Overview
Understanding ADA A1C testing is essential for effective diabetes management, as it provides critical insights into average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, with a threshold of 6.5% indicating poor control. The article emphasizes the importance of regular A1C testing and personalized care strategies, demonstrating that effective monitoring and lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve health outcomes and reduce complications associated with diabetes.
Introduction
The Hemoglobin A1C test stands as a cornerstone in the management of diabetes, offering critical insights into long-term blood sugar control. By measuring the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, this test not only aids in diagnosing diabetes but also informs ongoing treatment strategies. With the prevalence of diabetes rising globally, understanding A1C levels has never been more essential.
This article delves into the multifaceted role of the A1C test, exploring its significance in diagnosis, the latest guidelines for testing frequency, and innovative methods that enhance patient care. By equipping readers with knowledge about effective management strategies and addressing common misconceptions, it aims to empower individuals on their journey toward better health and diabetes control.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key Component of Diabetes Management
The ada a1c test is a crucial blood examination that offers important information about your average blood sugar readings over the prior two to three months. Specifically, it measures the percentage of hemoglobin—the protein found in red blood cells—that is glycated, or coated with sugar. An elevated ada a1c percentage is indicative of poor blood sugar control, which correlates with an increased risk of diabetes-related complications.
A commonly accepted diagnostic threshold for this condition is an ada a1c level of 6.5% or higher. Recent studies, like the Rancho Bernardo Study, have highlighted the importance of ada a1c in diagnosing the disease and effectively managing the condition. Furthermore, research by Yoshinaga in 1996, which involved 819 Japanese government officials and their spouses, demonstrated that combining A1C with an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) enhances the prediction of progression to the condition, particularly in individuals exhibiting glucose intolerance.
The research specified incident hyperglycemia based on a 2-hour plasma glucose measurement of ≥ 11.1 mmol/l in an OGTT or fasting blood glucose of ≥ 6.7 mmol/l. Additionally, it is important to consider that the combination of A1C, Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG), and Body Mass Index (BMI) are effective predictors of the risk of this condition. Notably, from 2012 to 2022, the excess medical expenses per individual linked to the condition increased from $10,179 to $12,022, emphasizing the importance of managing A1C levels to mitigate these costs.
Thus, understanding the implications of the ada a1c test is crucial for anyone managing their condition, as it directly reflects the efficacy of their treatment plan and overall blood sugar control. By educating yourself about the four lesser-known strategies to boost your health—such as:
- Incorporating specific dietary changes
- Enhancing physical activity
- Utilizing stress reduction techniques
- Engaging in community wellness programs
you can empower your journey towards reversing the condition and improving your overall health. Furthermore, it is essential to confront widespread misunderstandings regarding the control of this condition, such as the notion that it is exclusively passed down genetically or that lifestyle modifications cannot greatly influence your state.
Participating in community wellness programs and educational resources directly connected to ada a1c control can further support your health goals.
The Importance of A1C Levels in Diabetes Diagnosis and Management
Ada a1c values play a crucial role in both the diagnosis and continuous management of the condition. Specifically, an ada a1c measurement ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, while a value of 6.5% or higher confirms the diagnosis of the condition. Monitoring ada a1c readings through regular testing is essential for healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of current treatment plans and make timely adjustments in medications and lifestyle interventions, ensuring optimal blood sugar control.
This proactive oversight is essential for avoiding complications related to blood sugar issues, such as cardiovascular disease and neuropathy. Notably, from 2012 to 2022, excess medical costs per person related to the condition increased from $10,179 to $12,022, underscoring the financial implications of effective management and the importance of monitoring ada a1c levels. The American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee states, “There remains strong consensus that establishing a uniform approach to diagnosing GDM will benefit individuals with GDM, caregivers, and policymakers,” which reinforces the need for standardized testing of ada a1c in diagnosing the condition.
Furthermore, at the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego, transformative patient success stories illustrate how personalized care has empowered individuals to reverse type 2 diabetes. For instance, patients have reported significant improvements in their ada a1c readings and overall health through customized treatment plans that focus on lifestyle changes and education about insulin resistance. Essential strategies, including a comprehensive understanding of insulin resistance and alternative treatment options, such as dietary adjustments and holistic therapies, are crucial for effective management.
These insights not only assist patients in controlling their blood sugar during pregnancy to prevent gestational complications but also emphasize the dangers of conventional treatments, which can result in serious health risks, including issues from medication side effects. The staging of Type 1 Diabetes further illustrates how ADA A1C measures are utilized in clinical decision-making, providing a framework for early diagnosis and intervention in at-risk populations. Ultimately, the proactive use of ada a1c metrics aids in guiding clinical decisions, reinforcing their importance in the comprehensive management of the condition.
ADA Guidelines for A1C Testing: Recommendations for Optimal Care
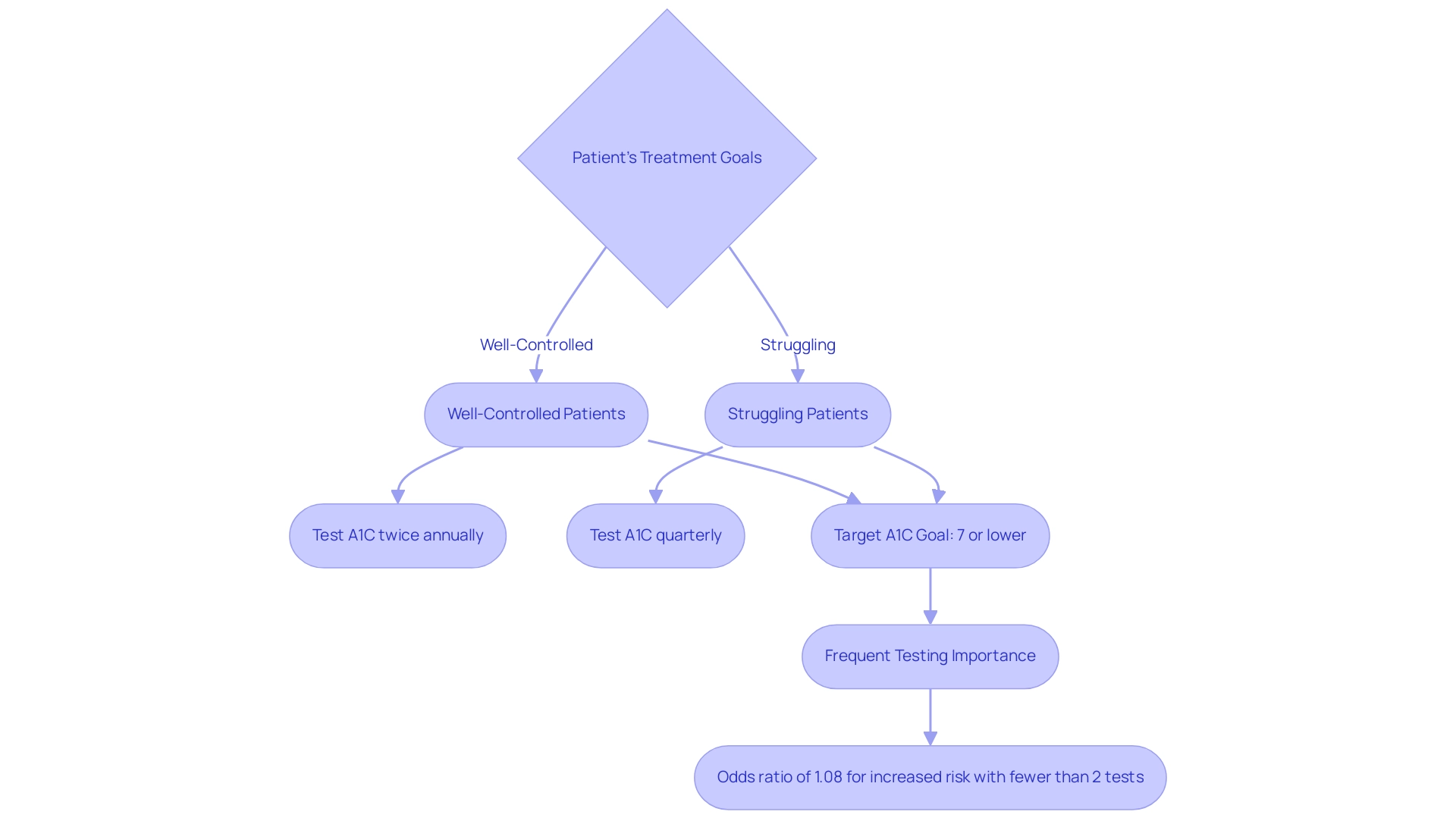
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) establishes clear guidelines for testing frequency of ADA A1C based on patients’ treatment goals and glycemic control. For adults with blood sugar issues who are effectively controlling their condition, the ADA A1C recommendations advise testing A1C readings at least twice annually. However, for those whose treatment regimen has changed or who are struggling to meet glycemic objectives, it is advised to conduct quarterly testing for ADA A1C.
A common target A1C goal of 7% or lower, referred to as ADA A1C, is generally advised for most adults with blood sugar issues; nevertheless, individual targets may differ significantly based on personal health circumstances and the presence of comorbidities. According to recent statistics, frequent testing correlates with improved health outcomes, with data showing that more than three tests per year are associated with an odds ratio of 1.08 for increased risk of cardiovascular events compared to fewer than two tests. This underscores the importance of regular monitoring and individualized care.
Moreover, specialist views emphasize that reaching ideal ADA A1C levels is essential for long-term oversight and prevention of complications linked to the condition. As Mårtensson J. states, ‘Hemoglobin A1c and Permissive Hyperglycemia in Patients in the Intensive Care Unit with Diabetes’ emphasizes the significance of careful ADA A1C management in critical care settings. Furthermore, it is crucial to quickly refer patients to a nephrologist when there is uncertainty regarding the cause of kidney disease, challenging treatment issues, or rapidly advancing kidney disease, as these factors can greatly affect the control of blood sugar.
Moreover, case studies, such as those addressing cognitive function and lipid-lowering agents, illustrate that concerns regarding treatment choices should be balanced with evidence-based practices. As we look ahead to the latest ADA A1C guidelines for 2024, it is vital to stay informed about the evolving recommendations and best practices in managing blood sugar health.
Practical Considerations for A1C Testing: Timing and Frequency
The ada a1c testing is an essential part of controlling blood sugar levels, usually performed in a healthcare provider’s office without the requirement for fasting. Consistency in testing is vital, as it allows for better monitoring of glucose levels over time. It is generally advisable to align ada a1c tests with routine check-ups to facilitate regular assessments.
According to recent findings, the age-adjusted percentage of adults aware of their prediabetes rose significantly from 6.5% in 2005–2008 to 17.4% in 2017–2020, indicating a growing awareness of the significance of controlling the condition. Furthermore, the NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) highlights the global variation in diagnosis and prevalence based on fasting glucose and hemoglobin A1c, underscoring the need for tailored approaches in different populations. At the Integrative Wellness Center, we empower patients to eliminate anxiety over complications related to blood sugar issues through holistic care and education, actively working to dispel traditional myths about handling these conditions.
We help patients understand that insulin resistance is a significant factor in their health, and addressing it is essential for effective treatment. To maintain adherence to ada a1c testing schedules, setting reminders through mobile applications or calendar alerts can be particularly effective. The frequency of testing should be personalized based on individual health status and treatment objectives, as collaboratively determined with their healthcare team.
Furthermore, research indicates that using reminders can positively affect adherence to ada a1c testing, resulting in better outcomes. As highlighted in a report on geographic variation in diagnosed conditions prevalence, localized health strategies are essential in addressing these disparities, with diagnosed conditions prevalence among U.S. adults varying significantly by county. It is essential for patients to recognize that regular monitoring of ada a1c directly affects their overall health care and reduces concerns related to complications from blood sugar issues.
Innovations in A1C Testing: New Methods and Technologies for Better Diabetes Management
Recent advancements in ada a1c testing have revolutionized the management of blood sugar levels, particularly through the introduction of point-of-care testing devices that yield immediate results. Priced at approximately $138.00, these devices enhance accessibility, allowing healthcare providers to make timely treatment adjustments, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Additionally, the availability of home testing kits empowers patients to conveniently monitor their ada a1c levels, fostering a proactive approach to managing their condition.
These innovations not only enhance the patient experience but also support individualized care plans, as individuals can easily track their progress between medical appointments. In line with a holistic approach to reversing the condition, as emphasized by the Integrative Wellness Center, establishing ada a1c goals in diverse populations necessitates the integration of tools like continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and blood glucose monitoring (BGM) alongside A1C metrics. This comprehensive strategy is crucial, especially given the alarming rise in global cases of this condition, which have quadrupled over the past few decades, underscoring the urgent need for effective management approaches.
Furthermore, community wellness programs play a vital role in supporting patients through education, nutrition, and emotional support, helping to alleviate the anxiety associated with potential complications of diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding the Hemoglobin A1C test is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. This test not only helps in diagnosing diabetes but also plays a significant role in monitoring long-term blood sugar control. With A1C levels serving as a key indicator of overall health, regular testing is essential for making timely adjustments to treatment plans, thereby reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
The article highlights the importance of adhering to the American Diabetes Association’s guidelines for A1C testing frequencies, emphasizing that personalized care and regular assessments can lead to improved health outcomes. Innovations in A1C testing methods further enhance patient management, allowing for immediate results and fostering a proactive approach to diabetes care.
In summary, being informed about A1C levels and utilizing effective management strategies empowers individuals to take control of their health. By challenging misconceptions about diabetes and engaging with community resources, patients can significantly improve their condition and overall well-being. As diabetes rates continue to rise globally, prioritizing A1C management is essential for achieving better health outcomes and reducing the associated medical costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ADA A1C test?
The ADA A1C test is a blood examination that measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in red blood cells, providing information about average blood sugar levels over the prior two to three months.
What does an elevated ADA A1C percentage indicate?
An elevated ADA A1C percentage indicates poor blood sugar control, which is associated with a higher risk of diabetes-related complications.
What is the diagnostic threshold for diabetes based on the ADA A1C level?
A commonly accepted diagnostic threshold for diabetes is an ADA A1C level of 6.5% or higher.
How does the ADA A1C test relate to diabetes diagnosis and management?
The ADA A1C test is crucial for diagnosing diabetes and managing the condition, as it reflects the effectiveness of treatment plans and overall blood sugar control.
What are the ADA A1C levels indicating prediabetes and diabetes?
An ADA A1C level ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, while a level of 6.5% or higher confirms diabetes.
Why is regular monitoring of ADA A1C levels important?
Regular monitoring of ADA A1C levels helps healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary adjustments to medications and lifestyle interventions to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
What financial implications are associated with diabetes management?
Excess medical costs related to diabetes management increased from $10,179 to $12,022 per person from 2012 to 2022, highlighting the importance of effective management and monitoring of ADA A1C levels.
What strategies can help improve ADA A1C levels?
Strategies to improve ADA A1C levels include dietary changes, increasing physical activity, utilizing stress reduction techniques, and participating in community wellness programs.
What common misconceptions exist about diabetes control?
Common misconceptions include the belief that diabetes is solely genetically inherited and that lifestyle modifications have little impact on managing the condition.
How can personalized care impact diabetes management?
Personalized care, including customized treatment plans focusing on lifestyle changes and education about insulin resistance, can lead to significant improvements in ADA A1C readings and overall health.