventions and community-based programs. By fostering a supportive environment, we can improve management and prevention efforts, ultimately guiding individuals toward healthier lifestyles.
As we explore these issues, let’s reflect on the importance of taking action. Together, we can create a nurturing space that promotes understanding and encourages proactive measures. The 30-Day Diabetes Reset program offers a compassionate approach to managing this condition, providing the tools and support needed to make meaningful changes. Remember, you are not alone on this journey; there is a community ready to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
The global landscape of health is facing a formidable challenge as type 2 diabetes continues to rise at an alarming rate, affecting millions and reshaping public health priorities. It’s important to recognize that approximately 462 million individuals are currently living with this condition—and projections estimate that number could soar to 853 million by 2050. Understanding the epidemiology of type 2 diabetes is more critical than ever. This article delves into the trends and implications of this chronic illness, exploring the risk factors, historical context, and the urgent need for effective public health strategies. Many patients find that as the prevalence of type 2 diabetes escalates, they grapple with feelings of uncertainty and concern.
How can societies adapt to mitigate its impact and foster healthier communities? Together, we can explore these challenges and seek solutions that empower individuals to lead healthier lives.
Defining Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes
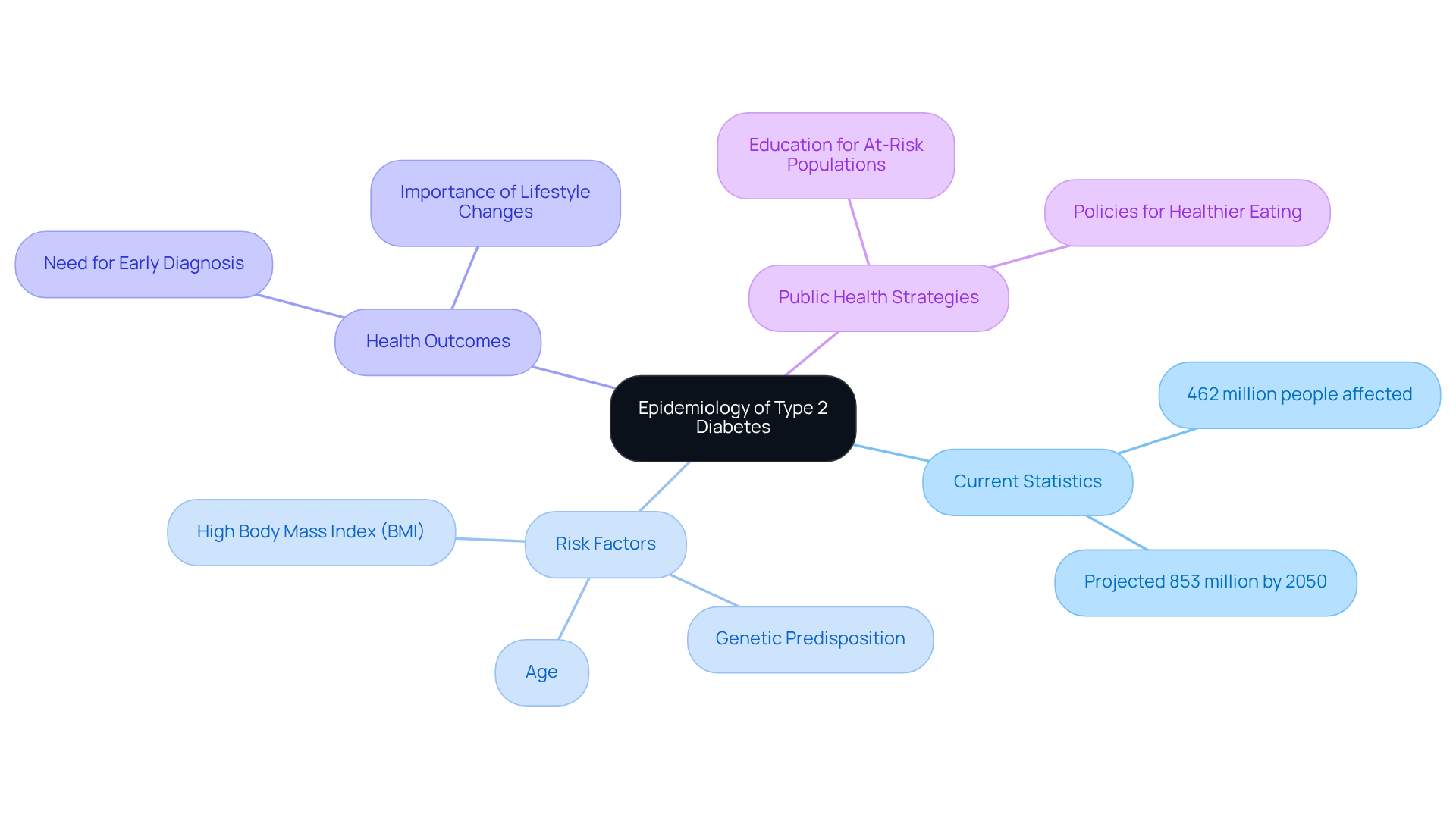
The epidemiology type 2 diabetes involves understanding how the second form of the disease affects people, where it spreads, and what we can do to help control it. This analysis includes important data on how often it occurs, the risk factors involved, and the health outcomes related to this condition. Right now, about 462 million people around the globe are living with type 2 diabetes, which represents roughly 6.28% of the world’s population. Unfortunately, this number is expected to grow to 853 million by 2050, influenced by urbanization, poor diets, and a lack of physical activity.
Key risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes include:
- A high body mass index (BMI)
- Age
- Genetic predisposition
Many find that the incidence peaks around the age of 55, with notable differences seen across various regions and ethnic groups. For example, Oceania has the highest prevalence rate at 12.3%, with countries like Fiji and Kiribati reporting alarming rates of 20,277 and 17,432 cases per 100,000, respectively.
It’s important to recognize that recent research underscores the urgent need for effective public health strategies to manage and prevent blood sugar issues. The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the significance of early diagnosis and lifestyle changes, like maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity. Public health initiatives should focus on educating at-risk populations and implementing policies that encourage healthier eating habits.
Understanding the epidemiology type 2 diabetes is crucial for developing targeted strategies and healthcare policies aimed at reducing its impact. By identifying vulnerable groups and addressing the root causes of this condition, healthcare providers can improve management and prevention efforts globally.
Historical Context and Evolution of Type 2 Diabetes Trends
The identification of this condition can be traced back to ancient civilizations, but it’s important to recognize that the second form of this illness began to gain attention in the early 20th century as obesity rates escalated. Many individuals have struggled with these changes, especially during the post-World War II era, which marked a pivotal shift in lifestyle. This period saw a surge in processed food consumption and a decline in physical activity, leading to a significant rise in category 2 blood sugar condition cases. In fact, the occurrence more than tripled from 1990 to 2010. By the 1980s, the epidemiology type 2 diabetes was recognized as a major public welfare crisis, prompting extensive research into its causes and management strategies.
Recent studies in epidemiology type 2 diabetes indicate concerning trends, especially among younger demographics and in low- and middle-income nations. The impact of unmanaged blood sugar levels is becoming more significant, with alarming statistics. For example, in India, the occurrence of the condition rose from 7.1% in 2009 to 8.9% in 2019. This emphasizes the urgent need for effective public wellbeing interventions. It’s vital to understand that lifestyle changes, including adhering to a nutritious diet and consistent physical exercise, play a crucial role in preventing or postponing the development of the second form of the condition. Numerous case studies illustrate the beneficial effects of these adjustments on well-being outcomes.
Transformative patient experiences, like those shared by individuals who have participated in Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, demonstrate the potential for reversing the condition through holistic methods. These inspiring cases highlight significant improvements in health outcomes, including weight loss, increased energy, and reduced reliance on medications. This underscores the importance of functional medicine in addressing insulin resistance and the risks associated with conventional treatments.
Today, comprehending the historical background of the condition related to epidemiology type 2 diabetes is crucial for tackling its increasing occurrence. By understanding these challenges, we can create effective prevention plans and support one another on this journey toward healthier living. Remember, you are not alone in this; there are paths to better health and wellbeing.
Current Trends in Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence
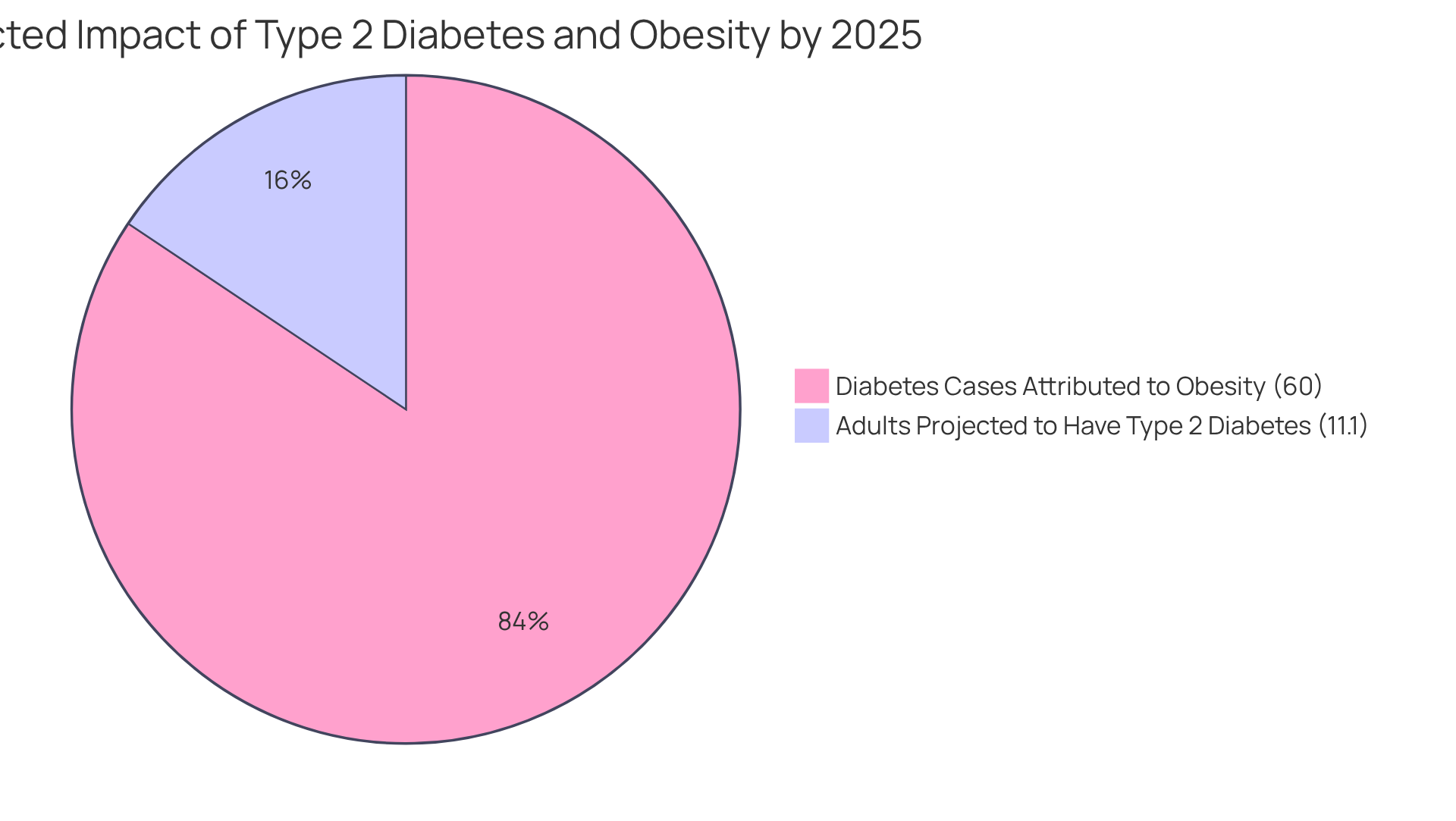
The worldwide occurrence of epidemiology type 2 diabetes is on the rise, and it’s important to recognize that this trend is affecting many lives. Forecasts suggest that by 2025, approximately 11.1% of the adult population will be impacted. This alarming situation is driven by several factors, including:
- Rising obesity rates
- Sedentary lifestyles
- Significant dietary shifts
Many patients find that obesity is a primary factor in the epidemiology of type 2 diabetes, representing almost 60% of instances, as elevated body mass index (BMI) continues to be a crucial risk factor.
As we look ahead, the International Diabetes Federation predicts that by 2030, the number of individuals living with diabetes could rise to 643 million. This increase is particularly concerning in developing economies and low- to middle-income nations, where healthcare resources are frequently limited. The urgency of this situation calls for prompt public wellness measures. We must focus on improving prevention and management strategies to address the rising crisis of diabetes. Together, we can work towards healthier living and a supportive community for those affected.
Implications of Type 2 Diabetes Epidemiology for Public Health
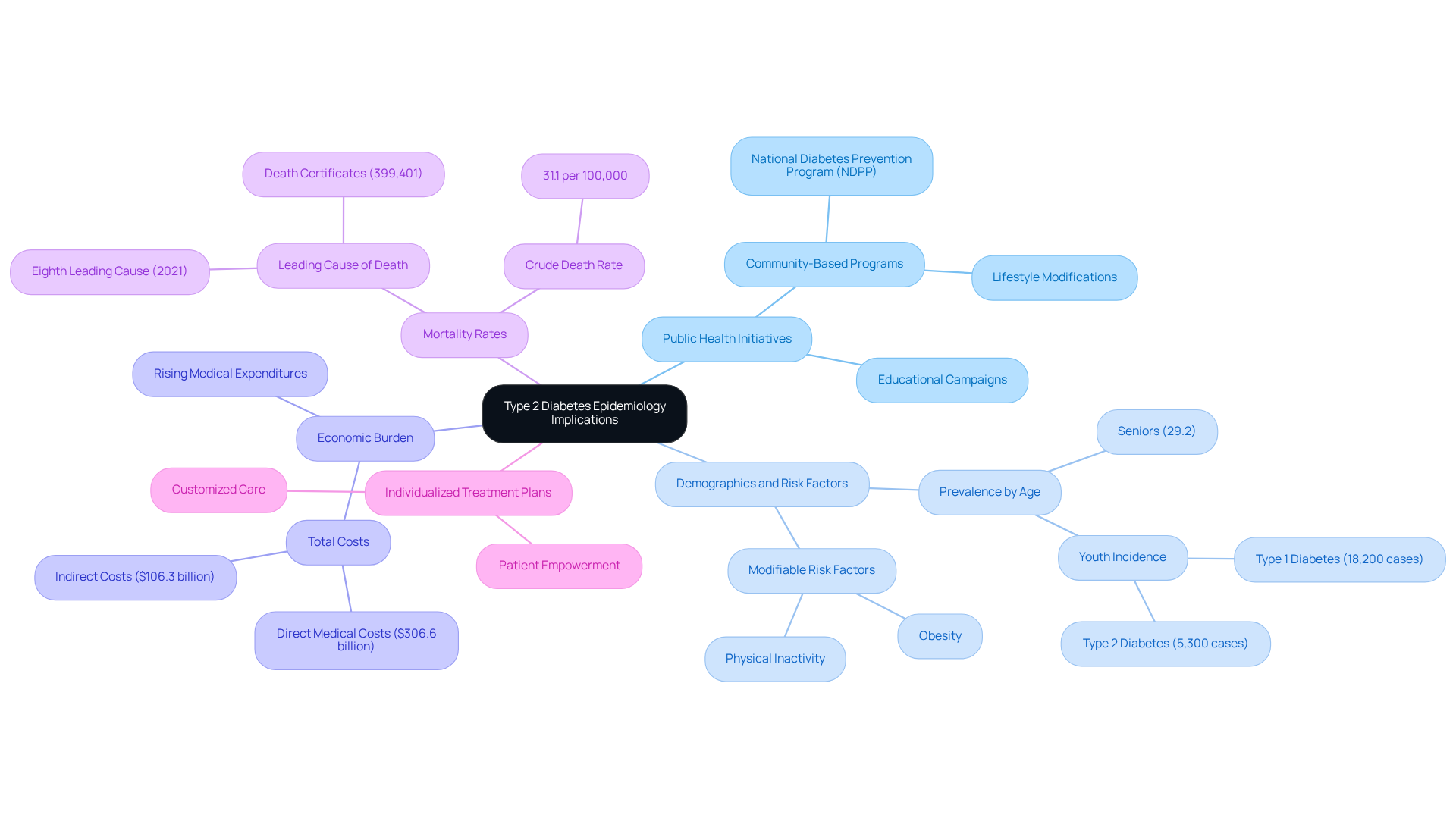
The epidemiology type 2 diabetes mellitus has significant consequences for public wellness initiatives. It’s important to recognize the impact this condition has on individuals and communities alike. By analyzing the demographics and risk factors associated with epidemiology type 2 diabetes, health authorities can implement targeted interventions, such as community-based lifestyle modification programs and educational campaigns. With around 38.4 million Americans impacted by the condition in 2021, the need for effective prevention strategies is evident. These strategies must address modifiable risk factors, including obesity and physical inactivity, which are critical in curbing the rising prevalence of the disease.
Moreover, the economic burden of type 2 diabetes, which reached an estimated $413 billion in 2022, highlights the necessity for improved access to healthcare services, early diagnosis, and effective management strategies in the field of epidemiology type 2 diabetes. Many patients find that joint actions among healthcare professionals, policymakers, and communities are vital to addressing this health crisis effectively. Programs such as the National Diabetes Prevention Program (NDPP) have shown that organized lifestyle modifications can lower the likelihood of developing the second form of sugar illness, which is a key aspect of epidemiology type 2 diabetes, by 58%. This emphasizes the success of community-based initiatives, which can be a source of hope and encouragement.
In San Marcos, CA, adopting a comprehensive strategy for managing blood sugar levels through customized treatment plans, nutrition, and exercise can empower patients to take control of their health. Participating in local wellness initiatives and making use of community resources can offer invaluable assistance for individuals handling type 2 diabetes. The breakthrough method for type 2 sufferers, which highlights the individuality of each person’s treatment, is vital for effective management.
Furthermore, the condition, particularly in the context of epidemiology type 2 diabetes, was the eighth primary cause of mortality in the United States in 2021, highlighting the seriousness of the problem and the necessity for urgent public wellness initiatives. As public health authorities continue to prioritize diabetes prevention, integrating these insights into healthcare policy will be crucial for enhancing the quality of life for individuals affected by this chronic condition. Together, we can foster a supportive environment that encourages healthier choices and empowers individuals on their journey to wellness.
Conclusion
Understanding the epidemiology of type 2 diabetes is essential for addressing the growing prevalence and its far-reaching implications on public health. Millions are affected by this condition worldwide, and it is expected to escalate further. This reality necessitates a comprehensive approach to management and prevention. It’s important to recognize the intricate web of risk factors, including obesity and lifestyle choices, as healthcare systems strive to strategize their responses to this chronic illness.
The article highlights significant trends in the epidemiology of type 2 diabetes, including rising incidence rates, particularly among younger populations and in developing nations. Many patients find that early diagnosis and lifestyle modifications are pivotal strategies in curbing this epidemic. Moreover, the historical context reveals how societal changes have contributed to the surge in cases, emphasizing the need for targeted public health interventions.
In light of these findings, fostering a collaborative environment among healthcare professionals, policymakers, and communities is crucial in combating the diabetes crisis. By implementing effective prevention strategies and promoting healthier lifestyle choices, we can significantly reduce the burden of type 2 diabetes. The call to action is clear: collective efforts and informed policies can pave the way for a healthier future. Together, we can enable individuals to reclaim their well-being and mitigate the impact of this pervasive condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the epidemiology of type 2 diabetes?
The epidemiology of type 2 diabetes involves understanding how the disease affects people, its prevalence, risk factors, and health outcomes associated with it.
How many people are currently living with type 2 diabetes worldwide?
Approximately 462 million people around the globe are living with type 2 diabetes, which is about 6.28% of the world’s population.
What is the projected number of people with type 2 diabetes by 2050?
The number of people living with type 2 diabetes is expected to grow to 853 million by 2050.
What factors are contributing to the increase in type 2 diabetes cases?
Key factors contributing to the increase include urbanization, poor diets, and a lack of physical activity.
What are the key risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes?
Key risk factors include a high body mass index (BMI), age, and genetic predisposition.
At what age does the incidence of type 2 diabetes typically peak?
The incidence of type 2 diabetes typically peaks around the age of 55.
Which region has the highest prevalence rate of type 2 diabetes?
Oceania has the highest prevalence rate of type 2 diabetes at 12.3%.
What are some of the alarming case rates reported in Oceania?
Countries like Fiji and Kiribati report alarming rates of 20,277 and 17,432 cases per 100,000, respectively.
What does the World Health Organization (WHO) emphasize regarding type 2 diabetes?
The WHO emphasizes the significance of early diagnosis and lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity.
What should public health initiatives focus on to combat type 2 diabetes?
Public health initiatives should focus on educating at-risk populations and implementing policies that encourage healthier eating habits.
Why is understanding the epidemiology of type 2 diabetes important?
Understanding the epidemiology of type 2 diabetes is crucial for developing targeted strategies and healthcare policies aimed at reducing its impact and improving management and prevention efforts globally.