Overview
Managing diabetes can be challenging, and blood sugar conversion tables serve as essential tools for individuals on this journey. These tables help translate glucose readings between different units, specifically mg/dL and mmol/L. This understanding is crucial for effective health management.
It’s important to recognize that when patients grasp these conversions, they empower themselves to make informed decisions about their diet and treatment. This knowledge can lead to better health outcomes and greater control over their condition.
Many patients find that having easy access to these conversion tables alleviates some of the stress associated with monitoring their blood sugar levels. By familiarizing themselves with these tools, they can navigate their health journey with more confidence. Encouragingly, this can foster a sense of community and support, reminding individuals that they are not alone in their struggles.
Ultimately, taking charge of one’s health is a powerful step. Understanding blood sugar conversions is just one way to enhance your journey toward a healthier lifestyle. Remember, every small step you take contributes to your overall well-being. Embrace the process and consider exploring programs like the 30-Day Diabetes Reset to further support your health goals.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding blood sugar levels is more than just a matter of numbers; it’s a vital aspect that can profoundly affect your overall health and well-being. As diabetes becomes increasingly common, especially among younger individuals, it’s essential to accurately interpret and convert blood glucose readings between different measurement units. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by these numbers? Blood sugar conversion tables can be your invaluable allies, helping you navigate the complexities of your condition and empowering you to make informed health decisions.
As you learn to convert readings from milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) to millimoles per liter (mmol/L) and vice versa, you’ll find that you gain a clearer understanding of your glucose levels. This newfound clarity can lead to more effective management strategies and, ultimately, improved health outcomes. It’s important to recognize that stable blood sugar levels are crucial for your well-being. In this article, we will explore:
- The significance of these conversion tables
- The benefits of maintaining stable blood sugar
- The resources available to enhance your diabetes care
Together, we’ll highlight the importance of education and personalized approaches in managing this chronic condition, ensuring you feel supported every step of the way.
What Are Blood Sugar Conversion Tables?
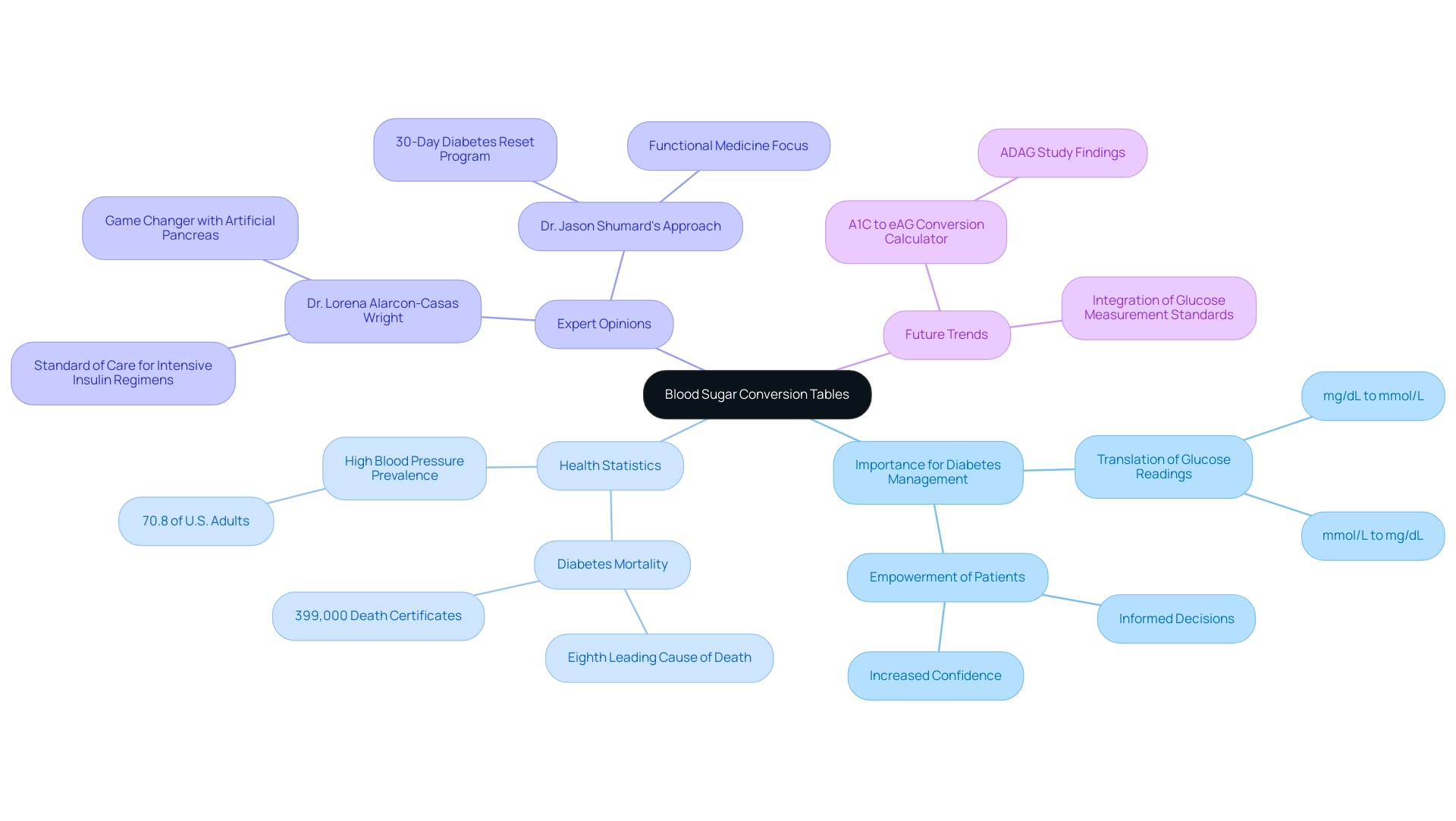
Blood sugar conversion tables are vital resources for individuals managing their condition. They allow for the translation of glucose readings between different units, specifically from milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) to millimoles per liter (mmol/L) and vice versa. This is especially important for those who encounter varying measurement standards across healthcare settings or when using different monitoring devices. In the United States, glucose levels are predominantly reported in mg/dL, while many other nations utilize mmol/L. Understanding the blood sugar conversion table is crucial for effective management of diabetes.
Recognizing the significance of these tables goes beyond mere conversions; they empower individuals to take control of their health. By accurately interpreting their glucose levels, patients can make informed decisions about their diet, medication, and overall management strategies. This empowerment is especially crucial, considering that diabetes was the eighth leading cause of death in the United States in 2021, with over 399,000 death certificates citing it as a contributing factor.
Moreover, did you know that 70.8% of U.S. adults aged 18 years or older with diagnosed conditions had high blood pressure? This statistic highlights the interconnected health risks associated with diabetes. Jason Shumard, a leader in functional medicine at Integrative Wellness Center, emphasizes the importance of personalized care in managing blood sugar conditions. His approach not only focuses on reversing type 2 diabetes but also addresses related issues like hypothyroidism, offering comprehensive health solutions tailored to individual needs.
Specialist viewpoints further underscore the importance of blood sugar conversion tables in health management. For instance, Dr. Lorena Alarcon-Casas Wright from the University of Washington Diabetes Institute has noted that these tools are likely to become standard care for individuals on intensive insulin regimens. They hold the potential to transform diabetes management, especially alongside innovations like the artificial pancreas.
Current statistics indicate that a significant percentage of individuals with diabetes are familiar with blood sugar conversion tables, enhancing their ability to manage their condition effectively. Many individuals who have utilized these tables report increased confidence in monitoring their glucose levels, leading to better health outcomes and a greater sense of control over their diabetes.
As we look toward 2025, glucose measurement standards continue to evolve. Ongoing discussions about integrating A1C to estimated Average Glucose (eAG) conversion calculators, based on findings from the A1c-Derived Average Glucose (ADAG) Study, aim to enhance patient-provider conversations about glucose regulation. This highlights the significance of blood sugar conversion tables in modern diabetes management. By prioritizing education and personalized care, Dr. Jason Shumard’s approach aligns with the growing recognition of these tools in empowering patients to reclaim their health.
If you’re looking for support on your journey, call 858-564-7081 to discover how Dr. Shumard can help you restore your health and get your life back!
The Importance of Blood Sugar Levels in Diabetes Management
Keeping stable glucose levels is crucial for individuals living with diabetes, as it significantly impacts their overall health and wellness. Elevated glucose levels, known as hyperglycemia, can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney dysfunction. It’s concerning that a significant percentage of adults with diabetes have A1C levels of 7.0% or higher, indicating poor glycemic control. This underscores the urgent need for improved management strategies, especially in light of alarming statistics like:
- 7,000 incorrect medications given to patients in hospitals
- 80,000 infections acquired in these settings
On the flip side, low glucose levels, or hypoglycemia, can provoke troubling symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Many patients find that typical risk factors for developing hypoglycemia include:
- Previous instances of low glucose levels
- Advanced age
- Chronic kidney disease
- Irregular eating habits
Understanding these risks is vital for effective management of the condition, highlighting the importance of consistent monitoring and utilizing a blood sugar conversion table for accurate interpretation of glucose readings.
By consistently monitoring their blood sugar levels and referring to a blood sugar conversion table for accurate readings, individuals can make informed adjustments to their diet, exercise routines, and medication regimens. This proactive approach not only enhances diabetes management but also significantly improves quality of life. Numerous individuals have shared transformative experiences after adopting structured monitoring practices, leading to improved glycemic control and fewer complications.
Testimonials from clients at Dr. Jason Shumard’s Functional Medicine Center showcase the positive impact of personalized guidance and holistic health solutions on their health journeys. Statistics reveal that maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential; individuals who use a blood sugar conversion table for consistent control are less likely to experience long-term complications. Additionally, the high cost of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) sensors and machines, approximately $5000 per year, highlights the financial implications of diabetes management. Dr. Shumard’s innovative methodologies provide actionable insights and practical tools that empower individuals to take charge of their health.
As Dr. Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” By nurturing an environment of education and support, the Integrative Wellness Center enables individuals to reclaim their well-being, leading to a healthier lifestyle and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions, which often come with risks such as increased insulin levels.
In conclusion, the importance of maintaining consistent glucose levels in managing health conditions related to insulin cannot be overstated. As we move through 2025, ongoing research continues to illuminate the effects of glucose variations on diabetes complications, reinforcing the necessity for effective monitoring and management strategies that prioritize holistic care.
Understanding Measurement Units: mg/dL vs. mmol/L
Managing blood sugar levels can feel overwhelming, especially when it comes to understanding the different units of measurement: milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) and millimoles per liter (mmol/L). It’s important to recognize that mg/dL reflects the weight of glucose in a specific volume of fluid, while mmol/L quantifies the number of glucose molecules in that same volume. This distinction is crucial for effective diabetes management, as you may encounter readings in either unit.
To help you monitor your blood sugar accurately, here are some simple conversion formulas:
- To convert mg/dL to mmol/L, divide the mg/dL value by 18.
- To convert mmol/L to mg/dL, multiply the mmol/L value by 18.
Understanding these conversions is vital, especially with the rising prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Did you know that there were 5,293 new diagnoses among children and adolescents aged 10 to 19? This statistic underscores the importance of education in glucose management—a principle that Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes in his practice.
Many patients find that grasping the differences between mg/dL and mmol/L helps them interpret their readings more effectively. For example, if you receive a reading of 180 mg/dL, using a blood sugar conversion table to convert it to mmol/L can align your understanding with your healthcare provider’s recommendations. This knowledge not only aids in managing your health but also fosters better communication with your healthcare team.
In real-life situations, individuals often share their experiences of converting glucose measurements. For instance, after a meal, a patient might see their glucose level at 200 mg/dL, which converts to approximately 11.1 mmol/L. Such conversions are essential for maintaining optimal glycemic control, especially in non-critical care settings where the blood sugar conversion table is recommended for capillary glucose testing.
Instruction on nutrition, physical activity, and medication supervision is essential for clients with diabetes, as emphasized by recent news.
To effectively monitor and improve your progress in managing glucose levels, consider utilizing various tracking methods. Fitness apps, journals, and pedometers can be great tools. Setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can significantly enhance your focus and motivation. For example, you might aim to walk 10,000 steps daily or reduce your carbohydrate intake by 10% over the next month.
Recent studies, including a multicenter trial involving 9,230 individuals, have shown that understanding and managing blood sugar levels effectively can lead to improved health outcomes. The trial compared liberal glucose control with tight glucose control, revealing trends that suggest better management can reduce the risk of complications such as liver and kidney injury. This aligns with Dr. Shumard’s comprehensive approach, which emphasizes empowering individuals with actionable insights and practical tools for their health journey.
In summary, the distinction between mg/dL and mmol/L is not merely academic; it has real implications for managing blood sugar. By mastering these conversions and understanding their significance, you can take proactive steps in your health journey, ultimately leading to a better quality of life. Embracing local lifestyle changes, like utilizing parks for exercise and shopping at farmers’ markets for fresh produce, can further enhance your diabetes management efforts. Remember, you are not alone on this journey, and there are many resources and communities available to support you.
Converting Blood Sugar Levels to A1C: A Step-by-Step Guide
Converting blood sugar levels to A1C values is an important step in understanding diabetes management. The commonly utilized formula is:
A1C (%) = (Average Blood Glucose (mg/dL) + 46.7) / 28.7.
This formula empowers individuals to estimate their A1C percentage based on their average glucose readings. For instance, if a patient has an average blood glucose level of 150 mg/dL, the calculation would be:
A1C = (150 + 46.7) / 28.7 = 6.8%.
It’s important to recognize that understanding the blood sugar conversion table is essential. It helps interpret A1C values, which indicate a patient’s sugar control over the preceding two to three months. This metric is vital for healthcare providers to tailor effective treatment plans that meet individual needs.
Current statistics reveal a concerning reality: approximately 70.8% of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes also have elevated blood pressure. This highlights the interconnectedness of managing this illness and overall health. Furthermore, the average medical expenses linked to diabetes have surged from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022, underscoring the financial burden of this chronic condition.
Many patients find that maintaining optimal A1C levels can be a struggle, often leading to severe complications if not managed properly. Experts emphasize the importance of regular monitoring and understanding A1C as a key component of diabetes management. Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.”
Transformative experiences from Dr. Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program highlight the effectiveness of personalized functional medicine strategies. For example, one patient shared, “I lost 55 lbs. My A1C started at 9.1 after 8 months it is now 5.7.” Such testimonials emphasize the program’s success in enabling individuals to take control of their condition through lifestyle modifications and personalized care.
It’s also crucial to note that three in four adults with diabetes live in low- and middle-income countries, showcasing the global impact of this issue. Real-life examples illustrate the practical application of the blood sugar conversion table for understanding A1C. Patients who actively monitor their glucose levels and convert them to A1C values often report improved health outcomes and a greater sense of control over their condition. This proactive strategy not only aids in managing blood sugar levels but also empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle choices that can enhance their overall health.
In summary, the ability to transform average glucose levels to A1C values is a fundamental skill for diabetes management. It offers essential insights that can significantly improve care and outcomes, guiding individuals toward a healthier future.
From A1C to Average Blood Sugar: How to Convert
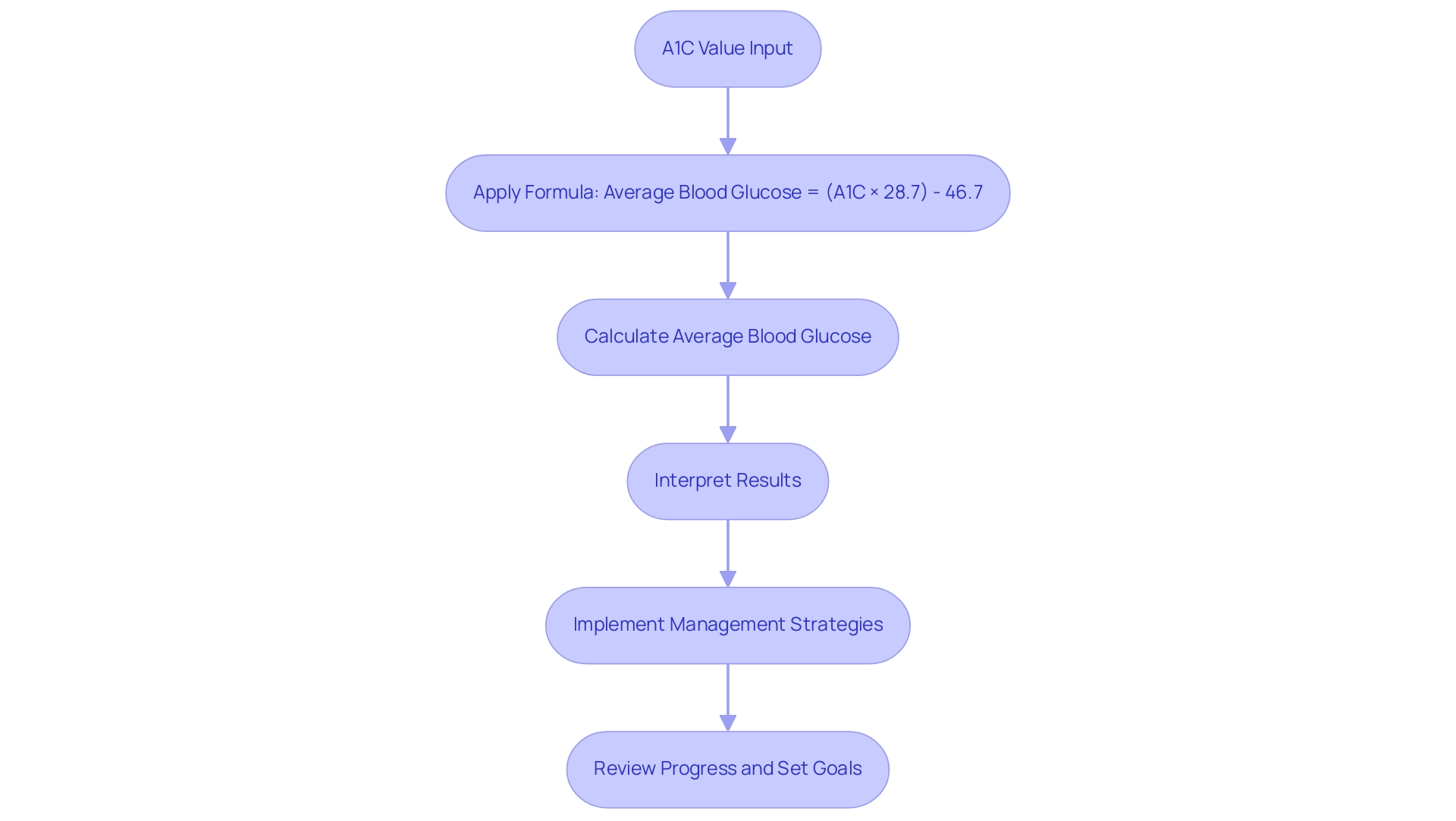
To convert A1C values back to average blood sugar levels, the following formula is utilized:
Average Blood Glucose (mg/dL) = (A1C × 28.7) – 46.7.
For instance, if a patient has an A1C of 7%, the calculation would be: Average Blood Glucose = (7 × 28.7) – 46.7 = 170.9 mg/dL. This conversion, outlined in the blood sugar conversion table, is crucial for patients seeking to understand how their A1C results relate to daily glucose levels. This understanding allows them to customize their management strategies effectively.
It’s important to recognize that comprehending A1C levels is especially vital in light of current trends. Recent data shows that a substantial percentage of U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes—80.6%—have a systolic pressure of 130 mmHg or higher or are on medication for hypertension. This highlights the interconnectedness of blood sugar management and overall health, emphasizing the need for effective strategies.
Moreover, statistics reveal that 5,293 children and adolescents aged 10 to 19 years were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus in recent years. This underscores the urgency for effective management strategies. By understanding the implications of A1C results, individuals can make informed decisions about their health.
Many patients find that real-world examples demonstrate this point: individuals express feeling empowered after learning how to interpret their A1C results. This newfound knowledge enables them to take proactive measures in their health management. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By offering individuals actionable insights and practical tools, the center cultivates an environment where people can reclaim their health and well-being.”
Incorporating effective strategies for progress tracking can further enhance the management of blood sugar levels. Consider utilizing fitness apps, journals, and pedometers, along with setting SMART goals. For instance, an individual might set a goal to reduce their A1C by a certain percentage within a specific timeframe, fostering accountability and motivation. Research indicates that structured goal-setting can significantly improve performance, as evidenced by goal-setting persistence scores that improved from 3.4 (SD = 2.0) to 3.8 (SD = 1.9) in specific conditions.
Understanding A1C is not merely about numbers; it is about fostering a deeper awareness of one’s health and making informed lifestyle choices. Regularly reviewing one’s progress not only fosters accountability but also allows for the adaptation of goals in response to changing fitness levels.
In summary, utilizing a blood sugar conversion table to transform A1C values into average glucose levels is an essential skill for managing chronic conditions. This provides individuals with actionable insights that can lead to improved health outcomes. This understanding aligns with the principles of the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, which empowers patients to take control of their health.
Common Mistakes in Blood Sugar Conversion and How to Avoid Them
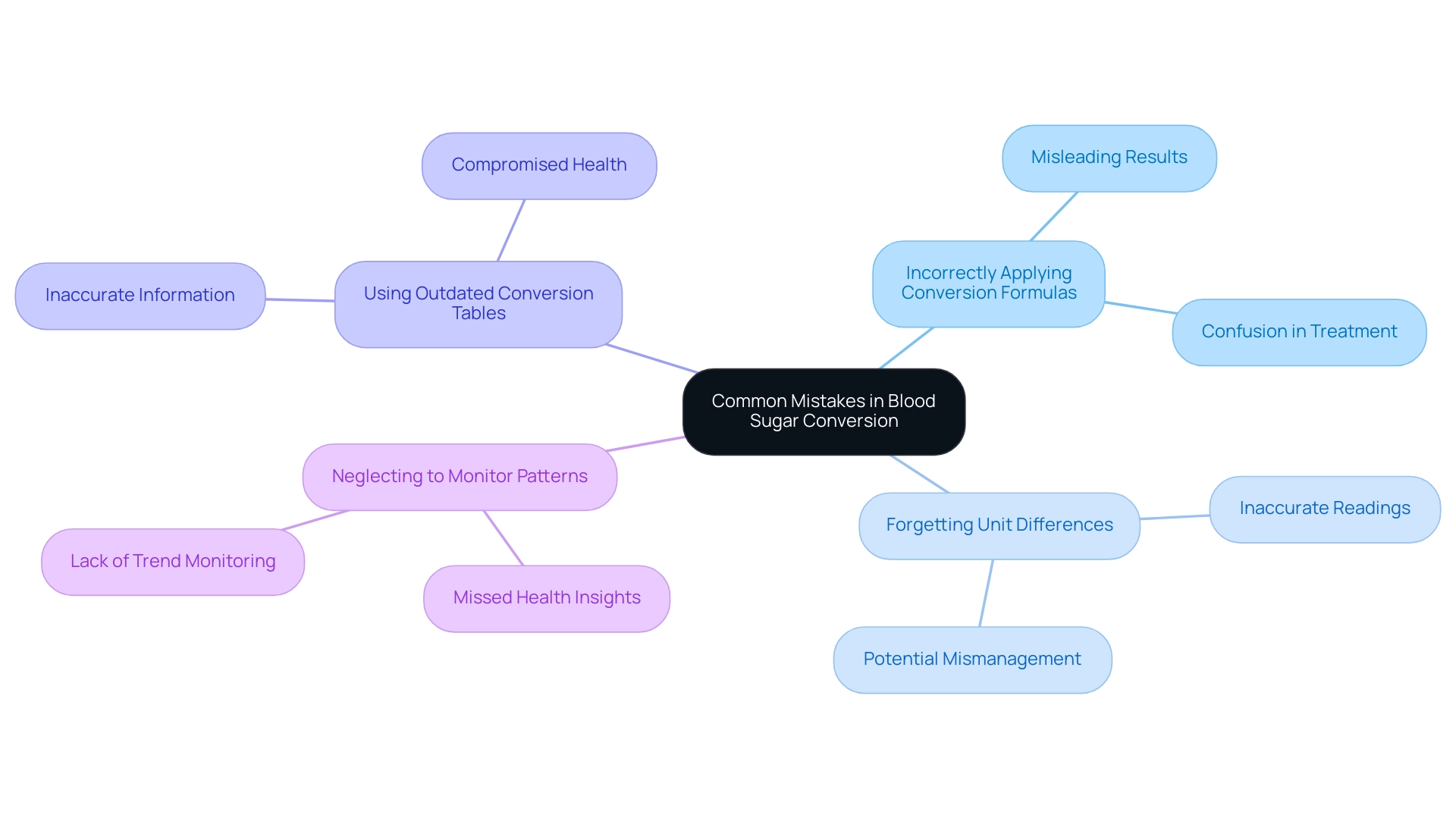
Frequent errors in glucose conversion can significantly impact diabetes management, especially when considering broader health concerns. It’s essential to be aware of some common pitfalls:
-
Incorrectly applying conversion formulas: Double-checking the formulas used for conversion is crucial. Misapplication can lead to misleading results, which can affect treatment decisions.
-
Forgetting to account for unit differences: Blood glucose readings can be reported in either mg/dL or mmol/L. Always confirm the units before performing any conversions to avoid confusion.
-
Using outdated blood sugar conversion tables: Conversion standards can evolve, so referring to the most current resources is essential. Relying on outdated charts may result in inaccuracies that could compromise health.
-
Neglecting to monitor patterns: Instead of fixating on individual readings, focus on overall trends in your glucose levels. This broader perspective can provide a clearer understanding of your diabetes management and help identify patterns that may require attention.
Real-life examples illustrate the importance of avoiding these pitfalls. Many patients who diligently monitor their glucose levels and refer to the blood sugar conversion table while following updated guidelines often report enhanced management of their condition. For instance, one individual shared that by consistently applying the proper conversion formulas and tracking trends, they were able to stabilize their glucose levels more effectively.
Specialist guidance highlights that frequent errors in glucose conversion are widespread among individuals with diabetes. A significant number may overlook unit differences or fail to update their conversion resources, leading to potential mismanagement of their condition. Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.”
This philosophy underscores the importance of recognizing common traps and applying strategies to avoid them, ultimately improving comprehension and utilization of the blood sugar conversion table, which can lead to better health outcomes.
Furthermore, challenges in noninvasive glucose assessment reveal the complexities of precise glucose conversion. Issues like overmodeling of calibration data and fluctuations in skin conditions can hinder the accuracy of these systems, highlighting the need for reliable techniques in tracking glucose levels. This is particularly relevant given the alarming statistics of 7,000 incorrect medications and 80,000 infections in hospitals, emphasizing the critical need for individuals to take charge of their health through informed management practices.
In summary, preventing mistakes in glucose conversion calculations is vital for effective diabetes management. By staying informed and vigilant, patients can reclaim control over their health and enhance their quality of life.
Tools and Resources for Effective Blood Sugar Management
Effective blood sugar management is supported by a variety of tools and resources designed to empower individuals on their health journey, especially through the innovative and patient-centered approach of Dr. Jason Shumard at Integrative Wellness Center.
- Blood Sugar Conversion Charts: These essential quick references help you convert blood sugar levels between mg/dL and mmol/L, making it easier to understand and communicate your glucose levels.
- Online Calculators: Many websites and applications offer glucose conversion calculators, simplifying the process and making it accessible for daily use.
- Diabetes Management Apps: A growing variety of applications allow you to record your glucose readings, monitor trends over time, and automatically compute conversions. These tools not only make monitoring simpler but also enhance your engagement in managing your health. Recent research suggests that these condition management applications can significantly improve patient outcomes. Users have reported better control over their glucose levels and overall well-being. Furthermore, an increase of just 500 steps per day is linked to a 2-9% reduced risk of cardiovascular morbidity and all-cause mortality, underscoring the importance of physical activity in managing diabetes-related health issues.
- Educational Resources: Comprehensive educational materials, including books, seminars, and online courses, provide valuable insights into managing your condition and understanding blood glucose levels. Dr. Jason Shumard’s center emphasizes patient education through its 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, equipping you with the knowledge and tools necessary for effective health transformation. Many patients have shared life-changing outcomes and a renewed sense of empowerment in managing their health through this holistic approach.
As Diabetes Canada states, “Reduction of free sugars consumption should not result in an over-consumption of other unhealthy foods,” highlighting the importance of making mindful dietary choices in managing blood sugar levels. Additionally, the Continuous Glucose-EGA (CG-EGA) has been introduced as a new method to evaluate CGM accuracy, incorporating both point accuracy and rate of change, providing current insights into management technology for blood sugar.
Utilizing these resources can greatly enhance your ability to manage your condition effectively, leading to improved health outcomes and a greater sense of empowerment in your daily life. As educators in the field emphasize, incorporating a blood sugar conversion table and management applications into your daily routine can provide essential assistance in navigating the intricacies of care.
Reach out to us today at Integrative Wellness Center to discover more about our extensive testing, including thorough evaluations that exceed standard lab work, and how our tailored plans can enable you to conquer Type 2 diabetes. During your consultation, you can expect personalized guidance tailored to your unique health needs. Call (858) 564-7081 or visit DrShumard.com to register for a free consultation.
Key Takeaways: Mastering Blood Sugar Conversions
Mastering glucose conversions is essential for effectively managing your condition, especially when you refer to a blood sugar conversion table alongside holistic lifestyle strategies. It’s important to recognize that understanding the difference between mg/dL and mmol/L is crucial for accurate monitoring. These units represent different measurement systems, and using a blood sugar conversion table can aid in this process. For example, a blood glucose level of 100 mg/dL translates to approximately 5.6 mmol/L, which is vital for individuals using various monitoring devices.
Many patients find that regularly utilizing a blood sugar conversion table to convert blood sugar levels to A1C and vice versa helps them track long-term glucose control. Studies indicate that maintaining an A1C level below 7% significantly reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications, highlighting the importance of consistent monitoring. Awareness of common mistakes can also prevent errors in calculations. Miscalculating conversions when using a blood sugar conversion table can lead to inappropriate treatment choices, emphasizing the need for precision in monitoring.
Utilizing tools and resources, such as Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems, can greatly improve the management of blood sugar levels. A recent consensus on CGM standardization has led to the creation of the Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) report, which visualizes glucose data. This report assists both clinicians and individuals in understanding glucose patterns and management strategies. It is instrumental in enhancing blood sugar management by providing clear insights into fluctuations.
In certain situations, such as hospitalization, manual mode may be necessary for managing blood sugar levels due to acute changes in an individual’s condition. This highlights the importance of adaptability in care.
Incorporating holistic lifestyle changes can profoundly impact managing type 2 blood sugar issues. Engaging in regular outdoor exercise in San Marcos, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, and participating in community wellness programs offered by Integrative Wellness Center can make a significant difference. By mastering these conversions with the help of a blood sugar conversion table and embracing these lifestyle strategies, individuals can improve their diabetes management and overall health outcomes. Real-life instances demonstrate this point: patients who have effectively utilized glucose conversion mastery alongside lifestyle changes report better control over their levels and a greater sense of empowerment in managing their health.
Statistics show that those who actively engage in understanding their blood sugar conversion table experience a significant reduction in time-weighted blood glucose levels. Intensive control groups achieve averages of 115 mg/dL compared to 144 mg/dL in conventional groups. This mastery not only fosters a proactive approach to health but also leads to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.
Conclusion
Mastering blood sugar conversions is a pivotal aspect of effective diabetes management, allowing individuals to navigate their health with confidence. It’s important to recognize that understanding the differences between mg/dL and mmol/L is not just a technical detail; it significantly impacts how patients interpret their glucose levels and adjust their management strategies. Many patients find that regularly converting blood sugar levels to A1C and vice versa enhances their tracking of long-term glucose control, which is essential in reducing the risk of serious complications associated with diabetes.
Awareness of common mistakes in blood sugar conversion is equally important. Simple errors can lead to inappropriate treatment decisions, emphasizing the need for accuracy and diligence in monitoring. Utilizing available tools and resources, such as Continuous Glucose Monitoring systems and educational materials, can greatly enhance one’s ability to manage diabetes effectively. These resources empower patients to take an active role in their health, leading to improved outcomes and a greater sense of control.
Incorporating holistic lifestyle changes, such as engaging in regular physical activity and maintaining a balanced diet, further complements the technical skills learned through blood sugar conversion mastery. Real-life experiences highlight that those who embrace both the educational and lifestyle aspects of diabetes management report better control over their glucose levels and an enhanced quality of life. As knowledge and proactive management strategies intertwine, individuals can reclaim their health and navigate the complexities of diabetes with improved confidence and empowerment. Remember, you are not alone on this journey; support and resources are available to help you thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are blood sugar conversion tables and why are they important?
Blood sugar conversion tables are tools that allow individuals to translate glucose readings between different units, specifically from milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) to millimoles per liter (mmol/L) and vice versa. They are important for effective diabetes management, especially for those encountering varying measurement standards across healthcare settings or using different monitoring devices.
How do blood sugar conversion tables empower individuals managing diabetes?
These tables empower individuals by enabling them to accurately interpret their glucose levels, which helps them make informed decisions regarding their diet, medication, and overall management strategies. This empowerment is crucial for better health outcomes, particularly given the serious health risks associated with diabetes.
What are some health risks associated with diabetes?
Diabetes is linked to several health risks, including cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney dysfunction. In 2021, diabetes was the eighth leading cause of death in the United States, with over 399,000 death certificates citing it as a contributing factor.
What percentage of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions have high blood pressure?
Approximately 70.8% of U.S. adults aged 18 years or older with diagnosed conditions have high blood pressure, highlighting the interconnected health risks associated with diabetes.
How are blood sugar conversion tables expected to change diabetes management in the future?
Experts suggest that blood sugar conversion tables are likely to become standard care for individuals on intensive insulin regimens. They have the potential to transform diabetes management, especially with innovations such as the artificial pancreas.
What role does personalized care play in managing blood sugar conditions?
Personalized care is crucial as it addresses individual needs and conditions, such as reversing type 2 diabetes and related issues like hypothyroidism. This tailored approach can lead to better management and health outcomes.
What are the risks of elevated and low glucose levels?
Elevated glucose levels (hyperglycemia) can lead to serious complications, while low glucose levels (hypoglycemia) can cause symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Understanding these risks is vital for effective diabetes management.
How can consistent monitoring and blood sugar conversion tables improve diabetes management?
Consistent monitoring and using blood sugar conversion tables allow individuals to make informed adjustments to their diet, exercise, and medication regimens, enhancing diabetes management and improving overall quality of life.
What are the financial implications of diabetes management?
The cost of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) sensors and machines can be approximately $5000 per year, highlighting the financial burden associated with diabetes management.
What is the significance of ongoing research in glucose measurement standards?
Ongoing research aims to integrate A1C to estimated Average Glucose (eAG) conversion calculators, enhancing patient-provider conversations about glucose regulation and reinforcing the importance of blood sugar conversion tables in modern diabetes management.