Overview
An A1C level of 8.5 indicates poor blood glucose control, which is associated with significant health risks such as cardiovascular disease and nerve damage. The article emphasizes the importance of understanding this measurement and outlines effective management strategies, including dietary modifications, regular physical activity, and support systems, all of which are essential for reducing complications and improving overall health outcomes.
Introduction
Understanding one’s A1C level is crucial for effective diabetes management, particularly when it exceeds the recommended target of 7%. An A1C level of 8.5 signals not only suboptimal control but also a heightened risk for serious health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular issues
- Nerve damage
The prevalence of prediabetes, especially among Hispanic adults, underscores the urgent need for awareness and proactive management strategies. This article delves into the implications of elevated A1C levels, highlighting essential lifestyle modifications, the importance of regular monitoring, and the role of support systems in fostering effective diabetes care.
By adopting a holistic approach that encompasses:
- Nutrition
- Physical activity
- Emotional well-being
Individuals can significantly reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall health outcomes.
Understanding the Implications of an A1C Level of 8.5
An A1C 8.5 measurement indicates that average blood glucose readings have surpassed the recommended target of below 7% for individuals with diabetes, signaling suboptimal diabetes control. This elevation is linked to serious health risks, such as:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney damage
- Nerve damage
- Vision-related problems
This highlights the importance of understanding one’s A1C measurement. Recent studies indicate that around 34.5% of Hispanic adults were identified as having prediabetes, with only 20.9% being conscious of their condition, highlighting the essential need for awareness and proactive care.
In fact, there are an estimated 15.0 million Hispanic adults with prediabetes in 2021, highlighting the prevalence of this issue. Regular monitoring of A1C levels is crucial, as this test offers several advantages over fasting plasma glucose (FPG), including its ability to capture chronic hyperglycemia and its stability under various conditions, making it a reliable metric for diagnosing and initiating management of blood sugar levels. As noted in the case study titled ‘Advantages of A1C in Diabetes Monitoring,’ A1C can effectively identify long-term glucose control and is less influenced by acute changes in blood sugar.
The Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego emphasizes a holistic approach to health, seeking to address the root causes of this condition and empower patients to take control of their health. For example, numerous patients have effectively reversed their condition through personalized programs that incorporate:
- Dietary changes
- Exercise routines
- Stress reduction techniques
This highlights the center’s dedication to transformative results. Consulting healthcare professionals can help assess individual risks and develop tailored strategies for improvement, as highlighted by experts who suggest considering A1C time in range (TIR) when evaluating treatment intensification.
Comprehending and regulating A1C measurements, particularly maintaining a target of A1C 8.5, efficiently can greatly lessen the chances of complications linked to high blood sugar. Moreover, addressing the emotional aspects of diabetes management, such as anxiety about potential complications, is integral to the holistic regimen offered, ensuring that patients not only manage their physical health but also their mental well-being.
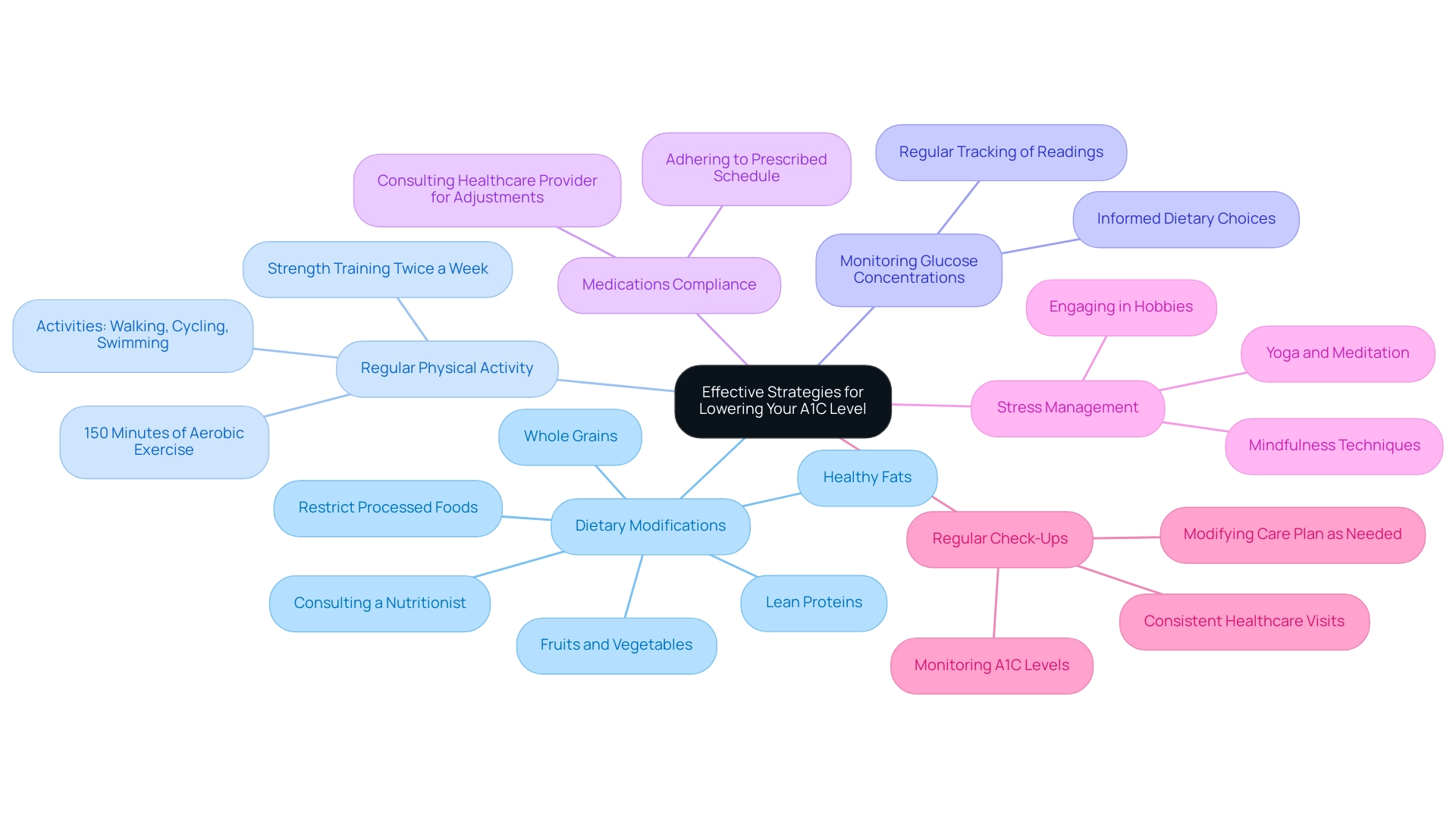
Effective Strategies for Lowering Your A1C Level
- Dietary Modifications: A balanced diet is essential for effectively managing A1C values, particularly for those targeting an A1C of 8.5. Focus on incorporating whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a diverse array of fruits and vegetables. It is essential to restrict the consumption of processed foods, added sugars, and high-carbohydrate meals, all of which can result in spikes in blood glucose. A study found that food insecurity and low-quality diets are associated with higher A1C levels of 8.5, highlighting the need for discussions between clinicians and patients about access to nutritious foods. In addition, having a poor diet (not eating enough healthy foods), even if someone was food secure, is significantly associated with an elevated A1C level of 8.5. Working with a nutritionist can assist in developing a tailored meal plan that aligns with personal health objectives and supports a comprehensive approach to managing blood sugar. This approach can also help alleviate the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of this condition by fostering a sense of control over one’s health.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly is recommended for individuals managing diabetes. Activities like walking, cycling, or swimming not only support weight management but also improve insulin sensitivity, thus reducing blood sugar. Research shows that dietary modifications can lead to a decrease in HbA1c levels, with a significant change noted at A1C of 8.5, showing a β value of -0.35 among women and -0.08 among men. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises at least twice a week can further improve metabolic health and contribute to A1C reduction, complementing a holistic strategy for reversing the condition. This holistic approach begins by re-examining the source of your condition, which is crucial for effective management.
- Monitoring Glucose Concentrations: Regularly tracking glucose readings is essential for understanding how various foods and activities affect your body. This self-monitoring enables informed dietary and exercise choices, which are crucial for effective diabetes management and empowerment in health.
- Medications Compliance: Sticking to your prescribed medication schedule is crucial for managing sugar concentrations. Should you encounter difficulties in managing your A1C measurements, particularly if your A1C is at 8.5, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider to explore potential adjustments to your treatment plan, ensuring that the approach remains comprehensive and effective.
- Stress Management: Elevated amounts of stress can negatively influence sugar regulation. It is beneficial to adopt stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation. Participating in pleasurable hobbies and activities can also enhance overall well-being and aid in stabilizing blood sugar, reflecting a comprehensive approach to managing the condition. Addressing stress can also reduce the anxiety that often comes with managing this condition.
- Regular Check-Ups: Consistent visits with your healthcare team are crucial for monitoring your A1C levels, particularly if your A1C is 8.5, and modifying your care plan as needed. These routine examinations offer a chance to assess progress, tackle any issues, and guarantee that your health strategy remains effective, highlighting the significance of addressing underlying causes in a comprehensive way.
The Role of Nutrition in Diabetes Management
Effective management of the condition hinges on a holistic approach that encompasses proper nutrition, particularly the inclusion of foods with a low glycemic index (GI). These foods, including whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables, have a slower impact on sugar levels, making them essential for maintaining stable glucose levels. Recent statistics indicate that 94.2% of patients received a test for A1C 8.5, highlighting the importance of regular monitoring in effectively managing diabetes.
Portion control is equally significant in dietary management; utilizing smaller plates and precisely measuring serving sizes can help prevent overeating. Furthermore, it is vital to monitor carbohydrate intake and maintain consistency in meal timing to regulate sugar levels effectively. Staying hydrated also plays a crucial role, as dehydration can hinder blood sugar control.
Choosing water or herbal teas rather than sugary drinks can enhance the control of blood sugar. Many patients experience anxiety surrounding the potential complications of the condition, which can be alleviated through effective management strategies. The case studies from the Integrative Wellness Center emphasize transformative patient success narratives, such as individuals who have effectively reversed their condition by re-examining its source and adopting a holistic regimen.
As noted by the Diabetes and Nutrition Study Group (DNSG), ‘We believe these dietary recommendations reflect the current evidence base and will continue to be updated.’ This underscores the need for patients to stay informed about dietary trends that can enhance their health outcomes. Additionally, nutrition therapy for individuals with blood sugar issues requires self-management, which can be challenging due to the complexity of food quality and personal dietary preferences.
Health professionals play a crucial role in empowering patients by providing practical advice that aligns with their values and treatment goals, ultimately enhancing skills and competencies for improved health outcomes.
Understanding the Importance of Physical Activity
Consistent physical exercise is a fundamental element of efficient sugar regulation for individuals with type 2. It is recommended to engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days of the week, which can include activities such as:
- Walking
- Biking
- Swimming
- Participating in group fitness classes
Including strength training exercises two to three times weekly further boosts muscle mass and enhances insulin sensitivity, which is essential for regulating blood glucose.
Research indicates that both young and older adults experienced increases in basal glucose uptake in brain regions critical to cognitive function after just 12 weeks of aerobic interval exercise, highlighting the cognitive benefits of physical activity as well. Additionally, the U-TURN study found that participants with type 2 conditions who undertook intensive lifestyle changes experienced improvements in the physical component of quality-of-life scores, emphasizing the holistic benefits of such activities. To truly address this condition at its root level, it is essential to recognize the role of physical activity in empowering patients towards better health outcomes and alleviating the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about complications related to this illness.
For those who are new to exercise, breaking activity into shorter sessions throughout the day can be particularly beneficial. Finding enjoyable activities is essential, as it promotes motivation and consistency in maintaining an exercise routine. As indicated in the findings of several case studies, including the latest Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, different types of physical activity, such as flexibility and balance exercises, can significantly enhance health and glycemic control in individuals with type 2.
Addressing barriers to exercise and reducing sedentary time are vital strategies for maximizing health benefits. Ultimately, incorporating physical activity into daily life not only helps in blood sugar management but also positively impacts overall well-being, aligning with a holistic regimen that addresses the underlying causes of the condition.
Setting Realistic Goals for A1C Management
Establishing SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—plays a crucial role in enhancing management of the condition through a holistic lens. For instance, rather than making a vague commitment to ‘eat healthier,’ a SMART goal could specify, ‘I will incorporate at least one vegetable into each meal this week.’ This level of specificity allows for clearer tracking of progress and aligns with our commitment at the Integrative Wellness Center to address health at the root level by re-examining the source of your condition.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting these goals in response to personal progress and encountered challenges is essential. Celebrating small victories, such as successfully meeting these goals, can significantly enhance motivation and commitment to managing health. Furthermore, research highlights that effective goal-setting significantly supports individuals in achieving glycaemic targets, such as maintaining an a1c 8.5, in both prediabetes and type 2 conditions.
The influence of self-efficacy on HbA1C values, especially in relation to a1c 8.5, was significant (F (1,85) = 10.39, p = .002), highlighting the importance of self-management in reaching these goals. Insights from a study on group clinics for blood sugar management reveal that integrating self-management support with routine care enhances patient outcomes. As Hanh Nguyen-Vaselaar, DNP, NP-C, notes in her pilot study, statistically significant improvements were observed in physical activity and a1c 8.5 levels when SMART goals were met.
This emphasizes the importance of organized goal-setting within a comprehensive approach in health care, making it an essential tactic for effective oversight. Additionally, by addressing the root causes of this condition, patients can alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications, further promoting overall health and well-being.
The Importance of Support Systems
Creating a strong support system is essential for effective management of blood sugar conditions. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we empower patients to eliminate anxiety over complications related to blood sugar through holistic care and education. This network can include:
- Family
- Friends
- Healthcare professionals
- Committed support groups for individuals managing their condition
Interacting with individuals who have comparable experiences enables the sharing of emotional support and practical guidance, greatly reducing the psychological burden linked to the condition. Recent evaluations, such as those conducted by Barrera et al., have demonstrated the effectiveness of internet-based support interventions in enhancing self-management of the condition, illustrating the importance of accessibility to these resources. In the words of one patient, ‘Joining the support group helped me realize I am not alone in this journey, and it brought me a sense of peace I never thought I could find.’
Additionally, the case study titled ‘Results of Moderated Mediation Analysis’ highlights how health-related distress significantly affects self-efficacy and resilience, with social support playing a crucial moderating role in this relationship. Joining local or online support networks fosters connections with peers navigating similar challenges, facilitating a sense of community. These groups offer vital resources, support, and responsibility, which are key in upholding compliance with health plans.
Furthermore, healthcare teams at the Integrative Wellness Center promote Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) to reinforce the importance of these support systems. By actively participating in these supportive environments, individuals can cultivate a network that enhances motivation and contributes positively to their diabetes management journey, ultimately helping them to find new peace in life.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing an A1C level of 8.5 is crucial for preventing serious health complications associated with diabetes. Elevated A1C levels signify the need for immediate intervention through lifestyle modifications, including:
- Improved nutrition
- Increased physical activity
- Stress management
These strategies are not merely recommendations; they form the foundation of a holistic approach essential for effective diabetes management.
Regular monitoring of A1C levels and the establishment of realistic, SMART goals empower individuals to take control of their health. Engaging with healthcare professionals and support systems can provide the necessary guidance and encouragement to navigate the complexities of diabetes care. By fostering a supportive environment and addressing both physical and emotional health, patients can significantly reduce their risk of complications and enhance their overall well-being.
Ultimately, a proactive approach to managing A1C levels not only improves individual health outcomes but also fosters a greater awareness of the importance of diabetes management within communities. By prioritizing education, self-management, and support, individuals can lead healthier lives while mitigating the risks associated with diabetes, ensuring a brighter future for themselves and their families.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does an A1C measurement of 8.5 indicate for individuals with diabetes?
An A1C measurement of 8.5 indicates that average blood glucose readings have exceeded the recommended target of below 7%, signaling suboptimal diabetes control and increasing the risk for serious health issues such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision-related problems.
Why is awareness of A1C levels important, particularly among Hispanic adults?
Awareness of A1C levels is crucial because studies show that around 34.5% of Hispanic adults have prediabetes, yet only 20.9% are aware of their condition. This highlights the need for proactive care and monitoring to prevent further health complications.
What advantages does the A1C test offer over fasting plasma glucose (FPG)?
The A1C test offers several advantages, including the ability to capture chronic hyperglycemia and its stability under various conditions, making it a reliable measure for diagnosing and managing blood sugar levels over time.
What holistic approaches does the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego recommend for managing diabetes?
The Integrative Wellness Center emphasizes a holistic approach that includes dietary changes, exercise routines, and stress reduction techniques to address the root causes of diabetes and empower patients to take control of their health.
How can dietary modifications help manage A1C levels?
A balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables is essential for managing A1C levels. Reducing processed foods, added sugars, and high-carbohydrate meals can help prevent spikes in blood glucose.
What role does physical activity play in managing diabetes?
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly can improve insulin sensitivity and support weight management, contributing to lower A1C levels. Incorporating strength training at least twice a week can further enhance metabolic health.
Why is monitoring glucose concentrations important?
Regularly tracking glucose readings helps individuals understand how different foods and activities affect their blood sugar levels, allowing for informed dietary and exercise choices crucial for effective diabetes management.
How important is medication compliance in managing A1C levels?
Adhering to a prescribed medication schedule is vital for managing blood sugar concentrations. If difficulties arise in managing A1C levels, particularly at 8.5, consulting a healthcare provider for potential adjustments is essential.
What stress management techniques can aid in diabetes management?
Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and meditation can help reduce stress, which negatively affects blood sugar regulation. Engaging in enjoyable activities can also enhance overall well-being and stabilize blood sugar levels.
Why are regular check-ups with healthcare providers essential?
Regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring A1C levels, especially for those with a measurement of 8.5, and for modifying care plans as needed. These visits help assess progress and ensure that health strategies remain effective.