Overview
The article focuses on understanding and managing A1C levels for diabetics, emphasizing the importance of the A1C test as a key tool for monitoring blood sugar control and guiding treatment decisions. It supports this by detailing how lifestyle changes, such as adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and collaborating with healthcare providers, can significantly improve A1C levels and overall health outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding the nuances of the A1C test is crucial for individuals navigating the complexities of type 2 diabetes. This essential diagnostic tool provides a snapshot of average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, helping patients and healthcare providers alike assess glucose control and make informed treatment decisions.
With elevated A1C levels linked to serious health risks, the importance of maintaining optimal numbers cannot be overstated. This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, offering insights into:
- Effective lifestyle changes
- Monitoring strategies
- The collaborative role of healthcare professionals in empowering individuals to take charge of their diabetes journey
By embracing holistic approaches and personalized care, patients can significantly improve their health outcomes and enhance their overall well-being.
What is the A1C Test and Why is it Important for Diabetics?
The A1C test, clinically known as the hemoglobin A1C test, is an essential tool for individuals managing type 2 blood sugar issues. It assesses the average blood sugar concentrations over the preceding two to three months, providing a comprehensive picture of glucose control. The result is expressed as a percentage, reflecting the proportion of hemoglobin molecules in the blood that have sugar attached.
An A1C measurement of 6.5% or above signifies the condition, rendering it an essential diagnostic criterion. For individuals diagnosed with this condition, keeping A1C levels for diabetics under 7% is generally advised, as high levels can greatly heighten the risk of severe health issues, such as cardiovascular disease and nerve damage. Integrating holistic lifestyle approaches is crucial for effective control of the condition.
Emphasizing a balanced, diabetes-friendly diet rich in local produce—such as avocados, tomatoes, and seasonal berries—regular outdoor exercise in San Marcos’s beautiful parks like Lake San Marcos and Discovery Lake, and engaging in community wellness programs can significantly enhance your health outcomes. These lifestyle changes, combined with personalized guidance from Dr. Jason Shumard, empower patients to take control of their health journey. Additionally, while A1C testing is more expensive than fasting plasma glucose (FPG) tests, it eliminates the need for fasting and additional tests, potentially saving costs in the long run.
This aspect highlights the long-term advantages of A1C testing.
The significance of the A1C test cannot be exaggerated; it serves not only to evaluate blood sugar control but also to inform vital treatment choices and lifestyle changes. Remember, a proactive approach—including incorporating stress management techniques and utilizing community resources—can lead to better health outcomes and more tailored diabetes management strategies. By adopting a diet abundant in fiber from local produce and participating in regular physical activities, individuals can effectively manage A1C levels for diabetics and enhance their overall well-being.
Understanding How the A1C Test Works: Measurement and Interpretation
The A1C test is a straightforward procedure that measures a1c levels for diabetics and can be performed through a simple blood draw, either in a clinical setting or using home testing kits, making it accessible for regular monitoring. This test assesses the average blood glucose readings over the prior 2 to 3 months, which is important for determining a1c levels for diabetics and provides a wider viewpoint than daily glucose measurements. According to recent data, a result of 5.7% or lower is classified as normal, while values between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes.
An A1C measurement of 6.5% or greater verifies a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, highlighting the importance of monitoring a1c levels for diabetics. Notably, half of the subjects with fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels of 7 mmol/L (≤126 mg/dL) had A1C values in the 6.00–6.49% range, which highlights the correlation between these measurements and A1C levels for diabetics. A1C results may also be reported as estimated Average Glucose (eAG), which can differ from home meter readings due to the timing of blood glucose checks.
Frequent testing is essential, as it allows for effective modifications to treatment strategies and lifestyle changes, ultimately aiding in improved control of a1c levels for diabetics. By incorporating structured goal-setting techniques like SMART goals, patients can enhance their focus and motivation in managing their condition. This proactive approach, emphasized by Dr. Jason Shumard’s integrative functional medicine strategies, empowers individuals to take charge of their health, ensuring they stay engaged and informed about their progress.
Additionally, utilizing various tracking methods such as fitness apps, journals, and pedometers can further aid in monitoring progress. Research indicates that goal-setting persistence scores can positively impact performance, with scores improving from 3.4 (SD = 2.0) to 3.8 (SD = 1.9) in specific conditions, underscoring the effectiveness of structured goal-setting. The economic effect of this condition cannot be ignored; in 2022, the total estimated expenses related to diagnosed cases in the United States reached $413 billion, highlighting the necessity for effective prevention and oversight strategies.
With advancements in testing techniques, the reliability and convenience of the A1C test continue to improve, ensuring that more patients can effectively monitor their a1c levels for diabetics.
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do Your Numbers Mean?
A1C results play a crucial role in assisting individuals in handling their condition. Generally, A1C levels for diabetics that are below 7% signify good control, while values exceeding this threshold may indicate the need for modifications in diet, exercise, or medication strategies. For instance, a patient with an A1C of 8% should consider increasing physical activity, perhaps by enjoying the scenic parks and trails in San Marcos, CA, or adjusting their dietary intake with fresh produce from local farmers’ markets, which are abundant in nutrient-rich options like avocados and berries.
Diabetes educators emphasize that understanding these results is not merely about numbers; it’s about interpreting what they mean for one’s health and lifestyle. Working closely with healthcare providers to examine A1C levels for diabetics is essential for effective control of the condition. Recent findings underscore the impact of home monitoring, as intervention groups measuring their A1C levels for diabetics at home and discussing them with healthcare professionals demonstrated improved outcomes.
This collaborative method, along with lifestyle changes—such as participating in community wellness programs or practicing stress reduction techniques like yoga—can significantly improve blood sugar regulation. Furthermore, studies indicate a strong correlation between device-measured and laboratory-measured A1C levels for diabetics, with a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.83, reinforcing the reliability of A1C levels for diabetics as a key metric in diabetes management. Additionally, the use of insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) is associated with a lower incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which highlights the importance of A1C levels for diabetics in guiding treatment decisions.
Statistics indicate that the likelihood of having fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 7.0 mmol/l exceeds 90% in specific demographic combinations for individuals with screen-detected elevated A1C levels for diabetics, further highlighting the importance of A1C values. As patients interpret their A1C results and consider their A1C levels for diabetics, they can make informed decisions that lead to healthier outcomes, especially when empowered by a holistic approach to managing their condition. Numerous patients have recounted their experiences, mentioning that adopting lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, has significantly enhanced their A1C levels for diabetics and improved their overall well-being.
However, it is important to recognize the potential risks of conventional treatments for blood sugar management, which can sometimes lead to increased insulin levels and insulin resistance. This highlights the necessity for a more comprehensive approach, including functional medicine, to effectively manage type 2. Personalized guidance from healthcare experts, like Dr. Shumard, can offer customized strategies that align with personal health objectives, ensuring thorough assistance for managing the condition.
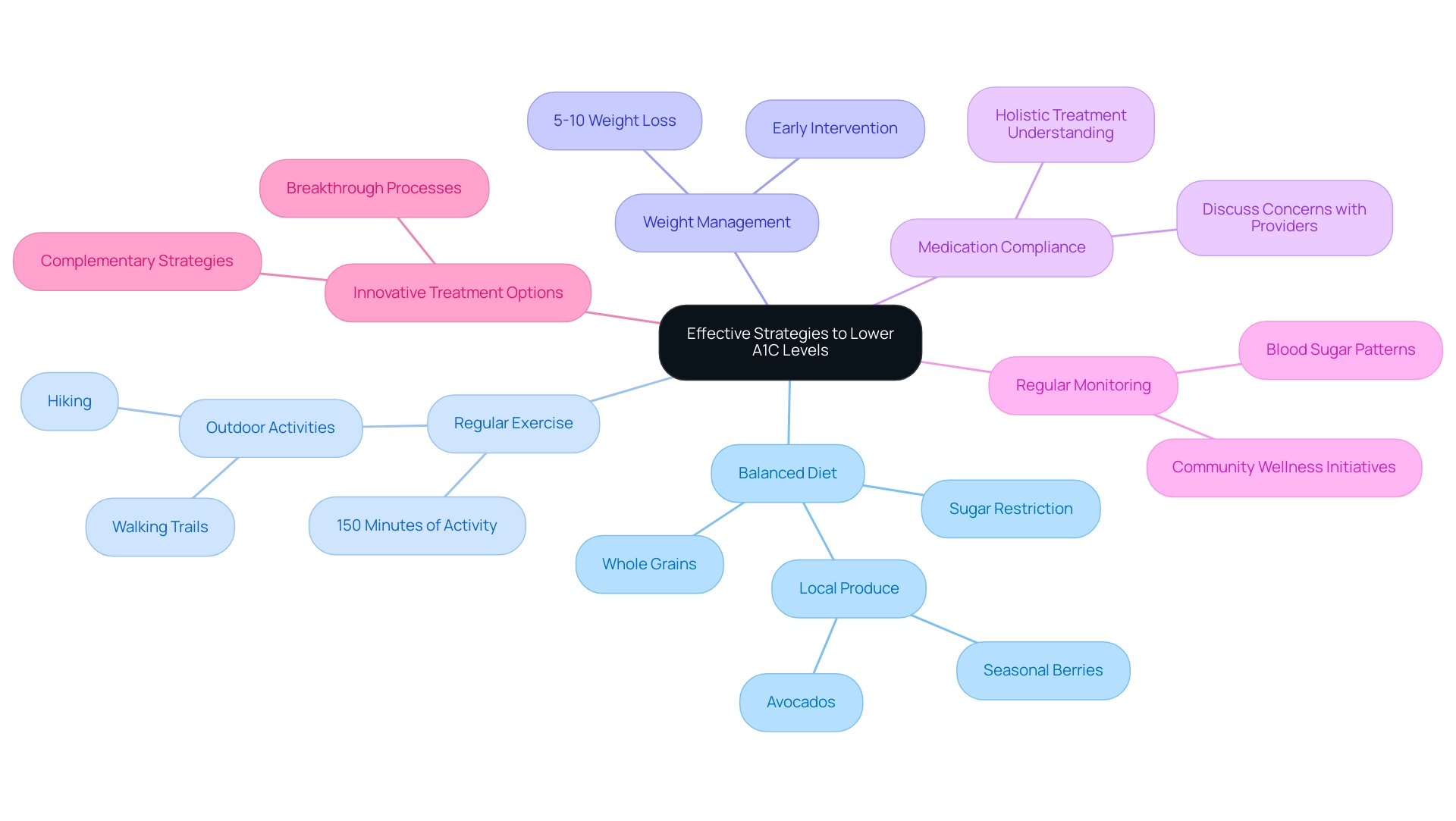
Effective Strategies to Lower Your A1C Levels
To effectively reduce a1c levels for diabetics, it is crucial to adopt a multifaceted approach that encompasses various lifestyle changes tailored to your unique needs as a type 2 diabetes patient. Remember, treatment can’t be a one-size-fits-all approach; each individual requires a strategy that considers their specific circumstances and preferences. Here are key strategies to consider:
- Balanced Diet: A diet abundant in whole grains, lean proteins, and a variety of fruits and vegetables is essential for managing a1c levels for diabetics. Incorporating local produce from San Marcos, like avocados and seasonal berries, can enhance your meals. Restricting sugar consumption and steering clear of refined carbohydrates can result in more consistent blood sugar readings. Recent studies have demonstrated that dietary impacts are significant; for instance, a higher dietary risk variability (DRV) score has been inversely linked with HbA1c values, indicating that as dietary quality enhances, A1C values can drop by approximately 0.023% for every two-point increase in the DRV score.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week—such as walking the scenic trails of Lake San Marcos or hiking at Discovery Lake—can significantly help in reducing A1C values. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for glucose regulation in individuals with type 2. The beautiful San Marcos weather and outdoor lifestyle make it easier to incorporate physical activity into your daily routine.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is essential. Research indicates that even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can lead to significant improvements in a1c levels for diabetics. This is especially crucial considering the rising occurrence of type 2 conditions in youth from diverse racial and ethnic backgrounds, as emphasized in the case study titled “Trends in Type 1 and Type 2 Conditions in Youth (2002-2018).” This highlights the need for early intervention and education on the prevention of this condition.
- Medication Compliance: Adhering to prescribed diabetes medications is critical. Patients should discuss any concerns regarding their medications with healthcare providers to ensure optimal management of their condition. Understanding how your treatment fits within a holistic approach can empower you to take charge of your health.
- Regular Monitoring: Consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels enables individuals to recognize patterns and make timely adjustments to their diet and exercise routines. This proactive strategy is key to managing blood sugar levels effectively and may prevent complications down the line. Taking part in community wellness initiatives in San Marcos can also offer assistance and resources customized for your health journey.
- Innovative Treatment Options: Consider exploring new and tested breakthrough processes for type 2 blood sugar control that can offer additional support and resources for your journey. These innovative approaches can complement traditional strategies and provide new avenues for achieving better health outcomes.
In 2024, implementing these evidence-based strategies will be essential for anyone looking to manage their a1c levels for diabetics effectively. By incorporating expert insights and local resources into daily practices, individuals can make considerable progress toward improved health control. Furthermore, it is important to note that statistical tests were two-tailed with a significance threshold of 0.05 in the studies discussed, reinforcing the reliability of the findings.
The Role of Regular Monitoring and Healthcare Collaboration in A1C Management
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and A1C tests is fundamental to effective management of A1C levels for diabetics. Under the guidance of Dr. Jason Shumard, who holds a Doctorate of Chiropractic and has extensive experience in functional medicine, patients can explore an approach that emphasizes education and personalized care, which is essential for reversing Type 2 conditions. Dr. Shumard, the owner of DrShumard.com, offers various services including:
- Diabetes education
- Lifestyle modification strategies
- Medication adherence support
The collaboration between patients and healthcare providers is crucial, enabling the assessment of individual treatment plans and necessary adjustments. This teamwork can manifest through consistent check-ups, discussions about lifestyle modifications, and the exploration of new control technologies, such as predictive continuous glucose monitoring (P-CGM) systems. These technologies not only enhance patient accountability but also provide insights into blood glucose patterns, leading to reduced medication use.
Dr. Shumard’s dedication to holistic health solutions is especially pertinent amid increasing hospital safety issues, where a shocking 7,000 incorrect medications and 80,000 infections underscore the necessity for proactive oversight. A recent systematic review highlighted that effective quality enhancement strategies significantly affect the care of individuals with diabetes, reinforcing the necessity for regular monitoring. Open communication with healthcare professionals is essential, assisting patients in staying informed and supported throughout their care journey.
Notably, in 2021, diabetes was listed on 399,401 death certificates as a contributing cause of death, illustrating the critical need for ongoing collaboration and proactive management to improve outcomes. Real-world examples consistently show that when patients interact with their healthcare teams, particularly through tailored advice from experts like Dr. Shumard, the outcomes in managing A1C levels for diabetics are more favorable, demonstrating the power of collaboration. The challenges and principles of successful team-based care implementation further emphasize the importance of shared goals, clear roles, and effective communication among team members.
A Holistic Approach to Managing A1C Levels: Lifestyle and Education
Effectively managing A1C levels for diabetics requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond medication alone. Key components include:
-
Nutrition Education: A solid understanding of how various foods influence blood sugar readings is essential. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices, which significantly contributes to maintaining A1C levels for diabetics. Recent studies have demonstrated that structured nutrition education can lead to notable enhancements in A1C levels for diabetics.
-
Physical Activity: Regular exercise is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar readings. Tailoring physical activity to fit one’s lifestyle not only enhances compliance but also promotes overall well-being. Participating in activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can significantly lower A1C levels for diabetics when integrated consistently into daily routines. For individuals beginning a walking program, it’s advantageous to:
- Assess your current fitness state
- Establish achievable goals such as a daily 10-15 minute walk
- Choose a secure and pleasant environment
- Progressively extend duration and frequency
Monitoring your progress via a journal or application can assist in sustaining motivation and acknowledging accomplishments, which is essential for effective oversight. HbA1c values were assessed at baseline, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months, highlighting the importance of regular monitoring in achieving effective management. Studies indicate that structured walking programs can enhance A1C levels for diabetics by up to 1.0% over six months, showcasing their effectiveness.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can adversely affect blood sugar levels. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga have proven effective in reducing stress and enhancing emotional balance. Incorporating these practices can lead to improved A1C levels for diabetics and better quality of life.
-
Support Networks: Establishing a community of support through groups or coaching sessions fosters motivation and provides a platform for sharing experiences. Peer support has been demonstrated to enhance compliance with health care plans, resulting in improved health outcomes. The Routine Care (RC) Program, which included regular counseling sessions with specialist nurses, serves as an example of how structured support can address individual issues related to blood sugar control.
-
Continuous Learning: Staying updated on diabetes care and the latest research is crucial for adapting treatment strategies effectively. As Olga Gortzi emphasizes, “A key strategic theme is to strengthen research-based understanding of T2DM and public health to improve the lives of young people and adults living with or at high risk of developing T2DM.” Engaging in ongoing education not only enhances one’s knowledge but also empowers individuals to take charge of their health management.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is essential for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as it serves as a key indicator of overall glucose control and long-term health outcomes. The A1C test provides a comprehensive view of average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, allowing for proactive adjustments to treatment plans. By maintaining an A1C level below the recommended threshold of 7%, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of serious health complications, emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring and informed decision-making.
Implementing effective lifestyle changes, such as:
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods
- Engaging in regular exercise
- Managing stress
plays a critical role in lowering A1C levels. Collaborating with healthcare professionals, like Dr. Jason Shumard, enhances this process by providing personalized guidance and support tailored to individual needs. The integration of innovative technologies and community resources further empowers patients to take charge of their diabetes management.
Ultimately, a holistic approach that combines education, lifestyle modifications, and healthcare collaboration is vital in achieving optimal A1C levels. By embracing these strategies, individuals can improve their health outcomes, enhance their quality of life, and navigate their diabetes journey with confidence and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test, and why is it important?
The A1C test, or hemoglobin A1C test, measures average blood sugar concentrations over the previous two to three months. It is essential for diagnosing and managing type 2 diabetes, with a result of 6.5% or above indicating diabetes.
What do the A1C test results indicate?
A result of 5.7% or lower is normal, 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, and 6.5% or greater verifies a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.
How often should A1C testing be done?
Frequent testing is important for making effective modifications to treatment strategies and lifestyle changes, aiding in improved control of A1C levels.
What lifestyle changes can help manage A1C levels?
A balanced, diabetes-friendly diet rich in local produce, regular outdoor exercise, and participation in community wellness programs can significantly enhance health outcomes.
How is the A1C test performed?
The A1C test is a simple blood draw that can be done in a clinical setting or using home testing kits, making it accessible for regular monitoring.
What are the advantages of the A1C test compared to fasting plasma glucose (FPG) tests?
While A1C testing is more expensive than FPG tests, it does not require fasting and can potentially save costs in the long run by providing a comprehensive view of blood sugar control.
How can patients effectively track their progress in managing diabetes?
Patients can utilize tracking methods such as fitness apps, journals, and pedometers, along with structured goal-setting techniques like SMART goals to enhance their focus and motivation.
What role does Dr. Jason Shumard play in diabetes management?
Dr. Jason Shumard provides personalized guidance and emphasizes integrative functional medicine strategies to empower patients in managing their health journey.
What are the economic implications of diabetes management?
In 2022, the total estimated expenses related to diagnosed diabetes cases in the United States reached $413 billion, highlighting the necessity for effective prevention and oversight strategies.
How does the A1C test impact treatment choices?
The A1C test serves to evaluate blood sugar control and informs vital treatment choices and lifestyle changes, promoting better health outcomes for individuals with diabetes.