Overview
The article focuses on the ADA clinical guidelines for diabetes management, emphasizing their role in improving care and health outcomes for patients. It supports this by detailing key areas such as medication oversight, lifestyle interventions, and the importance of patient education, which collectively empower individuals to better manage their condition and engage proactively with healthcare providers.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) serves as a guiding light, offering annual clinical guidelines that reflect the latest research and expert consensus. These guidelines are not merely a collection of recommendations; they embody a comprehensive approach to enhancing care and improving health outcomes for individuals living with diabetes.
With a strong emphasis on patient-centered strategies, the 2023 updates pave the way for a more personalized approach to treatment, addressing critical aspects such as:
- Medication management
- Lifestyle interventions
- The integration of innovative therapies
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, understanding and implementing these guidelines becomes essential for patients seeking to take control of their health and engage proactively with their healthcare providers.
This article delves into the key recommendations for managing diabetes, the transformative role of lifestyle changes, effective blood sugar monitoring practices, and the vital importance of educational resources and community support in empowering patients on their health journey.
Overview of ADA Clinical Guidelines for Diabetes Management
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) publishes yearly ADA clinical guidelines aimed at enhancing care and improving health results for individuals living with this condition. These guidelines are based on the latest research and expert agreement, addressing critical aspects of health control such as diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing care. For instance, the 2023 updates underscore the importance of patient-centered approaches, which are further reinforced by the upcoming 2024 standards aiming to enhance these strategies.
Key focus areas include:
- Medication oversight
- Lifestyle interventions
- Integration of advanced therapies such as ‘fish skin grafts‘ for wound care, as noted in the updated Table 12.2
Notably, the risk of type 1 condition increases as the number of relevant autoantibodies detected increases, emphasizing the need for early detection and ongoing monitoring. The important function of pharmacists is also emphasized, with the American Pharmacists Association observing that pharmacists contribute significantly to managing blood sugar conditions by instructing individuals, optimizing medication plans, and working alongside other healthcare specialists to deliver thorough care.
Comprehending the ADA clinical guidelines allows patients to better advocate for their well-being and engage proactively with their healthcare providers. The ADA clinical guidelines emphasize real-world practices that reflect individualized care, particularly in specialized scenarios like pregnancy, where managing blood sugar levels is crucial to preventing gestational complications and reducing cardiovascular risks. Participants are encouraged to utilize tracking methods, including:
- Continuous glucose monitoring
- Fitness apps
- Journals
to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—that enhance their wellness journey.
Recent case studies illustrate that community pharmacists can greatly assist in self-management and enhance well-being results, empowering patients to reach their wellness objectives effectively.
Key Recommendations for Type 2 Diabetes Management
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) clinical guidelines emphasize the significance of a comprehensive approach for managing type 2 conditions, which includes lifestyle changes, adherence to medication, and careful monitoring. At Dr. Jason Shumard’s Integrative Wellness Center, we are dedicated to these principles, offering personalized functional medicine strategies designed to meet individual wellness needs. Dr. Shumard, possessing advanced education in functional endocrinology and clinical nutrition, highlights the significance of a comprehensive approach to handling blood sugar issues.
Among the key recommendations are:
- Adopting a balanced diet that emphasizes whole foods while minimizing processed sugars, supported by local resources such as San Marcos farmers’ markets;
- Engaging in a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly. This strategy is reinforced by evidence showing that structured exercise can significantly reduce HbA1c levels and enhance insulin sensitivity in high-risk individuals. For instance, a case study on structured exercise training demonstrated that participants experienced an average reduction in HbA1c levels by 1.5%, comparable to effects achieved with common antidiabetic medications;
- Consistently monitoring blood glucose levels to maintain optimal control;
- Taking prescribed medications as directed, with necessary adjustments tailored to individual circumstances; and
- Scheduling regular check-ups with healthcare providers to evaluate overall health and the effectiveness of blood sugar control efforts.
Such a holistic approach not only aims to stabilize blood sugar levels but also follows the ADA clinical guidelines to actively mitigate the risk of diabetes-related complications. According to recent data, the medical costs related to the condition rose from $10,179 to $12,022 per individual between 2012 and 2022, emphasizing the urgent need for effective management strategies. The International Diabetes Federation emphasizes a proactive approach, stating, “The IDF has proposed a simple 3-step plan for the prevention of this condition in high-risk individuals that includes (1) identification of those who may be at increased risk, (2) risk evaluation, and (3) intervention to prevent it.”
Additionally, barriers such as lack of time, training, and organizational resources often hinder the implementation of lifestyle diabetes prevention strategies in clinical practice. As Eirik Årsand notes, “Individuals with T2D, website developers, online group moderators, care services, and patient organizations should be aware of this important window for lifestyle change, and encourage participation in online groups.” This further emphasizes the necessity of community support and engagement in lifestyle modification efforts, which we actively foster at our center.
For personalized guidance and support tailored to your unique needs, consider reaching out to Dr. Shumard in San Marcos, CA. Call 858-564-7081 to find out how Dr. Shumard can assist you in regaining your well-being and reclaiming your life!
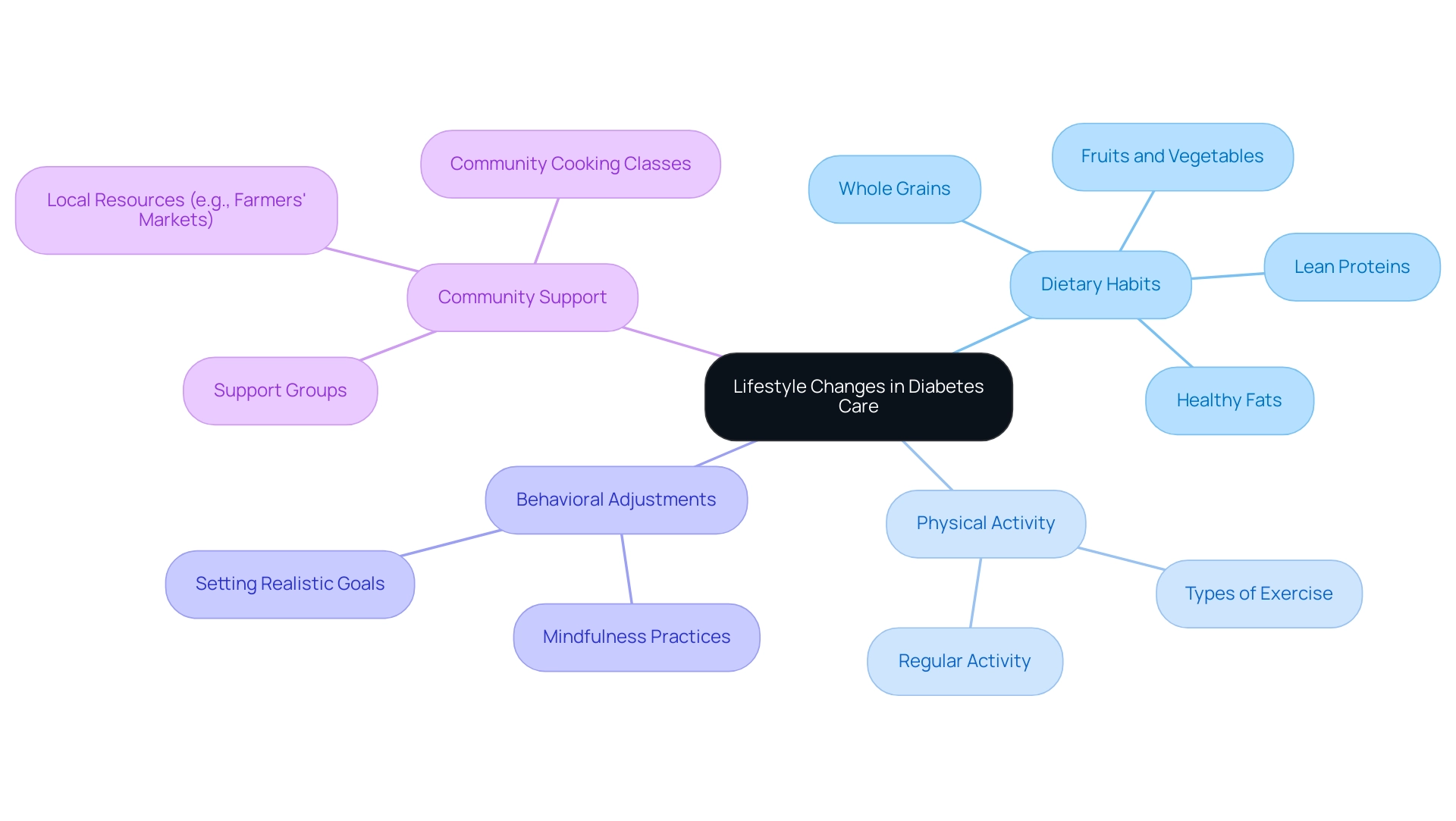
The Role of Lifestyle Changes in Diabetes Care
Adopting healthy lifestyle modifications is crucial for effective control of type 2 blood sugar issues. These changes encompass various dietary habits, physical activity levels, and behavioral adjustments. A diabetes-friendly diet should prioritize whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a rich array of fruits and vegetables.
Notably, in 2012, 37% of adults over the age of 20 in the U.S. were affected by prediabetes, highlighting the urgent need for lifestyle interventions. According to the ADA clinical guidelines, patients of any age with a BMI of 25 kg/m² or higher, along with additional risk factors, are at an increased risk for the condition and should be proactive about their health. Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine not only aids in weight management but also enhances insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for blood sugar control.
Effective strategies for fostering these lifestyle changes include:
- Setting realistic goals
- Exploring enjoyable physical activities
- Engaging with healthcare professionals or support groups for guidance and motivation
Additionally, leveraging local resources such as farmers’ markets can offer access to fresh produce, further supporting a diabetes-friendly diet. Research indicates that such modifications can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar levels and general well-being.
For example, a thorough examination of lifestyle strategies for cardiovascular health and the prevention of type 2 conditions in low-and-middle-income nations (LMICs) showed significant success in improving cardiometabolic results and preventing type 2 conditions among vulnerable groups. Moreover, understanding the risks associated with conventional diabetes treatments, such as increased insulin levels, emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to care. As one patient noted, “After switching to a whole foods diet and reducing my reliance on insulin, I felt more energetic and my blood sugar levels stabilized.”
By adopting these healthy lifestyle choices and the support of the community in San Marcos, individuals can pave the way for better handling of their condition and improved quality of life. Lesser-known strategies, such as mindfulness practices and community cooking classes, can further empower individuals to take control of their health.
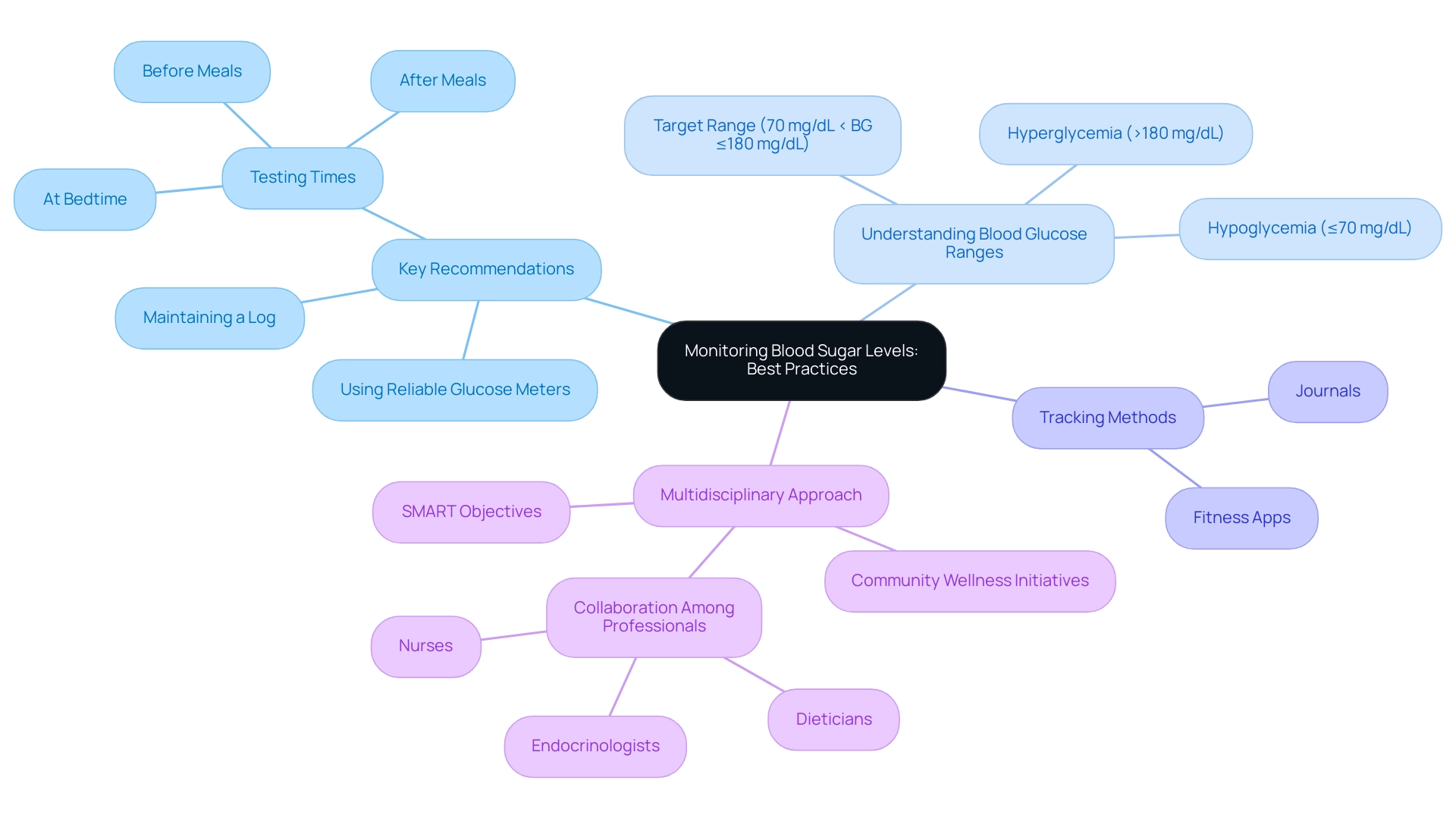
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Best Practices
Effective blood sugar monitoring, as highlighted in the ADA clinical guidelines, is crucial for successful diabetes control, especially for individuals with Type 2 diabetes. Adopting best practices can significantly enhance health outcomes. Key recommendations include:
- Testing blood glucose levels at strategic times—before and after meals, as well as at bedtime—to ensure comprehensive tracking.
- Maintaining a detailed log of results, which aids in recognizing patterns and trends.
- Utilizing a reliable glucose meter and ensuring it is properly calibrated for accuracy.
- Understanding target blood glucose ranges, typically defined as:
- Hypoglycemia (≤70 mg/dL)
- Target range (70 mg/dL < BG ≤180 mg/dL)
- Hyperglycemia (>180 mg/dL)
- Using tracking methods such as fitness apps and journals to monitor progress effectively.
To generate the AGP curve effectively, it is recommended to have at least 7 days of BGM data and a minimum of 30 readings, providing a comprehensive overview of blood glucose levels. Recent advancements in continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) promise improved accuracy, further supporting the development of closed-loop insulin delivery systems. As noted by Ph.D. expert Boris Kovatchev, the development of these metrics was supported by grant RO1 DK 51562 from the National Institutes of Health and by the JDRF Artificial Pancreas Consortium.
Additionally, studies suggest that better glycemic control correlates with reduced risk fluctuations, underscoring the importance of effective monitoring. Patients should understand how different factors—such as diet, physical activity, stress, and illness—can influence blood sugar levels, which allows for timely modifications in their care plan. This highlights the need for a multidisciplinary approach involving collaboration among healthcare professionals like endocrinologists, nurses, and dieticians.
A case study on a multidisciplinary method to address diabetes illustrates that effective collaboration enhances outcomes for individuals by systematically controlling blood glucose levels. Furthermore, integrating comprehensive lifestyle approaches, such as participating in community wellness initiatives, sustaining a balanced diet abundant in local produce, and emphasizing stress reduction, can enable individuals to manage their health more efficiently and attain improved outcomes. Establishing SMART objectives—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can greatly enhance focus and motivation in managing health.
For instance, an individual might set a target to reduce their fasting blood glucose levels by a certain percentage within a specified timeframe. By prioritizing effective monitoring, structured goal-setting, and consistent progress tracking, patients can cultivate a sense of achievement and improve their overall health condition.
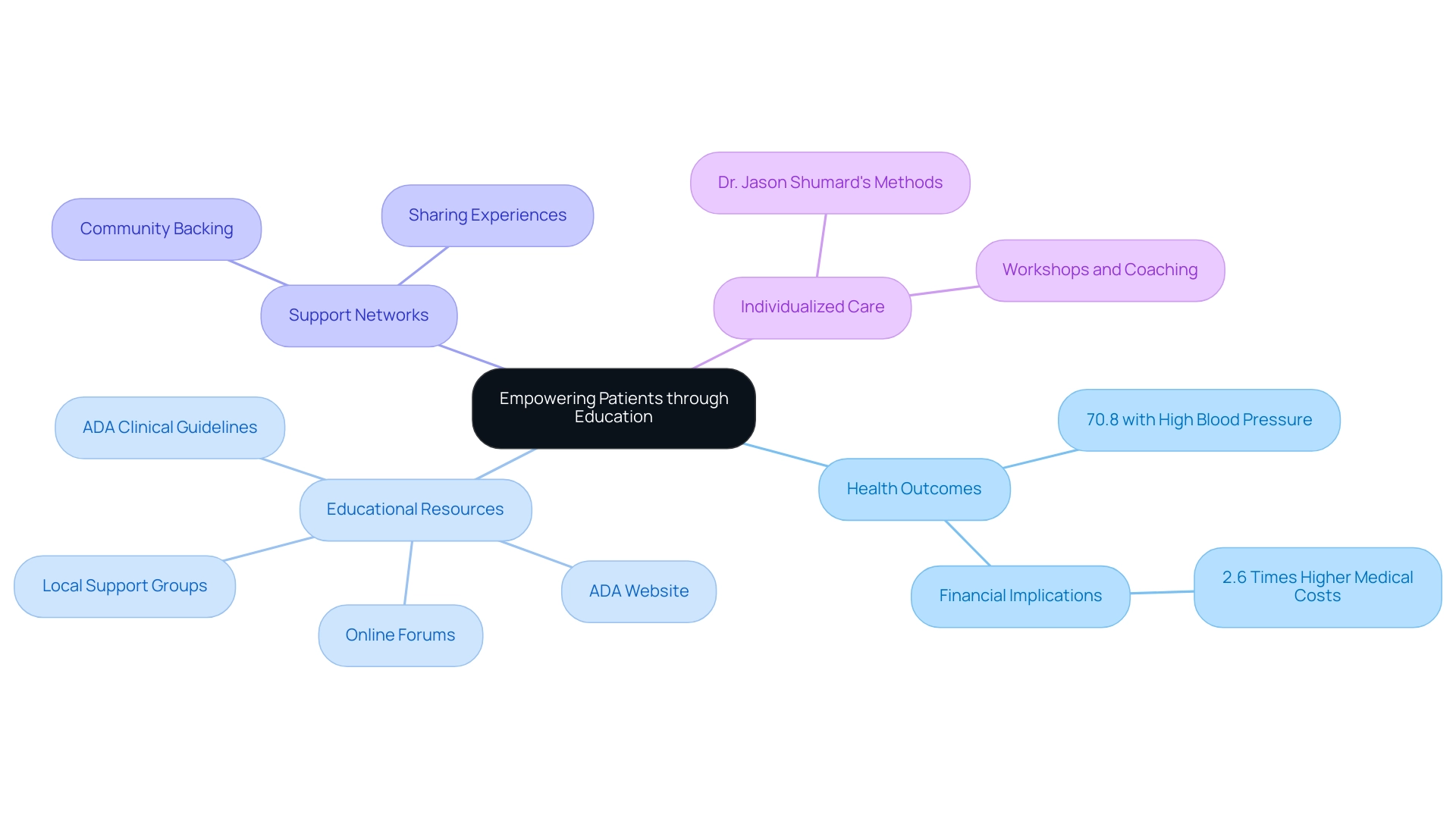
Empowering Patients: Educational Resources and Support
Empowerment through education serves as a cornerstone for effective control of blood sugar. With 516 participants involved in community-based self-management programs for chronic conditions, it’s evident that access to educational resources significantly influences health outcomes. This program revealed that 70.8% of participants had a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or were on medication for hypertension, underscoring the critical need for informed self-care.
The typical healthcare costs for individuals with diagnosed conditions are 2.6 times greater than those without, emphasizing the financial consequences of effective condition oversight. Patients can tap into a wealth of resources, including:
- The ADA clinical guidelines
- The ADA’s website
- Online forums
- Local support groups
These resources offer essential information and community backing. These educational materials often cover:
- Meal planning
- Exercise strategies
- Stress management techniques
Equipping individuals with the knowledge necessary to make informed choices.
Moreover, Dr. Jason Shumard’s functional medicine method highlights individualized care, enabling individuals to not only manage but potentially reverse their condition through comprehensive programs customized to their requirements. Healthcare providers also contribute by offering workshops and personalized coaching sessions, which assist individuals in effectively applying the ADA clinical guidelines. The systematic review of self-care education for type 2 conditions confirms that such interventions enhance knowledge, self-efficacy, and overall quality of life, leading to improved control of type 2 conditions.
Notably, the review concludes that DSME has a positive effect on lifestyle and clinical status, further emphasizing the importance of these educational interventions. By engaging with these resources, individuals create a supportive network where they can share experiences, ask questions, and receive encouragement on their path to better health. Additionally, it is critical to recognize the urgency of diabetes management, as diabetes was noted as a cause of death in 399,401 death certificates in 2021.
With the right education and support, patients can find new peace in life, shed unwanted pounds, and mitigate their risks for complications. Don’t wait any longer; call our office at 858-564-7081 today to see if you qualify for a FREE consultation and learn how to eliminate dependency on insulin and other diabetes-related drug therapies.
Conclusion
The American Diabetes Association’s updated clinical guidelines for 2023 highlight the critical importance of a patient-centered approach in managing diabetes. By focusing on comprehensive strategies that include medication management, lifestyle interventions, and innovative therapies, these guidelines offer a framework for enhancing health outcomes. The emphasis on early detection, particularly in the case of type 1 diabetes, underscores the necessity for proactive health monitoring and collaboration with healthcare providers.
Implementing lifestyle changes is paramount in the management of type 2 diabetes. Adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and consistently monitoring blood glucose levels can lead to significant health improvements. The integration of community support and educational resources not only empowers patients but also fosters a collaborative environment that enhances diabetes self-management.
Effective blood sugar monitoring practices are essential for achieving optimal health. By leveraging technology such as continuous glucose monitors and setting SMART goals, patients can gain better control over their condition. This structured approach promotes accountability and encourages meaningful progress in diabetes management.
Ultimately, the combination of education, support, and personalized care forms the backbone of successful diabetes management. By actively engaging with these resources and strategies, individuals can take charge of their health, reduce their risks for complications, and improve their overall quality of life. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, embracing these guidelines is not just beneficial; it is essential for a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the ADA clinical guidelines?
The ADA clinical guidelines are yearly publications by the American Diabetes Association aimed at enhancing care and improving health outcomes for individuals with diabetes. They are based on the latest research and expert consensus, covering critical aspects such as diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing care.
What key areas do the 2023 ADA guidelines focus on?
The 2023 ADA guidelines emphasize patient-centered approaches and include key focus areas such as medication oversight, lifestyle interventions, and the integration of advanced therapies like fish skin grafts for wound care.
How does the detection of autoantibodies relate to type 1 diabetes?
The risk of developing type 1 diabetes increases with the number of relevant autoantibodies detected, highlighting the importance of early detection and ongoing monitoring.
What role do pharmacists play in diabetes management according to the ADA guidelines?
Pharmacists significantly contribute to managing diabetes by educating patients, optimizing medication plans, and collaborating with other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care.
How can patients advocate for their well-being using the ADA guidelines?
Understanding the ADA guidelines allows patients to engage proactively with their healthcare providers and advocate for individualized care, particularly in specialized scenarios such as pregnancy.
What tracking methods are recommended for managing diabetes?
Recommended tracking methods include continuous glucose monitoring, fitness apps, and journals to help set SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound.
What are the key recommendations for managing type 2 diabetes?
Key recommendations include: 1. Adopting a balanced diet focused on whole foods and minimizing processed sugars. 2. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly. 3. Consistently monitoring blood glucose levels. 4. Taking prescribed medications as directed with necessary adjustments. 5. Scheduling regular check-ups with healthcare providers.
Why is a holistic approach important in managing diabetes?
A holistic approach aims to stabilize blood sugar levels and mitigate the risk of diabetes-related complications while following ADA clinical guidelines.
What challenges do individuals face in implementing lifestyle diabetes prevention strategies?
Common barriers include lack of time, training, and organizational resources, which can hinder the implementation of effective lifestyle changes in clinical practice.
How can community support impact diabetes management?
Community support and engagement are crucial for encouraging lifestyle modifications, as highlighted by the need for participation in online groups and support networks for individuals with diabetes.