Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management requires careful consideration of various lifestyle factors, including alcohol consumption. The interplay between alcohol and blood sugar levels can pose significant challenges for individuals living with diabetes, making it essential to understand the potential risks and benefits.
This article delves into the relationship between alcohol and diabetes, offering insights into:
- Safe drinking practices
- The types of alcoholic beverages that may be more suitable
- Strategies for monitoring blood sugar levels while enjoying social occasions
By fostering awareness and providing practical guidelines, individuals can make informed choices that support their overall health and well-being.
Understanding the Relationship Between Alcohol and Diabetes
The relationship between alcoholic drinks and diabetes is significant, as alcohol intake can considerably affect glucose levels through various mechanisms. While moderate consumption of alcoholic drinks and diabetes may cause a temporary rise in glucose levels, excessive drinking of alcoholic drinks poses a higher risk, often resulting in hypoglycemia, especially in individuals using insulin or certain medications for managing sugar levels. This is primarily due to its interference with the liver’s capacity to release glucose into the bloodstream, complicating effective blood sugar management.
It is essential for individuals managing blood sugar issues in San Marcos to understand these dynamics, as local community wellness programs, such as the San Marcos Support Group and nutrition workshops at the local community center, provide education and resources that can empower informed choices regarding alcoholic drinks and diabetes. Engaging in outdoor activities, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, and participating in community initiatives can foster a supportive environment for managing blood sugar. Additionally, holistic approaches, such as mindfulness and stress management techniques offered through local wellness centers, can further enhance health outcomes.
As noted by I.C.S., ‘more intervention studies with a longer intervention period are necessary to confirm the results,’ highlighting the ongoing need for research in this area. Furthermore, the Diabetes Prevention Program study demonstrated a reduction in HbA1c of approximately 3% after 4 years of metformin medication, underscoring the significance of effective management strategies, which may include holistic approaches addressing root causes of the condition. The existing evidence highlights the necessity for individuals with blood sugar issues to approach the consumption of alcoholic drinks and diabetes cautiously, considering its implications for overall health and glycemic control, especially within the supportive framework of their community.
Guidelines for Safe Alcohol Consumption with Diabetes
-
Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Engaging in a conversation with your healthcare team about beverage consumption is paramount. Customized guidance can assist you in comprehending how alcohol may influence your glucose levels and overall management. A key component of this dialogue involves re-examining the root causes of your condition, as individualized guidance is crucial, especially given the updated recommendations for individuals with prediabetes or a history of gestational issues, which now require a preconception evaluation to ensure optimal health outcomes. Importantly, managing your diabetes effectively can help reduce the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of the disease.
-
Choosing low-carbohydrate options is crucial for effective glucose management when selecting alcoholic drinks and diabetes. Consider options like spirits mixed with soda water or dry wines, which minimize carbohydrate intake while still allowing for social enjoyment. This aligns with the growing focus on health-conscious drinking alternatives, contributing to an overall holistic approach to your health.
-
Eat Before Drinking: Consuming a meal or snack prior to drinking can aid in stabilizing glucose levels. This practice helps reduce the effects of beverages on blood sugar variations, thus encouraging a more balanced approach to drinking and easing some anxiety regarding your health management.
Limit Consumption: Adhering to moderate drinking guidelines is crucial. The general recommendation is to limit intake to one drink per day for women and two for men. This moderation is particularly important for individuals managing diabetes to avoid potential complications associated with excessive beverage consumption. Notably, binge drinking affects approximately half of adolescents and adults who drink, underscoring the need for caution and responsible drinking.
-
Stay Hydrated: It is vital to maintain hydration while consuming beverages. Alternating alcoholic beverages with water can help prevent dehydration and assist in regulating blood sugar levels. By doing so, you contribute to a safer drinking experience and support overall health, aligning with a holistic approach to wellness.
As part of these guidelines, healthcare professionals are encouraged to utilize practical tools such as a standard drink chart to help patients estimate their beverage consumption accurately. This approach aims to reduce alcohol-related health risks and improve patient understanding of safe drinking practices. These guidelines are supported by healthcare professionals, including Aaron White, a Senior Scientific Advisor to the NIAAA Director, who highlights the significance of responsible beverage consumption in the context of health management.
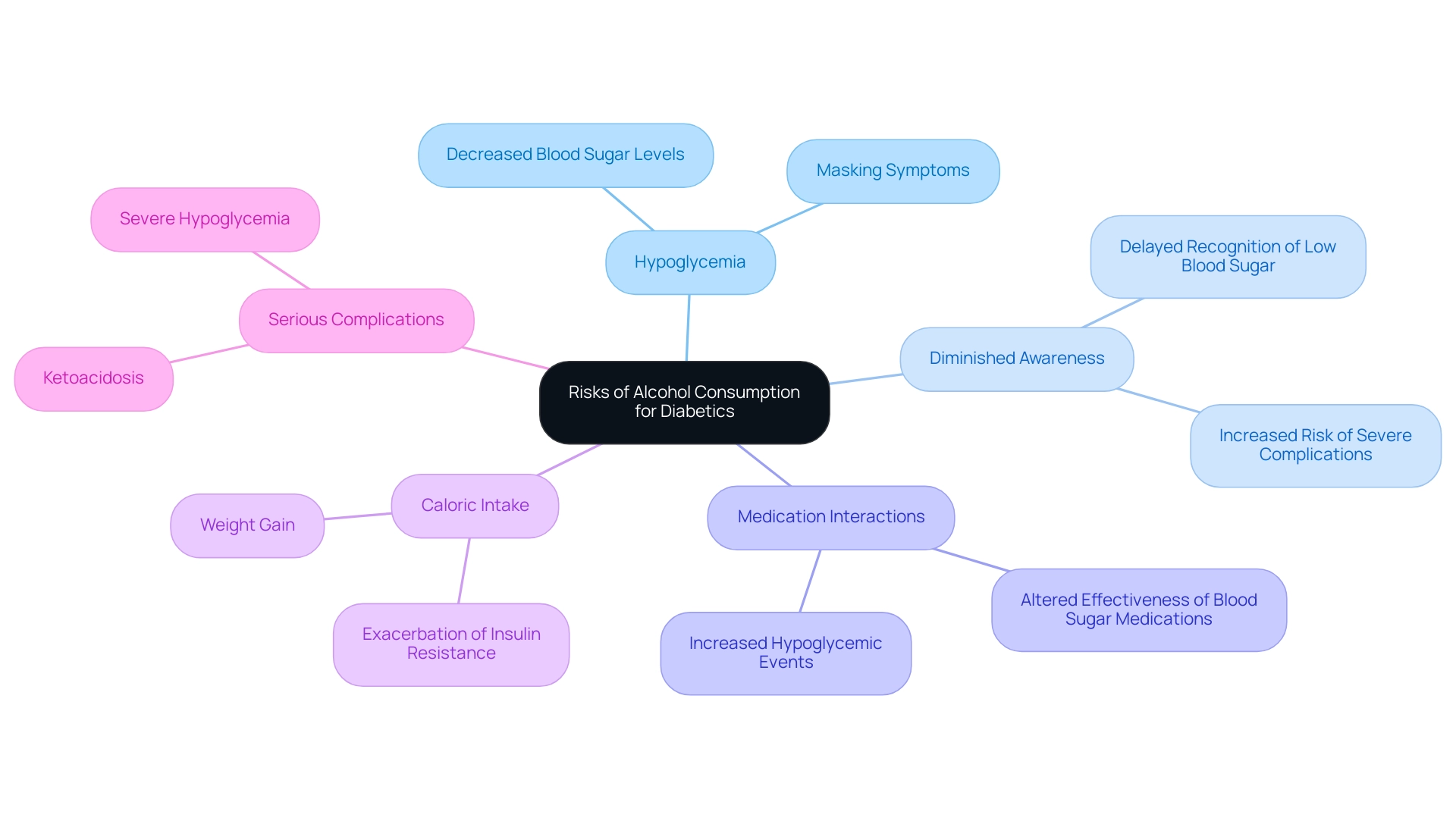
Risks of Alcohol Consumption for Diabetics
Individuals with diabetes must exercise caution when consuming alcoholic drinks and diabetes-related beverages due to several significant risks that can adversely affect their health management. These include:
- Hypoglycemia: Alcohol consumption can lead to decreased blood sugar levels, resulting in hypoglycemia if blood glucose is not monitored diligently. This risk is especially crucial considering that alcoholic drinks and diabetes can be impacted by ethanol, which hinders gluconeogenesis, the body’s process of generating glucose, thereby increasing the possibility of dangerously low glucose levels.
The consumption of alcoholic drinks and diabetes can lead to decreased awareness of symptoms, as alcohol can mask signs of hypoglycemia, such as dizziness, sweating, and confusion. This diminished awareness can delay recognition of low blood sugar, potentially resulting in severe complications associated with alcoholic drinks and diabetes. Interactions with medications can arise from alcoholic drinks and diabetes, as alcohol may negatively interact with blood sugar medications, altering their effectiveness and heightening the risk of adverse effects.
For instance, certain medications used to stimulate insulin production can lead to increased hypoglycemic events when combined with alcoholic drinks and diabetes. Increased caloric intake from alcoholic drinks and diabetes can lead to high levels of calories that, if unaccounted for, can contribute to weight gain and exacerbate insulin resistance. This is particularly relevant in managing type 2 diabetes, especially concerning the impact of alcoholic drinks and diabetes on weight control, which is crucial for effective treatment.
- Serious Complications: Excessive consumption of alcoholic drinks and diabetes can result in severe complications like ketoacidosis and hypoglycemia, which are crucial for individuals managing blood sugar levels. The consequences of hypoglycemia occurrences linked to alcoholic drinks and diabetes in blood sugar management highlight the significance of comprehending these dangers. For example, a case study named ‘Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes in Aboriginal Cohort’ emphasized that individuals who consumed alcoholic drinks and diabetes management beverages without proper blood glucose monitoring often encountered severe hypoglycemic incidents, requiring urgent medical care.
Dr. Mary Ann Emanuele, a professor in the Department of Medicine at Loyola University, emphasizes that understanding these interactions is vital for maintaining optimal health in diabetic patients. Therefore, awareness of the interactions between alcoholic drinks and diabetes is essential for effective health management.
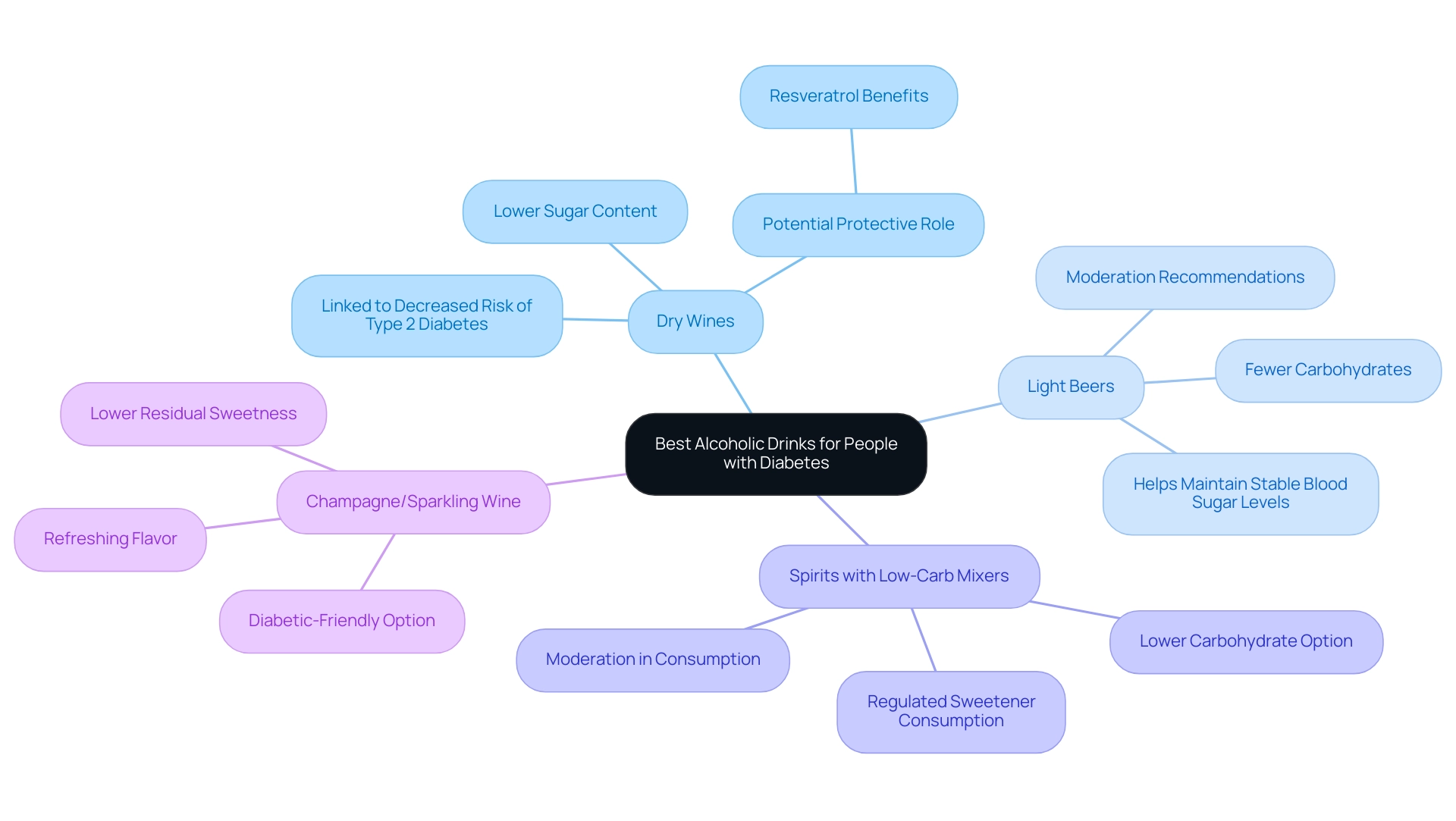
Best Alcoholic Drinks for People with Diabetes
- Dry Wines: Both red and white dry wines typically contain less sugar than their sweeter counterparts, making them a favorable choice for individuals with blood sugar concerns. Research indicates that moderate wine consumption could be linked to a decreased risk of type 2 conditions, highlighting the relationship between alcoholic drinks and diabetes, possibly due to beneficial compounds such as resveratrol. A meta-analysis titled ‘Meta-Analysis of Alcoholic Drinks and Diabetes’ found that wine consumption is linked to a significant decrease in the risk of type 2 diabetes, highlighting the potential protective role of alcoholic drinks and diabetes.
- Light Beers: Light beers typically contain fewer carbohydrates than regular beers, which can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. This makes them a wise option for those managing their condition related to alcoholic drinks and diabetes while enjoying an occasional drink. Furthermore, consuming spirits in moderation, specifically between 7–15 g/day, has shown a peak risk reduction of 5% for type 2 conditions, making it an interesting option for some.
- Spirits with Low-Carb Mixers: Spirits like vodka, gin, or whiskey combined with low-carb mixers such as soda water or tonic water provide a lower carbohydrate option. These combinations enable a more regulated consumption of sweeteners while still enjoying a variety of flavors. Experts recommend moderation in the consumption of alcoholic drinks and diabetes management goals.
- Champagne or Sparkling Wine: These beverages, especially brut varieties, tend to have lower residual sweetness. Their refreshing flavor combined with lowered sweetener content makes them a popular choice among those seeking diabetic-friendly options.
As noted by Xiuling Wang from the Department of Medical Microbiology, School of Medicine, Wuhan University, “moderate consumption of alcoholic drinks and diabetes management goals can align, particularly when mindful of overall carbohydrate intake.
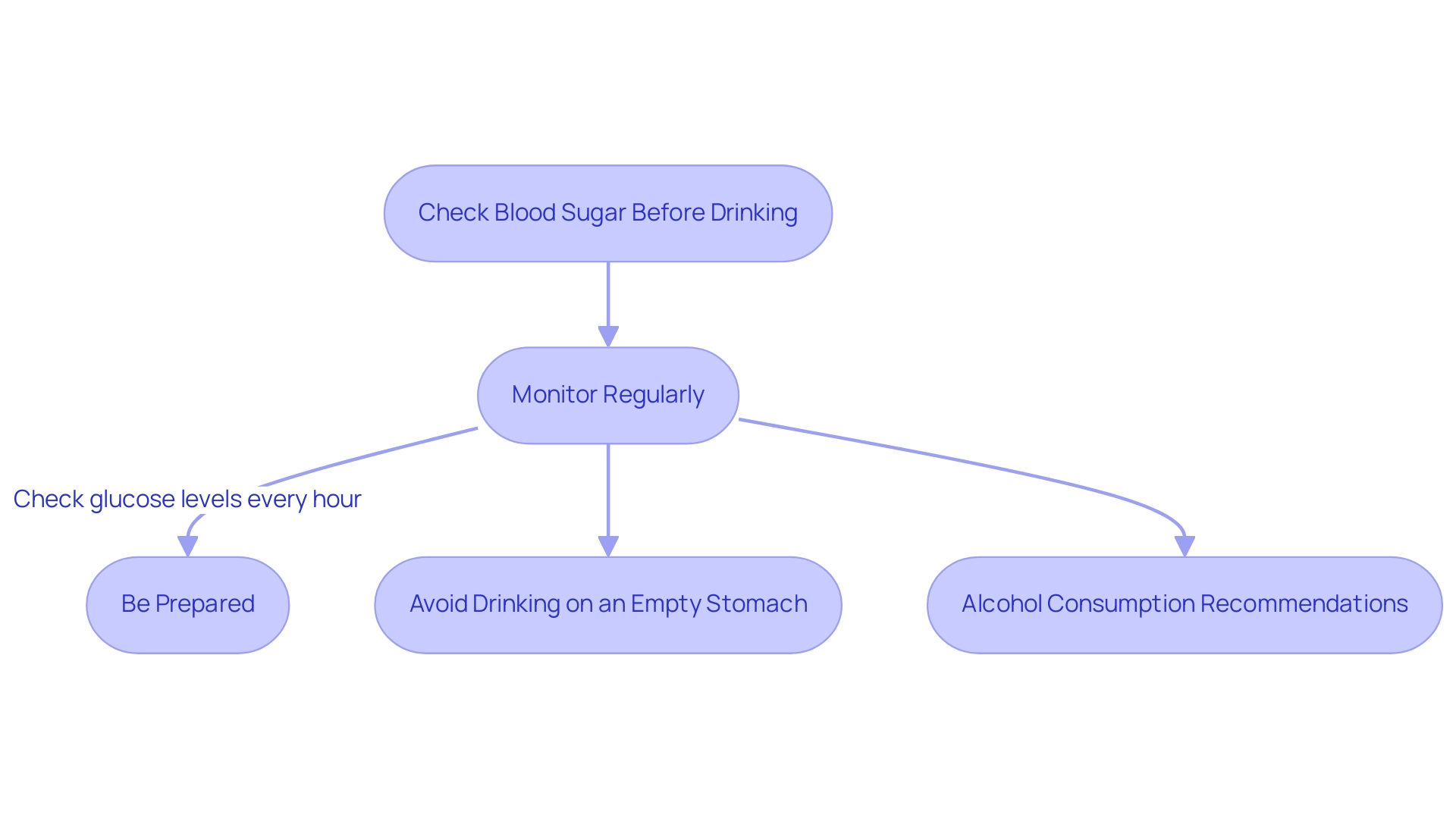
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels While Drinking
-
Check Blood Sugar Before Drinking: It is imperative to measure your blood sugar levels prior to consuming any alcoholic drinks and diabetes-related beverages. This initial measurement establishes a baseline, allowing you to monitor how beverages affect your glycemic control.
-
Monitor Regularly: Consistent observation is crucial during beverage consumption. It is advised to monitor your glucose levels every hour to identify any major variations, as alcohol can influence glucose levels unpredictably. In fact, consuming more than three alcoholic drinks and diabetes can result in elevated glucose and A1C levels, making it crucial to remain vigilant.
- Be Prepared: Always carry fast-acting glucose or snacks, such as glucose tablets or a small piece of candy, to quickly address potential hypoglycemia. Being ready guarantees that you can react efficiently if your glucose levels decrease unexpectedly.
- Avoid Drinking on an Empty Stomach: Consuming alcoholic drinks and diabetes on an empty stomach can lead to unstable blood sugar levels. Ensure that you have eaten beforehand to help maintain stable glucose levels throughout the drinking period. The American Diabetes Association recommends that women should restrict their consumption of alcoholic drinks and diabetes-related risks to one beverage daily, while men should limit their intake to two alcoholic drinks daily to manage blood sugar effectively.
-
Learn More: To further enhance your understanding of blood sugar management while consuming beverages, consider engaging with quizzes such as ‘Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar.’ Additionally, case studies like ‘Glycemic Care in Clinical Settings’ provide valuable insights into effective blood sugar management practices in clinical settings.
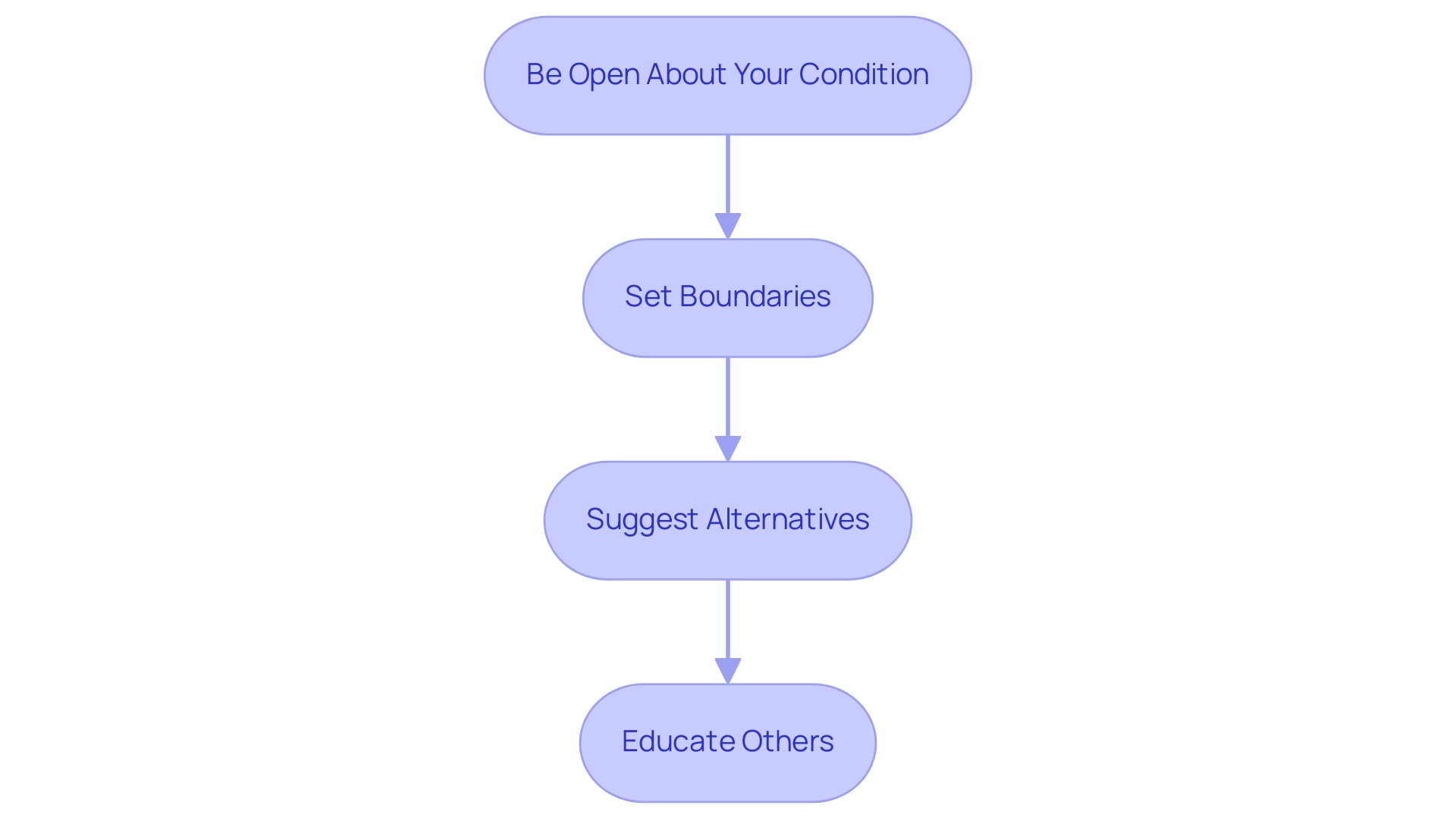
Communicating with Friends and Family About Alcohol
- Be Open About Your Condition: It is essential to communicate your health status to friends and family, explaining how it affects your beverage intake. This transparency can foster a supportive environment, promoting understanding among your social circle. As highlighted by Katharine D Barnard-Kelly, online resources are widely used by individuals with blood sugar issues to obtain information about controlling their consumption of alcoholic drinks and diabetes. Participating in local community wellness initiatives in San Marcos, such as health education workshops, can further enhance this understanding.
- Set Boundaries: Clearly outline your drinking limits to your friends and family. Do not hesitate to seek their assistance in adhering to these boundaries, which can be crucial for maintaining your health. Establishing these limits early can prevent misunderstandings in social situations, especially during community gatherings that promote healthy lifestyles, which include discussions about alcoholic drinks and diabetes while participating in outdoor activities in local parks.
- Suggest Alternatives: Propose non-alcoholic beverages for social events. By introducing enjoyable alternatives, you can partake in social interactions without compromising your health, especially regarding alcoholic drinks and diabetes, while also encouraging others to consider these options. Utilizing local farmers’ markets for fresh ingredients can help create delicious mocktails that align with your dietary needs.
- Educate Others: Take the initiative to share valuable information about beverage use and health conditions within your social network. By fostering awareness and understanding, you can enhance the support system around you, making social gatherings more enjoyable and safe. The findings from recent studies indicate that effective communication strategies significantly contribute to better management of the condition, aligning with patient preferences for engagement. Furthermore, think about creating a personal action plan customized to your situation, which can assist you in proactively managing your beverage intake alongside your health care. Additionally, as you gather information, utilizing tools to organize this knowledge can streamline your approach to managing both alcoholic drinks and diabetes, while also tapping into community resources available in San Marcos, such as local fitness classes and outdoor group activities.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between alcohol and diabetes is crucial for effective management of the condition. The article highlights that while moderate alcohol consumption can be manageable, excessive drinking poses significant risks, including hypoglycemia and potential interactions with diabetes medications. It is vital for individuals with diabetes to engage in open discussions with healthcare providers to tailor alcohol consumption strategies that align with their health needs.
Adopting safe drinking practices, such as:
- Choosing low-carbohydrate beverages
- Eating before drinking
- Adhering to moderation guidelines
can help mitigate the risks associated with alcohol. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels during social occasions is essential to maintain glycemic control and prevent complications. Furthermore, communicating openly with friends and family about diabetes can foster a supportive environment, encouraging responsible drinking habits and the exploration of non-alcoholic alternatives.
Ultimately, informed choices around alcohol consumption can contribute to better health outcomes for individuals with diabetes. By understanding the interplay between alcohol and blood sugar levels and implementing practical strategies, individuals can enjoy social occasions while prioritizing their health and well-being. Emphasizing awareness and proactive management will empower those living with diabetes to navigate their lifestyle choices confidently.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does alcohol consumption affect glucose levels in individuals with diabetes?
Alcohol intake can significantly affect glucose levels, potentially causing a temporary rise in glucose levels with moderate consumption. However, excessive drinking poses a higher risk of hypoglycemia, especially in those using insulin or certain medications, due to its interference with the liver’s ability to release glucose into the bloodstream.
What community resources are available for individuals managing diabetes in San Marcos?
Community wellness programs, such as the San Marcos Support Group and nutrition workshops at the local community center, provide education and resources. Engaging in outdoor activities, focusing on a balanced diet, and participating in community initiatives can support blood sugar management.
What holistic approaches can enhance health outcomes for individuals with diabetes?
Holistic approaches include mindfulness and stress management techniques offered through local wellness centers, which can further improve health outcomes for individuals managing diabetes.
What should individuals with diabetes discuss with their healthcare provider regarding alcohol?
Individuals should engage in conversations about beverage consumption to understand how alcohol may influence glucose levels and overall management. This discussion should also involve examining the root causes of their condition and personalized guidance.
What are some recommended alcoholic drink options for better glucose management?
Choosing low-carbohydrate options, such as spirits mixed with soda water or dry wines, is crucial for effective glucose management while still allowing for social enjoyment.
Why is it important to eat before drinking alcohol?
Consuming a meal or snack prior to drinking can help stabilize glucose levels, reducing the effects of beverages on blood sugar variations and promoting a more balanced approach to drinking.
What are the guidelines for moderate alcohol consumption for individuals with diabetes?
The general recommendation is to limit intake to one drink per day for women and two for men. This moderation is essential to avoid complications associated with excessive drinking.
How can individuals stay hydrated while consuming alcohol?
Alternating alcoholic beverages with water is vital to prevent dehydration and assist in regulating blood sugar levels, contributing to a safer drinking experience.
What tools can healthcare professionals use to help patients manage alcohol consumption?
Healthcare professionals can utilize practical tools like a standard drink chart to help patients estimate their beverage consumption accurately and reduce alcohol-related health risks.