Overview
An A1C level of 4.6 indicates excellent blood sugar control, significantly reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. The article supports this by explaining that such a level reflects stable average blood glucose, while also emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring and awareness of external factors that can influence A1C readings, ensuring effective diabetes management.
Introduction
The A1C test serves as a vital benchmark in the management of diabetes, measuring the percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin in the blood. With thresholds indicating normalcy, prediabetes, and diabetes, understanding A1C levels is crucial for individuals aiming to maintain optimal health.
This article delves into the significance of A1C testing, interpreting results, and the implications of various A1C levels on health outcomes. It also highlights the importance of a holistic approach to diabetes management, emphasizing:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Regular monitoring
- The need for education to empower patients
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, informed management strategies become essential in mitigating complications and enhancing quality of life.
Understanding the A1C Test: Significance and Interpretation
The A1C test, commonly referred to as glycated hemoglobin, is a crucial diagnostic tool that quantifies the percentage of glucose molecules bound to hemoglobin in the bloodstream. A normal A1C level is generally recognized as being below 5.7%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate a state of prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of the condition.
For instance, an A1C of 4.6 is indicative of effective blood sugar control, falling well within the normal range. Comprehending these results is essential for individuals overseeing their condition, as it informs critical decisions regarding lifestyle adjustments and treatment strategies. Roopa Naik highlights the significance of consistent observation, stating, ‘Comprehending your A1C figures is crucial for effective control of blood sugar and avoidance of complications.’
Moreover, the need for increased education and awareness regarding A1C levels and their implications is underscored by recent studies, particularly among Hispanic adults, where awareness of prediabetes stood at just 20.9% from 2017 to 2020. This emphasizes the importance of community wellness initiatives in empowering patients through education, nutrition, and support, which are vital for effective control of blood sugar. Additionally, incorporating holistic health approaches, such as stress management, dietary adjustments, and physical activity, can further enhance health and reverse the condition.
The total direct and indirect expenses related to the diagnosed condition in the United States reached $413 billion in 2022, illustrating the economic burden of the ailment and the critical role of tracking A1C values in managing healthcare expenses. With an annual incidence of diagnosed conditions in youth estimated at 18,200 for type 1 and 5,300 for type 2, understanding A1C levels is imperative. As healthcare continues to progress, interpreting glycated hemoglobin remains a central focus in the treatment of sugar-related conditions, guiding both patients and clinicians in optimizing care and improving health outcomes.
Implications of an A1C of 4.6: What It Means for Your Health
An A1C 4.6 indicates outstanding blood sugar control, significantly lowering the chances of complications related to the condition. This stage indicates that average blood glucose has remained stable within a desirable range, a critical factor in the management of blood sugar conditions. However, it is essential to recognize that consistently low A1C readings can heighten the risk of hypoglycemia, particularly for individuals using medication for their condition.
Recent findings underscore that the average incidence of complications for individuals with normal A1C values is approximately 1% per year, reinforcing the importance of vigilance. Furthermore, conditions such as:
- Alcohol use disorder
- Blood transfusions
- Chronic kidney failure
- Pregnancy
can lead to falsely low A1C results, making it crucial to consider these factors in assessments. Regular monitoring of A1C levels and ongoing consultations with healthcare providers are vital to safely maintaining A1C 4.6 within this optimal range.
At the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego, we empower patients through personalized care strategies that address the root causes of type 2 conditions. Our transformative success narratives, including case studies that illustrate the effectiveness of our holistic approach, highlight how patients have reversed their condition and alleviated the anxiety associated with potential complications. For instance, the case study by Yoshinaga in 1996 evaluated the predictive power of A1C and OGTT for the progression of the condition, finding that the combination of both tests provides a more precise prediction of its advancement.
Shimazaki’s observation further emphasizes this need for comprehensive assessments in glucose management. By addressing the psychological aspects of this condition, we help patients eliminate worries about complications, fostering a more peaceful approach to their health. For additional details and updates concerning blood sugar conditions, consider signing up for our email notifications.
Effective Management Strategies for Maintaining Optimal A1C Levels
To achieve and sustain optimal A1C values in a holistic manner, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Balanced Diet: Prioritize whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while minimizing the intake of sugars and processed foods. This is essential in addressing the root causes of the condition and can help alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications. Research indicates that a balanced diet can significantly influence blood sugar control. For example, the PREDIMED trial, which tracked nearly 7,000 participants for 4.8 years, indicated that adherence to a Mediterranean diet was linked to enhanced fasting glucose readings, illustrating the significant effect of diet on blood sugar management. As noted by Hiroyuki Umegaki from the Department of Geriatrics at Nagoya University, a well-structured diet is crucial for effective diabetes management.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week. This is not simply about weight reduction; regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and tackles the underlying problems of insulin resistance, which can aid in achieving an A1C of 4.6. Experts advocate for incorporating activities that you enjoy to ensure long-term adherence.
- Weight Management: Striving for and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, as even modest weight loss can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar levels. The average 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk score in individuals with high blood sugar is 8.0%, highlighting the significance of weight control in lowering related health risks.
- Medication Adherence: If you have been prescribed medications, it is essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions to ensure optimal blood sugar control. Effective medication oversight can complement lifestyle adjustments and enhance overall health control, challenging traditional treatment approaches.
- Regular Monitoring: Consistently checking your blood glucose readings will keep you informed about your diabetes control and enable you to adjust your management plan as necessary. According to recent statistics, fiber consumption in low-fat diets demonstrated an increase from 14.9 g/day at baseline to 17.2 g/day after 12 months, indicating that dietary changes can lead to enhancements in A1C values over time. Regular monitoring allows you to assess how these changes impact your A1C of 4.6 levels, facilitating timely adjustments to your regimen. By re-examining the source of your condition, you can better understand and address these factors holistically.
Factors Influencing A1C Variability: Understanding Your Results
A variety of factors significantly influence A1C variability in individuals with Type 2 diabetes, including cases where a1c 4.6 is observed, and understanding these elements is crucial for effective diabetes management. These factors include:
-
Dietary Changes: Sudden modifications to dietary habits can lead to notable fluctuations in blood glucose readings, which in turn affect A1C results.
Recent studies have indicated that specific dietary adjustments can lead to substantial changes in a1c 4.6 readings over time.
-
Physical Activity: Variations in exercise routines play a critical role in blood sugar control.
Regular physical activity helps stabilize blood glucose, while inconsistent exercise may contribute to variability.
-
Illness or Stress: Both acute and chronic stressors can increase blood glucose, thereby affecting A1C.
Stress control is crucial for sustaining stable blood sugar amounts, as the worry regarding possible complications of the condition can further worsen these fluctuations.
-
Medications: Certain drugs prescribed for blood sugar control or other health concerns can change blood glucose amounts, resulting in variations in A1C readings.
The mean corrected insulin response (CIR) in individuals with Type 2 was found to be 0.6, and the mean HOMA-IR was 7, indicating significant insulin resistance that can contribute to A1C variability.
A comprehensive strategy for managing the condition starts with reassessing the underlying causes, enabling patients to tackle their health at a basic foundation. Understanding these factors is essential for accurately interpreting results, such as an a1c 4.6.
As noted by Jennifer Sargent, Primary Handling Editor,
Collaboration with diabetes educators is vital for patients to grasp how these elements affect their condition.
Furthermore, a recent study titled A1C Variability and Atherosclerosis Progression highlights that higher A1C variability, particularly in patients with an a1c 4.6 level, is associated with increased risk for atherosclerosis, emphasizing the importance of monitoring A1C levels closely.
The research discovered a notable connection between A1C variability and the advancement of intima-media thickness (IMT) in the carotid artery, indicating that individuals with greater A1C variability may require more intensive monitoring and oversight strategies.
Such insights can guide individuals in making informed choices about their health management strategies. Additionally, acknowledgment is given to the commitment and dedication of the participants in the Prevention Program (DPP), which underscores ongoing efforts to improve health outcomes.
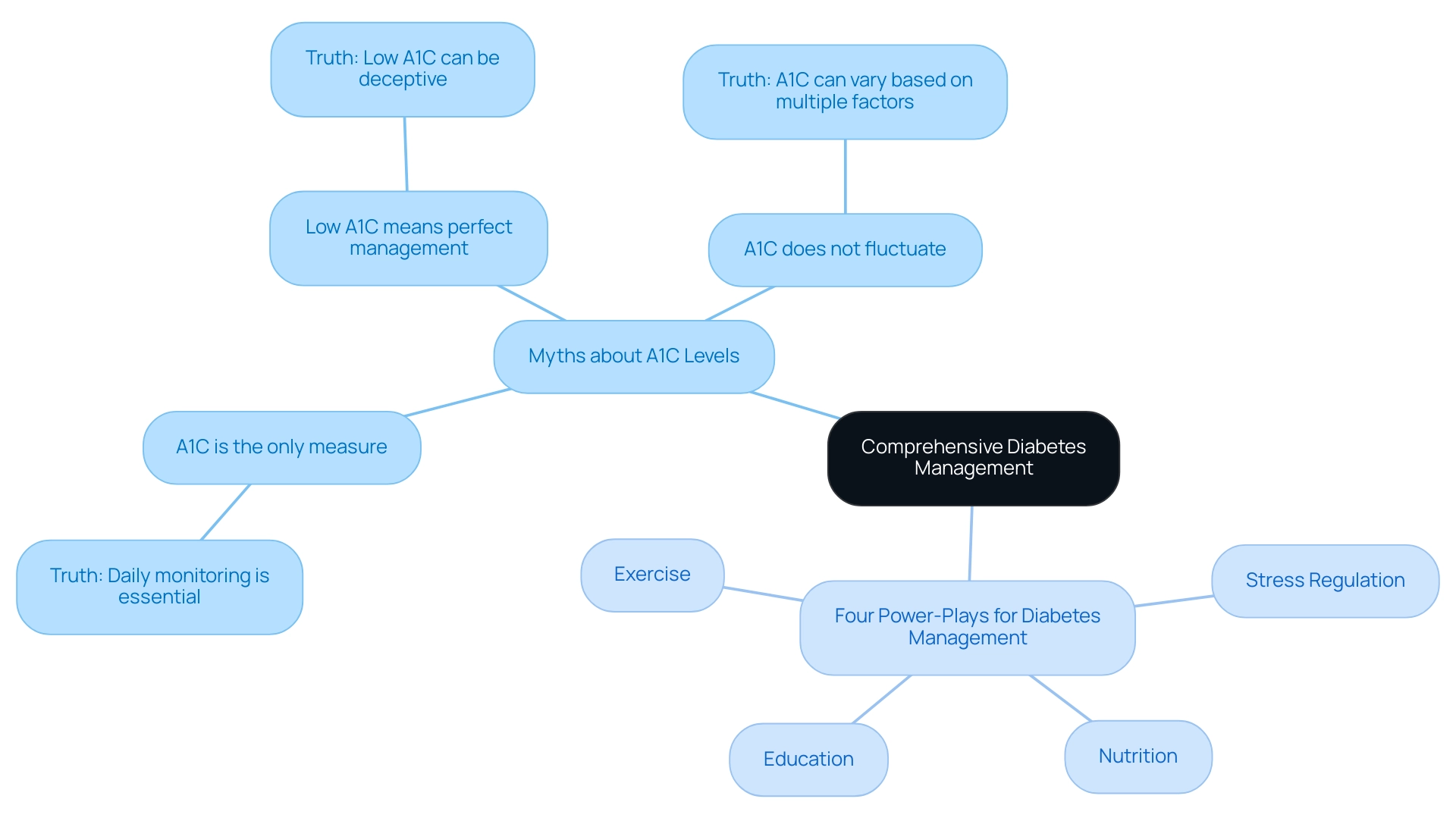
Debunking Myths: A1C Levels and Comprehensive Diabetes Management
Several myths persist regarding A1C levels that can mislead individuals managing their condition. Firstly, there is a common misconception that A1C is the only measure of blood sugar management. In reality, while A1C is an important indicator, daily blood glucose monitoring, along with comprehensive health assessments and a holistic approach to health, are equally essential for effective control.
This is supported by a study where participants were recruited from a large general medicine clinic in New York City, achieving a response rate of 87%. Secondly, many believe that a low A1C signifies perfect management of the condition. However, a low A1C can be deceptive if accompanied by frequent episodes of hypoglycemia, highlighting the need for a balanced approach.
Additionally, the notion that A1C values do not fluctuate is misleading; in fact, A1C can vary based on multiple factors, and monitoring trends over time is crucial rather than relying on a single reading. The ‘Diabetes Knowledge and Beliefs Survey’ found prevalent suboptimal knowledge and beliefs about the condition, indicating a need for educational interventions to empower patients in their self-management. Identifying these myths allows individuals to embrace a more knowledgeable viewpoint on the control of this condition, highlighting the significance of thorough monitoring beyond just A1C levels, such as achieving an A1C of 4.6.
Furthermore, implementing the four lesser-known power-plays, such as:
- Focusing on nutrition
- Exercise
- Stress regulation
- Education
can significantly improve control of blood sugar levels. As noted by Yu Ko, ‘A healthy diet for diabetics is generally the same as for everyone else,’ reinforcing the idea that diabetes management involves more than just A1C readings, and should incorporate transformative health solutions that address root causes.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C levels is essential for effective diabetes management, as they provide critical insights into blood sugar control and overall health. This article has explored the significance of the A1C test, detailing how various levels indicate different health states—from normal to diabetes—and the implications of these readings for individuals. Regular monitoring and a comprehensive understanding of A1C results empower patients to make informed decisions about their health, ultimately reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
The importance of lifestyle modifications cannot be overstated. Implementing a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and adhering to prescribed medications are vital strategies for maintaining optimal A1C levels. Additionally, recognizing the factors that influence A1C variability—such as stress, illness, and medication—enables individuals to take proactive steps in their diabetes management.
Dispelling common myths surrounding A1C levels emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to diabetes care. A1C is not the sole measure of diabetes control; integrating daily monitoring and comprehensive health assessments is crucial for effective management. By fostering education and awareness, patients can navigate their diabetes journey with confidence, making empowered choices that contribute to better health outcomes.
In a landscape where diabetes prevalence continues to rise, understanding and managing A1C levels is paramount. By prioritizing informed strategies and a holistic approach, individuals can significantly enhance their quality of life and mitigate the economic burden associated with diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and what does it measure?
The A1C test, also known as glycated hemoglobin, quantifies the percentage of glucose molecules bound to hemoglobin in the bloodstream, providing insight into blood sugar control over time.
What are the normal and abnormal A1C levels?
A normal A1C level is below 5.7%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diabetes diagnosis.
What does an A1C level of 4.6 indicate?
An A1C level of 4.6 indicates effective blood sugar control and falls well within the normal range, significantly lowering the chances of complications related to diabetes.
Why is understanding A1C levels important for individuals with diabetes?
Understanding A1C levels is crucial for effective blood sugar control and helps inform lifestyle adjustments and treatment strategies to avoid complications.
What factors can lead to falsely low A1C results?
Conditions such as alcohol use disorder, blood transfusions, chronic kidney failure, and pregnancy can lead to falsely low A1C results.
How does the economic burden of diabetes relate to A1C tracking?
The total direct and indirect expenses related to diabetes in the U.S. reached $413 billion in 2022, highlighting the importance of tracking A1C values in managing healthcare expenses.
What is the significance of regular monitoring of A1C levels?
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is vital for safely maintaining optimal blood sugar control and managing the risk of complications.
How can holistic health approaches benefit individuals with diabetes?
Incorporating holistic health approaches, such as stress management, dietary adjustments, and physical activity, can enhance overall health and potentially reverse diabetes conditions.
What role do community wellness initiatives play in diabetes education?
Community wellness initiatives empower patients through education, nutrition, and support, which are essential for effective blood sugar management, particularly among populations with low awareness of prediabetes.
What is the importance of personalized care strategies in managing diabetes?
Personalized care strategies address the root causes of type 2 diabetes, helping patients manage their condition effectively and reduce anxiety regarding potential complications.