Introduction
The A1C test plays a pivotal role in the management of diabetes, serving as a reliable indicator of average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. This test is essential not only for monitoring the effectiveness of blood sugar control but also for guiding treatment adjustments for those living with diabetes.
With the rising prevalence of prediabetes and diabetes-related complications, understanding the implications of A1C levels has never been more critical. This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, what various levels signify for health, and the lifestyle changes that can help maintain optimal A1C readings.
By exploring these themes, readers will gain valuable insights into effective diabetes management strategies and the importance of regular monitoring in preventing long-term health issues.
Understanding the A1C Test: What It Measures and Why It Matters
The A1C test, often called the glycated hemoglobin test, plays an essential role in management by assessing the average glucose concentrations over the prior two to three months. This test yields a percentage that reflects the effectiveness of blood sugar control during this timeframe. For individuals with blood sugar issues, maintaining an optimal A1C of 4.9 is crucial, as it not only helps in tracking their condition but also enables necessary modifications to treatment strategies.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we believe in a holistic approach to reversing type 2 conditions, addressing root causes, and empowering patients through comprehensive insights and personalized care. Healthcare professionals routinely order the A1C test to evaluate long-term glucose control, with a target of achieving an A1C of 4.9 to identify potential risks for diabetes-related complications. Based on recent discoveries, the efficacy of A1C measurements, such as achieving an A1C of 4.9, in detecting blood sugar disorders is well-established, emphasizing its significance as a primary instrument in managing the condition.
As stated, ‘In conclusion, we found that A1C level was effective and convenient for screening of blood sugar issues.’ The significance of the A1C test is underscored further by the prevalence of prediabetes among various demographic groups, with an estimated 15 million Hispanic adults reported to have prediabetes in 2021, a prediabetes percentage of 34.5% and awareness at only 20.9%. These statistics affirm that vigilant monitoring through the A1C of 4.9 test is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring effective management of the condition.
Additionally, a case study titled “Hypoglycemia in Diabetic Patients” revealed that in 2020, there were 51,000 hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia in adults with the condition, resulting in a hospitalization rate of 2.2 per 1,000 adults. This data reflects the risks associated with managing blood sugar levels, reinforcing the necessity of regular A1C testing and monitoring, especially for patients aiming for an A1C of 4.9, as part of a comprehensive, integrative approach to patient health. Furthermore, addressing the anxiety that often accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of this condition is vital.
By concentrating on a comprehensive approach that investigates the underlying factors of the condition, we aim to empower our patients, assisting them in not only managing their health but also easing the emotional weight linked to it.
What Does an A1C of 4.9 Mean for Your Health?
An A1C measurement of a1c 4.9 is usually considered to be within the normal range, indicating that sugar concentrations have been effectively managed over the past months. This stage indicates a low risk of advancing to type 2 diabetes, reflecting effective management of glucose for individuals already diagnosed. According to health experts, since the A1C test assesses glucose amounts over a period of time, it offers more information about blood sugar than a single blood sugar test.
It is essential to recognize that individual health factors, lifestyle choices, and dietary habits can significantly influence A1C levels. Regular monitoring and consultations with healthcare professionals, especially in a holistic care environment such as the Integrative Wellness Center, are essential for maintaining optimal health and reducing the risk of future complications related to this condition. Numerous patients have expressed that embracing a holistic approach has eased their anxiety regarding managing their condition, enabling them to concentrate on their overall well-being.
Notably, pregnant women with Type 1 condition are advised to maintain an A1C of 6.5% or lower to reduce potential health risks. Emerging insights, such as those from Yoshinaga 1996, suggest that a combination of A1C and oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) can enhance the precision of predictions regarding the progression of this condition. Additionally, a case study titled ‘Risk of Heart Failure per 1% Increase in A1C’ revealed that each 1% increase in A1C is associated with a 39% increased risk of heart failure, emphasizing the critical role of comprehensive assessments and a holistic approach in diabetes management.
We invite you to learn more about how our integrative strategies can support your journey towards better health.
Factors That Influence A1C Levels
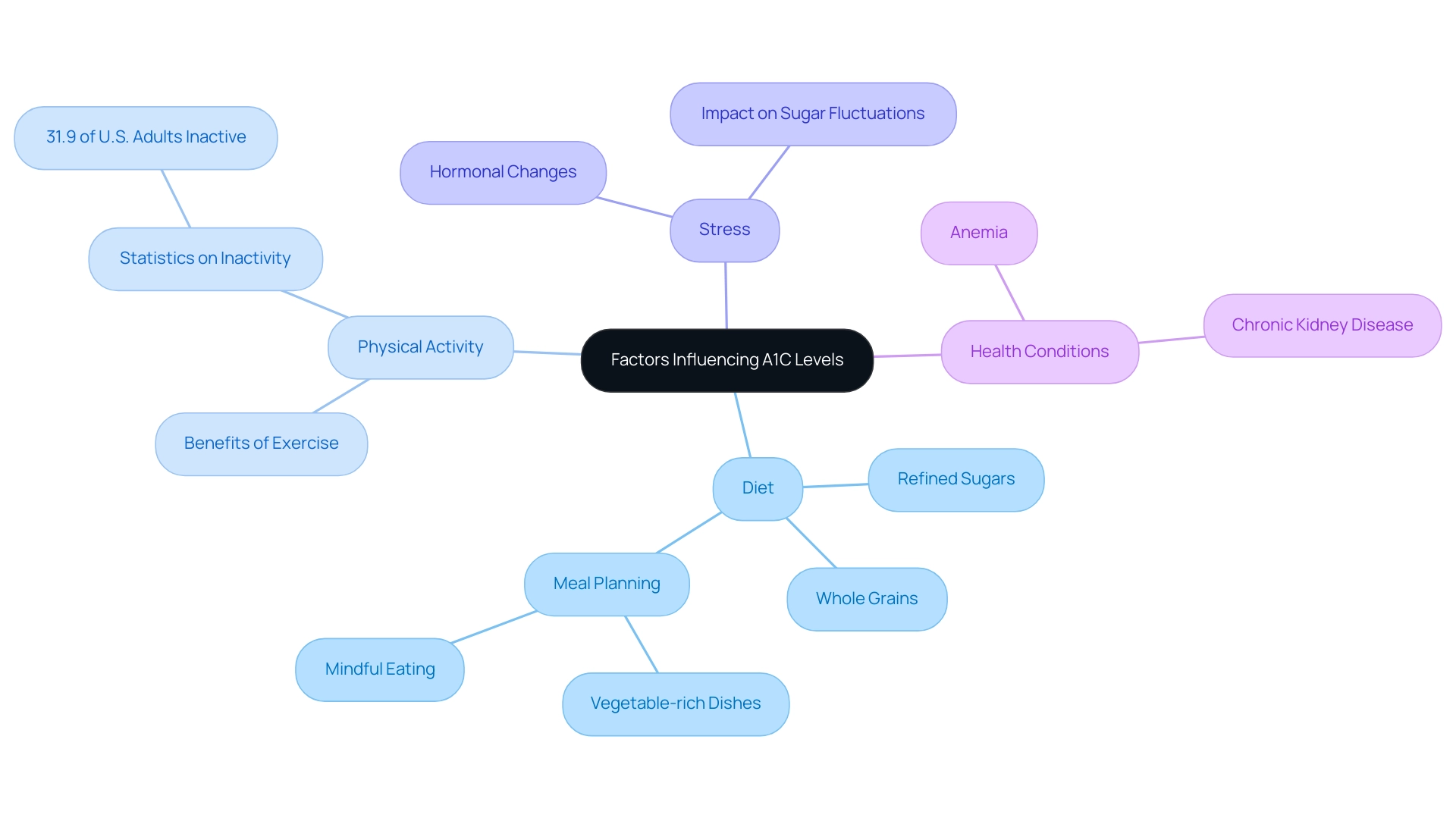
Understanding the root causes of Type II Diabetes is paramount for reclaiming health. A1C values can be impacted by various factors, and an example of a healthy A1C level is a1c 4.9, which is influenced by diet, physical activity, stress, and underlying health conditions. A diet rich in refined sugars and carbohydrates can significantly increase glucose concentrations, highlighting the significance of whole grain choices for sugar regulation and energy.
Regular physical activity is essential for reducing and stabilizing these figures; however, recent statistics reveal that 31.9% of U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes participate in minimal physical activity, defined as less than 10 minutes per week of moderate or vigorous exercise. This inactivity can negatively impact sugar control and, therefore, lead to A1C readings such as a1c 4.9. Furthermore, stress can exacerbate sugar fluctuations due to hormonal changes, while health conditions such as anemia and chronic kidney disease may skew A1C test results, making an A1C of a1c 4.9 less reliable.
Significantly, the average baseline fasting plasma glucose (FPG) for individuals with high blood sugar is 5.4 mmol/l, highlighting the necessity for a thorough strategy to keep blood sugar readings within a target range. A case study by Yoshinaga in 1996 involving 819 Japanese government officials and their spouses with an A1C of a1c 4.9% defined incident hyperglycemia based on FBG ≥ 6.7 mmol/l, illustrating the real-world implications of A1C levels on the incidence of the condition. As Xuanping Zhang notes, effective management of this condition necessitates a holistic understanding of these variables, particularly for those aiming to prevent or delay the onset of type 2, as evidenced by systematic reviews examining the relationship of a1c 4.9 to future incidence.
To enhance your blood sugar management, consider integrating specific strategies such as:
- Meal planning with vegetable-rich dishes, which support regulation and overall health.
- Exploring lesser-known tips like mindful eating and stress-reduction techniques.
These strategies can further empower you in your journey towards better health.
Lifestyle Changes to Maintain Healthy A1C Levels
To sustain healthy A1C levels and alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of this condition, individuals should prioritize a balanced diet that includes:
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Fruits
- Vegetables
while minimizing the intake of added sugars and processed foods. This approach is part of a holistic regimen that addresses the root causes of the condition, empowering patients at the Integrative Wellness Center. Notably, prediabetes awareness among Hispanic adults was reported at 20.9% from 2017 to 2020, underscoring the critical need for effective management strategies.
Recent studies indicate that consistent dietary adjustments can lead to significant improvements in A1C, highlighting the importance of nutrition in diabetes management. Moreover, participating in consistent physical activity, targeting a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, is essential for effective sugar regulation. Exercise not only aids in lowering blood glucose but also enhances insulin sensitivity, as evidenced by findings from the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study (HPFS), which revealed a significant interaction between a Western diet and health outcomes.
Moreover, the case study on medication modifications showed that a predefined algorithm for medication adjustments led to decreased insulin dosages and cessation of sulfonylurea in the low-carbohydrate group, highlighting the real-world effect of lifestyle changes on achieving an A1C of 4.9. Managing stress through mindfulness, yoga, or meditation techniques can also contribute positively to overall health and A1C measurements. Consistently tracking glucose levels and consulting healthcare professionals guarantees that individuals obtain personalized guidance customized to their specific requirements, emphasizing the significance of a proactive strategy in managing the condition, particularly considering the risks associated with conventional treatments.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
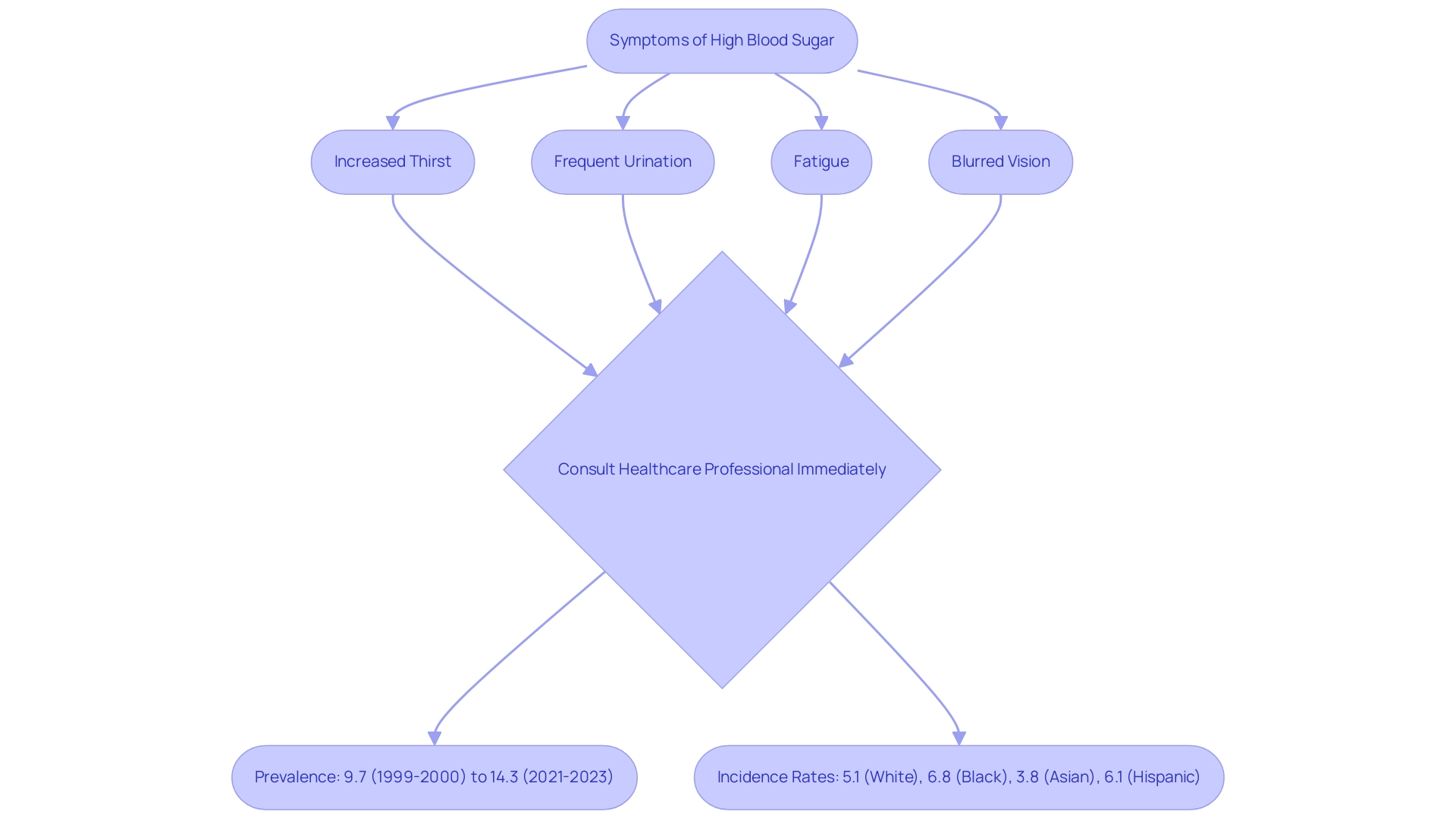
For individuals experiencing symptoms of high blood sugar—such as increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, or blurred vision—it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional promptly. The age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed cases of the condition has increased alarmingly, from 9.7% in 1999-2000 to 14.3% as of August 2021-2023, according to Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H. This trend underscores the growing public health issue that requires immediate attention.
Incidence rates further illustrate this concern, with:
- 5.1 per 1,000 for White, non-Hispanic adults
- 6.8 per 1,000 for Black, non-Hispanic adults
- 3.8 per 1,000 for Asian, non-Hispanic adults
- 6.1 per 1,000 for Hispanic adults
Significant changes in A1C levels, especially when lifestyle modifications do not yield the expected results, necessitate immediate professional consultation to address concerns related to a1c 4.9. In 2019, hypoglycemia resulted in around 60,000 hospital discharges, or 2.5 per 1,000 adults with the condition, highlighting the critical necessity for timely intervention.
The direct medical expenses for diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar reached $306.6 billion in 2022, emphasizing the economic burden that necessitates urgent medical advice. Routine check-ups are vital for identifying potential complications early, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment plans. Establishing a strong partnership with healthcare providers is essential for effective management of the condition, as evidenced by patient success stories at the Integrative Wellness Center.
For instance, one patient shared, ‘Thanks to the holistic approach here, I’ve not only managed my condition but also reclaimed my health and vitality.’ Another noted, ‘The support and personalized care I received transformed my understanding of managing this condition.’ These testimonials reflect how addressing the root causes of this condition empowers individuals to take control of their health.
Understanding the Importance of Regular Monitoring
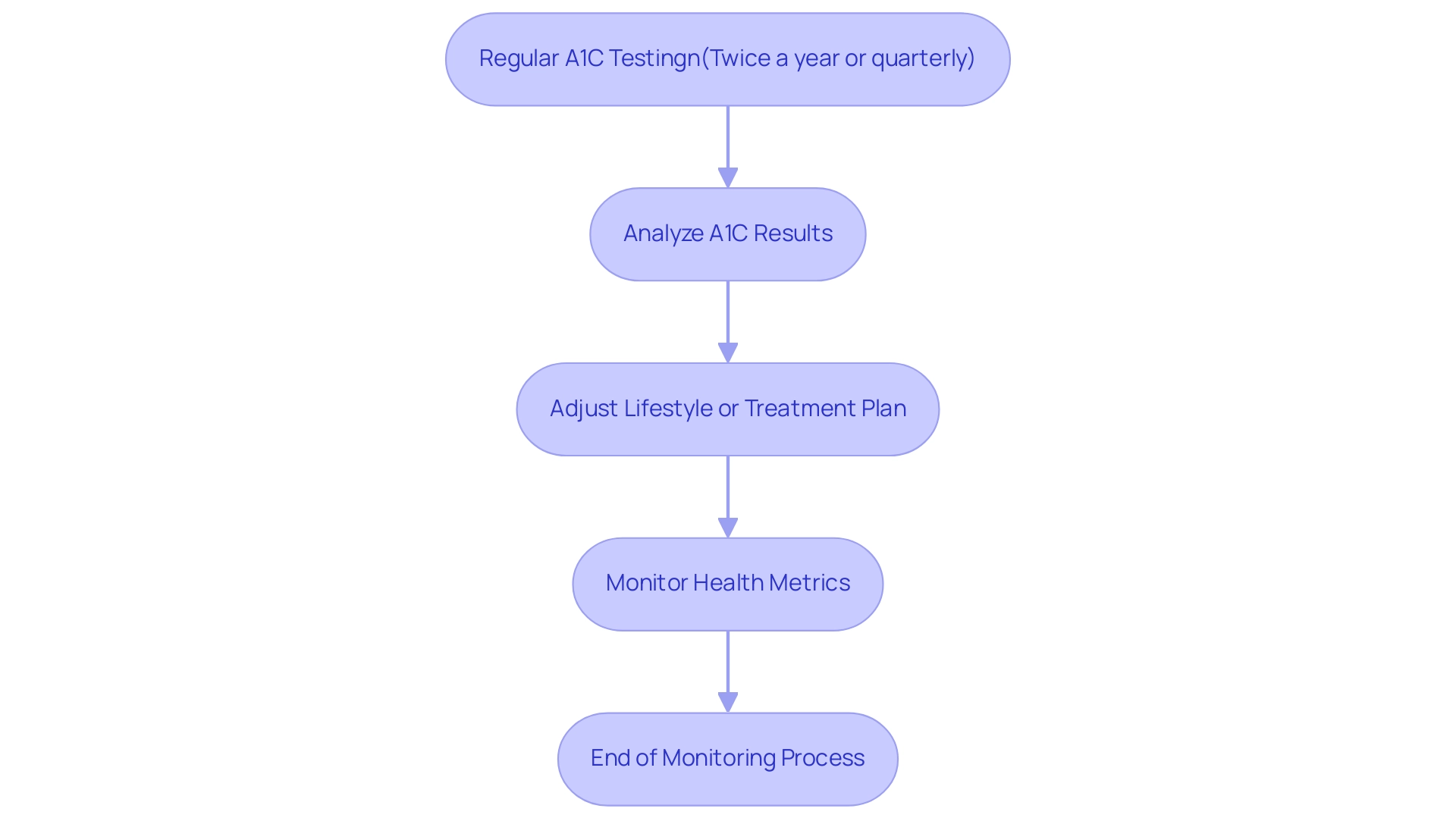
Consistent observation of A1C readings, including achieving an A1C of 4.9, is essential for efficient management of the condition, enhancing at-home glucose testing. According to current recommendations, individuals who meet their targets for blood sugar should undergo A1C testing for an A1C of 4.9 at least twice a year, while those requiring adjustments should be tested quarterly. This regularity in monitoring empowers individuals to discern the impact of their lifestyle choices on blood sugar readings, facilitating timely modifications to their management plans.
The importance of these metrics is highlighted by findings from the ARIC study, which demonstrated that A1C of 4.9 levels and fasting glucose levels are strong predictors of diagnosed conditions. Moreover, the NHANES III study highlighted the significance of both single and repeat glucose values in understanding undiagnosed conditions, emphasizing the need for consistent monitoring. E.S., a study designer and data analyst, noted, “We also found that both A1C of 4.9 and fasting glucose strongly predict subsequent risk of diagnosed conditions, but the very high risk observed for individuals with both elevated fasting glucose and A1C of 4.9 suggests a dual role for these factors in the prediction of such conditions.”
Comprehensive health monitoring is crucial, as indicated by the statistic that 93.0% of individuals had their cholesterol checked, complementing A1C monitoring. “The ‘ABCs of Diabetes Management’ case study illustrates the challenges in achieving optimal management of the condition, where only 11.1% of individuals met all criteria for A1C of 4.9, blood pressure, cholesterol, and smoking, while 36.8% met less stringent goals. By staying informed about their health metrics, individuals can proactively take steps to prevent complications and promote their overall well-being.”
Furthermore, statistics reveal that in 2020, the hospitalization rate for hypoglycemia was 2.2 per 1,000 adults with the condition, reinforcing the necessity of regular monitoring to mitigate such risks. For instance, patients like John, who embraced a holistic method at the Integrative Wellness Center, successfully reversed their type 2 condition through personalized care and education. By focusing on lifestyle changes and comprehensive monitoring, he eliminated his anxiety over potential complications.
By adopting a holistic approach, such as that offered by the Integrative Wellness Center, patients can empower themselves through education and personalized care, ultimately striving to reverse type 2 diabetes and eliminate anxiety over complications.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is crucial for effective diabetes management, as it provides essential insights into average blood glucose levels over time. This test not only indicates how well an individual’s blood sugar is controlled but also serves as a guide for necessary treatment adjustments. With the alarming rise in prediabetes and diabetes-related complications, the importance of regular A1C monitoring cannot be overstated.
Maintaining optimal A1C levels involves a multifaceted approach, including:
- Dietary modifications
- Regular physical activity
- Stress management
Lifestyle changes such as adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods and engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly can significantly impact A1C levels. Furthermore, understanding the various factors that influence these levels empowers individuals to take charge of their health.
For those experiencing symptoms of high blood sugar or witnessing significant changes in A1C levels, timely consultation with healthcare professionals is essential. Establishing a strong partnership with healthcare providers enhances diabetes management and facilitates early intervention, preventing potential complications. Regular monitoring of A1C levels, coupled with a proactive approach to lifestyle changes, can lead to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life for those living with diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, measures the average glucose concentrations over the prior two to three months. It is crucial for managing blood sugar issues, as it reflects the effectiveness of blood sugar control during that timeframe.
What is the target A1C level for individuals with blood sugar issues?
The target A1C level for individuals with blood sugar issues is 4.9. Maintaining this level is important for tracking their condition and making necessary treatment modifications.
How does the A1C test compare to single blood sugar tests?
The A1C test provides more comprehensive information about blood sugar levels over time compared to a single blood sugar test, as it assesses glucose amounts over a period of two to three months.
What are the implications of having an A1C level of 4.9?
An A1C level of 4.9 is considered within the normal range, indicating effective management of sugar concentrations and a low risk of advancing to type 2 diabetes for individuals already diagnosed.
What role does the Integrative Wellness Center play in managing blood sugar levels?
The Integrative Wellness Center employs a holistic approach to reversing type 2 conditions by addressing root causes and empowering patients with personalized care and insights.
What are the statistics regarding prediabetes among Hispanic adults?
In 2021, an estimated 15 million Hispanic adults had prediabetes, with a prevalence rate of 34.5% and only 20.9% awareness of their condition.
Why is regular A1C testing important?
Regular A1C testing is essential for monitoring blood sugar levels and preventing complications associated with diabetes, as evidenced by hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia.
What A1C level should pregnant women with Type 1 diabetes maintain?
Pregnant women with Type 1 diabetes are advised to maintain an A1C of 6.5% or lower to reduce potential health risks.
How does A1C relate to the risk of heart failure?
Each 1% increase in A1C is associated with a 39% increased risk of heart failure, highlighting the importance of comprehensive assessments in diabetes management.
How can a holistic approach help patients manage their health?
A holistic approach can ease anxiety related to managing blood sugar levels and enable patients to focus on their overall well-being, as many patients have reported positive experiences with this method.