Overview
The article addresses the American Diabetes Association’s A1C guidelines, emphasizing the importance of maintaining an A1C level below 7% for effective diabetes management and reducing complications. It supports this by detailing the guidelines’ recommendations for individualized monitoring and lifestyle modifications, which collectively empower individuals to take control of their health and improve their blood sugar management outcomes.
Introduction
The management of diabetes is a multifaceted challenge that requires a deep understanding of various factors, with the A1C test serving as a critical cornerstone in this process. This test not only provides insights into average blood glucose levels over the preceding months but also plays a pivotal role in guiding treatment strategies and lifestyle modifications.
With the prevalence of diabetes on the rise, particularly in the United States, healthcare providers and patients alike must prioritize effective blood glucose management to mitigate potential complications.
This article delves into the significance of A1C levels, the American Diabetes Association’s guidelines, and the lifestyle changes necessary for achieving optimal health outcomes. By exploring these essential components, individuals can gain valuable insights into managing their diabetes more effectively and fostering a proactive approach to their health.
Understanding A1C: The Cornerstone of Diabetes Management
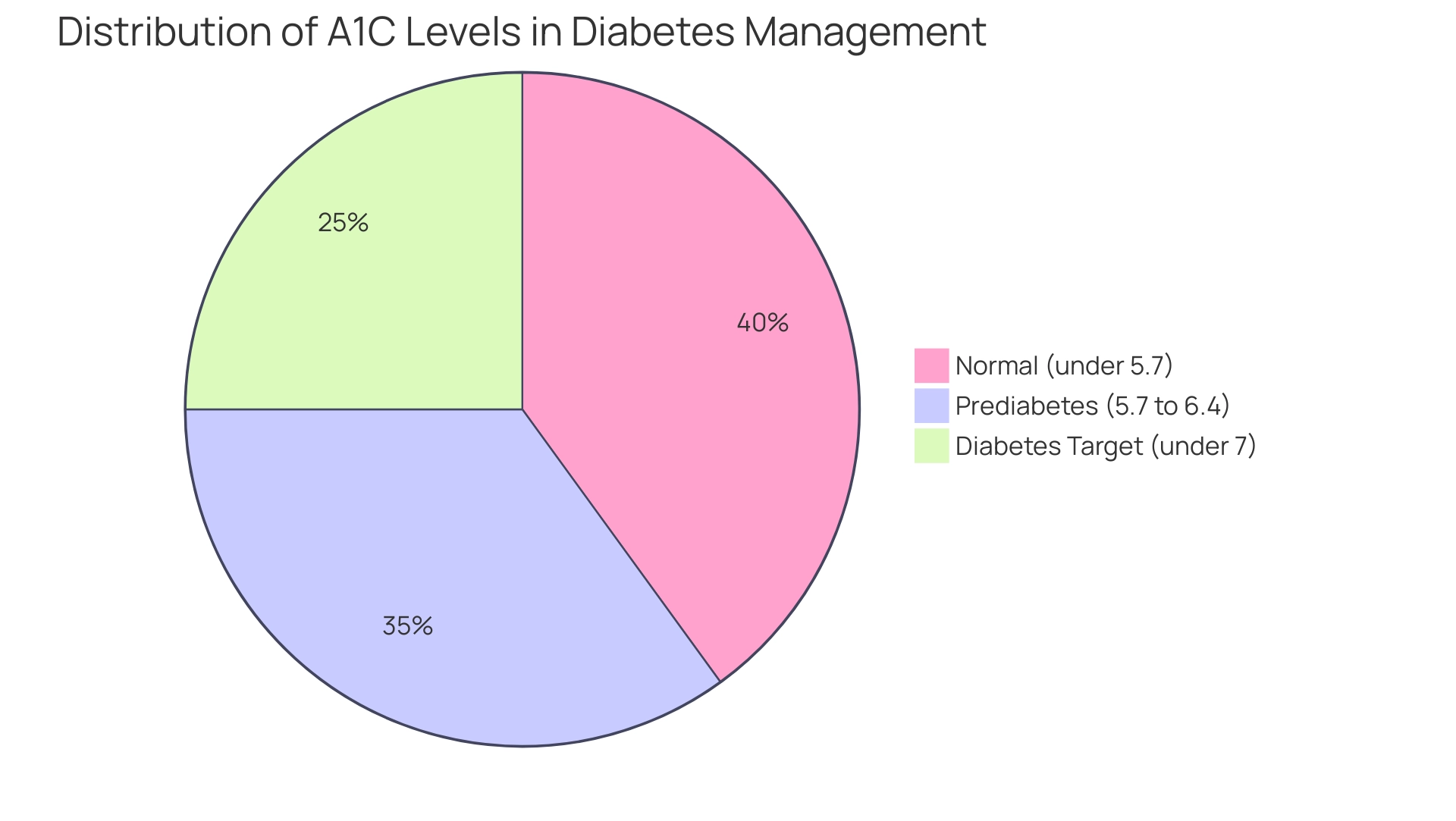
The A1C test, widely recognized as the hemoglobin A1C test, quantifies the percentage of hemoglobin proteins in the blood that are glycated, indicating average blood glucose levels over the preceding two to three months. For individuals managing blood sugar levels, this test is essential for assessing the effectiveness of their blood glucose management strategies. According to the A1C guidelines established by the American Diabetes Association, an A1C level under 5.7% is classified as normal, while levels ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes.
For those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, the A1C guidelines from the American Diabetes Association typically recommend a target of less than 7%, although this target may be adjusted based on individual health circumstances and goals. Understanding and monitoring these levels empower individuals and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment plans and necessary lifestyle modifications, ultimately promoting optimal health outcomes. To further enhance patient care, integrating a holistic approach that addresses the root causes of the condition can significantly reduce anxiety around potential complications, allowing patients to find new peace in their lives.
This method highlights the significance of reassessing the origin of the condition, which is essential for creating effective handling strategies. Notably, the prevalence of this condition in the U.S. has seen a marked increase, with the age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed cases rising from 1999-2000 to August 2023, as noted by Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H., who states, “The age-adjusted prevalence of total and diagnosed cases increased between 1999–2000 and August 2021–August 2023.” This highlights the urgent requirement for effective blood glucose control strategies, particularly noting that in 2020, the crude rate of emergency department visits for hypoglycemia was 8.6 per 1,000 adults.
Additionally, understanding conditions like Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA), characterized by slow autoimmune β-cell destruction, is crucial for timely insulin initiation and management to prevent deterioration, further emphasizing the complexity of managing this condition. By adopting an integrative wellness framework, individuals can gain a fuller understanding of their condition, equipping them to actively participate in their health journey.
American Diabetes Association A1C Guidelines: Key Recommendations
The A1C guidelines from the American Diabetes Association establish that adults with diabetes should maintain an A1C level of less than 7% to effectively reduce the risk of complications related to the condition. However, at the Integrative Wellness Center, we believe that a holistic approach can empower individuals to eliminate anxiety over potential health complications and find new peace in life. For specific populations, such as older adults or those with limited life expectancy, the ADA advises a personalized approach that adheres to the A1C guidelines of the American Diabetes Association, allowing for higher A1C targets when clinically appropriate.
This agreement is supported by a Professional Practice Committee of 21 international specialists, who concur that creating a standardized method for handling the condition aids individuals, caregivers, and policymakers equally. Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential, in accordance with the A1C guidelines from the American Diabetes Association, with checks recommended every three to six months to ensure compliance with these individualized targets. The ADA emphasizes the significance of lifestyle modifications, promoting dietary changes and increased physical activity as essential components in comprehensive management of the condition, in line with the A1C guidelines from the American Diabetes Association.
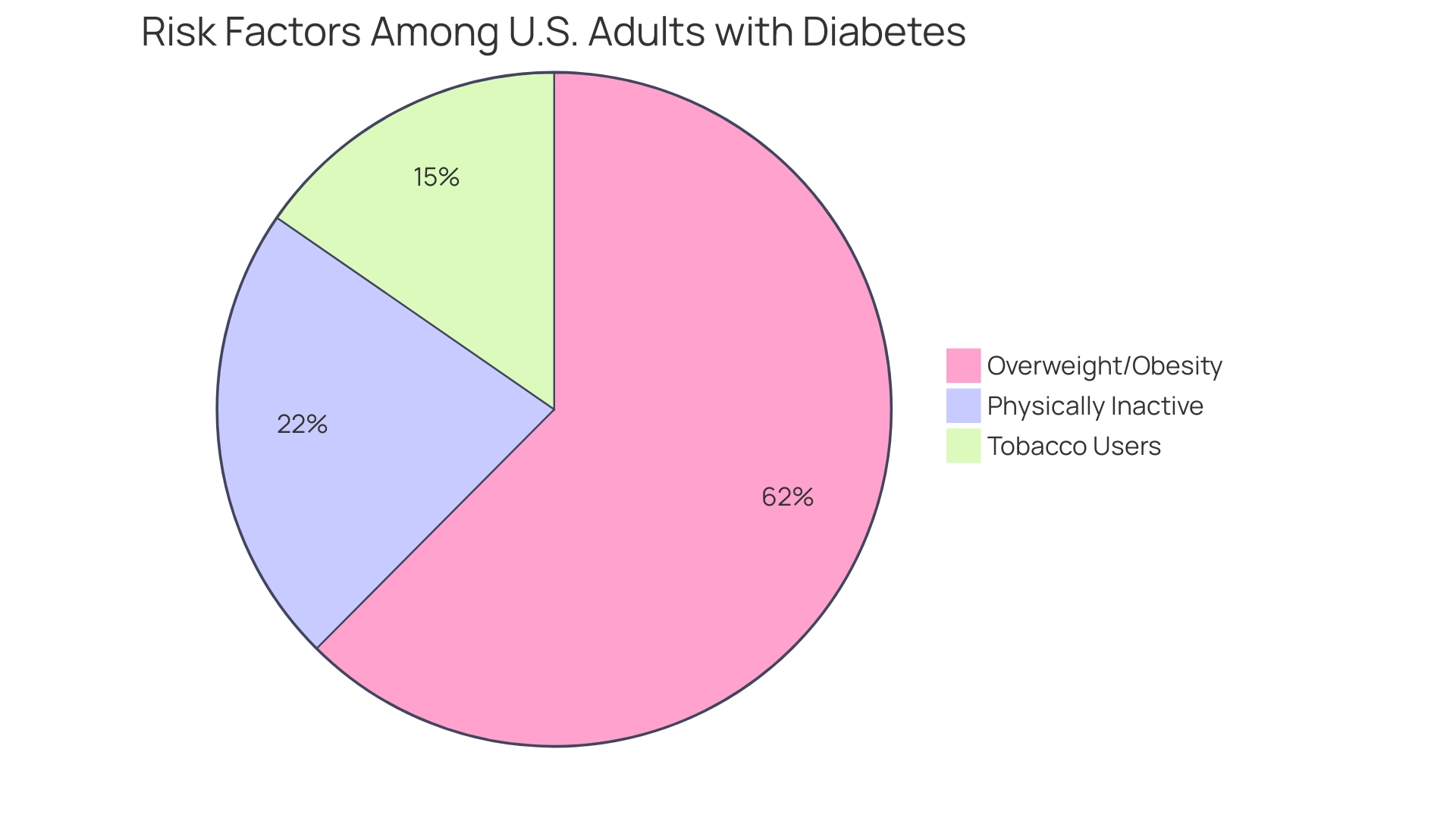
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we tackle root causes and enhance health through transformative success stories, demonstrating how holistic approaches can result in overcoming chronic health challenges. For instance, one case study highlighted a patient who, after adopting our holistic approach, was able to reduce their A1C from 9% to 6.5% within six months, significantly decreasing their risk of complications. A broader evaluation of risk factors for complications associated with diabetes found that among U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions:
- 22.1% were tobacco users
- 89.8% were overweight or had obesity
- 31.9% were physically inactive
Disturbingly, only a fraction of adults with this condition are successfully meeting A1C targets as outlined in the A1C guidelines from the American Diabetes Association, underscoring the urgent need for effective implementation of these strategies. By incorporating extensive insights and treatment alternatives for reversing Type 2 conditions, the Integrative Wellness Center is committed to creating a supportive atmosphere that promotes positive health results and assists individuals in finding tranquility in their health journey.
Factors Affecting A1C Levels
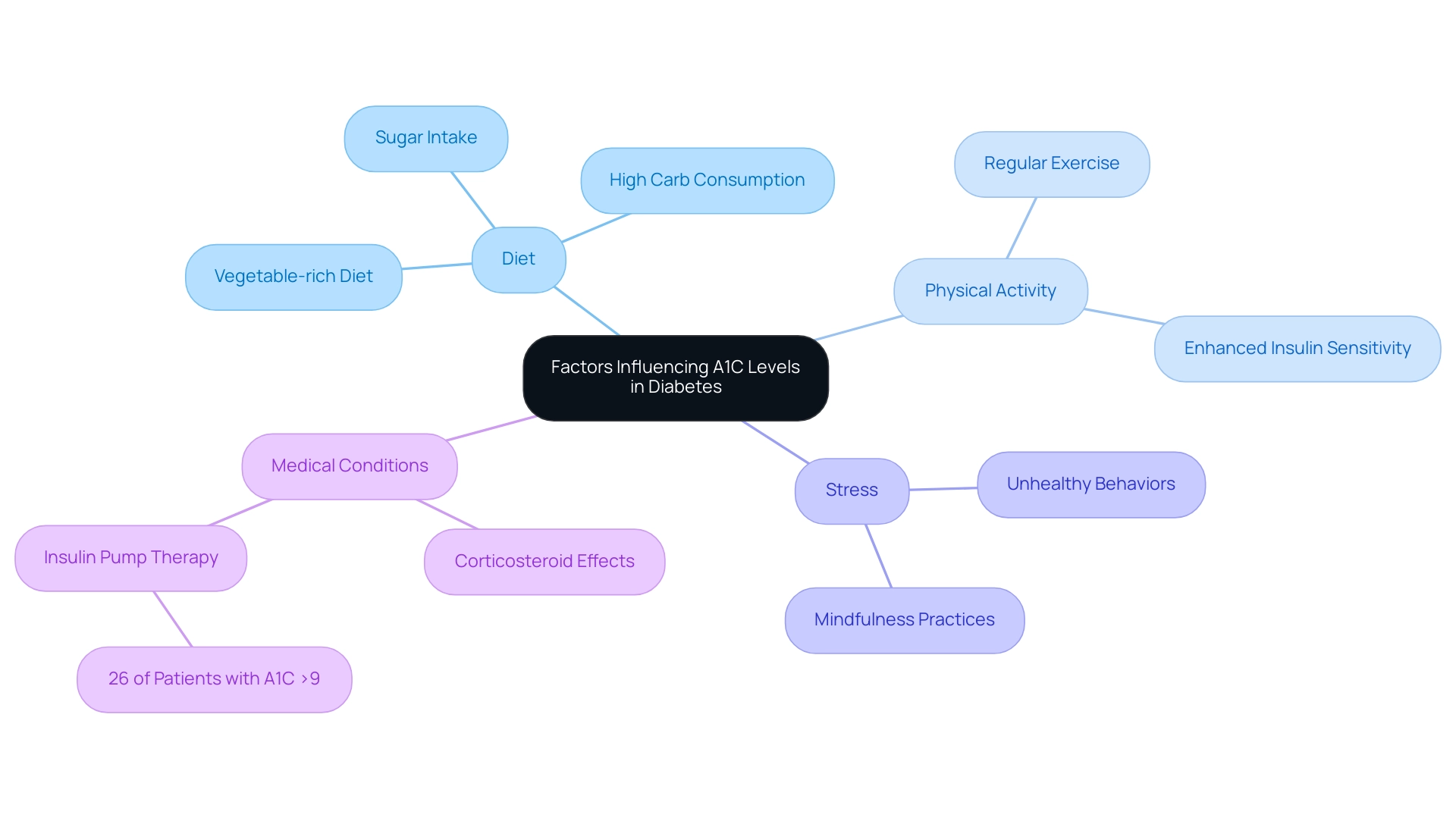
A1C levels in patients with diabetes-related issues are influenced by a multitude of factors, including diet, physical activity, stress, and specific medical conditions, according to the A1C guidelines established by the American Diabetes Association. Recent findings indicate that a substantial proportion of patients—1,030 individuals or 26%—with A1C levels exceeding 9% utilized insulin pump therapy, illustrating the complexity of controlling the condition. Statistical analyses using SAS and Stata were employed to account for repeated measures and provide odds ratios and confidence intervals, underscoring the rigor of the research.
Diet plays a critical role; particularly, a vegetable-rich diet can support blood sugar regulation and overall health, while high consumption of carbohydrates and sugars can lead to increased blood glucose levels, consequently elevating A1C. In contrast, regular physical activity is proven to enhance insulin sensitivity, contributing to lower A1C levels. For instance, a recent study presented at the American Diabetes Association’s 81st Scientific Sessions highlighted the impact of lifestyle changes on adherence to A1C guidelines set by the American Diabetes Association.
Furthermore, the NHANES data indicates a 21.5% prevalence of prediabetes among reproductive-age women, supporting the adoption of inclusive diagnostic criteria for gestational conditions. Stress is an important factor; it can trigger unhealthy behaviors such as overeating or decreased physical activity, which negatively impact blood sugar control. Medications such as corticosteroids are also recognized to affect A1C levels, further complicating care for the condition.
As S.R. and O.E., guarantors of the relevant research, noted, they had complete access to all data, underscoring the importance of integrity in studies related to blood sugar control. Comprehending these complex influences provides individuals with the knowledge to make informed lifestyle decisions, ultimately resulting in more effective management through personalized care and community support, as recommended by the A1C guidelines of the American Diabetes Association.
Furthermore, endorsements from individuals who have effectively controlled their condition through these strategies emphasize the transformative effect of lifestyle modifications. One patient shared how incorporating more vegetables into their diet not only improved their A1C levels but also enhanced their overall energy and well-being. Another lesser-known power-play involves mindfulness practices, which can significantly reduce stress and improve dietary choices, further aiding in blood sugar control.
Embracing these insights can empower individuals to take charge of their health and achieve lasting results.
Monitoring A1C: When and How Often
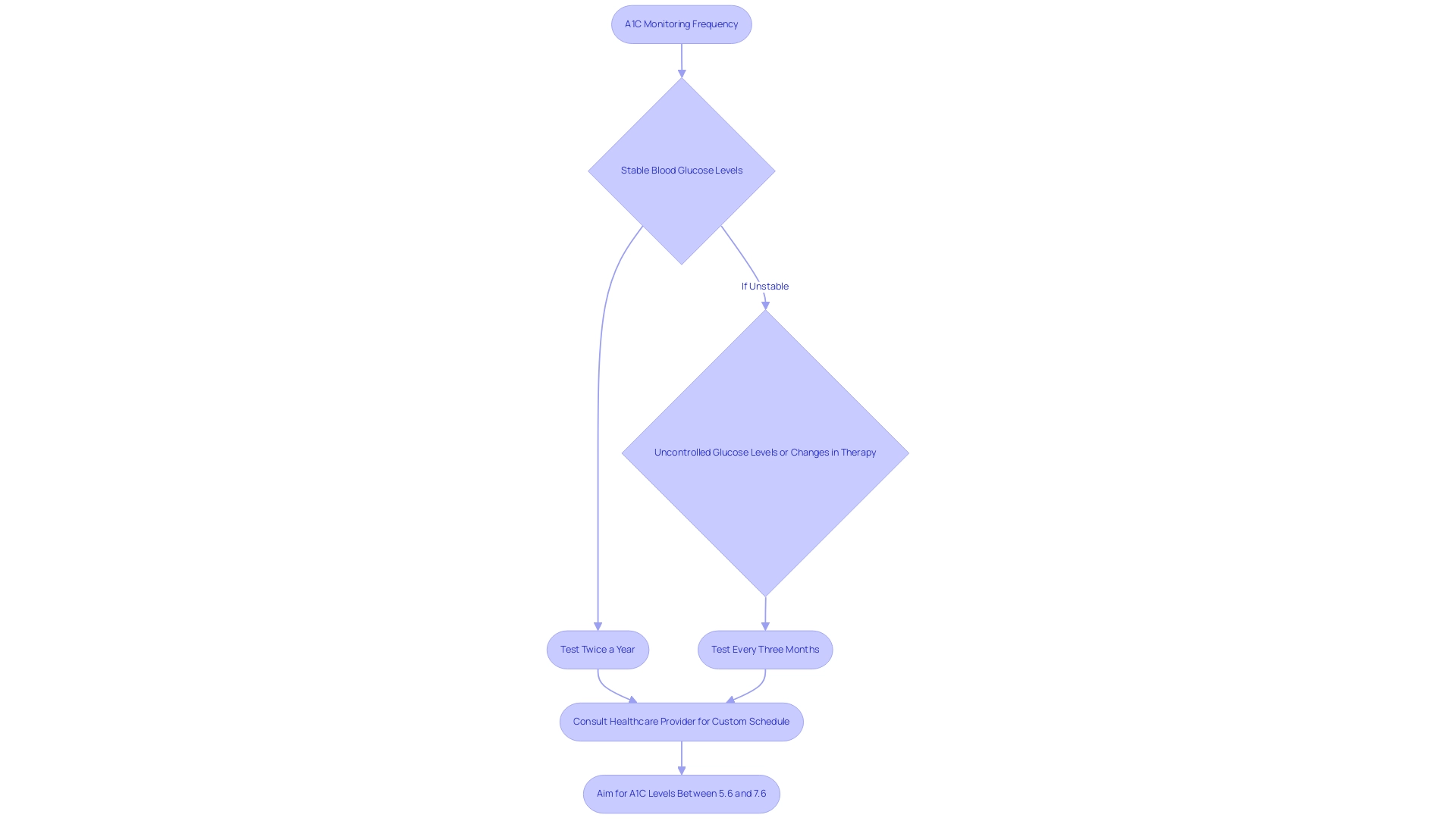
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) highlights the significance of comprehending insulin resistance in controlling blood sugar levels, especially for women during pregnancy to prevent gestational complications. Insulin resistance can complicate blood sugar management, making it crucial to monitor A1C levels regularly. The ADA recommends that adults with the condition adhere to the A1C guidelines by undergoing A1C testing at least twice a year when blood glucose levels are stable.
However, for those experiencing changes in therapy or uncontrolled glucose levels, testing should occur every three months. This approach not only aids in tracking an individual’s progress but also facilitates timely treatment adjustments. Research indicates that individuals who follow these suggestions attain improved results in controlling their condition.
Conversations with healthcare providers are crucial to develop a customized A1C testing schedule that corresponds with personal management plans. Furthermore, understanding the dangers of traditional treatments for insulin resistance, which can lead to severe complications, is vital. The ADA Professional Practice Committee observes that a uniform method for diagnosing gestational GDM advantages patients, caregivers, and policymakers equally.
By adhering to tailored monitoring frequencies, individuals with this condition can maintain stable A1C levels—ideally between 5.6% and 7.6% (38 to 60 mmol/mol)—as recommended by the A1C guidelines, optimizing their health outcomes. Additionally, individuals with prediabetes or a history of gestational conditions should undergo a preconception evaluation, highlighting updates in postpartum care. Insights from case studies, such as Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY), can also provide valuable perspectives on personalized testing schedules and the implications of insulin resistance.
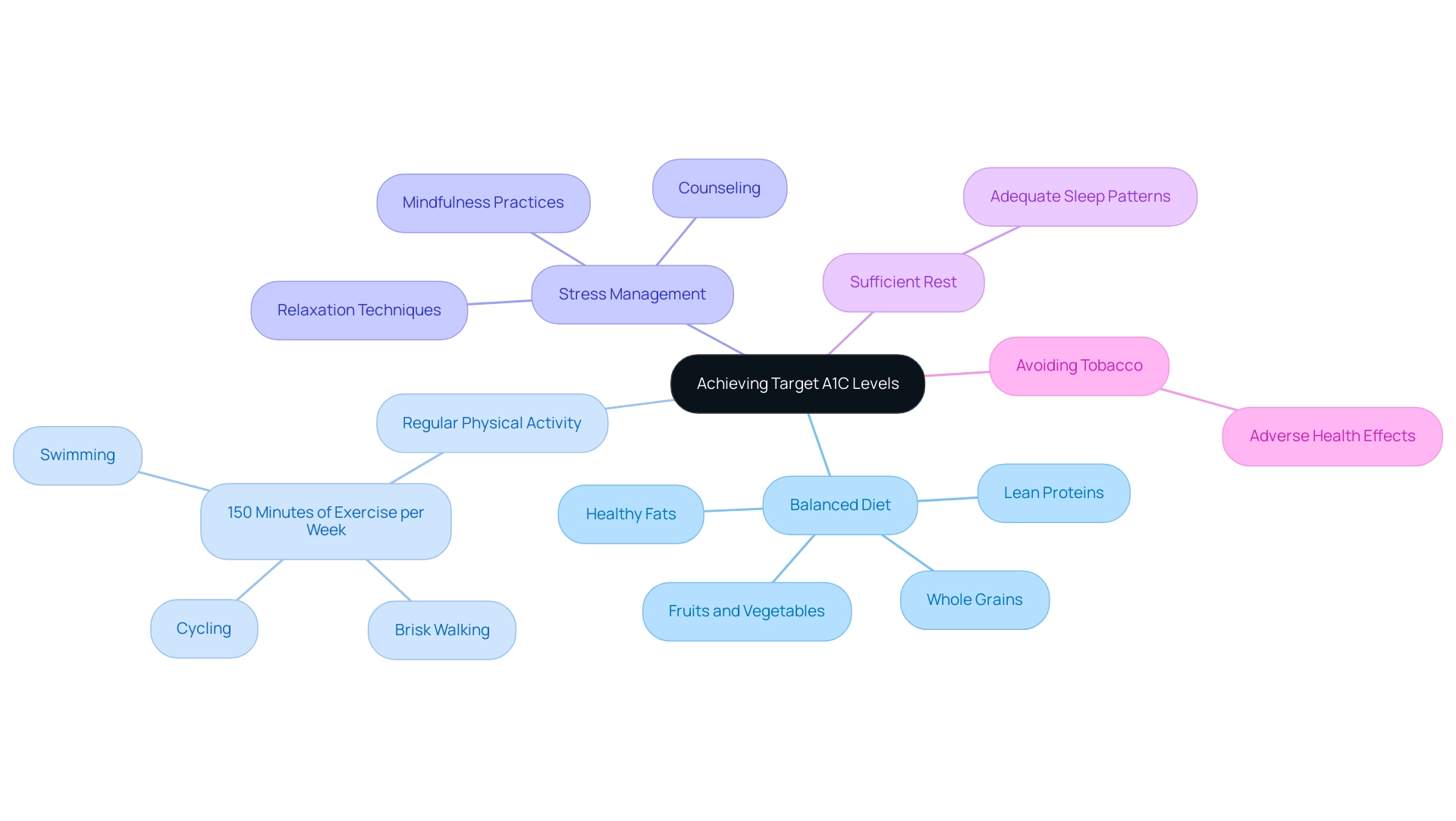
Lifestyle Modifications to Achieve Target A1C Levels
To achieve target A1C levels, individuals with blood sugar issues should prioritize several essential lifestyle changes in accordance with the A1C guidelines from the American Diabetes Association as part of a comprehensive, holistic strategy. A balanced diet is crucial; this includes incorporating:
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
- A variety of fruits and vegetables
to promote overall health and glycemic control. Recent studies emphasize that maintaining a diet rich in these components can directly influence A1C levels, with lifestyle changes showing significant improvements.
Notably, the prevalence of undiagnosed conditions related to blood sugar is concerning, with rates increasing from 1.6% in underweight or normal weight adults to 2.8% in overweight adults, and reaching 7.9% in adults with obesity. This statistic highlights the significance of lifestyle modifications in the control of blood sugar. Regular physical activity is equally vital; engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can substantially help lower A1C levels, as highlighted by the A1C guidelines from the American Diabetes Association.
Moreover, managing stress through mindfulness practices, counseling, or relaxation techniques has been shown to stabilize blood sugar levels effectively, a key aspect of the integrative approach advocated at the Integrative Wellness Center. Sufficient rest is another essential element, as inadequate sleep patterns can worsen insulin resistance and impede the control of the condition. Avoiding tobacco use is essential as well, given its adverse effects on overall health.
As Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics mentions, ‘Prevalence of total, diagnosed, and undiagnosed blood sugar conditions in adults’ emphasizes the urgent need for effective handling strategies. Additionally, the case study titled ‘Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes’ emphasizes the importance of structured diagnostic testing and confirmatory testing for abnormal results, linking these practices to the lifestyle changes discussed for achieving target A1C levels as outlined in the A1C guidelines from the American Diabetes Association. Significantly, tackling the anxiety that frequently comes with managing health conditions is essential; our comprehensive approach not only emphasizes lifestyle modifications but also on enabling individuals to feel more in control of their well-being.
Embracing this holistic regimen, which begins by reassessing the cause of your condition, not only empowers individuals but also increases their chances of reaching and maintaining their A1C targets according to the A1C guidelines from the American Diabetes Association, thereby enhancing their overall control of the illness.
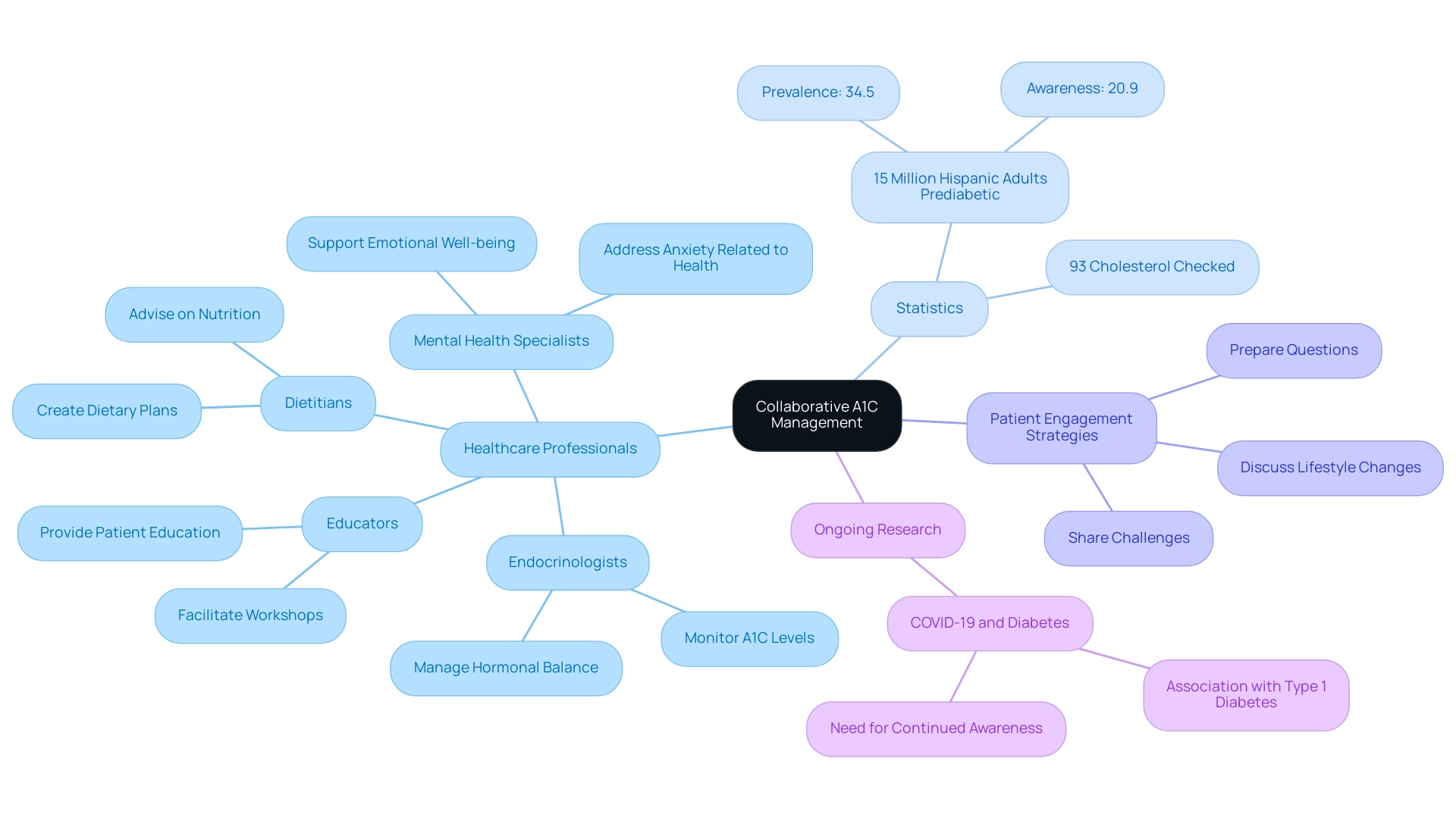
Working with Healthcare Professionals on A1C Management
Effective control of blood sugar requires a comprehensive team strategy, involving various healthcare professionals such as endocrinologists, educators, dietitians, and mental health specialists. This collaboration is essential, as an estimated 93.0% of patients have had their cholesterol checked, indicating proactive health monitoring within the care team for individuals with blood sugar issues. Notably, obesity is the leading cause of Type 2 conditions, accounting for almost 60% of cases, which underscores the importance of addressing lifestyle factors in management strategies.
Dr. Jason Shumard, D.C., the owner of DrShumard.com, holds a Doctorate of Chiropractic and a B.S. degree in Kinesiology, and is a sought-after practitioner in San Diego specializing in Type 2 blood sugar disorders and thyroid conditions. At Dr. Shumard’s Integrative Wellness Center, individuals are empowered to take control of their health through a holistic approach that addresses the underlying causes of the condition.
Here, individuals receive education on functional medicine practices, including tailored dietary plans and lifestyle changes, aimed at reversing Type 2 conditions and hypothyroidism, thus alleviating anxiety over potential complications. Furthermore, in 2021, an estimated 15.0 million Hispanic adults had prediabetes, with a prevalence of 34.5% and an awareness rate of only 20.9%, highlighting the need for targeted interventions in specific populations. Regular communication with healthcare experts allows for tailored treatment plans that meet individual needs and promptly address any concerns regarding A1C levels, following the a1c guidelines american diabetes association, or other vital health metrics.
Patients are encouraged to take an active role in their healthcare by preparing questions, discussing lifestyle changes, and sharing challenges they encounter. This collaborative dynamic not only enhances management of the condition but also creates a supportive environment conducive to achieving health goals. As noted by MD Rabiul Islam from the School of Pharmacy at BRAC University,
Diabetes mellitus, the fastest growing global public health concern: early detection should be focused,
underscoring the critical nature of teamwork in improving patient outcomes and ensuring comprehensive care.
Additionally, ongoing research, such as that regarding the association between COVID-19 and new onset of Type 1 diabetes, emphasizes the need for continued awareness and adaptation in diabetes care.
Conclusion
Understanding the management of diabetes is essential for both patients and healthcare providers, particularly in light of the rising prevalence of the condition. The A1C test stands out as a vital tool, providing crucial insights into average blood glucose levels and guiding treatment strategies. Adhering to the American Diabetes Association’s guidelines, which recommend maintaining A1C levels below 7% for most adults, can significantly reduce the risk of complications. Regular monitoring and personalized care are paramount in achieving these targets, as evidenced by numerous case studies illustrating successful outcomes through holistic approaches.
Moreover, lifestyle modifications such as:
- A balanced diet
- Regular physical activity
- Stress management
play a pivotal role in optimizing A1C levels. These changes not only enhance blood glucose control but also contribute to overall well-being. By integrating these practices into daily routines, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their diabetes effectively.
Collaboration with healthcare professionals is equally important. A multidisciplinary approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their unique needs, fostering a supportive environment conducive to achieving health goals. As diabetes remains a significant public health concern, prioritizing effective management strategies, including understanding A1C levels and embracing lifestyle changes, is crucial for improving health outcomes and enhancing quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and what does it measure?
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin proteins in the blood, indicating average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months.
What do the A1C levels indicate regarding blood sugar management?
According to the American Diabetes Association, an A1C level under 5.7% is normal, while levels from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, a target A1C level of less than 7% is generally recommended.
How often should A1C levels be monitored?
The American Diabetes Association recommends monitoring A1C levels every three to six months to ensure compliance with individualized targets.
What holistic approach is suggested for managing diabetes?
A holistic approach addresses the root causes of diabetes, which can help reduce anxiety about potential complications and promote optimal health outcomes. This may include lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and increased physical activity.
What are some risk factors associated with diabetes in U.S. adults?
Among U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes, 22.1% are tobacco users, 89.8% are overweight or have obesity, and 31.9% are physically inactive.
What has been the trend in the prevalence of diabetes in the U.S.?
The age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed diabetes cases has increased from 1999-2000 to August 2023, highlighting the urgent need for effective blood glucose control strategies.
What is the significance of understanding conditions like Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA)?
Understanding LADA is crucial for timely insulin initiation and management to prevent deterioration of the condition, emphasizing the complexity of diabetes management.
How can individuals benefit from adopting an integrative wellness framework?
An integrative wellness framework can empower individuals to gain a fuller understanding of their condition, allowing them to actively participate in their health journey and improve their overall well-being.