Overview
An A1C level of 6.7% indicates a prediabetic state, which heightens the risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney issues, necessitating proactive management strategies. The article underscores the importance of lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and collaboration with healthcare professionals to effectively manage A1C levels and reduce health risks associated with diabetes.
Introduction
The A1C test serves as a critical benchmark in diabetes management, providing insights into average blood glucose levels over a two- to three-month period. A reading of 6.7% indicates a concerning trend, placing individuals in the prediabetes category and highlighting the urgent need for proactive health strategies.
This article delves into the implications of such a reading, exploring effective management techniques that can mitigate associated health risks. It emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach, integrating:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Dietary adjustments
- Regular monitoring
to empower individuals in their journey toward better health. By understanding the significance of A1C levels and the strategies available, patients can take informed steps to improve their well-being and reduce the likelihood of complications linked to diabetes.
Understanding the A1C Test: What Does a Level of 6.7 Mean?
The A1C test is an essential diagnostic instrument that assesses average blood glucose readings over a period of two to three months. An A1C of 6.7% signifies that your average blood sugar has consistently exceeded the normal range, indicating a heightened risk for complications related to the condition. This stage falls within the prediabetes category, underscoring the necessity for proactive management strategies to achieve an A1C of 6.7 and mitigate future health risks.
Alongside A1C measurements, embracing a comprehensive strategy to reversing the condition can empower patients through education and tailored care. This includes understanding the underlying factors of the condition and implementing effective lifestyle changes such as:
- Embracing nature
- Nutrition
- Community support
Key strategies include:
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Optimizing dietary choices
- Managing stress through mindfulness practices
- Fostering social connections for emotional support
Moreover, a random plasma glucose level of ≥200 mg/dL (≥11.1 mmol/L) signifies a clear clinical diagnosis of the condition, providing further context for understanding A1C levels. Recent studies reveal that approximately 97.6 million U.S. adults aged 18 years or older had prediabetes as of 2021, with demographic disparities evident as Hispanic individuals represented 5.0 million diagnosed cases and 1.9 million undiagnosed cases. Expert insights, such as those from Roopa Naik, emphasize that understanding the interpretation of A1C results is vital for making informed health decisions.
As we approach 2024, emerging research continues to underscore the significance of A1C testing and its implications for managing blood sugar levels, with alternative biomarkers such as fructosamine and glycated albumin gaining recognition for their roles in monitoring chronic hyperglycemia. Addressing the anxiety that accompanies diabetes management is also crucial; a holistic approach can help alleviate concerns about potential complications, promoting a healthier mindset and improved overall well-being.
Effective Strategies for Managing Your A1C Levels
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Prioritize whole foods, including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is essential to limit processed foods and sugary beverages, as these can lead to elevated blood sugar readings. Recent studies indicate that dietary changes play a significant role in managing A1C values, and behavioral interventions promoting low-carbohydrate diets show promise in achieving an A1C of 6.7 while reducing hemoglobin A (HbA1c) readings over a six-month period. A randomized clinical trial demonstrated that such interventions can effectively lower HbA1c among individuals with elevated untreated values. Dr. Lydia A. Bazzano noted the importance of these dietary changes, stating that they can significantly impact overall health outcomes, reinforcing the integrative approach offered at the Integrative Wellness Center. One individual shared, “After altering my diet, I felt more energetic and less worried about my condition.”
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly, such as brisk walking or cycling. Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week. Research emphasizes that regular physical activity can lead to significant improvements in A1C measurements, potentially achieving an A1C of 6.7, with customized exercise programs showing effectiveness in diabetes management, further endorsing our comprehensive approach at the Integrative Wellness Center. A client remarked, “Incorporating exercise into my routine has not only helped my A1C but also eased my worries about complications.”
- Monitor Carbohydrate Intake: Pay close attention to the carbohydrate content of your meals. Collaborating with a dietitian can help create a personalized meal plan that aligns with your goal of achieving an A1C of 6.7, ensuring you maintain a balanced approach to nutrition. This structured dietary approach is crucial, as it can significantly impact A1C outcomes, helping to achieve an A1C of 6.7 and countering traditional treatment myths. One patient remarked, “Collaborating with a dietitian significantly impacted my ability to manage my carb intake and alleviate my anxiety regarding my blood sugar.”
- Stay Hydrated: Consistent hydration is vital for regulating blood sugar levels. Consuming sufficient water during the day can assist in reducing spikes in blood glucose, a crucial element in managing the condition, reinforcing the holistic strategies utilized at the Integrative Wellness Center. A recommendation from an individual stated, “Staying hydrated has made my condition feel more manageable.”
- Stress Management: Engage in activities that reduce stress, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Chronic stress can adversely affect blood sugar control, making it imperative to incorporate stress-reducing practices into your daily routine, as emphasized by patient experiences shared at the Integrative Wellness Center. One client shared, “Practicing mindfulness has helped me cope with the anxiety that comes with managing my condition.”
- Regularly checking your blood sugar readings is essential for understanding how lifestyle choices influence achieving an A1C of 6.7. This proactive approach allows for timely adjustments to your diet and exercise regimen, ensuring optimal diabetes management. Furthermore, managing A1C values can have long-term health effects, as shown by the average 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk score of 8.0%, highlighting the significance of lifestyle modifications and the transformative experiences shared by individuals at the Integrative Wellness Center. A patient reflected, “Monitoring my measurements regularly has given me peace of mind and control over my health.
Health Implications of an A1C Level of 6.7: Risks and Considerations
An A1C of 6.7% serves as a critical threshold, indicating an increased risk for developing a range of complications associated with diabetes. These complications include:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Elevated A1C values can contribute to vascular damage, heightening the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Research indicates a direct correlation between higher A1C readings and the incidence of cardiovascular diseases, emphasizing the need for careful monitoring of glucose readings.
- Nerve Damage: Persistently high blood sugar readings may compromise nerve health, potentially leading to diabetic neuropathy. This condition can result in pain, tingling, and loss of sensation, particularly in the extremities.
- Kidney Damage: A sustained increase in A1C can impose significant stress on the kidneys, raising the likelihood of kidney disease. Maintaining optimal A1C levels is crucial for kidney health and overall well-being.
- Eye Damage: Individuals with elevated A1C levels face a heightened risk of diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can lead to severe vision impairment or even blindness.
Understanding these implications underscores the necessity of proactive management and regular monitoring of A1C levels. At the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego, we emphasize a holistic method to managing blood sugar issues that addresses root causes and empowers individuals. Transformative success narratives from those we serve illustrate how tailored care, such as that offered by Dr. Shumard, has assisted many in reversing type 2 conditions, alleviating concerns over complications through comprehensive insights and treatment options. For instance, one patient, after following our tailored program, reported not only a significant drop in their A1C readings but also a newfound confidence in managing their health, free from the fear of complications.
As emphasized by Xuanping Zhang, to better define A1C ranges that might identify individuals who would benefit from interventions to prevent or delay type 2 conditions, we conducted a systematic review of published prospective studies that have examined the relationship of A1C to future incidence. Furthermore, the 1996 research by Yoshinaga highlighted the significance of utilizing various diagnostic criteria for improved risk evaluation, showing that A1C measurements, when paired with other tests, can offer a more accurate forecast of disease progression. Moreover, studies indicate that the medication metformin can lower the occurrence of high blood sugar conditions by at least 30%, emphasizing the necessity for proactive management of A1C values. Importantly, the A1C test does not require fasting and can be performed at any time of the day, making it accessible for regular monitoring. Consequently, keeping A1C values beneath a1c of 6.7 is crucial for reducing health risks and complications.
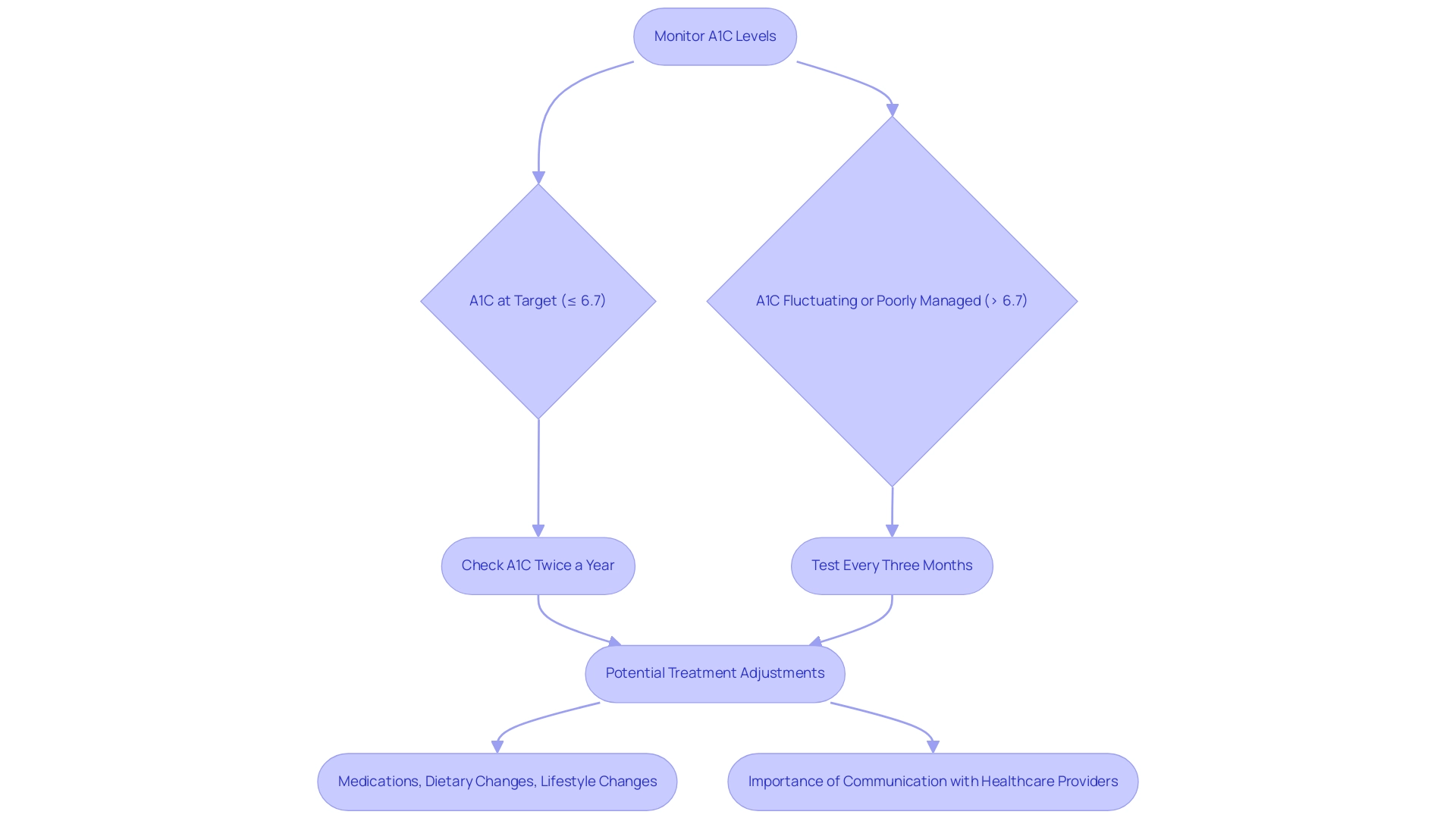
The Importance of Regular Monitoring and Treatment Adjustments
Regular monitoring of A1C measurements is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies, especially to achieve an A1C of 6.7 within a holistic framework aimed at addressing root causes. This approach could assist individuals in reducing the anxiety that comes with the concern regarding the possible complications of their illness. For patients achieving their targets, it is advisable to check A1C values at least twice a year, particularly to monitor for an A1C of 6.7.
Conversely, those with fluctuating or poorly managed blood sugar levels, particularly those with an A1C of 6.7, should undergo testing every three months. This systematic assessment allows healthcare providers to implement necessary treatment adjustments, including modifications to medications, dietary guidelines, and lifestyle changes, thereby ensuring that the management strategy remains effective for patients with an A1C of 6.7. As healthcare experts often advise, let your doctor know if any factors apply to you, emphasizing the importance of open communication regarding an A1C of 6.7 and any variations in your health status.
It’s important to note that estimated Average Glucose (eAG) readings are generally lower than meter readings taken in the morning or before meals, which can impact how A1C results are interpreted. Furthermore, landmark trials such as ACCORD, ADVANCE, and VADT have demonstrated that lower A1C values correlate with a reduced risk of microvascular complications; specifically, further lowering A1C to an A1C of 6.7 from 7% is associated with a significant reduction in these risks. However, caution is warranted given some concerning outcomes observed in the ACCORD trial.
Staying engaged with your healthcare provider about your A1C results, especially when managing an A1C of 6.7, and potential treatment adjustments, along with a commitment to re-examining the source of your condition and adopting a holistic approach, is vital for achieving optimal management and challenging prevailing myths around care.
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals for Optimal A1C Management
Effective management of A1C levels requires close collaboration with healthcare professionals such as doctors, dietitians, and educators specializing in blood sugar control to achieve an A1C of 6.7. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we emphasize a holistic approach to reversing the condition by addressing root causes and empowering individual health. This is pivotal in developing individualized care plans that cater to your specific health needs and objectives, ultimately eliminating anxiety about developing traumatic and debilitating complications.
Regular consultations enable timely adjustments to medication, dietary guidance, and lifestyle modifications based on your ongoing progress. A thorough review examined 6,339 publications, identifying 35 qualified studies that emphasize the importance of interdisciplinary education in healthcare, aligning with our commitment to empowering individuals. As Kunal D. Patel observes, ‘Interprofessional education in managing diabetes-related care is essential for improving outcomes.’
The research involved 11 adult individuals with type 1 or type 2 sugar intolerance, emphasizing the practical use of these results. Published in volume 4, issue 3, on pages 356-375, this review adds to its credibility. Open communication with your healthcare team fosters an atmosphere of support and responsiveness, allowing for the prompt addressing of any concerns.
Additionally, platforms like Enhance-d exemplify how technology can enhance this collaboration by providing users with a free online dashboard to actively manage their condition, thus improving engagement and quality of life. Strategies such as mindfulness practices, regular physical activity, and participating in support groups can significantly aid in achieving peace in life while managing blood sugar levels. By empowering individuals through collaborative efforts at the Integrative Wellness Center, diabetes management transforms into a shared journey, aiming for an A1C of 6.7, which enhances both outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion
Managing an A1C level of 6.7% is not merely a matter of concern; it is a pivotal call to action for better health. This level signifies the onset of prediabetes and the associated risks of diabetes complications, including:
- cardiovascular disease
- nerve damage
- kidney impairment
Understanding these implications is crucial for individuals striving to take charge of their health and mitigate future risks.
Implementing effective strategies such as:
- adopting a balanced diet
- engaging in regular physical activity
- monitoring carbohydrate intake
- managing stress
can significantly improve A1C levels. These lifestyle modifications are complemented by regular monitoring and collaboration with healthcare professionals, ensuring that each individual’s approach to managing their diabetes is tailored and effective.
Ultimately, a holistic approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and ongoing support can empower individuals to take control of their diabetes journey. By embracing these strategies, patients not only enhance their well-being but also reduce the likelihood of complications, fostering a healthier future. Taking proactive steps today can lead to transformative outcomes and a renewed sense of confidence in managing one’s health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and what does an A1C of 6.7% indicate?
The A1C test measures average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. An A1C of 6.7% indicates that the average blood sugar has consistently been above the normal range, placing the individual in the prediabetes category and highlighting a heightened risk for related health complications.
What management strategies can help achieve an A1C of 6.7%?
Effective management strategies include embracing nature, focusing on nutrition, engaging in community support, regular physical activity, optimizing dietary choices, managing stress through mindfulness practices, and fostering social connections for emotional support.
What is the significance of a random plasma glucose level of ≥200 mg/dL?
A random plasma glucose level of ≥200 mg/dL (≥11.1 mmol/L) provides a clear clinical diagnosis of the condition, offering additional context for understanding A1C levels.
How prevalent is prediabetes among U.S. adults?
As of 2021, approximately 97.6 million U.S. adults aged 18 years or older were reported to have prediabetes, with notable demographic disparities, including 5.0 million diagnosed and 1.9 million undiagnosed cases among Hispanic individuals.
Why is understanding A1C results important?
Understanding A1C results is vital for making informed health decisions, as emphasized by experts like Roopa Naik.
What alternative biomarkers are being recognized for monitoring blood sugar levels?
Emerging research highlights the significance of alternative biomarkers such as fructosamine and glycated albumin for monitoring chronic hyperglycemia.
How can addressing anxiety improve diabetes management?
A holistic approach to diabetes management can alleviate anxiety about potential complications, promoting a healthier mindset and improved overall well-being.
What dietary changes can help manage A1C values?
Adopting a balanced diet that prioritizes whole foods, limiting processed foods and sugary beverages, and collaborating with a dietitian for personalized meal planning can significantly impact A1C values.
What role does physical activity play in managing A1C levels?
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly and incorporating strength training can lead to significant improvements in A1C measurements.
Why is it important to monitor carbohydrate intake?
Paying attention to carbohydrate intake is crucial for managing blood sugar levels, and working with a dietitian can help create a personalized meal plan to achieve A1C goals.
How does hydration affect blood sugar levels?
Staying hydrated is essential for regulating blood sugar levels, as sufficient water intake can help reduce spikes in blood glucose.
What stress management techniques can benefit individuals managing diabetes?
Activities such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress, which negatively impacts blood sugar control.
Why is regularly checking blood sugar readings important?
Regularly monitoring blood sugar readings helps individuals understand how lifestyle choices affect their A1C levels, allowing for timely adjustments in diet and exercise for optimal diabetes management.