Introduction
The A1C test serves as a critical barometer in the management of diabetes, providing insights into average blood sugar levels over a two to three-month period. This diagnostic tool not only aids in the identification of diabetes and prediabetes but also plays a pivotal role in shaping effective management strategies for patients.
With A1C levels categorized into distinct ranges, understanding the implications of these numbers is essential for individuals navigating their health journey. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, particularly among younger populations, the importance of accurate A1C testing and interpretation cannot be overstated.
This article delves into the nuances of the A1C test, exploring its benefits, limitations, and the various factors that can influence its accuracy, ultimately empowering patients to take charge of their diabetes management effectively.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key Diagnostic Tool for Diabetes
The A1C test, also known as the a1c diagnostic of diabetes or glycated hemoglobin test, is a vital diagnostic instrument that assesses average blood sugar concentrations over a two to three-month duration, playing a crucial role in managing blood sugar conditions. Quantified as a percentage, elevated A1C readings signify inadequate blood sugar management, with a threshold of 6.5% or higher confirming an A1C diagnostic of diabetes type 2. Meanwhile, levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, significantly raising the risk of developing the condition if not addressed.
This test is pivotal in informing management strategies and enhancing health outcomes for patients at the Integrative Wellness Center. A recent case study titled ‘ABCs of Diabetes Management’ reveals that only 11.1% of individuals meet all criteria for A1C, blood pressure, cholesterol, and smoking, highlighting the challenges in achieving optimal management. Furthermore, it is vital for women with a history of gestational issues to undergo testing for blood sugar levels no later than 12 weeks postpartum, given their heightened risk.
Dr. Shumard’s personalized care approach not only empowers patients with comprehensive insights and treatment options but also addresses root causes holistically, challenging traditional misconceptions about the condition. This comprehensive routine can reduce anxiety related to possible complications of blood sugar issues, providing individuals a sense of control over their well-being. As noted in Balintescu A.’s study, ‘Hemoglobin A1c and Permissive Hyperglycemia in Patients in the Intensive Care Unit with Diabetes,’ the A1C test’s role is undeniably critical in effective management of the condition. Therefore, comprehending A1C values is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes to manage their blood sugar regulation effectively, highlighting the importance of the A1C diagnostic of diabetes for enhancing their long-term well-being. To explore more about your treatment options and how we can support you, learn more about treatment options available at the Integrative Wellness Center.
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do the Numbers Mean for Your Health
Comprehending the A1C diagnostic of diabetes is crucial for efficient management of blood sugar conditions, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes. A1C measurements are categorized as follows:
- Normal: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher.
For individuals identified with the condition, a common goal is to reach an A1C diagnostic of diabetes measurement below 7%. This target is particularly significant as it correlates with the A1C diagnostic of diabetes, which indicates a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications, including cardiovascular disease and neuropathy.
Recent data indicates a notable rise in the age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed blood sugar conditions from 1999 to August 2023, as reported by Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H., in NCHS Data Brief No. 516. This underscores the pressing need for effective management strategies. Furthermore, it is critical to monitor A1C levels in younger populations, where the annual incidence of diagnosed conditions was estimated at 18,200 for type 1 and 5,300 for type 2.
Comprehending these A1C thresholds enables individuals to assess their management effectiveness and make informed adjustments, which may include dietary changes, increased physical activity, or medication adherence. Emphasizing a holistic approach to managing the condition, we begin by re-examining the root causes of your illness, which can help alleviate the anxiety surrounding potential complications of the disease. This empowerment allows patients to tackle wellness at the fundamental stage.
Keeping A1C readings within suggested ranges not only aids in long-term wellness results but also acts as an A1C diagnostic of diabetes to reduce issues related to blood sugar conditions. Furthermore, controlling maternal glucose amounts during pregnancy is vital, as emphasized by the HAPO Follow-up Study data, to decrease long-term metabolic risks for offspring, further demonstrating the significance of A1C management.
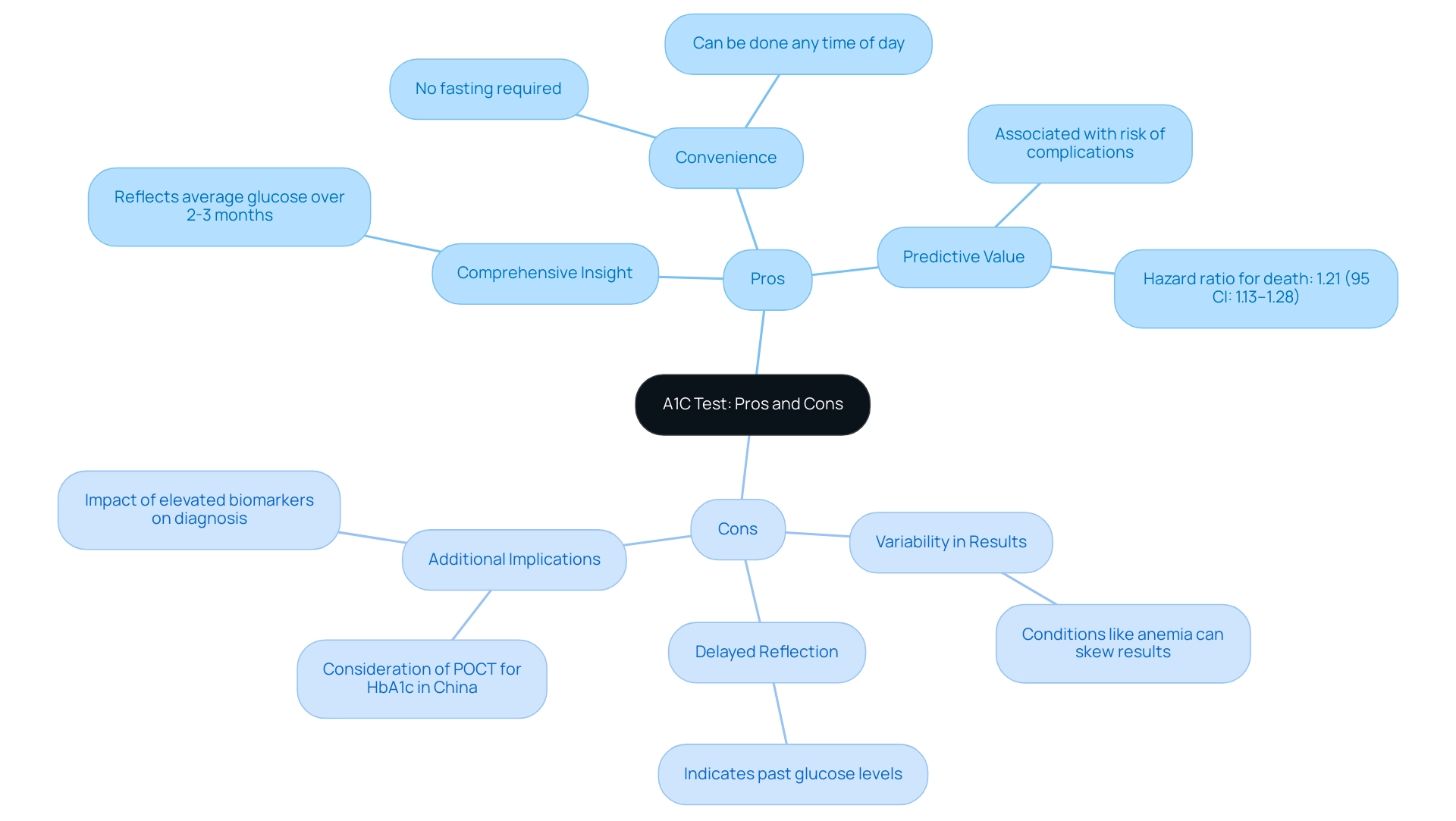
Pros and Cons of the A1C Test: A Comparative Analysis
The A1C test provides numerous benefits for managing diabetes:
- Comprehensive Insight: It offers a holistic perspective on blood sugar regulation, reflecting average glucose amounts over the past two to three months, crucial for understanding the wider implications of diabetes.
- Convenience: Unlike other tests, the A1C does not necessitate fasting and can be conducted at any time during the day, facilitating easier access for patients.
- Predictive Value: Elevated A1C values have been associated with a heightened risk of diabetes-related complications, emphasizing the role of the A1C diagnostic of diabetes, with a glycated hemoglobin value hazard ratio for death from any cause standing at 1.21 (95% CI: 1.13–1.28), underscoring its importance in long-term well-being outcomes.
Despite these benefits, the A1C test also has notable limitations:
- Variability in Results: Various medical conditions, such as anemia or kidney disease, can skew A1C results, leading to potentially misleading interpretations.
- Delayed Reflection: As a lagging indicator, the A1C test primarily indicates past glucose amounts rather than providing real-time data on current blood sugar control.
At the Integrative Wellness Center, we acknowledge the significance of re-evaluating the origin of your condition and addressing wellness at the root level, which can help ease the worry that frequently accompanies concerns about possible complications. Furthermore, the consideration of holistic health solutions emphasizes the need for addressing underlying conditions like hypothyroidism and cognitive decline through functional medicine.
The potential consideration of point-of-care testing (POCT) for the HbA1c diagnostic of diabetes in future clinical practice in China highlights the evolving landscape of managing blood sugar levels, taking into account geographic location, local financial situations, and resident compliance. A recent study evaluated the predictive significance of having increased values of both HbA1c and FPG, revealing that individuals without a prior diagnosis of high blood sugar had varying probabilities of also being elevated for the A1C diagnostic of diabetes based on demographic factors, which highlights the importance of integrated testing approaches.
Factors Influencing A1C Accuracy: What You Need to Know
Patients should be aware that several critical factors can influence the accuracy of the A1C diagnostic of diabetes, which is essential for better management of their condition. Key among these factors are:
- Hemoglobin Variants: Conditions such as sickle cell disease and thalassemia can lead to misleading A1C readings, necessitating alternative methods for monitoring glucose control. Recent studies have highlighted the significant impact of these variants on A1C results, urging healthcare providers to consider them during evaluations.
- Anemia: Patients with low red blood cell counts might receive artificially low A1C results, which could misrepresent their glycemic control.
- Recent Blood Loss or Transfusion: These events can temporarily skew A1C results, making it crucial for patients to inform their healthcare providers about any recent medical interventions.
- Age and Ethnicity: Genetic factors contribute to variations in A1C values across different populations. Research utilizing linear regression models, which controlled for diabetic characteristics and lifestyle factors, analyzed the relationship between age and HbA1c. In a recent study published in volume 13, issue 23 of a prominent journal, the association was evaluated across various red blood cell percentile groups, confirming a significant negative correlation with age. However, the interaction between RBC groups and age was not statistically significant, indicating that while age influences A1C levels, RBC group variations do not significantly alter this relationship.
Understanding these influences empowers patients to engage in informed discussions with their healthcare providers about the validity of their A1C diagnostic of diabetes results. Yanping Zhang emphasizes that healthcare professionals should pay attention to patients with low literacy and low criticality in rural areas and develop interventions to enhance their literacy, thereby improving their blood sugar management. Acknowledging the complex factors influencing test accuracy can result in better-suited management strategies and the possibility for further testing when suitable.
A1C Testing in Diabetes Management: Strategies for Effective Monitoring
Incorporating the a1c diagnostic of diabetes into diabetes management effectively requires a structured approach that empowers patients to take control of their health and find peace in life by eliminating worries about complications.
- Regular Testing: The latest guidelines recommend scheduling A1C tests at least twice a year. However, for individuals with poorly managed blood sugar conditions, more frequent testing, such as an a1c diagnostic of diabetes, may be necessary to monitor progress accurately.
- The relationship of A1C measurements with the a1c diagnostic of diabetes and the risk for complications is significant, particularly among diverse populations, including African American and non-Hispanic White individuals.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Engaging in regular physical activity and adhering to a balanced diet can significantly impact blood sugar control, which is often reflected in improved A1C results. Lifestyle modifications are central to a holistic approach, enhancing metabolic health and reducing the risk of complications such as ischemic heart disease and hyperglycemic crises, which accounted for significant hospitalization cases in 2020.
By making these choices, individuals can alleviate anxiety and foster a sense of well-being.
- Medication Adherence: Consistent use of prescribed medications is crucial for managing blood sugar concentrations effectively. Non-adherence can lead to fluctuations in glucose levels, subsequently affecting the a1c diagnostic of diabetes results.
Comprehending the mechanisms of β-cell damage, such as virus-triggered death and immune-mediated loss, can further emphasize the importance of medication adherence in a comprehensive care plan, allowing patients to feel more secure in their wellness management.
- Monitor Daily: Daily blood glucose monitoring complements the A1C diagnostic of diabetes by providing a comprehensive view of blood sugar control. This dual approach enables individuals to make informed adjustments to their management strategies, alleviating anxiety over potential complications and helping them feel more in control of their health.
- Communicate with Healthcare Providers: Open dialogue about the A1C diagnostic of diabetes results and management strategies during healthcare appointments is essential for aligning treatment plans with personal wellness goals. As noted by the American Diabetes Association, efforts must be made to consistently apply terminology that empowers individuals with this condition and recognizes the individual at the center of care. This communication can help reduce fears and build confidence in managing their condition.
By following these strategies, individuals can harness a holistic approach to diabetes management, fostering optimal health outcomes, reducing the risk of complications, and ultimately finding peace in life without the worry of diabetes-related issues.
Conclusion
The A1C test is a cornerstone in diabetes management, providing crucial insights into average blood sugar levels over a significant period. Understanding A1C results allows individuals to categorize their health status—normal, prediabetes, or diabetes—and to implement effective management strategies. With rising diabetes prevalence, particularly among younger populations, the importance of accurate testing and interpretation is paramount.
While the A1C test offers numerous advantages, such as convenience and predictive value for complications, it is essential to recognize its limitations. Factors like:
- hemoglobin variants
- anemia
- recent medical interventions
can affect accuracy, emphasizing the need for informed discussions with healthcare providers. A comprehensive approach to diabetes management—encompassing regular testing, healthy lifestyle choices, medication adherence, and open communication—empowers patients to take control of their health.
Ultimately, mastering the nuances of the A1C test not only aids in effective diabetes management but also fosters a sense of control and confidence in navigating one’s health journey. By prioritizing A1C monitoring and addressing underlying health concerns, individuals can significantly enhance their well-being and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test?
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, assesses average blood sugar concentrations over a two to three-month period and is crucial for managing blood sugar conditions.
How is the A1C test result quantified?
A1C results are quantified as a percentage. Elevated readings indicate inadequate blood sugar management.
What do different A1C levels indicate?
Normal: Below 5.7%, Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%, Diabetes: 6.5% or higher.
What A1C level is considered a target for individuals with diabetes?
A common goal for individuals with diabetes is to achieve an A1C level below 7%, which is associated with a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications.
Why is the A1C test important for women with a history of gestational issues?
Women with a history of gestational issues should have their blood sugar levels tested no later than 12 weeks postpartum due to their heightened risk of developing diabetes.
What challenges are highlighted regarding diabetes management?
A case study revealed that only 11.1% of individuals meet all criteria for A1C, blood pressure, cholesterol, and smoking, indicating difficulties in achieving optimal management.
How can individuals use their A1C results to manage their health?
Understanding A1C thresholds allows individuals to assess their management effectiveness and make informed changes, such as dietary adjustments, increased physical activity, or medication adherence.
What does recent data indicate about the prevalence of blood sugar conditions?
There has been a notable rise in the age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed blood sugar conditions from 1999 to August 2023, highlighting the need for effective management strategies.
What is the significance of controlling maternal glucose levels during pregnancy?
Controlling maternal glucose levels is vital to decrease long-term metabolic risks for offspring, underscoring the importance of A1C management.