Overview
The ADA dietary guidelines promote better health through a comprehensive approach to nutrition that emphasizes whole foods, carbohydrate control, and balanced meal planning, which are essential for managing blood sugar levels effectively. The article supports this by detailing key principles such as nutrient-dense food choices, portion control, and the importance of hydration, illustrating how these practices can empower individuals to take charge of their health and alleviate concerns related to their condition.
Introduction
Managing diabetes effectively requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses nutrition, physical activity, and continuous education. Central to this strategy are the American Diabetes Association (ADA) dietary guidelines, which advocate for a balanced diet rich in whole foods and nutrient-dense options. These guidelines not only aim to control blood sugar levels but also address the underlying factors contributing to diabetes, empowering individuals to take charge of their health.
From understanding the types of carbohydrates to implementing meal planning and creating a supportive network, this article explores essential strategies for navigating the complexities of diabetes management. By integrating these principles, individuals can cultivate a sustainable lifestyle that promotes both physical and mental well-being, ultimately enhancing their quality of life while managing this chronic condition.
Foundations of ADA Dietary Guidelines: Nutrition for Health
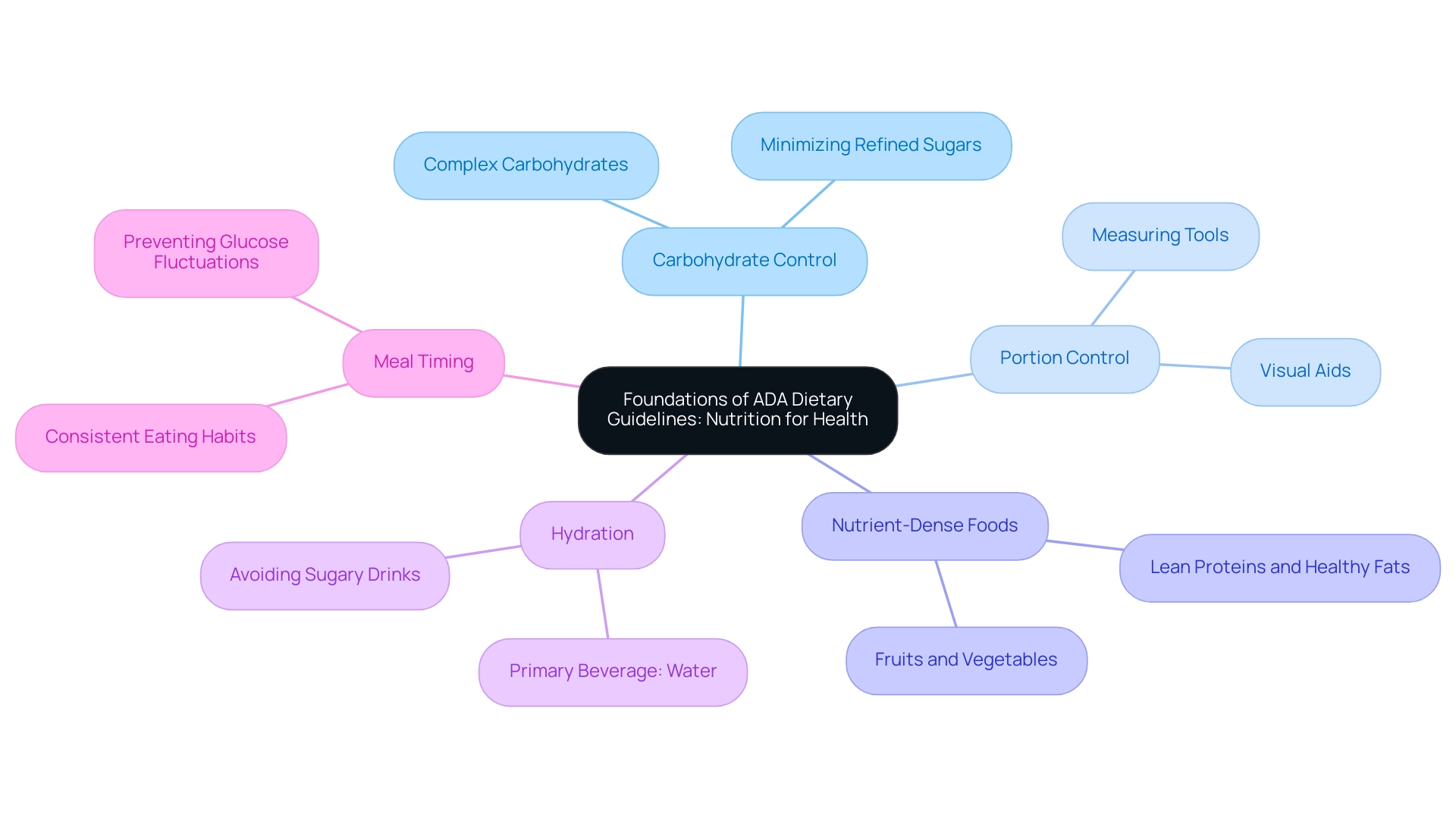
The ADA dietary guidelines promote a comprehensive and balanced approach to nutrition, emphasizing the importance of whole foods in effectively managing blood sugar levels. These guidelines align with a holistic approach to reversing the condition, as they focus on addressing root causes and empowering patient well-being, which can help alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications of the illness. Key principles include:
- Carbohydrate Control: A thorough comprehension of carbohydrate varieties and servings is essential for dealing with blood sugar issues. Emphasizing complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables while minimizing refined sugars can significantly improve glycemic control. Efficient carbohydrate handling is associated with improved overall wellness results for individuals with blood sugar issues, emphasizing the idea that tackling dietary origins can reduce complications related to the condition.
- Portion Control: Controlling portion sizes is essential for maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Employing measuring tools or visual aids can simplify this process, allowing patients to make informed dietary choices. Research indicates that following portion control guidelines can result in better glycemic status, especially for individuals facing weight challenges, disputing the belief that strict dieting is the sole answer to managing blood sugar levels.
- Nutrient-Dense Foods: Individuals should prioritize foods that are rich in nutrients yet low in calories, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These nutrient-rich selections not only promote overall well-being but also serve a crucial function in weight control, essential for blood sugar care and emphasizing the significance of comprehensive nutrition.
- Hydration: Sufficient hydration is essential for well-being. Water should be the primary beverage of choice, while sugary drinks must be avoided to prevent spikes in blood glucose levels. Hydration has been demonstrated to positively influence metabolic well-being, making it a crucial element of daily nutrition within a comprehensive approach to blood sugar control.
- Meal Timing: Regular meal timing helps regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Maintaining consistent eating habits throughout the day is important, as it aids in preventing extreme fluctuations in glucose levels. The ADA dietary guidelines suggest that individuals with blood sugar issues strive to create a routine that meets their dietary requirements, with expert views emphasizing the advantages of organized meal timing for overall management.
In conclusion, the ADA dietary guidelines provide a strong framework for those managing blood sugar levels, highlighting the importance of whole foods and balanced nutrition as essential components in achieving optimal well-being.
Regular evaluation of glycemic control, as demonstrated in the case study on glycemic management, is essential for effective care. Patients meeting treatment goals are advised to assess their glycemic status at least twice a year. This comprehensive approach not only addresses the immediate needs of Type 2 patients but also empowers them to take control of their health journey, including re-examining the source of their condition to enhance their overall well-being.
Implementing ADA Guidelines: Meal Planning and Dietary Strategies
To effectively implement the ADA dietary guidelines, consider the following comprehensive meal planning and dietary strategies:
- Create a Balanced Plate: Utilize the plate method to visually divide your plate into sections for non-starchy vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. This approach simplifies meal preparation and promotes balanced nutrition, which is crucial for managing diabetes.
- Plan Ahead: Develop a weekly meal plan that encompasses a diverse array of foods from all food groups. This proactive strategy not only helps to prevent impulsive eating but also promotes a balanced diet that adheres to the ADA dietary guidelines.
- Incorporate Healthy Snacks: Include nutritious snacks such as nuts, yogurt, or fresh fruit between meals to sustain energy levels and mitigate blood sugar spikes. Recent studies indicate that food insecure participants have shown greater improvements in HbA1c levels (–0.12) compared to food secure participants (+0.39), highlighting the importance of consistent and healthy snack options.
- Read Nutrition Labels: Mastering the skill of reading nutrition labels is essential for making informed food choices. Focus on understanding serving sizes, carbohydrate content, and the presence of added sugars to guide your eating habits effectively.
- Adjust Recipes: Transform your favorite recipes to enhance their healthfulness by substituting ingredients or reducing portion sizes. For example, opt for whole grain pasta in place of white pasta, or replace heavy sauces with lighter, tomato-based options that are more suitable for a diabetes-friendly diet.
- Stay Flexible: While meticulous planning is vital, maintaining adaptability in accordance with ADA dietary guidelines is equally important. Life’s unpredictability necessitates having a variety of quick and healthy meal options readily available, ensuring adherence to the ADA dietary guidelines even amid changing circumstances.
Expert insights suggest that confidence in cooking and meal preparation can significantly influence dietary choices; however, barriers such as time and energy must be addressed to foster healthier eating habits. Techniques to address these obstacles might involve preparing meals on weekends or using rapid cooking methods to conserve time during hectic weekdays.
By applying these techniques, individuals dealing with blood sugar management can establish a sustainable eating routine that meets both their nutritional requirements and lifestyle choices.
Understanding Carbohydrates: Types and Impact
Carbohydrates are primarily categorized into two types, each with distinct implications for blood glucose management:
- Simple Carbohydrates: These sugars are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, causing swift spikes in blood glucose levels. Common sources include candy, soda, and certain fruits. Due to their potential to disrupt blood sugar balance, it is advisable to minimize their consumption.
- Complex Carbohydrates: In contrast, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains like quinoa and brown rice, legumes, and vegetables, undergo slower digestion, providing a more consistent energy release. According to ADA dietary guidelines, incorporating a higher proportion of complex carbohydrates into meals can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Whole grains, in particular, are rich in fiber, which aids in slowing glucose absorption and improving overall blood sugar control as recommended by ADA dietary guidelines. San Marcos restaurants are increasingly incorporating these healthier grains into their menus, offering delicious options that support blood sugar control and provide lasting energy.
Glycemic Index (GI): Comprehending the glycemic index of foods is essential for controlling blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI are recognized to cause a gradual rise in blood sugar levels, making them more appropriate for those managing blood sugar. Notable examples of low-GI foods include oats, barley, and sweet potatoes.
Recent studies have emphasized the significance of choosing low-GI options according to ADA dietary guidelines to reduce postprandial blood glucose variations, thereby aiding effective condition oversight.
In the context of prevalence, the incidence rate of diagnosed conditions among Hispanic adults is 6.1 per 1,000, highlighting the importance of effective dietary management in this population. Furthermore, a study titled “Effect Modification by Subgroups” found significant positive associations between starch intake and the risk of type 2 conditions across various subgroups, indicating that increased starch consumption is linked to a higher risk of developing the issue. As pointed out by S.S.-B., “careful dietary choices are essential for managing the condition effectively,” reinforcing the need for individuals to adhere to the ADA dietary guidelines and focus on carbohydrate quality in their diets.
Transformative patient success stories, such as that of M.L., illustrate how personalized care and dietary changes can lead to significant health improvements. M.L. experienced a remarkable transformation, losing 55 lbs and reducing his A1C from 9.1 to 5.7 after adopting a diet rich in whole grains and other healthy foods.
His fasting glucose levels decreased from 133 to 85, and his regular doctor has reduced his blood pressure medications by fifty percent, illustrating the significant effect of dietary choices on controlling blood sugar.
The Role of Physical Activity in Diabetes Management
Engaging in regular physical activity presents a multitude of benefits for individuals managing diabetes, which include:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Regular exercise enhances the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively, leading to optimal blood glucose control. Recent findings indicate that incorporating physical activity significantly improves insulin sensitivity, a crucial factor in managing blood sugar levels. This holistic approach complements our philosophy at the Integrative Wellness Center, where we emphasize addressing the root causes of this condition to empower patient health.
- Weight Management: Consistent physical activity supports the maintenance of a healthy weight, which is vital for reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. A case study titled “Heart Disease Risk Reduction in Women with Diabetes” highlights that women with this condition who engage in regular moderate to vigorous exercise have a 40% lower risk of developing heart disease compared to those who do not exercise, even after adjusting for other risk factors. This highlights the significance of exercise in weight control and overall well-being, demonstrating our dedication to a holistic strategy for reversing metabolic conditions.
- Enhanced Mental Health: Physical activity is correlated with improved mood and reduced stress levels, contributing positively to overall mental well-being. Consistent participation in physical activity not only enhances bodily well-being but also strengthens mental toughness, thus reducing worries associated with possible issues arising from blood sugar conditions. This aligns with our belief in treating the whole person, not just the symptoms of the condition.
- Types of Exercise: It is recommended to incorporate a blend of aerobic activities—such as walking, jogging, or swimming—and strength training exercises using weights or resistance bands. The ADA dietary guidelines recommend aiming for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly, distributed over several days to maximize wellness benefits.
Integrating physical activity into strategies for managing blood sugar is essential for cardiometabolic well-being, as recent reports highlight. As fitness specialists emphasize, the role of physical activity in enhancing insulin sensitivity is essential for effective health control. This holistic approach aligns with evidence-based practices in wellness oversight, akin to the insights provided by Southern KW regarding the significance of comprehensive strategies in addressing well-being conditions.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Diet
Monitoring your dietary intake according to the ADA dietary guidelines and its effect on health is essential for effective management, particularly within a holistic framework aimed at addressing root causes and empowering patient health. This involves several key practices:
-
Keeping a Food Diary: Documenting your daily food intake is a valuable strategy for identifying patterns that influence blood sugar levels.
Research indicates that effective use of food diaries can significantly aid in managing blood sugar levels, alleviating anxiety over potential complications. By re-examining the source of your condition through this practice, you can better understand the underlying factors affecting your health.
-
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: Consistent monitoring of your blood glucose levels is crucial, following the frequency recommended by your healthcare provider.
This practice enables you to understand how different foods affect your blood sugar, fostering informed dietary choices that align with ADA dietary guidelines and reducing worry about complications. The knowledge acquired can assist you in alleviating the anxiety that often comes with managing this condition.
-
Adjusting Portions and Choices: Based on your observations from monitoring, be prepared to modify portion sizes or substitute foods to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
Studies have shown that participants who demonstrated knowledge of meal preparation techniques and portion control experienced better glycaemic management. For instance, the mean baseline BMI for consistent trackers was 34.2 with a standard deviation of 7.6, underscoring the significance of mindful eating practices.
-
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals: Engaging in regular discussions with your healthcare team can yield valuable insights and tailored advice for your dietary adjustments.
Research by Inada et al. highlights the importance of personalized dietary strategies, noting that there was no significant change in HbA1c, total caloric intake, or body weight without such strategies. This strengthens the notion that knowledgeable dietary changes are essential for effective management of blood sugar levels.
These combined practices not only improve your awareness of food’s effect on your health but also enable you to make informed decisions that adhere to ADA dietary guidelines, promoting better health results. By adopting this holistic approach, which includes re-examining the source of your condition, you can actively participate in managing your health and reducing the anxiety associated with its complications.
Building a Support Network for Diabetes Management
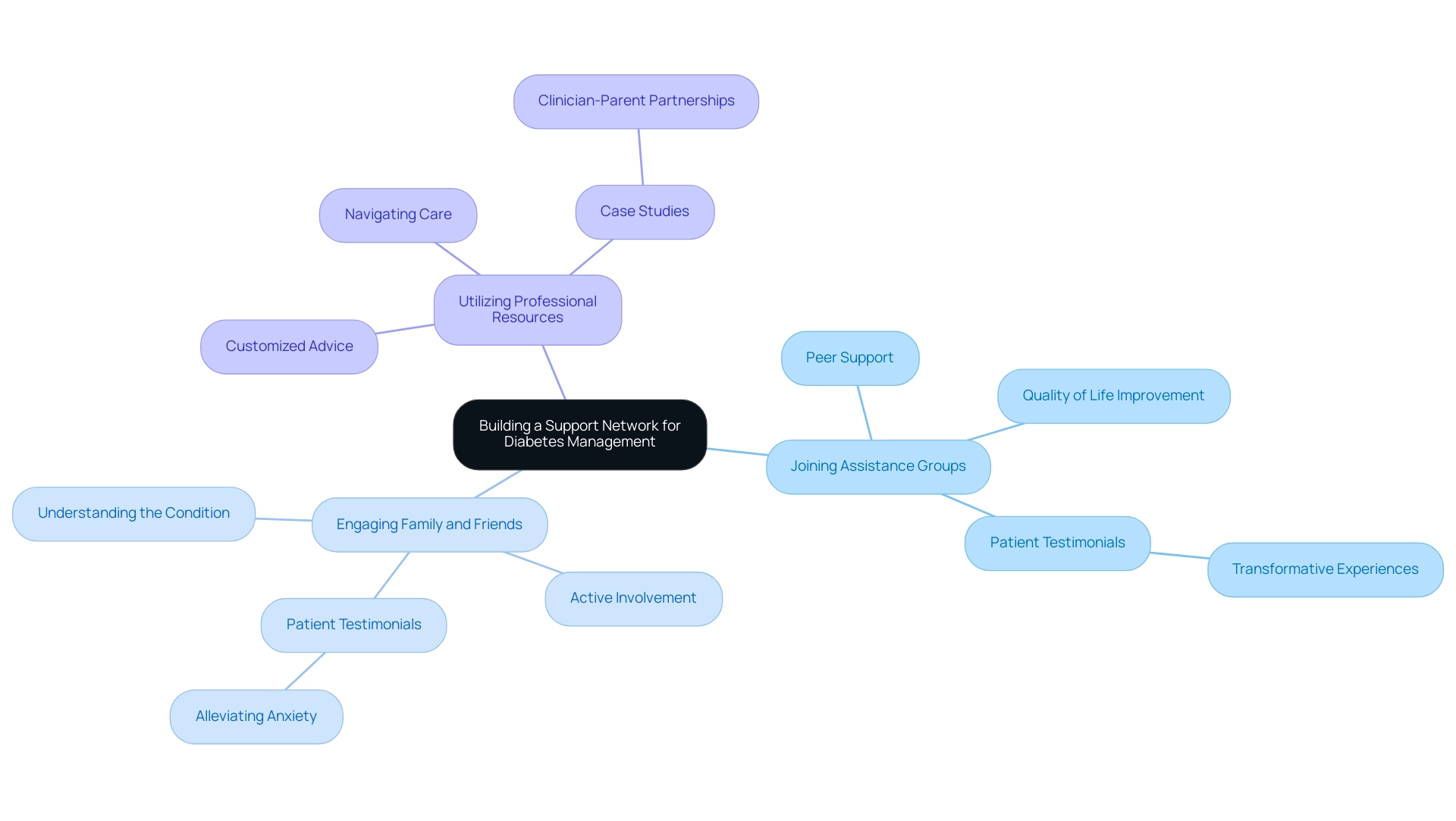
Creating a strong assistance network is crucial for efficient management of the condition and can be approached through several strategies:
- Joining Assistance Groups: Participating in diabetes-related assistance groups, whether face-to-face or virtual, provides a chance to exchange experiences and tactics with others encountering similar difficulties. Research indicates that such peer interactions significantly enhance quality of life, self-management, and self-efficacy among individuals with Type 2. For example, a telecare exploratory RCT published in Patient Educ Couns in 2009 indicated that a telephone peer-delivered intervention for motivation and assistance resulted in significant enhancements in HbA1c levels, showcasing its influential role in managing health care related to blood sugar. Furthermore, patient testimonials emphasize transformative experiences at the Integrative Wellness Center, where group meetings cultivate an atmosphere of encouragement and collective achievement in reversing related health complications. One patient shared, ‘The support I received from my group helped me manage my condition better and reduced my fears about complications.’
- Engaging Family and Friends: Involving loved ones in your diabetes management journey can be invaluable. Informing family members about the condition not only promotes understanding but also encourages their active involvement in your wellness decisions. Expert notes, ‘A narrative synthesis of the results showed that peer assistance significantly improved QOL, self-management, self-efficacy, and HbA1c control in patients with T2DM, but had no significant effect on depression,’ signifying the importance of having a helpful network that includes family. Testimonials from patients illustrate how family involvement can alleviate anxiety over complications and empower individuals to take charge of their health. One patient remarked, ‘Having my family involved has alleviated my concerns about complications; they comprehend what I’m experiencing and back my decisions.’
- Utilizing Professional Resources: Working with healthcare experts like dietitians, educators, or coaches who focus on blood sugar control and follow ADA dietary guidelines can offer customized advice and assistance. These specialists are prepared to assist in navigating the intricacies of care, ensuring that your plan is both effective and sustainable. The comprehensive method adopted by the Integrative Wellness Center aims to tackle the underlying factors of the condition by incorporating ADA dietary guidelines, empowering patients through education and guidance. Moreover, drawing comparisons from the case study titled ‘Building clinician-parent partnerships to enhance care for chronically critically ill children,’ highlights the significance of partnerships in health care and the necessity for collaboration between patients and their support networks. By integrating these strategies, you can create a supportive environment that enhances your ability to manage your condition effectively, ultimately leading to a more empowered and anxiety-free life.
Staying Informed: Resources and Continued Learning
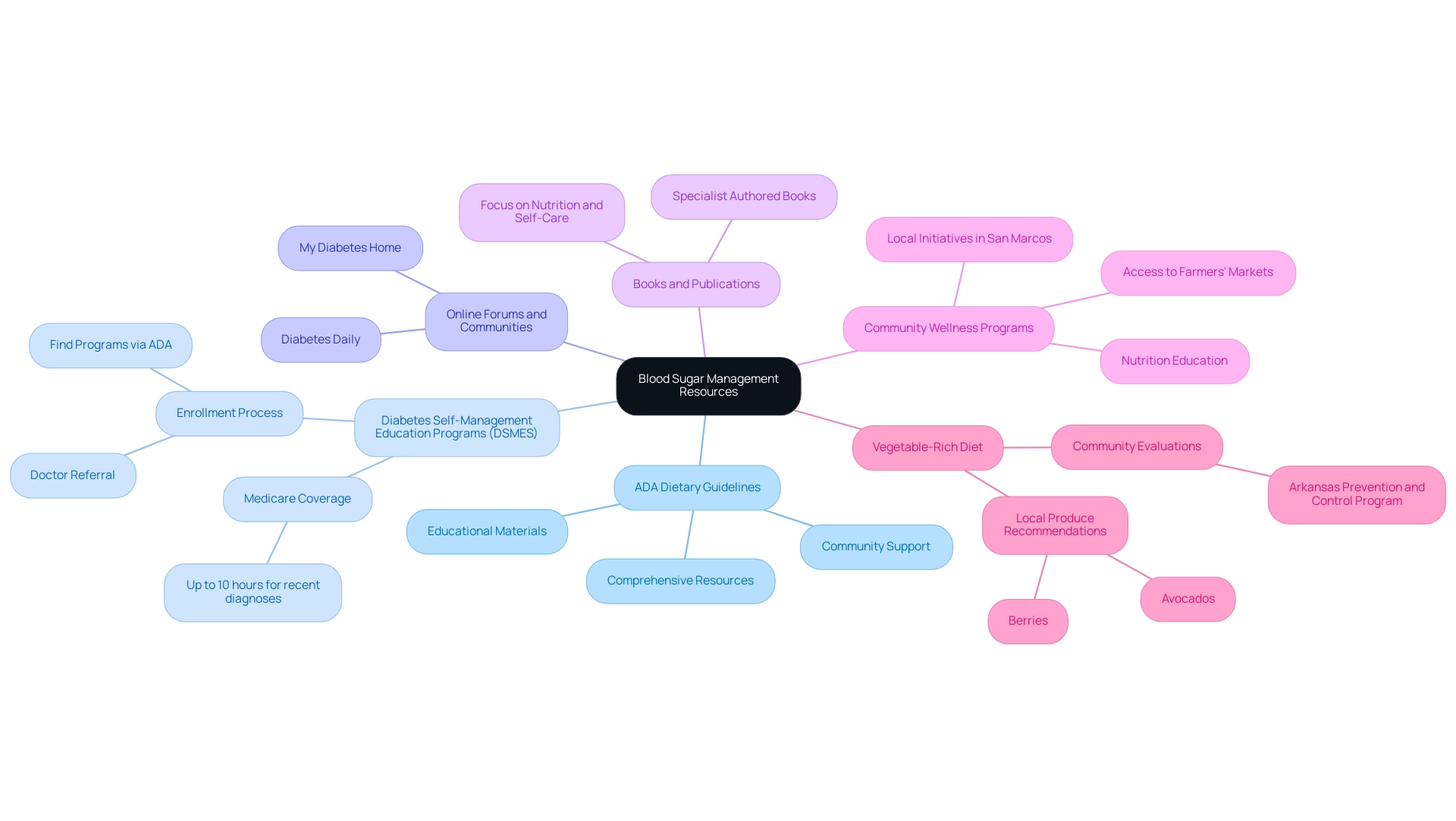
Staying informed about blood sugar management is crucial for effective self-care. Here are key resources to consider:
-
The ADA dietary guidelines provide a wealth of comprehensive resources, educational materials, and community support tailored for individuals managing this condition.
Their resources aim to improve understanding and self-management of the condition.
-
Diabetes Self-Management Education Programs (DSMES): Many hospitals and clinics offer DSMES, which are customized educational programs aimed at empowering individuals in managing their condition through nutrition and lifestyle changes. Medicare covers up to 10 hours of these programs for patients diagnosed within the last year, highlighting their accessibility and importance.
To enroll in DSMES, individuals should ask their doctor for a referral or visit the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists or the American Diabetes Association to find a program nearby that follows ADA dietary guidelines.
-
Online Forums and Communities: Platforms like Diabetes Daily and My Diabetes Home facilitate connections among individuals living with the condition, allowing them to share experiences and access a treasure trove of information about effective management strategies.
-
Books and Publications: Seek out books authored by specialists in blood sugar management that focus on nutrition, exercise, and self-care.
Consistently interacting with reliable sources improves your understanding and offers practical methods for effectively managing the condition.
-
Community Wellness Programs in San Marcos: Participating in local wellness initiatives, such as those provided at regional clinics and community groups, can offer extra assistance and resources customized for managing blood sugar levels.
These programs often incorporate outdoor activities, nutrition education focusing on local produce, and community engagement to foster a supportive environment.
Additionally, visiting local farmers’ markets can help you access fresh, nutritious options that are beneficial for your diet.
-
Vegetable-Rich Diet: Emphasizing vegetable-rich dishes is fundamental for maintaining blood sugar regulation and general well-being.
Including local produce, like avocados and berries, can improve your nutrition and encourage better wellness results.
Additionally, real-world instances, such as the Arkansas Prevention and Control Program, demonstrate how community evaluations can customize health initiatives to address local requirements.
This program conducts assessments in collaboration with various communities, identifying strengths and resources to increase participation and retention in health programs.
By addressing social determinants of health, the program identifies resources that support participants in managing their health effectively.
For those interested in exploring additional programs or nominating a community for assessments, contacting the Arkansas Diabetes Prevention and Control Program is recommended.
Overall, leveraging these resources can lead to better outcomes in diabetes management.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes is a comprehensive journey that integrates nutrition, physical activity, and continuous education, all grounded in the principles set forth by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) dietary guidelines. By emphasizing a balanced diet rich in whole foods, individuals can effectively control blood sugar levels while addressing the root causes of their condition. Understanding the importance of carbohydrate management, portion control, and nutrient-dense food choices is essential in fostering better health outcomes.
Implementing practical strategies, such as:
- Meal planning
- Creating a supportive network
can further enhance diabetes management. Regular physical activity not only improves insulin sensitivity but also aids in weight management and supports mental well-being. Monitoring dietary choices through food diaries and regular blood sugar checks empowers individuals to make informed decisions, while professional guidance ensures that personalized strategies are in place.
Building a robust support network, whether through:
- Peer groups
- Family involvement
- Professional resources
is vital for maintaining motivation and successfully navigating the challenges of diabetes. Ongoing education and access to resources, such as diabetes self-management programs and community wellness initiatives, provide valuable tools for individuals to enhance their self-care practices.
Ultimately, adopting a holistic approach to diabetes management fosters an empowered mindset, enabling individuals to take charge of their health and improve their quality of life. By integrating nutrition, physical activity, and support systems, effective diabetes management becomes not just a goal, but a sustainable lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do the ADA dietary guidelines emphasize for managing blood sugar levels?
The ADA dietary guidelines promote a comprehensive and balanced approach to nutrition, emphasizing the importance of whole foods, carbohydrate control, portion control, nutrient-dense foods, hydration, and regular meal timing.
How does carbohydrate control contribute to blood sugar management?
Understanding carbohydrate varieties and serving sizes is crucial for managing blood sugar. Emphasizing complex carbohydrates from whole grains, legumes, and vegetables while minimizing refined sugars can significantly improve glycemic control.
Why is portion control important in managing blood glucose levels?
Controlling portion sizes helps maintain stable blood glucose levels. Utilizing measuring tools or visual aids can assist in making informed dietary choices, leading to better glycemic status, especially for those facing weight challenges.
What types of foods should individuals prioritize according to the ADA guidelines?
Individuals should prioritize nutrient-dense foods that are rich in nutrients but low in calories, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, which are essential for overall well-being and weight control.
What role does hydration play in blood sugar management?
Sufficient hydration is vital for well-being, with water being the primary beverage of choice. Avoiding sugary drinks helps prevent spikes in blood glucose levels and positively influences metabolic health.
How can meal timing affect blood sugar levels?
Regular meal timing helps regulate blood sugar levels by preventing extreme fluctuations in glucose. Consistent eating habits throughout the day are recommended to support effective management of blood sugar.
What is the significance of evaluating glycemic control?
Regular evaluation of glycemic control is essential for effective care, with patients advised to assess their glycemic status at least twice a year to empower them in managing their health journey.
What strategies can be used to implement the ADA dietary guidelines effectively?
Strategies include creating balanced plates, planning meals ahead, incorporating healthy snacks, reading nutrition labels, adjusting recipes for healthfulness, and staying flexible with meal options.
How can individuals ensure they are making informed food choices?
Mastering the skill of reading nutrition labels is essential, focusing on serving sizes, carbohydrate content, and added sugars to guide healthy eating habits.
Why is flexibility important in meal planning for blood sugar management?
Flexibility is important because life can be unpredictable. Having a variety of quick and healthy meal options available ensures adherence to the ADA dietary guidelines even during changing circumstances.