Overview
The main focus of the article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) diet recommendations for effective diabetes management. The article outlines key principles such as balanced macronutrient distribution, incorporating fiber-rich foods, and the importance of meal planning, emphasizing that these strategies can significantly improve glucose control and overall health outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
Introduction
Managing diabetes effectively requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses dietary choices, physical activity, and community support. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) lays out a comprehensive framework that emphasizes balanced nutrition, meal planning, and the importance of understanding food labels. By adhering to core principles such as maintaining a balanced macronutrient distribution and incorporating fiber-rich foods, individuals can stabilize blood glucose levels and enhance overall health.
Additionally, exploring various dietary patterns, from low-carbohydrate diets to plant-based options, offers diverse strategies for effective management. This article delves into the essential components of the ADA diet, providing insights into how individuals can implement these practices to achieve better health outcomes and foster a supportive environment for sustained diabetes management.
Core Principles of the ADA Diet for Diabetes Management
The ADA diet recommendations emphasize balanced nutrition as a cornerstone for effectively managing glucose levels. Key principles of this dietary approach include:
- Balanced Macronutrient Distribution: Aiming for an intake that consists of 45-60% carbohydrates from total daily calories is vital, though individual needs may vary. This distribution supports stable glucose management.
- Incorporating Fiber-Rich Foods: Emphasizing whole grains, fruits, and vegetables is crucial, as these foods enhance satiety and contribute to sugar stability.
- Limiting Added Sugars and Refined Carbohydrates: It is essential to reduce the consumption of sugary beverages, sweets, and processed foods, which can cause rapid increases in glucose levels.
- Regular Meal Timing: Consistency in meal timing plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels, helping to prevent extreme fluctuations.
- Portion Control: Monitoring portion sizes is critical for managing calorie intake and preventing overconsumption of carbohydrates.
Research suggests that organized nutritional management can lead to improved wellness outcomes; the optimal results from Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) programs are attained with a theory-based, structured curriculum and a contact time surpassing 10 hours. Moreover, by reassessing the origin of your condition, we can tackle well-being at the root level using a holistic approach. This approach not only empowers patients but also helps alleviate the anxiety associated with potential complications of the disease.
Moreover, supplementation with resveratrol has been demonstrated to lower C-reactive protein by 0.87, indicating the potential influence of food selections on overall wellness. By adhering to these principles and adopting a comprehensive viewpoint, individuals with blood sugar issues can utilize ADA diet recommendations to make knowledgeable food selections that enhance health and overall wellness.
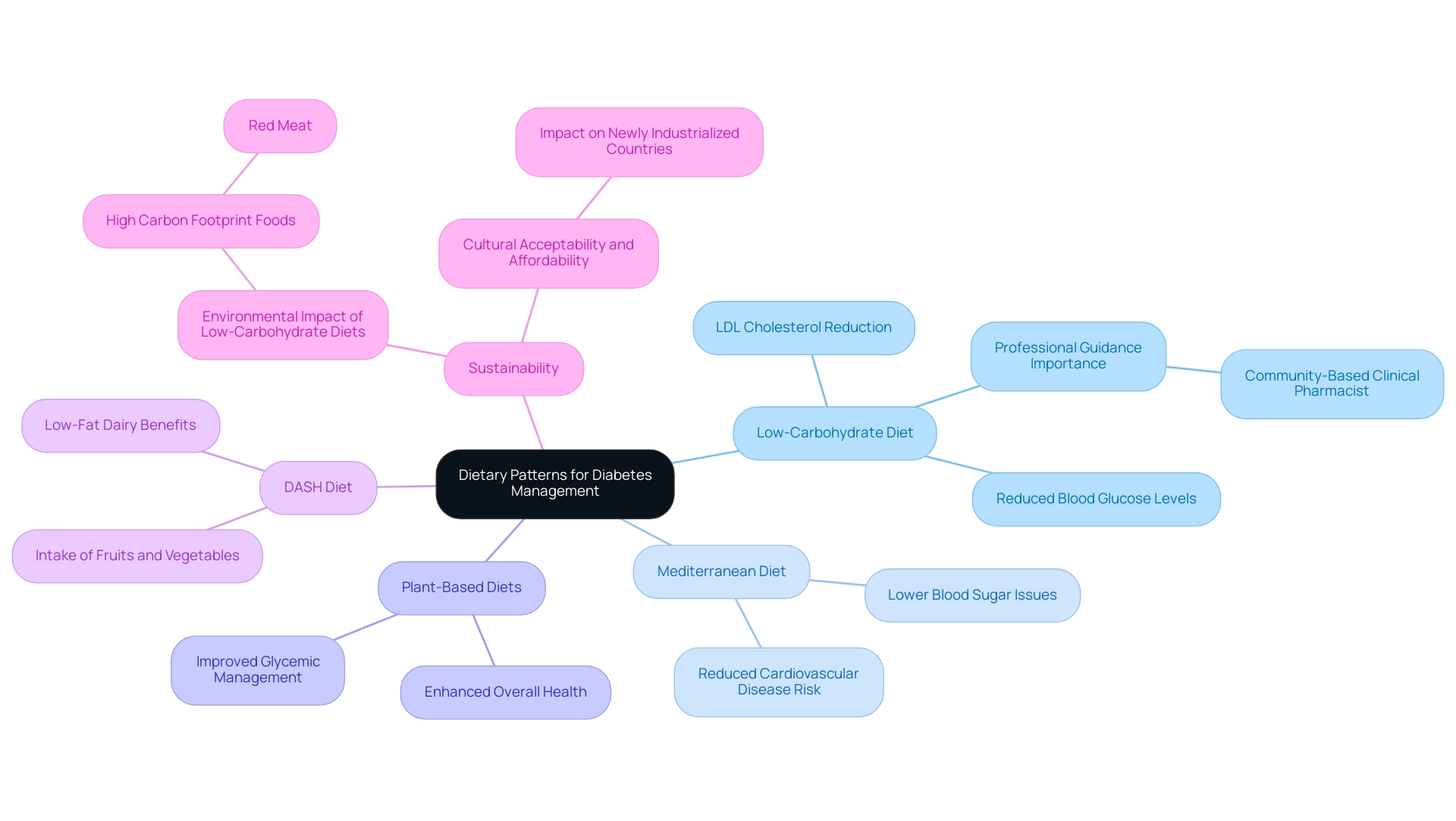
Exploring Dietary Patterns: Low-Carbohydrate and Beyond
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) endorses a variety of eating patterns as part of their ada diet recommendations, which have shown potential benefits for managing diabetes effectively. Among these, the Low-Carbohydrate Diet stands out for its ability to limit carbohydrate intake, which can lead to reduced blood glucose levels and enhanced insulin sensitivity. Notably, recent findings have indicated that individuals following a low-carbohydrate diet experienced a significant reduction in LDL cholesterol within just one month, surpassing the reduction seen in those on a standard low-calorie diet over six months.
A clinical pharmacist emphasized this by stating, ‘Recently, a small randomized controlled study demonstrated improved glycemic control and reduction of medication use led by a community-based clinical pharmacist,’ underscoring the importance of professional guidance in dietary choices.
Additionally, the Mediterranean Diet, characterized by its abundance of healthy fats, whole grains, and lean proteins, is linked to a lower occurrence of blood sugar issues and cardiovascular disease risk factors. Current research emphasizes the potential of ada diet recommendations in not only enhancing glycemic control but also in lowering the overall risk of the condition, making it an attractive choice for individuals pursuing sustainable wellness benefits.
Plant-Based Diets also merit attention; emphasizing fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains can significantly enhance overall health and glycemic management. Furthermore, the DASH Diet, originally designed to combat hypertension, promotes the intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy, offering additional benefits to those managing blood sugar levels.
However, it is essential to consider the sustainability of food choices. The case study titled ‘Sustainable Nutrition and Low Carbohydrate Diets’ discusses the potential environmental impact of widespread adoption of low-carbohydrate diets, noting that they often include foods with a high carbon footprint, such as red meat. This highlights the importance of cultural acceptability and affordability, particularly in newly industrialized countries experiencing rising diabetes rates.
Before making any significant nutritional changes, individuals should consult healthcare providers or registered dietitians for ada diet recommendations. These professionals can provide personalized recommendations tailored to individual wellness needs and preferences, ensuring that the chosen dietary pattern aligns with the individual’s management goals.
Importance of Meal Planning in Diabetes Management
Effective meal planning is essential for managing diabetes and involves several critical steps:
- Assess Nutritional Needs: Start by determining your daily caloric and macronutrient requirements, which should be tailored to your activity level and individual health objectives. Understanding these needs lays the foundation for a balanced diet.
- Create a Weekly Menu: Develop a weekly meal plan that includes a variety of food groups while following the ADA diet recommendations. This approach helps ensure that you consume at least half of your grains as whole grains, which is essential for sugar control.
- Prepare Grocery Lists: Formulate a shopping list based on your meal plan. This not only curtails impulse purchases but also guarantees that you have all the necessary ingredients for healthy meals.
- Batch Cooking: Consider preparing meals in bulk. This method saves time and ensures that nutritious options are readily available, which can help maintain adherence to your nutrition goals.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly assess your meal plan alongside your blood sugar levels. This ongoing evaluation allows you to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments, optimizing your nutritional strategy.
As mentioned by J.W.H., a formal analysis specialist, this research offers proof that endorses the use of nutritional interventions in the management of blood sugar conditions, which can aid in guiding product development and patient choices. Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance management of the condition. Programs like the Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) not only assist individuals in creating personalized healthy meal plans with the guidance of educators but also provide tailored support that leads to improved dietary adherence and better health outcomes.
According to educators in the field, meal planning is crucial for success in managing health conditions, as it allows individuals to anticipate their nutritional needs and make informed choices.
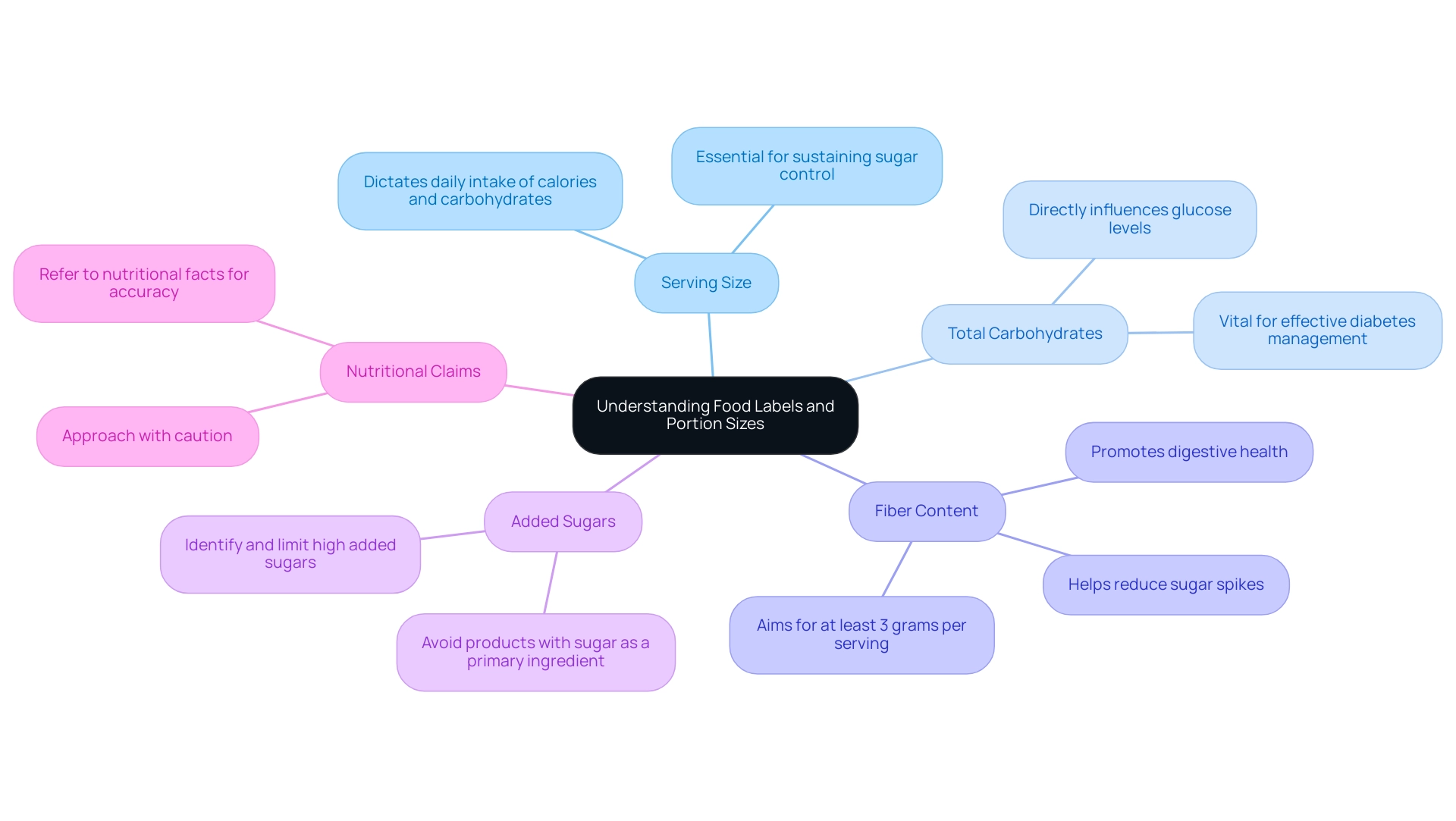
Understanding Food Labels and Portion Sizes
When navigating food labels, it is essential to focus on several key components that significantly impact diabetes management:
- Serving Size: Always assess the serving size, as it dictates your daily intake of calories and carbohydrates. Comprehending how this connects to your overall dietary objectives is essential for sustaining sugar control.
- Total Carbohydrates: Examine the total carbohydrate content per serving, as this directly influences glucose levels. Keeping track of carbohydrate intake is vital for effective diabetes management.
- Fiber Content: Foods high in fiber can help reduce sugar spikes; therefore, aim for options with at least 3 grams of fiber per serving. Fiber plays a fundamental role in regulating sugar levels and promoting digestive health.
- Added Sugars: It is critical to identify and limit foods high in added sugars, which can lead to elevated blood glucose levels. Products with sugar listed among the first ingredients should be avoided to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Nutritional Claims: Approach health claims found on packaging with caution, as they can often be misleading. Always refer to the nutritional facts for accurate and detailed information.
According to the CDC, 11.3% of the U.S. population has this condition, highlighting the importance of understanding food labels in managing it. As Dr. Rafael Perez-Escamilla emphasizes, ‘Understanding food labels is crucial for individuals with this condition to make informed dietary choices.’ Furthermore, a recent study titled ‘Correlation Between Disease Management and Nutrition Label Use’ found that patients diagnosed with this condition at a younger age and those with shorter disease duration were more likely to utilize nutrition labels effectively, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis and management in promoting better nutrition label utilization among affected individuals.
By comprehending these components, individuals can make informed food selections that are consistent with ADA diet recommendations, aiding their health management and overall well-being.
Incorporating Physical Activity into the ADA Diet
Incorporating physical activity into your routine can significantly improve management of blood sugar levels. The American Diabetes Association recommends engaging in at least 150–300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, complemented by strength training exercises on two or more days. Here are several key recommendations to effectively integrate exercise into your lifestyle:
-
Set Realistic Goals: Establish achievable fitness targets that align with your lifestyle and preferences. This could mean gradually increasing your activity levels to meet the recommended duration.
-
Choose Activities You Enjoy: Selecting physical activities you find enjoyable increases the likelihood of maintaining a consistent routine.
Options such as walking, cycling, swimming, or participating in group fitness classes can be effective and enjoyable.
-
Promote Self-Efficacy and Social Support: Surround yourself with supportive individuals and focus on building your confidence in your ability to engage in physical activity. This can enhance your commitment to maintaining an active lifestyle.
-
Monitor Glucose Levels: It’s crucial to check your glucose levels before and after exercising to gauge your body’s response to physical activity. Understanding how your body reacts can help you manage your diabetes more effectively.
-
Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential during exercise.
Drink plenty of water before, during, and after physical activity to prevent dehydration, especially if you are exercising with elevated glucose levels.
-
Consult with a Healthcare Provider: Prior to initiating any new exercise program, particularly if you have additional health considerations, it is advisable to seek personalized guidance from a healthcare provider. This can assist in confirming that your exercise regimen is secure and customized to your requirements.
Recent studies suggest that individuals with type 2 diabetes typically do not need to delay exercise due to elevated glucose levels, as long as they feel well and remain hydrated. Andrea M. Kriska, PhD, FACSM, observes that “exercise can still be beneficial even with elevated glucose levels,” reinforcing the importance of integrating physical activity into your routine. Furthermore, a case study on exercise with suboptimal blood glucose control emphasizes that participating in physical activity can improve general well-being and greatly boost the efficacy of nutritional efforts, in accordance with ADA diet recommendations, even when blood glucose is elevated.
By making exercise a regular part of your routine, you can improve your overall health and significantly enhance the effectiveness of your dietary efforts.
Maintaining a Supportive Community
A supportive community can profoundly influence the management of this condition through a holistic approach, helping to eliminate worry about developing traumatic and debilitating complications. Here are several strategies to cultivate such a community:
-
Join Support Groups: Participating in local or online support groups for those with health conditions is essential, enabling people to share experiences, challenges, and victories in a collaborative environment.
Recent findings underscore the effectiveness of these groups, with studies showing that participants who lacked cohabitation with their support person experienced a notable reduction in HbA1c levels, averaging a decrease of -0.64% at the six-month mark. Furthermore, the primary outcomes of management programs for blood sugar regulation include changes in HbA1c, blood pressure, lipid profile, and psychological measures, highlighting the multifaceted benefits of community support.
-
Participate in Workshops or Classes: Attending workshops that focus on managing conditions, nutrition, or physical fitness can foster connections with others who share similar wellness objectives, empowering patients through education and shared experiences.
-
Utilize Social Media: Social media platforms such as Facebook and Instagram can be valuable tools for connecting with communities dedicated to awareness and management of this condition, facilitating a sense of belonging and shared purpose while challenging common myths.
-
Involve Friends and Family: Communicating your health goals with family and friends encourages them to participate actively in your journey, providing the emotional support necessary for effective management and alleviating anxiety over potential complications.
-
Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting healthcare experts specializing in managing blood sugar levels equips individuals with personalized advice and assistance. The integration of social support into glucose regulation management has been highlighted in a systematic review of peer support studies published between January 2021 and December 2023, which identified nine relevant articles demonstrating the positive impact of community engagement on self-management and cardiometabolic outcomes. As noted by Chen Yuan, ‘Future research should focus on more rigorously designed and larger-sample studies’ to further understand these dynamics.
A robust support network not only fosters motivation and accountability but also offers invaluable insights for navigating the complexities of diabetes, ultimately empowering patients to re-examine the source of their diabetes and address their health at the root level.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes is a complex yet achievable goal that hinges on a comprehensive understanding of dietary choices, physical activity, and community support. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides a solid foundation for effective diabetes management through its emphasis on balanced nutrition, meal planning, and informed decision-making regarding food labels. By adhering to key principles such as:
- Balanced macronutrient distribution
- Incorporating fiber-rich foods
- Practicing portion control
individuals can significantly stabilize their blood glucose levels and improve their overall health.
Exploring various dietary patterns, including:
- Low-carbohydrate diets
- Mediterranean diets
- Plant-based diets
offers diverse strategies tailored to individual preferences and health needs. Each of these approaches presents unique benefits that can enhance glycemic control and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. Moreover, effective meal planning and understanding food labels empower individuals to make informed choices that align with their health goals.
Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines further complements dietary strategies, enhancing both physical and mental well-being. The role of community support cannot be overstated; engaging with support groups, workshops, and social networks fosters motivation and accountability, essential components for successful diabetes management.
Ultimately, a multifaceted approach combining nutrition, exercise, and social support forms the cornerstone of effective diabetes management. By embracing these principles, individuals can take charge of their health, reduce the risks associated with diabetes, and foster a lifestyle that promotes lasting wellness. The journey may be challenging, but with the right tools and support, improved health outcomes are well within reach.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key principles of the ADA diet recommendations for managing glucose levels?
The key principles include balanced macronutrient distribution (45-60% carbohydrates), incorporating fiber-rich foods (whole grains, fruits, vegetables), limiting added sugars and refined carbohydrates, maintaining regular meal timing, and practicing portion control.
Why is balanced macronutrient distribution important in the ADA diet?
A balanced macronutrient distribution supports stable glucose management, helping individuals maintain better control over their blood sugar levels.
How do fiber-rich foods contribute to glucose management?
Fiber-rich foods enhance satiety and contribute to sugar stability, which is important for managing blood glucose levels.
What types of foods should be limited according to the ADA diet?
The ADA diet recommends limiting added sugars and refined carbohydrates, such as sugary beverages, sweets, and processed foods, as they can cause rapid increases in glucose levels.
How does meal timing affect blood sugar levels?
Consistency in meal timing helps regulate blood sugar levels and prevents extreme fluctuations.
What role does portion control play in the ADA diet?
Monitoring portion sizes is critical for managing calorie intake and preventing the overconsumption of carbohydrates.
What benefits are associated with structured nutritional management in diabetes?
Organized nutritional management can lead to improved wellness outcomes, particularly when part of Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) programs, which should have a structured curriculum and over 10 hours of contact time.
What dietary patterns does the ADA endorse for managing diabetes?
The ADA endorses various eating patterns, including Low-Carbohydrate Diets, Mediterranean Diets, Plant-Based Diets, and the DASH Diet, each offering potential benefits for managing diabetes.
What is the significance of the Low-Carbohydrate Diet in diabetes management?
The Low-Carbohydrate Diet can lead to reduced blood glucose levels and enhanced insulin sensitivity, with studies showing significant reductions in LDL cholesterol.
Why is professional guidance important when making dietary changes?
Consulting healthcare providers or registered dietitians ensures that dietary changes are personalized and aligned with individual wellness needs and management goals.
What should individuals consider regarding the sustainability of their food choices?
Individuals should consider the environmental impact of their food choices, especially with diets that may include high carbon footprint foods, and ensure that their dietary choices are culturally acceptable and affordable.